A & P Lecture Exam 1
1/112
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Hematocrit Components and Precents
Erythrocytes: 37-52%
Buffy Coat: 1%
Plasma: 47-63%
Plasma Components
mixture of water, proteins, nutrients (vitamins, cholesterol), electrolytes (90% Na+), nitrogenous wastes, hormones, and gases (dissolved O2 and CO2)
Albumin
smallest and most abundant plasma protein, regulates liquid amount in blood, blood pressure, flow and fluid balance, formed in the liver
osmolarity of blood
total molarity of dissolved particles that can’t pass through blood vessels, to high means blood absorbs water increasing blood pressure, when too low blood leaves too much water in the tissue (edema)
globulins
provide immune system functions, alpha and beta are made in the liver and gamma are free floating antibodies produced by plasma cells
fibrinogen
precursor of fibrin, plasma protein, formed in the liver
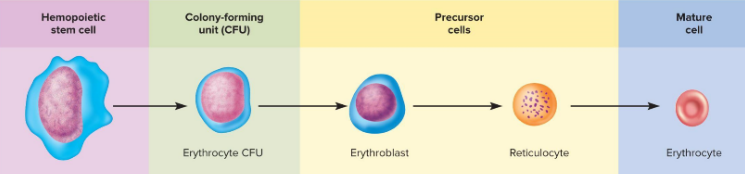
hemopoiesis
red bone marrow makes all formed elements from hemocytoblasts
erythrocyte function and structure
lose all organelles, no mitochondria so they don’t use the O2 they are moving, no nucleus so there is no reproduction, flexible membrane for durability and resilience, high surface area/volume ration, lives 120 days
hemoglobin
each has 4 heme groups that binds 1 O2 to its Fe,
factors increasing hematocrit
male (higher androgen amount), higher elevation, low body fat, high exercise
erythropoisis
kidney detects low erythrocytes and produces erythropoietin to stimulate the red bone marrow, hemocytoblasts with a nucleus gets smaller, becomes a hemoglobin sac and losses its organelles and nucleus, takes 3-5 days
iron absorption
vitamin C helps turn it to Fe2+, attached to cells to be transferred from the stomach into the liver until it is needed
erythrocyte death and recycling
macrophages in spleen hydrolyze goblins into amino acids, remove heme and separate iron which is reused, heme is lost (bilirubin into urine, bile from gallbladder into brown feces)
pernicious anemia
autoimmune attack of stomach tissue leading to inadequate vitamin B12 absorption, newborns
aplastic anemia
compete cessation of erythropoiesis, radiation of red bone marrow for leukemia
anemia effects
lethargic, shortness of breath, tissue death (necrosis) of high O2 using organs (brain, heart, kidneys, spinal cord), osmolarity is reduced (edema)
agglutinogens
antigens on surface of blood cells that activates an immune response, distinguish self from foreign matter
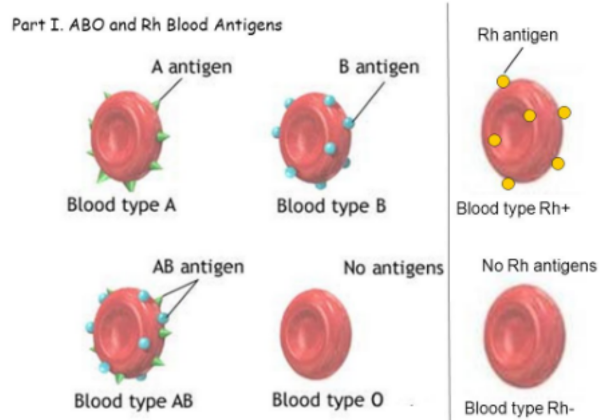
agglutinins
antibodies in blood plasma, gamma globulins secreted by plasma cells that bind to antigens and mark for destruction
agglutination
clumping when antibodies hold on to blood antigens, blocks small blood vessels, release hemoglobin
hemolytic disease of the newborn
when the mom is - and the first baby is + the mom will start producing Anti-D antibodies after birth that would attack a second + baby
neutrophil
aggressive antibacterial, rise in response to bacterial infection efficient phagocytosis
eosinophil
parasitic infections (malaria), collagen disease, allergies, release enzymes to destroy large parasites
basophils
increases with chickenpox, sinusitis, diabetes, secretes histamine (vasodilator) and heparin (anticoagulant)
lymphocytes
destroy cancer and virally infected cells, activates and coordinates other immune cells with antigens, secretes antibodies and provides immune memory
monocytes
increases with viral infections and inflammation, phagocytize pathogens and debris, activates other immune cells, can leave blood for tissue and turn into macrophages
leukopoiesis
myeloblasts form granulocytes, monoblasts form monocytes, lymphoblasts form lymphocytes, stored and released from red bone marrow
leukocyte life cycle
granulocytes are released after 8 days and live for 5 days, monocytes leave in 20 hours turn into macrophages and live for several years, lymphocytes provide long-term immunity and are continuously recycled from blood to tissue fluid to lymph to blood
platelets
secrete vasoconstrictors, stick together to form platelet plug for small breaks, secrete procoagulants (clotting factors), attract neutrophils and monocytes, secrete growth factors that stimulate mitosis for repair, circulate for 5-6 days
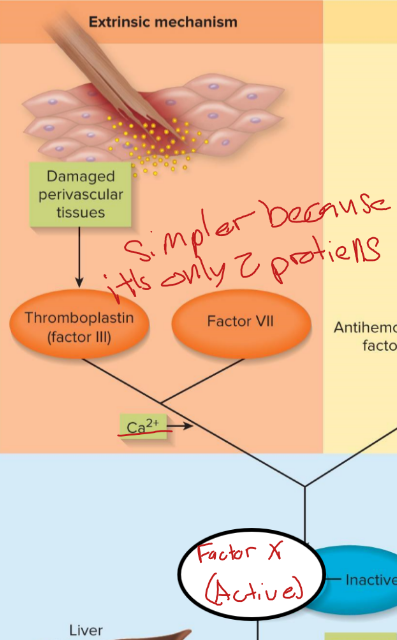
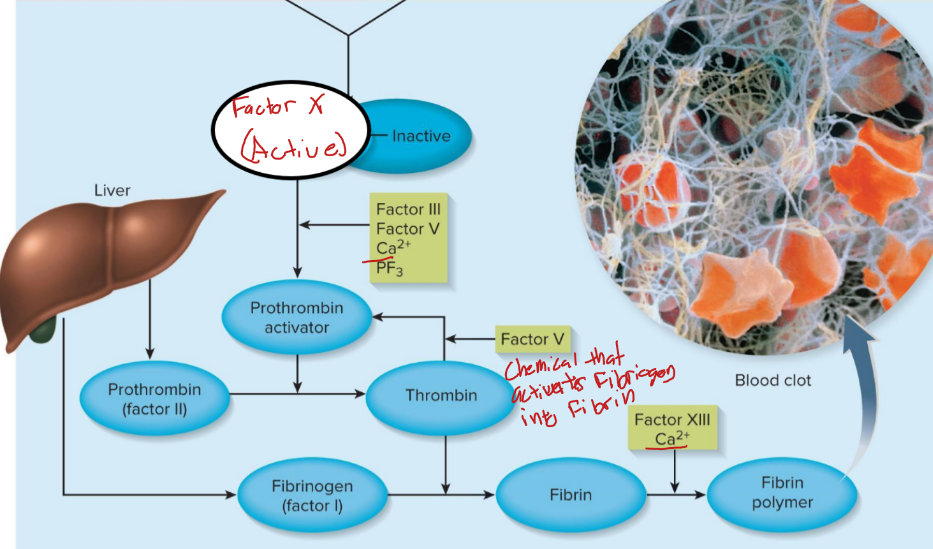
extrinsic pathway
factor 3 is released by damaged tissue, cascade is VII, V and X
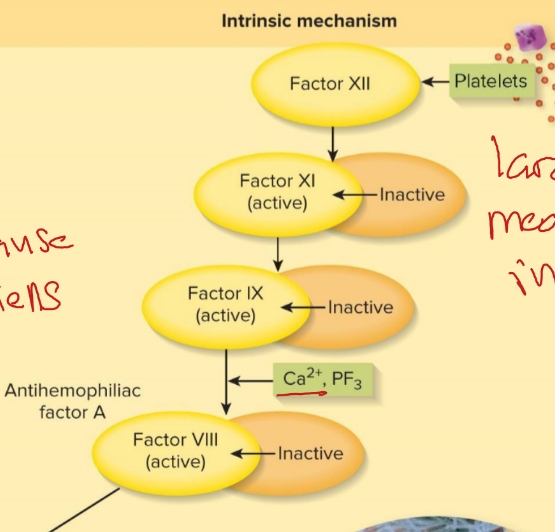
intrinsic pathway
platelets release factor XII, cascade is XI, IX, VIII, X
common pathway
factor X activates thrombin to convert fibrinogen to fibrin which is crossed linked by XIII
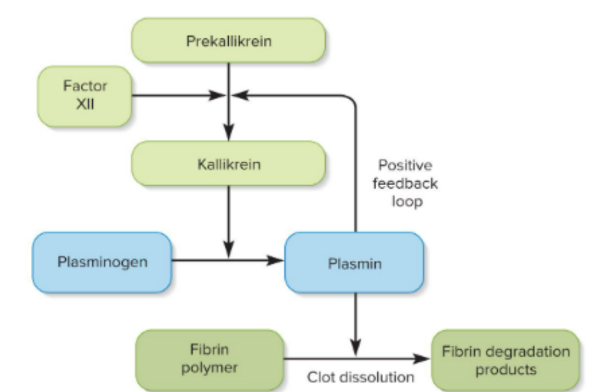
Fibrinolysis
break down of a clot, factor XII forms kallikrein enzyme which makes plasmin to dissolve the fibrin holding the clot
prevention of inappropriate clotting
platelets can’t stick to blood vessels only to collagen fibers that are exposed when there is damage to blood vessels, thrombin dilution by bloods continuous flow, antithrombin deactivate thrombin when it moves away from the clot, heparin keeps some blood flow to injury to bring building materials
hemophilia
hereditary diseases with deficiencies of a clotting factor, A missing factor VIII, B missing factor IX, C missing factor XI, treated with transfusion of plasma of clotting factors
thrombosis
abnormal clotting in a unbroken vessel
thrombus
unmoving blood clot, mostly likely in leg veins of inactive people due to less circulation
embolus
anything traveling in the blood vessels that can block them
pericardium
double-walled sac that encloses the heart to allow the heart to beat without friction
parietal pericardium
superficial outer layer of connective tissue
visceral pericardium
inside layer of the heart, epicardium when talking about the layers of the heart, adipose thick layers in some places, coronary vessels travel through this layer
endocardium
slippery inner lining of the heart, covers valve surfaces and is continuous with endothelium of blood vessels
myocardium
layer of cardiac muscles proportional to work load, spirals
atrioventricular sulcus
separates atria and ventricles on the outside, filled with coronary blood vessels and cushioned with adipose
pectinate muscles
internal ridges in right atrium and auricles to help direct blood flow into ventricles
trabeculae carneae
internal ridges in both ventricles the could prevent walls from sticking together from hydrogen bonds
right atrioventricular (AV) valve
three cusps (tricuspid), from right atria to right ventricle, first
left atrioventricular (AV) valve
two cusps (bicuspid), from left atria to left ventricle, enters second
chordae tendineae
connect AV valves to papillary muscles on ventricle floor to prevent them from flipping or bulging into the atria
pulmonary semilunar valve
control flow from right ventricle into the pulmonary trunk (artery going to the lungs)
aortic semilunar valve
controls flow from the left ventricle and the aorta (brings blood to the body)
pericardium
double walled sac the encloses the heart
epicardium
membrane covering the heart, adipose thick in some places, coronary blood vessels travel through this layer
endocardium
slippery inner lining of the heart and blood vessels, covers valve surfaces and is continuous with endothelium of blood vessels
myocardium
layer of cardiac muscle, spirals to wring out blood
fibrous skeleton of the heart
framework of collagenous and elastic fibers the provide structural support and attachment for cardiac muscles, electrical insulation between atria and ventricles to protect each other allowing for correct timing of contraction
pectinate muscles
internal ridges of myocardium in right atrium and both auricles, helps direct blood flow in the ventricles
trabeculae carneae
internal ridges in both ventricles that may prevent walls from sticking together after contraction
right AV valve
three cusps valve, between right atria and right ventricle, blood enters first
left AV valve
have two cusps, between left atria and left ventricle, blood enters second
pulmonary semilunar valve
controls blood flow between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk, open and closes because of blood flow and pressure
aortic semilunar valve
opening between left ventricle and aorta, open and closes because of blood flow and pressure
intercalated disc
joins cardiomyocytes end to end, electrical synapses, allows cells to contract together
mechanical junctions
tightly joins cardiomyocytes via transmembrane proteins of desmosomes that has an anchor in both cells that go through the intercalated disc, prevents contracting myocytes from being pulled apart
electrical junctions (gap junctions)
allows ions to flow between cells so myocardium of either the atria or ventricles contract in uniform
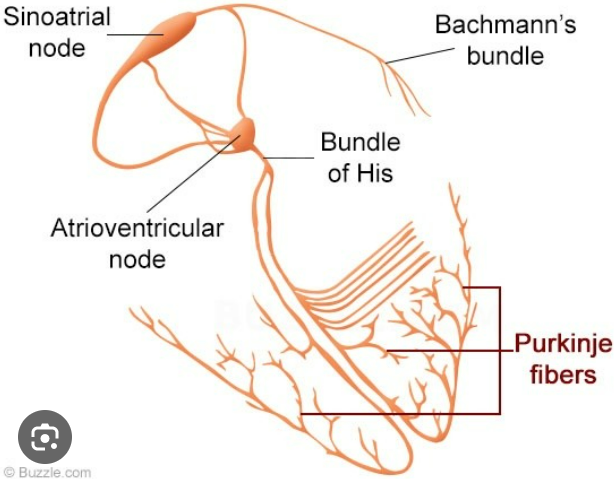
sinoatrial (SA) node
modified cardiomyocytes that depolarizes spontaneously which causes the other cells to contract, in right atrium near the base of the superior vena cava, stimulates two atria to contract almost simultaneously
atrioventricular node
electrical gateway to the ventricle, creates a delay that allows the ventricle to fill before it contracts, located right of the AV valves at the lower end of the interatrial septum
atrioventricular bundle (bundle of His)
forks into right and left bundle branches, pass through interventricular septum towards apex
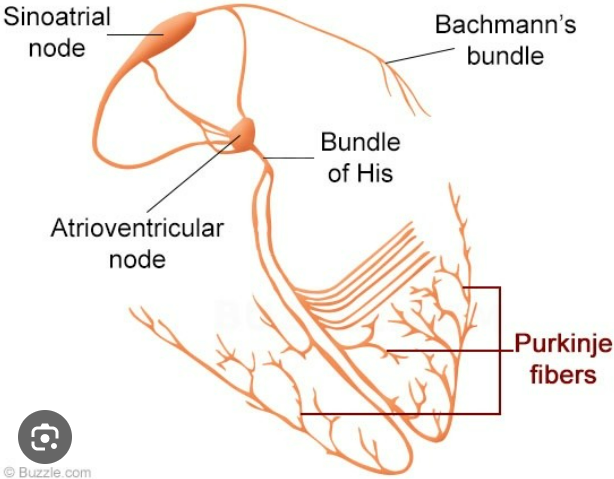
Subendothelial conducting networks (Purkinje fibers)
nerve like process that spread through the ventricular myocardium, bottom contracts before top pushing the blood up
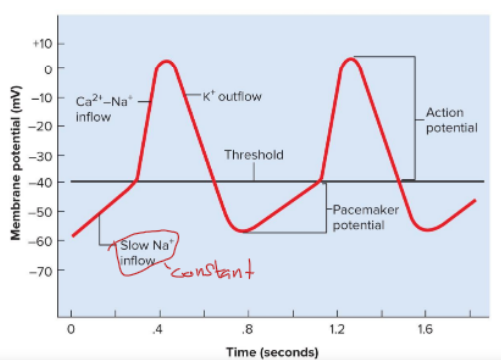
pacemaker potential
gradual depolarization up from -60mV due to slow Na+ inflow
depolarzation of pacemaker
when the membrane potential reaches -40 mV, fast Ca2+ and Na+ channels open peaking potential at 0 mV, then K+ channels open and K+ leave the cell causing repolarization
depolarization and contraction of generic myocytes
Na+ channels open in a positive feedback loop, Na+ close when voltage reaches +30 mV, Ca2+ slowly enters to prolong depolarization of membrane (plateau), Ca2+ transported out of the cell and K+ channels open creating a rapid outflow of K+ and return to -90mV
P wave
SA node fires, atria depolarizes and contracts
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization, complex shape due to difference in thickness and shape of two ventricles
ST segment
between the end of ventricular depolarization and the beginning of ventricular repolarization (systole), plateau
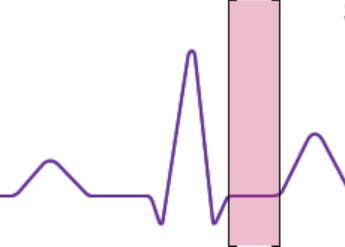
T wave
ventricular repolarization and relaxation
ventricle contraction controlling the AV and semilunar valves
when the ventricle relaxes internal pressure falls allowing the AV valves to open and blood to flow in, when the ventricle contracts, the AV valve closes and pressure pushes the semilunar valves open
S1 heart sound
louder and longer “lubb” occurs with the closure of the AV valves
S2 heart sound
softer and sharper, “dubb”, closure of the semilunar valves because the closure is gentler
S3 heart sound
rarely heard, “wosh” opening of left AV valve and filling of left ventricle
end-diastolic volume
amount when each ventricle is done filling, 130mL
isovolumetric contraction
ventricle begin to contract but do not eject blood
stroke volume
amount of blood the comes out during ejection, 70 mL
ejection fraction
percent that comes out during contraction, 54%, higher in healthier people
end-systolic volume
amount of blood left after contraction
isovolumetric relaxation
blood from aorta and pulmonary trunk breifly flow back closing semilunar valves
quiescent period
when all four chambers for relaxed (diastole)
cardiac output
amount ejected by each ventricle in 1 min, heart rate x stroke volume, increases with fitness
unbalanced ventricle output effects
right ventricle exceeds left so fluid accumulates in pulmonary tissue, left ventricle exceeds right so fluid accumulates in systemic tissue
autonomic nervous systems affects on the heart
does not initiate heartbeat but modulates rhythm and force, sympathetic system adrenergic by releasing norepinephrine which increases Ca2+ inflow and depolarizes SA node
acetylcholine (ACh)
started by the vagus nerve to slow down heart rate, opens K+ gates in the nodal cells
vagal tone
vagus nerve is always firing telling the hearth to slow down to lower blood pressure, lowers it from 100 bpm
baroreceptors
pressure sensors in the aorta and internal carotid arteries
chemorecptors
in aortic arch, carotid arteries, medulla oblongata, sensitive to blood pH, Co2, and O2
arteries
carry blood away from the heart
veins
carry blood to the heart, stores most blood in the body, thinner less muscular and elastic tissue, subjective to low blood pressure
capillaries
connect smallest arteries to smallest veins, gasses, nutrients, waste, and hormone pass, absent in tendons, ligaments, epithelia, cornea, and lens
tunica interna
lines blood vessels and is exposed to blood, secretes chemicals that stimulate dilation or constriction of the vessel, slippery, covers collagen fibers
tunica media
larger is arteries, smooth muscle, collagen, and elastic tissue, strengthens vessels and prevents rupture, regulates diameter
tunica externa
loose connective tissue the often merges with neighboring blood vessels, nerves, or organs, anchors vessels and contains small nerves and vessels
vasa vasorum
small vessels that supply blood to outer art of big transporting vessels