Parasites and Moulds
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Trichuris trichiura
A helminth causing human infections through ingesting embryonated eggs contaminated by soil. OVa are distinctly barrel-shaped, protruding convex, with a hyaline polar plug at each end. Infections with this whipworm can lead to trichuriasis, causing abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Enterobius vermicularis
A pinworm responsible for infections resulting from eggs transferred from the peri-anal region (usually finger to mouth). Ova are asymetrical ovalswith thin smooth shell and one flattened end resembling a deflated football.
Ascaris lumbricoides
A roundworm commonly infecting children through hand-to-mouth transmission of eggs, or through soil usually by sports or playground activities. Ova exhibit thik roughened shell with an albuminous coat.
Lodamoeba butschlii
A non-pathogenic amoeba characterized by a 'ball-in-socket' nucleus and large vacuole.
Entamoeba histolytica
A pathogenic amoeba causing dysentery, identifiable by the size and nuclei of its cysts.Typically 20 micrometers with up to four nuclei each with a small centrally placed karyosome and a distinctive thin rim of beaded chromatin. Intestinal
Ulocladium species
Molds classified as dematiaceous rapid growers, identified through their macroconidia.
Curvularia species
A type of mold with macroconidia that grow in a boomerang shape, characterized by transverse septa.
Alternaria species
Molds producing large, multi-celled macroconidia with a characteristic drumstick shape. Elongated beak of one conidium against the round blunt end of the next.
Onchocerca volvulus
A helminth that produces live larvae and is typically found in infected nodules.
Fusarium
Opportunistic pathogens linked to various infections, characterized by lavender, magenta, or pink-red colonies. Cotton or “wooly” . Microscopically long boat-shaped macro-conida with a hair-like “foot”.
Aspergillus species
Fungi associated with opportunistic infections, known for their widespread nature and laboratory contamination. Pulmonary aspergillus called “fungus ball” infections.
Mycobacterium abscessus
A rapidly growing mycobacterium known to cause infections in immunocompromised hosts.
Cryptococcus neoformans
A yeast responsible for cryptococcosis, identifiable by its capsule and budding cells.Poultry workers, groundskeepers, bird excrement or soil. Does not produce germ tubes. Phenoloxidase, Urease positive
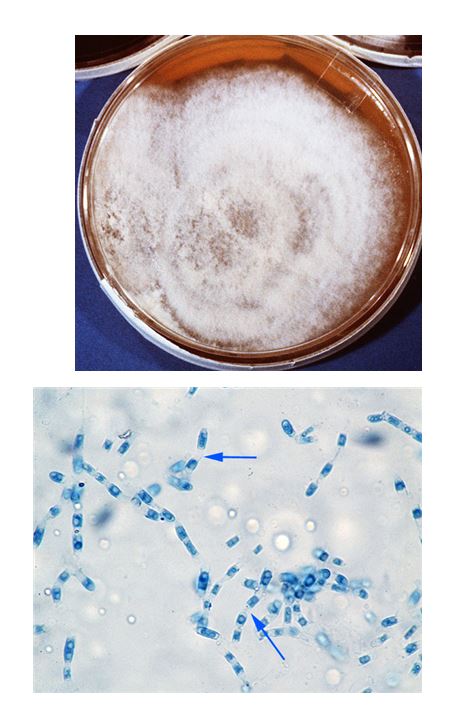
Coccidioides immitis
A dimorphic fungus that causes coccidioidomycosis, identified by spherules containing endospores. White, fluffy, “cob-webbed” colonies growing in 3-5 days. Respiratory infection followed by dissemination to organs, lymph nodes, and tissue. Unable to convert from the mold to yeast phase outside of host.
Schistosoma japonicum
A parasite with oblong eggs that have a LATERAL spine, 50-85 micrometers in size. Resides in the veins surrounding the intestinal tract or blood passages to the liver. Found in stool, not urine
Trichomonas vaginalis
A protozoan causing sexually transmitted infections, identified in vaginal secretions.
Penicillium species
Fungi producing green, granular colonies, some of which are pathogenic to humans. “Brush-like” arrangement of conidiophores.
Taenia solium
A cestode species known as the pork tapeworm, identifiable by its eggs and proglottids.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
The bacteria causing tuberculosis, identifiable by its niacin positivity.
Necator americanus
A species of hookworm known for infecting humans through skin penetration.
Entamoeba hartmanni
One to two nuclei often on either side of a chromatoidal bar wit rounded end with a central karyosome and peripheral chromatin ring. cyst is small ranging around 5 to 10 micrometers.
Endolimax nana
5-10 micrometers with 4 nuclei when mature.
Trichophyto rubrum
Causes itching, scaling skin infection of the feet known as tinea pedis as well as ringworm of the nails and body.
Microsporum canis
Animal ringworm. Associated with ringworm of the scalp or body from pet to human transmission.
Streptomyces species
Not acid-fast and exhibit branching filaments with spores and chains. colonies are typically waxy and heaped or glabrous.
Mycobacterium bovis
A type of acid-fast bacterium that causes tuberculosis in cattle and can infect humans through unpasteurized dairy products. Selectively inhibited by T2H unlike MTB.
Mycobacterium fortuitum
grows on MacConkey agar without Crystal violet.
Chrysosporium species
Not distinctive colonies, growing in 2-4 days with a gray, wooly surface. Conidia prefer singles rather than clusters at the tips of long, thin conidiophores.
Paragonimus westermani
The only helminth egg recovered from sputum samples. Pulmonary fluke infection. Eggs are 78-120 micrometers by 45-60 micrometers. Eggs have prominent shoulders and no terminal knob but o exhibit terminal shell thickening. Eggs are brownish-yellow in color.
Aspergillus fumigatus
Cornea,Respiratory,Skin,Ear, and Gastric infections. Rapid-growing blue-green cottony colony.
Aspergillus flavus
Respiratory, Skin, and Gastric infections.
Aspergillus niger
Respiratory, Skin, Ear, and Gastric infections.
Aspergillus terreus
Nail, Respiratory, Skin, and Gastric infections.Distinctly yellow pigmentation.
Tinea versicolor
a fungal infection caused by Malassezia species, leading to discolored skin patches. 3-5 micrometers in size, spaghetti and meatball arrangement. This condition often results in lighter or darker spots on the skin, particularly in warm, humid environments.
Schistosoma haematobium
110-170 micrometers with an oblong shape and terminal spine. Resides in the veins surrounding the bladder andis found in urine.
Trichophyton tonsurans
Scalp ringworm in the US but also infects nails and skin. yellow to buff, suede-like colony. Large, round, tear drop or club shaped microconidia produced perpendicularly. Best growth is achieved using thiamine.
Taenia solium
Pork ingestion.
Rhizopus
Hyaline, rapid-growing mold. Fluffy white to gray or brown. Found especially in diabetic patients.
Rhodotorula
Red colonies.
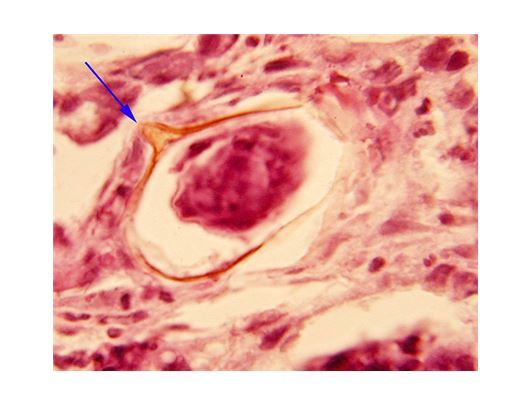
Schistosoma mansoni
large ovum with a spiked spine projection from the shell. over 100 micrometers.
Entamoeba coli
8-16 nuclei
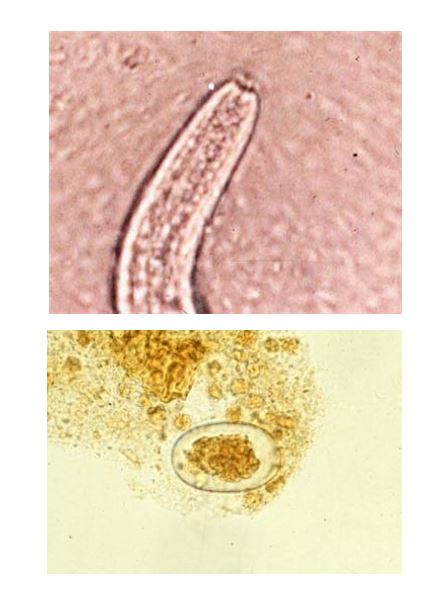
Strongyloides
Short buccal cavity worm.
Candida albicans
Blastoconidia in evenly distributed clusters. Pseudohyphae and germ tubes. Pathogenic yeast causing infections.
Candida glabrata
PRoduces pseudohyphae and uniform cells in tight clusers.
Candida tropicalis
delicate pseudohyphae from which blastoconidia are in singles or small irregular clusters at points of constriction.