Cellular Organelles
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
The body is comprised of trillions of cells that are classified into about how many different cell types?
200
selective barrier separating inside of cell (intracellular fluid) from outside of cell (extracellular fluid), which is comprised of a lipid bilayer along with many embedded proteins
plasma membrane
term for fluid inside the cell
intracellular
term for fluid outside of the cell
extracellular
Which part of a phospholipid is hydrophilic and polar: head or tail?
head
Which part of a phospholipid is lipophilic/hydrophobic and non-polar: head or tail?
tail
refers to proteins that completely span the plasma membrane
integral
refers to proteins that only partially span the plasma membrane
peripheral
What is the function of general surface proteins on the plasma membrane?
interact with neighboring cells
What is the function of surface receptors on the plasma membrane?
transmit signal into cell
plasma membrane proteins that are open on both ends and important for communication between the inside and outside of a cell
channels
plasma membrane proteins that are open on one end and closed on the other end to allow for selective passage of materials (example: carrier proteins)
transporters
largest single cellular component
nucleus
control center that contains the genetic material of the cell and is surrounded by a double phospholipid bilayer
nucleus
double phospholipid bilayer surrounding the nucleus and allowing substances to move into and out of the nucleus
nuclear envelope
complex, gel-like liquid between the plasma membrane and nucleus, surrounding all of the organelles
cytosol
cytosol + all distinct membrane-bound organelles
cytoplasm
What are the 6 main types of organelles in nearly all cells?
nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, lysosomes, peroxisomes, mitochondria
extensive membranous system distributed throughout the cytoplasm that is primarily involved in protein and lipid synthesis
endoplasmic reticulum
division of the ER that has ribosomes on its surface, responsible for protein synthesis
rough
After proteins are synthesized in ribosomes on the rough ER, where are they released? What happens there?
ER lumen, undergoes folding and modifications
After the proteins synthesized in the rough ER are released to the ER lumen and undergo folding and modifications, where are they transported to next?
Golgi complex
division of the ER that does not have ribosomes on its surface, responsible for lipid and carbohydrate synthesis and serves primarily as a final packaging and discharge site for molecules (proteins & lipids) transported to the Golgi complex
smooth
Why do some specialized cells, such as liver, skeletal muscle, and steroid hormone secreting cells, have an extensive smooth ER?
they function in storage of calcium and cholesterol
stack of flattened, membrane-bound sacs that process the raw materials from the ER into finished products, such as through glycosylation, and sort/direct these finished molecules into vesicles to their final destinations (whether another organelle of plasma membrane)
Golgi complex
process in which raw materials from the ER are turned into finished products by attaching a carbohydrate to a hydroxyl or functional group of another molecule, which is important for processing proteins and determining their structure, function, and stability
glycosylation
flattened, membrane-bound sacs in the Golgi complex
cisternae
The rough ER is primarily involved in the synthesis of which of the following?
A. proteins
B. lipids
C. carbohydrates
A
What are the 6 steps of the protein transport process?
synthesis in rough ER, packaging and budding in smooth ER, fusion with Golgi complex, processing and sorting in Golgi, budding from Golgi and transport to plasma membrane, fusion with plasma membrane
process in which a secretory vesicle in cytosol travels to and makes contact with the plasma membrane, triggering a fusion reaction between the two membranes so that the contents of the vesicle are released into extracellular fluid
**involves the interaction of many proteins in the budding from the Golgi complex and the fusion to the plasma membrane or organelle membrane
exocytosis
How does the sorting of proteins happen in the Golgi complex? What makes that possible?
each protein has a specific sorting signal attached to it when synthesized
What does the Golgi complex have that binds to the sorting signals on proteins so that those proteins can be organized and localized to certain regions?
specific recognition markers
molecules on the outside of a cell that bind specific cytosolic proteins that are involved in forming a coat around the vesicle, which allows a pulling motion to occur that forms exocytic vesicles that budded from the Golgi
coat protein acceptors
coat protein found inside the cell that is involved in the formation of vesicles for transport
clathrin
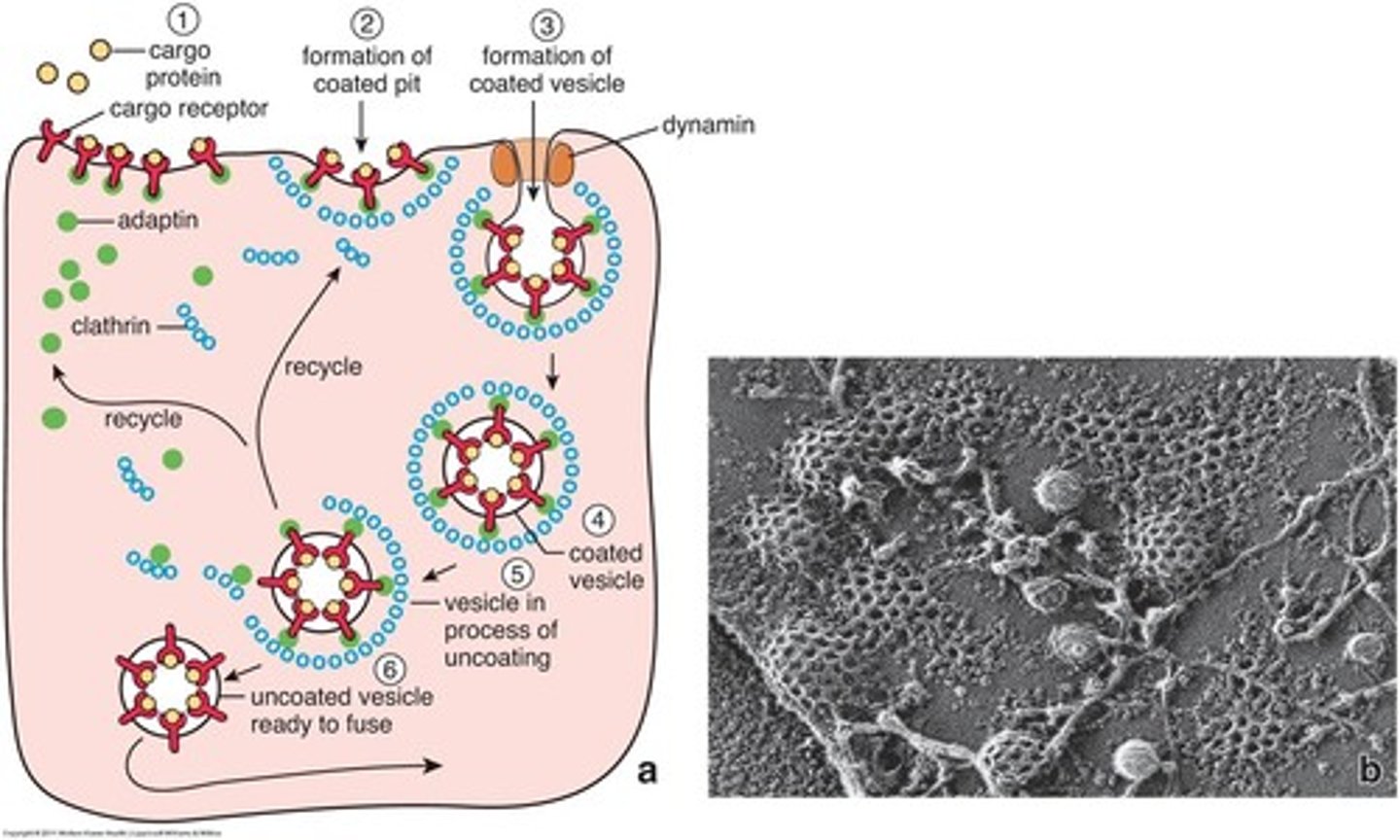
specific protein on the surface of a vesicle that budded from the Golgi that serves as a docking marker that binds to and interacts with t-SNARE on the surface of the plasma membrane (docking marker acceptor)
v-SNARE
protein on the surface of the plasma membrane (docking marker acceptor) that binds with v-SNARE to trigger the fusion between the vesicle and plasma membrane so that exocytosis can occur and contents can be released outside the cell
t-SNARE
What two proteins (one on vesicle, one on intracellular side of plasma membrane) must bind to trigger the fusion of membranes for exocytosis to occur? Where are these two proteins found?
v-SNARE on vesicle, t-SNARE on inside plasma membrane
membrane-bound organelles that serve as the intracellular digestive system since they contain hydrolytic enzymes that break down the organic compounds ingested by the cell via endocytosis; also removes worn-out organelles
lysosomes
What do lysosomes contain that helps them to break down organic compounds?
hydrolytic enzymes
1 of the 3 major endocytosis processes: "cell drinking", non-selective uptake of small molecules
pinocytosis
1 of the 3 major endocytosis processes: highly selective uptake triggered by a ligand binding to its receptor
receptor mediated endocytosis
1 of the 3 major endocytosis processes: internalization of large, multi-molecular particles like bacteria or erythrocytes (selective to an extent)
phagocytosis
membrane-bound organelles that contain oxidative enzymes and most of the cell's catalase
peroxisomes
enzyme that is important for the conversion of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen; found mostly in peroxisomes
catalase
reaction involved in the detoxification of various wastes produced in the cell and foreign toxins ingested by the cell, which occurs in peroxisomes
oxidation
power plants of the cell since they supply the cell with about 90% of its energy in the form of ATP; enclosed by a double membrane, and uses pyruvic acid made from glycolysis to carry out Krebs cycle and ETC
mitochondria
series of infoldings of the inner mitochondrial membrane; forms a labyrinth of sorts inside the mitochondria
cristae
breakdown of glucose by a series of enzymes in the cytosol to produce pyruvic acid
glycolysis
product of glycolysis that goes into the mitochondria and is converted to ATP via a series of enzyme reactions in the mitochondrial matrix (Krebs cycle)
pyruvic acid
In the Krebs cycle, in addition to ATP made from pyruvic acid, excess hydrogen comes in the form of what two molecules?
NADH, FADH2
After the Krebs cycle, the electron transport chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane converts excess hydrogens (NADH, FADH2) into ATP via their movement across the membrane. This generates about how many more ATPs in addition to what has been produced already?
28-32
substance that occupies 55% of total cell volume and is the site of many metabolic processes (i.e. glycolysis); ribosomal protein synthesis; and storage of fat, carbohydrates (glycogen), and secretory vesicles
cytosol
What three things are stored in cytosol?
fat, carbohydrates, secretory vesicles
intracellular scaffolding that gives the cell shape and structure, made of microfilaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments
also serves as an intracellular highway for the trafficking of vesicles to and from the plasma membrane
cytoskeleton
proteins in the cytoskeleton made of actin
microfilaments
proteins in the cytoskeleton made of tubulin
microtubules
proteins in the cytoskeleton made of many other different proteins, has a relatively middle diameter
intermediate filaments
What makes up microfilaments?
actin
What makes up microtubules?
tubulin
Molecular motors that power the movement of vesicles to and from the plasma membrane are what kind of enzymes?
ATPases
exocytosis molecular motor
(carries vesicles from cell body to axon terminal)
kinesin
endocytosis molecular motor
(carries vesicles to the cell body)
dynein
maintenance of a relatively stable environment; essential for the survival for each cell, and each cell contributes as a part of a body system to the maintenance of the internal environment shared by all cells
homeostasis
Which organelle serves as the digestive system of the cell?
A. ER
B. lysosome
C. peroxisome
D. Golgi
B
Which organelle is not membrane-bound?
A. lysosome
B. ribosome
C. mitochondrion
D. Golgi body
E. rough ER
B
Which of the following does not always involve the plasma membrane?
A. endocytosis
B. pinocytosis
C. formation of an endocytic vesicle
D. secretion
E. vesicle formation
E
The organelle that combines proteins with carbohydrates and packages them within the vesicle for secretion is...
A. Golgi complex
B. rough ER
C. smooth ER
D. ribosome
A
Which cell structure contains the enzymes required for oxidative phosphorylation?
A. inner mitochondrial membrane
B. smooth ER
C. rough ER
D. outer mitochondrial membrane
E. matrix of mitochondria
F. cytosol
A