MAN3025 Module 9: Individual Differences
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
the halo effect
Occurs when we form an impression of an individual based on a single trait.
employee assistance program (EAPs)
Includes a host of programs aimed at helping employees cope with stress, burnout, substance abuse, health problems, family and marital issues, and any general problem that negatively influences job performance.
correlates of job satisfaction
Stronger motivation, performance, job involvement, organizational commitment, and life satisfaction
Less absenteeism, tardiness, turnover, and perceived stress
stereotyping
The tendency to attribute to an individual the characteristics one believes are typical of the group to which that individual belongs.
emotional intelligence
The ability to monitor your own feelings and those of others and to use this information to guide your thinking and actions
The Big Five personality dimensions
Extroversion
Agreeableness
Conscientiousness
Emotional stability
Openness to experience
4 Core Self-Evaluations
Self-efficacy
Self-esteem
Locus of control
Emotional stability
values
Abstract ideals that guide one’s thinking and behavior across all situations
attitudes
Learned predispositions toward a given object. Consists of an affective, cognitive, and behavioral component.
cognitive dissonance
The psychological discomfort a person experiences between their cognitive attitude and incompatible behavior.
perception
The process of interpreting and understanding one’s environment
5 Distortions of Perception
Stereotyping
Implicit bias
The halo effect
The recency effect
Casual attribution
self-fulfilling prophecy
The phenomenon in which people’s expectations of themselves or others lead them to behave in ways that make those expectations come true.
work-related attitudes
Employee engagement, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment
employee engagement
An individual’s involvement, satisfaction, and enthusiasm for work
job satisfaction
The extent to which you feel positive or negative about various aspects of your work
organizational commitment
The extent to which an employee identifies with an organization and is committed to its goals
stress
The tension people feel when they are facing or enduring extraordinary demands, constraints, or opportunities and are uncertain about their ability to handle them effectively
7 Sources of Job Stress
Demands created by individual differences
Individual task demands
Individual role demands
Group demands
Organizational demands
Nonwork demands
Demands created by remote and hybrid work schedules
buffers to reduce stressors
Roll out employee assistance programs, recommend a holistic wellness approach, create a supportive environment, make jobs interesting, and make career counseling available.
organizational citizenship behaviors (OCBs)
Employee behaviors that are not directly part of employees’ job descriptions
counterproductive work behaviors (CWBs)
Types of behavior that harm employees and the organization as a whole
organizational behavior (OB)
The field dedicated to better understanding and managing people at work
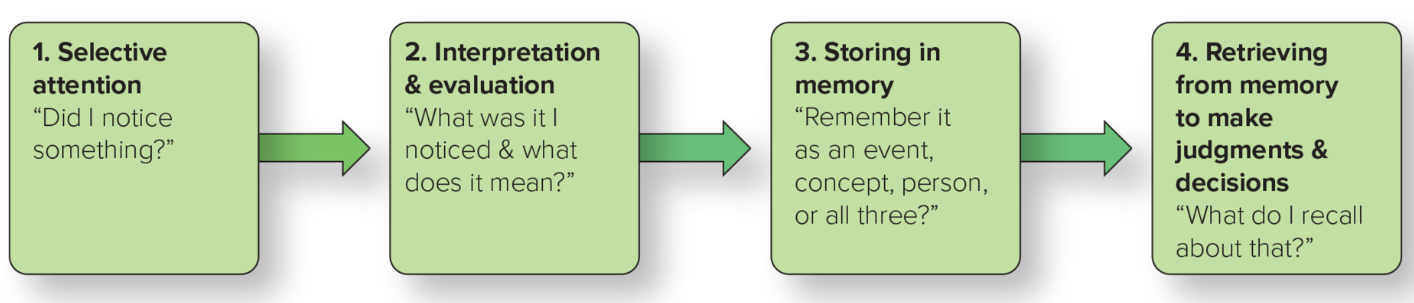
4 Steps in the Perceptual Process
Selective attention
Interpretation and evaluation
Storing in memory
Retrieving from memory to make judgements and decisions
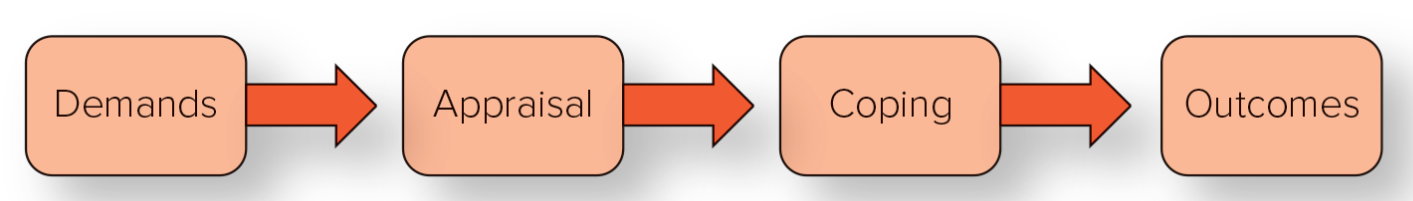
The Stress Process
Demands
Appraisal
Coping
Outcomes
holistic wellness program
Focuses on self-responsibility, nutritional awareness, relaxation techniques, physical fitness, and environmental awareness
implicit bias
The attitudes or beliefs that affect our understanding, actions, and decisions in an unconscious manner
the recency effect
The tendency to remember recent information better than earlier information
casual attribution
The activity of inferring causes for observed behavior
self-serving bias
Tendency to take more responsibility for our own successes than our failures
self-efficacy
The belief in one’s personal ability to do a task
generalized self-efficacy
The belief in one’s general ability to perform across different situations
4 Components of Emotional Intelligence
Self-awareness, the ability to read your own emotions
Self-management, the ability to control your emotions
Social awareness, having empathy to show others you care
Relationship management, the ability to communicate clearly and convincingly, disarm conflicts, and build strong personal bonds
extroversion
How outgoing, talkative, sociable, and assertive a person is
agreeableness
How trusting, good-natured, cooperative, and soft-hearted a person is
conscientiousness
How dependable, responsible, achievement-oriented, and persistent someone is
emotional stability
How relaxed, secure, and unworried a person is
Openness to experience
How intellectual, imaginative, curious, and broad-minded someone is