Cell junctions
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
1
New cards
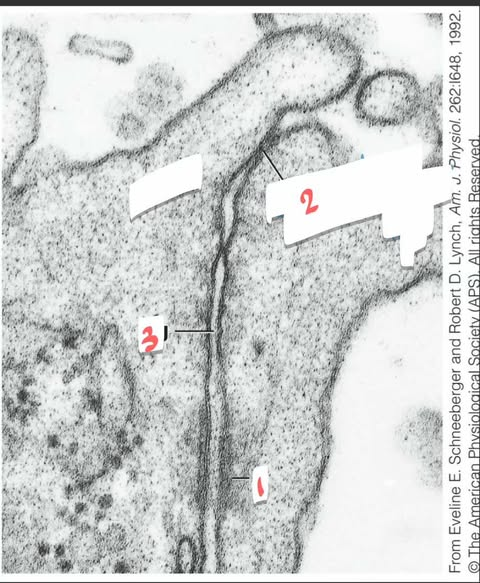
what is 2
tight junction
2
New cards
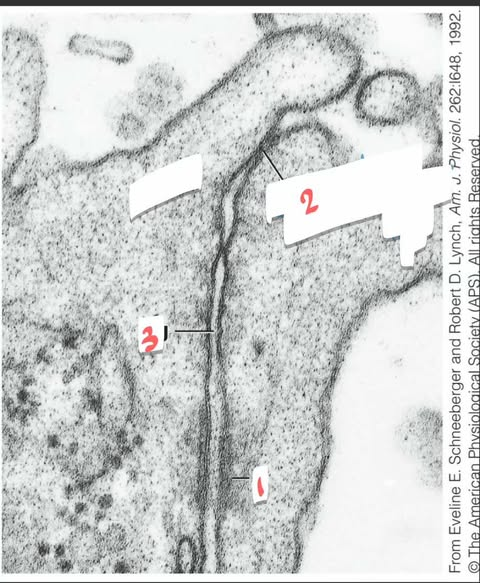
what is 3
adheren junction
3
New cards
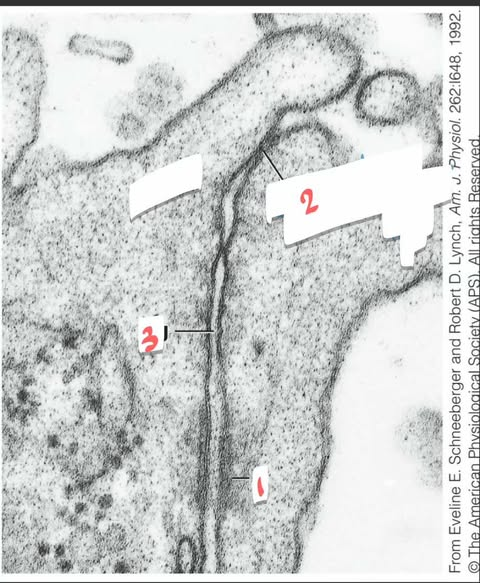
what is 1
desmosomes
4
New cards
Hemidesmosomes function is
cell-substratum adhesion
5
New cards
What is also attached to keratin
hemidesmosomes
6
New cards
Focal adhesions function is
cell motility, survival signals
7
New cards
Focal adhesions is attached to
actin
8
New cards
Gap junctions have what function
passage of solutes, communication
9
New cards
How are gap junctions attached to the cytoskeleton
no connection
10
New cards
What junctions are known for cell-cell adhesive strength (abbreviated)
AJ, D
11
New cards
Where are gap junctions, adheren junctions, desmosomes, tight junctions located
lateral membrane
12
New cards
Where are hemidesmosomes and focal adhesions located
basal membrane
13
New cards
Which cellular junction plays a key roles in cell locomotion
focal adhesion
14
New cards
Focal adhesions are
dynamic
15
New cards
focal adhesion are [blank] and [blank]
made, break easily
16
New cards
what binds hemidesmosomes
keratin intermediate filaments to integrin proteins
17
New cards
what binds focal adhesion
actin cytoskeleton to integrins to ecm
18
New cards
what sends a signal of survival to the nucleus
integrin signalling layer
19
New cards
what happens if there is no signal of survival to the nucleus
apoptosis
20
New cards
talin links
integrin to actin
21
New cards
what is needed for cell survival and proliferation
focal adhesion kinase (FAK), SRC kinase
22
New cards
Hemidesmosomes contain
dense cytoplasmic plaque, keratin filaments
23
New cards
What are the keratin filaments linked to in hemidesmosomes
ECM
24
New cards
How are keratin filaments linked to
integrins to ECM
25
New cards
What are hemidesmosomes anchored to
basement membrane
26
New cards
What type of channel is gap junction
communication
27
New cards
Gap junctions form
intercellular channels
28
New cards
What is made up of connexin proteins
gap junctions
29
New cards
connexin proteins are
1 subunit
30
New cards
what is a connexon
6 connexin proteins together
31
New cards
to form a transmembrane channel with a central pore is called
connexon
32
New cards
how many connexons form a gap junction
two
33
New cards
how many connexin proteins are in a gap junction
12
34
New cards
what is the size restriction in gap junctions
< 1000 Da
35
New cards
the central pore is
hydrophilic
36
New cards
what else provides tissue strength other than adheren junction and desmosomes
hemidesmosomes
37
New cards
Gap junctions are what type of communication
1 way
38
New cards
Even though gap junctions are 1 way communication it is [blank] cytoplasm
between two
39
New cards
Hemidesmosomes are
stationary
40
New cards
Keratin intermediate filaments in epithelial cells go
around nucleus
41
New cards
Cytoplasmic plaque has 3 characteristics
strength, made of keratin, electron dense
42
New cards
Desmosomes use what type of binding to anchor two cell together
intermediate filament
43
New cards
When cadherins interact with multiple proteins, what does it form
cytoplasmic plaque
44
New cards
Where does this cytoplasmic plaque form
inner surface of the plasma membrane
45
New cards
Cadherins interact with
multiple proteins
46
New cards
Desomosomes also contain
cadherins
47
New cards
Desmosomes primarily
adhesive
48
New cards
adherens junctions, desmosomes increase
tissue strength
49
New cards
what do adherens junctions connect
external enviroment to actin cytoskeleton
50
New cards
adheren junctions attach to
actin cytoskeleton
51
New cards
desmosomes attach to
keratin
52
New cards
adheren junctions provide a [blank] for signals to be transmitted
pathway
53
New cards
where are signals transmitted from (adheren junctions)
exterior to the cytoplasm and nucleus
54
New cards
zonula adherens are
AJ that form a belt that encircles the cell
55
New cards
AJ forms a belt near their
apical surface in epithelial cells
56
New cards
What are the two type of tight junctions
gate, fence
57
New cards
How does TJ contribute to cell polarity?
forming a barrier that blocks proteins
58
New cards
The function of tight junctions in general
cell-cell permeability and cell polarity
59
New cards
Tight junctions bind to
actin cytoskeleton
60
New cards
Fence function
blocks diffusion between apical – basolateral
61
New cards
Whats the cell attachment of tight junctions
neighbouring epithelial
62
New cards
Gate function
controls ion, protein, water between cells
63
New cards
What is the gate function also called what pathway
paracellular
64
New cards
Tight junctions are also known as
zonula occluden
65
New cards
Desmosomes are also known as
macula asheren
66
New cards
What can you use to visualize cell junctions
electron microscopy
67
New cards
Electron microscopy uses
electrons
68
New cards
What type of cells cannot be imaged in electron microscopy, why
live, vacuumed
69
New cards
Electron microscopy is also called
TEM (transmission)
70
New cards
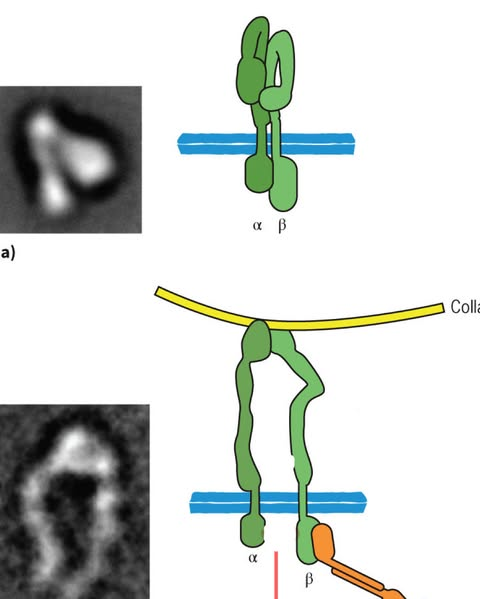
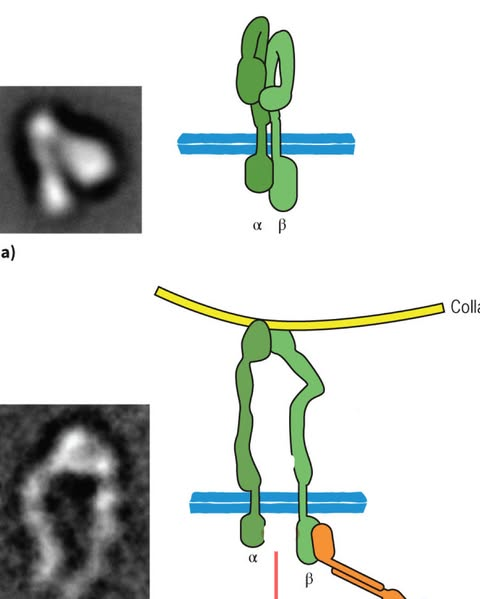
what type of integrin does the top one represent
inactive
71
New cards
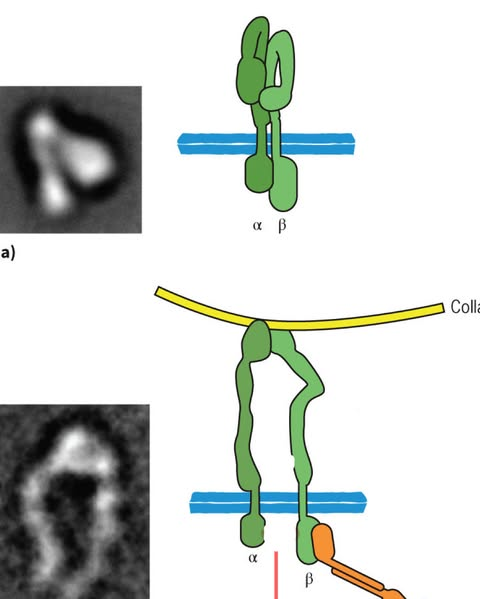
what does the bottom one represent
active
72
New cards
how do we know the bottom one is active?
there is space for activation
73
New cards
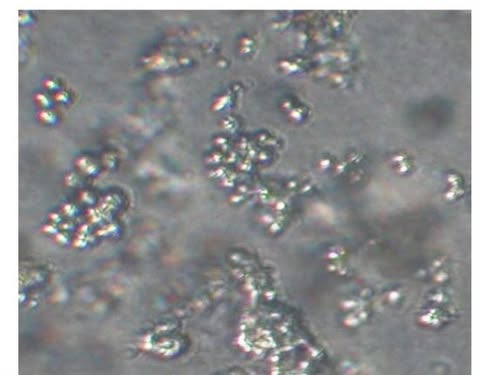
what is this a picture of?
breast cancer cells
74
New cards
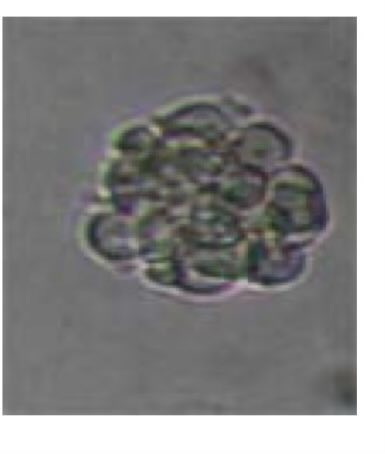
what is this a picture of?
normal cell
75
New cards
What happens when trypsin is added [] get cut
cadherins, integrins
76
New cards
What would disrupt cell adhesion [_,_]
Small peptides containing RGD, trypsin
77
New cards
Integrins often interact with
ECM proteins
78
New cards
What extend further than glycocalyx
ECM
79
New cards
Glycocalyx extends only a [] from the cell membrane
small distance
80
New cards
Fibronectin description is
interactive dimer
81
New cards
The function of fibronectin is to
linked to multiple molecules, improve signal survival
82
New cards
What are MMPs
matrix metalloproteases
83
New cards
What MMPs for connective tissue collagen
collagenases
84
New cards
What MMPs basement membrane collagen, gelatin
gelatinases
85
New cards
What MMPs for proteoglycan, laminin, fibronectin, gelatine
stromelysins
86
New cards
What does a neutrophil need to migrate through collagen
MMP
87
New cards
MMP are..
enzymes that can chop
88
New cards
Without MMP what happens to neutrophils in collagen
cant get through
89
New cards
Laminin are made up of [], linked by []
3 different proteins, disulfide bonds
90
New cards
What is involved in migration, growth differentiation
laminin
91
New cards
Differentiation is also known as
specialization
92
New cards
What forms separate but interconnected networks
laminin, collagen IV
93
New cards
what look like trimers organized into a cross-like shape
laminins
94
New cards
Proteoglycan look
feather like
95
New cards
Proteoglycan form a [blank] how [proteoglycans bind to_ which bind to_]
porous hydrated gel, cations, water molecules
96
New cards
Porous hydrated gel results in
increased resistance to crushing or compression
97
New cards
Increased resistance to crushing or compression is great in
joint
98
New cards
What provides ECM strength and resistance [_,_]
collagen, proteoglycan
99
New cards
What do proteoglycans consist of
core protein
100
New cards
The core protein in proteoglycans [], attached []
covalently, glycosaminoglycans