Econ Test 3 Study
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Say’s Law argues that a given ____________________ must create an equivalent ________________________ somewhere else in the economy.
value of supply; value of demand
Aggregate supply (AS) denotes the relationship between the __________________ that firms choose to produce and sell and the _________________, holding the price of inputs fixed.
total quantity; price level for output
In macroeconomics, _____________________ denotes the relationship between the total quantity of goods and services demanded and the price level for output.
aggregate demand (AD)
The term ”full employment GDP” is synonymous with which of the following?
potential GDP
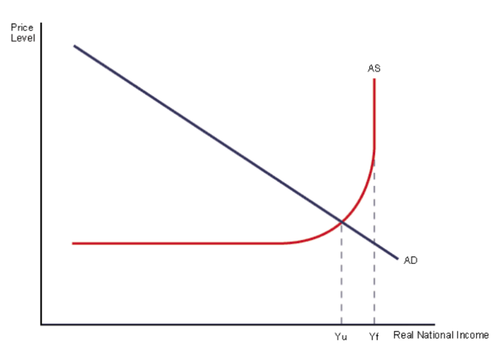
Referring to the diagram below, which of the following is a true statement?
There is insufficient aggregate demand to reach full employment.
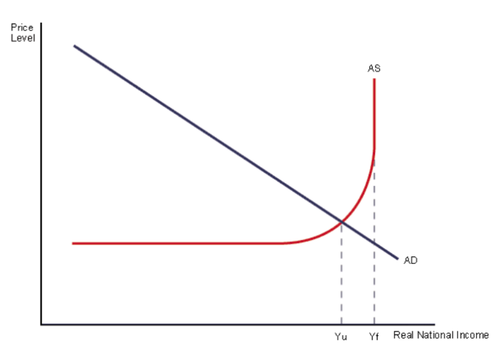
Refer to the graph below. A government creating economic policy in these circumstances should be most concerned about:
inflation but not unemployment.
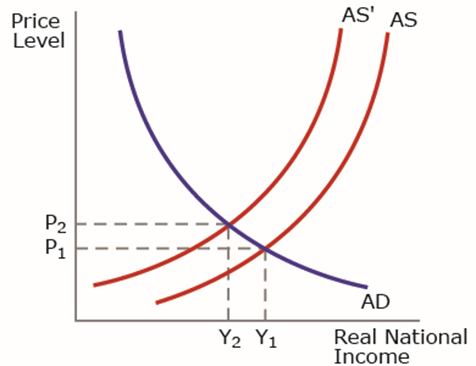
The graph below refers to a significant increase in oil prices. Which of the following is likely to result?
a rise in inflation from 2.0% to 3.0%
Why is productivity growth considered to be the most important factor in the AD/ASAD/AS model?
it shifts the AS curve in the long-term
When the economy of a country is operating close to its full capacity:
cyclical unemployment is close to zero.
The __________________ in an AD/AS diagram is most relevant to Keynes’s Law.
flat portion of the AS curve
Consumption, investment, government spending, exports, and imports are:
all complementary elements of a market-orientated economy.
According to the Keynesian framework, ________________________ may cause a recession, but not inflation.
a major trading partner's economic slowdown
Keynesian economics focuses on explaining why recessions and depressions occur, as well as offering a ______________________ for minimizing their effects.
policy prescription
The equilibrium quantity of labor and the equilibrium wage level decrease when:
labor demand shifts to the left, if wages are flexible.
The Keynesian economic framework is based on an assumption that:
prices and wages are sticky and do not adjust rapidly.
According to the _____________________ argument, a market-oriented economy has no obvious way to implement a plan of systematic wage reductions.
coordination
According to macroeconomic theory, evidence that high unemployment may be accompanied by low inflation, and low unemployment may be accompanied by high inflation is supported by the:
Keynesian Phillips curve tradeoff.
If a Phillips curve shows that unemployment is high and inflation is low in the economy, then that economy:
is producing at a point where output is less than potential GDP.
In a Keynesian AD-AS diagram, what name is given to the distance between an output level that is below potential GDP and the level of potential GDP?
recessionary gap
The economy is in a recession and the government wants to increase output. If the expenditure multiplier, i.e. ∆Y/∆G, equals 3 and the government increases spending, i.e. ∆G, by 250, how much will output increase, i.e. ∆Y, by?
750
The neoclassical perspective on macroeconomics emphasizes that in the long run, the economy seems to rebound back to its _____________ and its ____________________.
potential GDP; natural rate of unemployment
Which of the following is a distinguishing characteristic of the neoclassical view?
flexibility of wages and prices over time
In the neoclassical view, the economy has a ___________________________ to move back to potential GDP.
self-correcting tendency
The neoclassical view holds that long-term expansion of potential GDP due to _______________________ will determine ____________________.
economic growth; the size of the economy
In the neoclassical model, the AS curve shifts to the right over time as_______________________ and potential GDP expands.
productivity increases
Which of the following government policies would be supported by neoclassical macroeconomic assumptions?
focus on long-term growth and on controlling inflation
Over the long run, a surge in aggregate demand from a neoclassical perspective will most likely result in:
an increase in price level.
In the neoclassical view, changes in ____________________ can only have a short-run impact on output and on unemployment.
aggregate demand
From a neoclassical perspective, which of the following would most likely be viewed as an element that underpins long-run productivity growth in the economy?
investments in human capital
A typical neoclassical aggregate supply (AS) curve ______________ and a typical neoclassical Phillips curve __________________.
is vertical; is vertical