Energy and Mechanisms
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What are non-renewable energy sources?
Sources that will eventually run out.
How are fossil fuels formed?
Formed from the remains of dead organisms over a very long time. E.g. coal, oil and natural gas.
How is energy created through fossil fuels?
They’re burned to create steam. This turns turbines which drive generators that produce electricity.
What are the benefits of fossil fuels?
Many are currently in good supply
Easy to find
Allow generation of huge amount of electricity from one location
How does nuclear power generate electricity?
Steam is created using a nuclear reactors which then turns the turbines and drive generators.
What are the issues with nuclear power?
Rare, but can result in radioactive material being released into the environment
Strict procedures for disposal/storage of nuclear waste
What are renewable energy sources?
Sustainable sources that won’t run out and can replenish themselves quickly
How is solar energy made?
Photovoltaic cells convert solar energy into an electric current
What are the disadvantages of solar panels?
Produce no electricity at night
Installation and maintenance costs are high
How is electricity generated via wind?
Turbines drive the generators that are turned by the wind.
What are the disadvantages of wind energy?
Some feels that they’re too noisy and they don’t like the visual impact
How is hydro-electric energy harnessed?
Water is held in a reservoir and behind a dam. It’s then released, turning a turbine which generates electricity.
What are the disadvantages of hydroelectric energy?
Creating a reservoir involves flooding large areas of land
Habitats are destroyed
People are forced to move
What is tidal energy?
A form of hydro-electric that harnesses the energy from the tides of the sea to generate electricity.
How does biomass create electricity?
Fuel is create from organic materials such as crops, scrap wood and animal waste
What is the main disadvantage of biomass?
Can be a very expensive way of producing fuel
What do batteries convert chemical energy into?
Electrical energy
What is rotating motion?
Movement in a circle

What is linear motion?
Motion going in a straight line in one direction

What is reciprocating motion?
Motion moving backwards and forwards

What is oscillating motion?
Motion swinging backwards and forwards, like a pendulum

What is a lever?
A simple form of machine that changes the amount of effort or force needed to move a load. They consist of a rigid bar that pivots around a fulcrum.
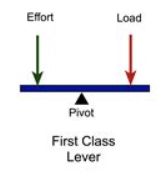
What is a first-order lever? Give examples.
When the fulcrum is in between the load and the effort. E.g. seesaws and scissors.
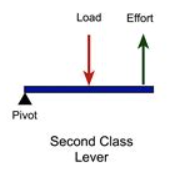
What is a second-order lever? Give examples.
When the load is applied between the effort and the fulcrum. E.g. nutcrackers and wheelbarrows.
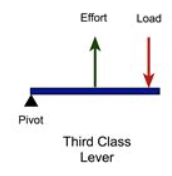
What is a third-order lever? Give an example.
When the effort is applied between the load and the fulcrum. E.g. lifting a dumbell.
What is the purpose of mechanical devices?
They’re used to transfer motion or force between mechanisms or to convert between different types of motion.
What do linkages do?
They transfer motion between two positions but also act as levers.
What does a push-pull linkage do?
Reverses the direction of linear motion. Also called a reversing linkage.
What does a bell crank do?
Change the direction of motion by an angle e.g. 90°
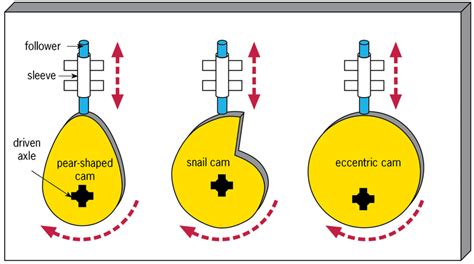
What do cams do? Give an example.
Convert rotary motion to reciprocating motion. E.g. provide the movement of the needle in a sewing machine.
What are the main type of cam?
Eccentric circles
Pear-shaped
Snail-shaped
What can gears change?
The speed or force of the motion they transfer.
What do spurs gears transfer?
Rotary motion
What do bevel gears and worm and worm wheels change?
Rotary motion through 90°
What does a rack and pinion gear do?
Change rotary motion into linear motion
What is a pulley?
A pair of grooved wheels with a belt running in the groove
What does a pulley do?
Transfers rotary motion with both wheels moving in the same direction. They can change the speed or force of the motion they transfer.
What are examples of pulleys in use?
Used in drills, lathes and sewing machines