1. electron transport chain
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
throughout stages of respiration so far, many coenzymes (NAD and FAD) have been reduced as they accepted H
these coenzymes are transported to ETC at cristae where they release this H and reoxidised
H atoms split into protons (H+ ions) and electrons
electrons passed along a series of electron carriers embedded in inner membrane of cristae and release energy which powers production of ATP- known as ‘oxidative phosphorylation’ because it depends on presence of O2
ELECTRON CHAIN TRANSPORT- DIAGRAM
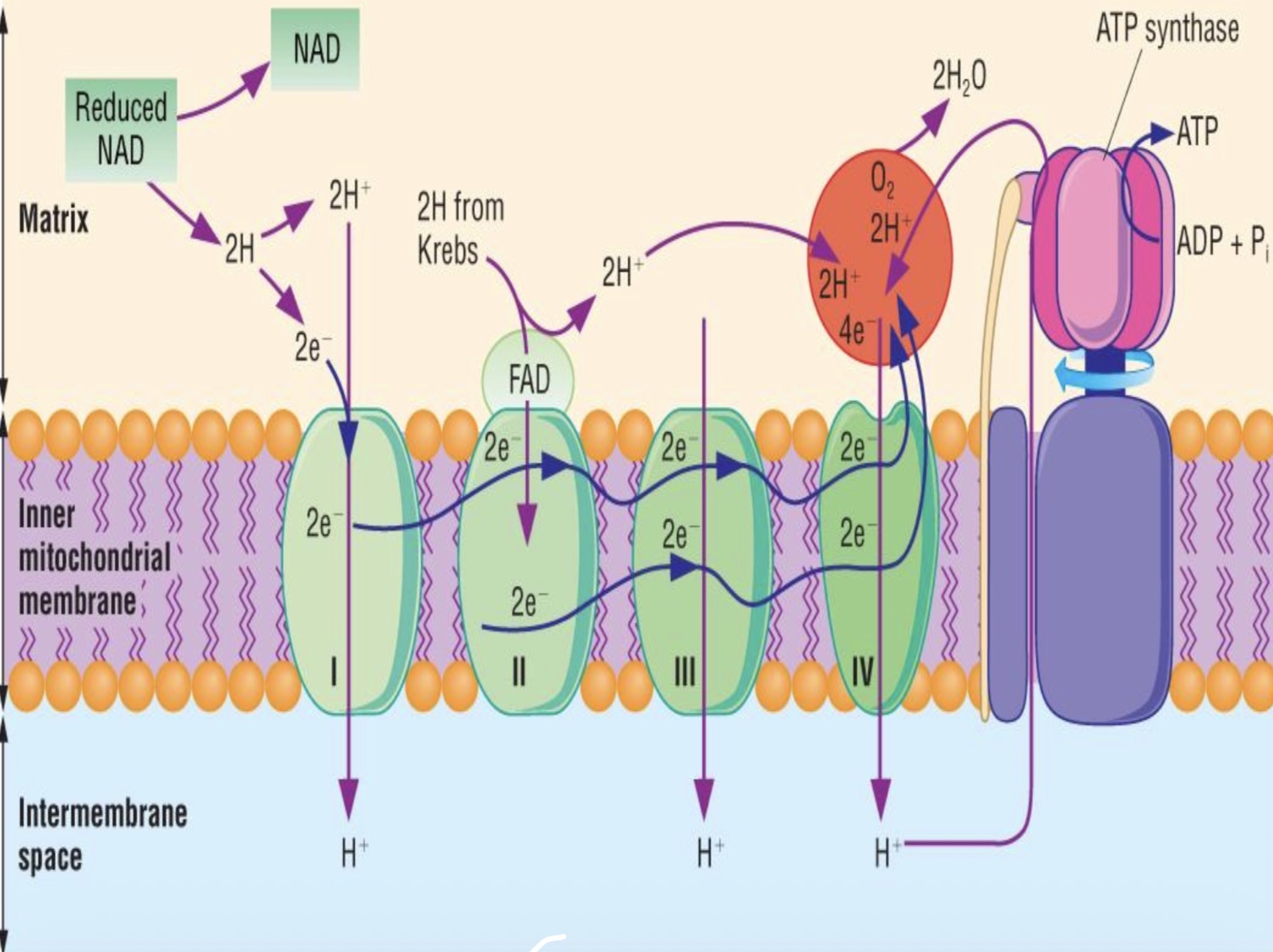
ELECTRON CARRIERS- NAD
each carrier is at lower energy level than one before
electrons from reduced NAD are accepted by next carrier in chain, then passed along chain
energy released by the electrons as they move down energy levels is used to drive ATP synthesis
scientists believe its likely to be 5 ATP molecules synthesized for every 2 reduced NAD that is reoxidised
ELECTRON CARRIERS-FAD
coenzyme FAD is associated with second carrier in chain
scientists believe its likely to be 3 ATP molecules synthesised for every 2 reduced FAD that’s reoxidised
ELECTRON CARRIERS
cytochromes are protein pigments w/ an iron group
cytochrome oxidase is an enzyme
both these carriers are reduced and oxidised as they accept then lose electrons
FINAL ELECTRON ACCEPTOR
O2 accepts electrons at end of chain
O2 also accepts H+ ions
so O2 is reduced and water is formed
CHEMIOSMOSIS
proposed by Peter Mitchell
theory suggests that energy provided by electrons is used to actively transport H+ ions (protons) in matrix across inner membrane into intermembrane space
now a conc gradient between intermembrane space and matrix
also pH gradient and electrochemical gradient
so protons want to diffuse back into matrix
but bc inner membrane is generally impermeable to protons, only way they can move down the gradient is through special pores that span inner membrane
PORES
these pores (or channels) are part of stalked particles embedded in inner membrane
stalked particles are associated with ATPase enzyme
as H+ ions flow through channels down their electrical, pH and conc gradients, they drive rotation part of enzyme and join ADP + Pi to form ATP
ETC EVIDENCE
if you break open cells to isolate mitochondria, mitochondria will produce ATP if supplied with glucose and oxygen
electron microscopes show inner mitochondrial membrane to be covered in stalked particles that greatly increase SA for enzyme action
stalked particles and membranes associated with them that have been separated from rest of mitochondria are shown to be capable of ATP synthesis