Mitosis and Meiosis
1/15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is Genetics?
the study of heredity and the variation of inherited characteristics through DNA
Chromosome
tightly coiled packages of DNA found in the nucleus during mitosis
Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs).
Chromatin
the tangled fibrous complex of DNA found in the nucleus during interphase
Genes
specific DNA sequence that contains a set of instructions for a specific trait
e.g. gene for eye colour, gene for ear shape
humans have approximately 30 000 genes
Allele
one of two or more forms of a gene
allele for blue eye colour or allele for brown eye colour
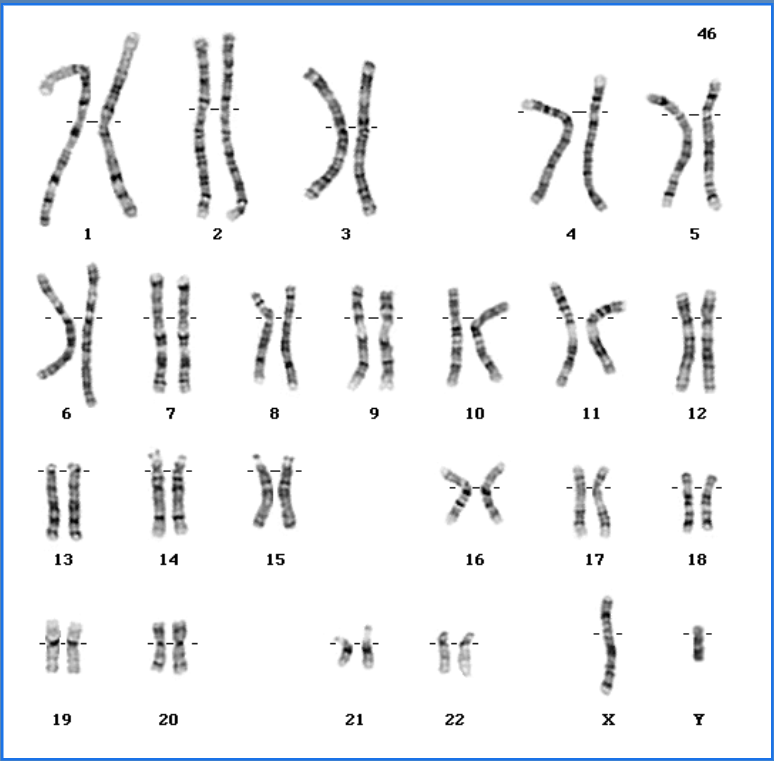
Karyotype
a picture of all the chromosomes of a cell arranged in homologous pairs
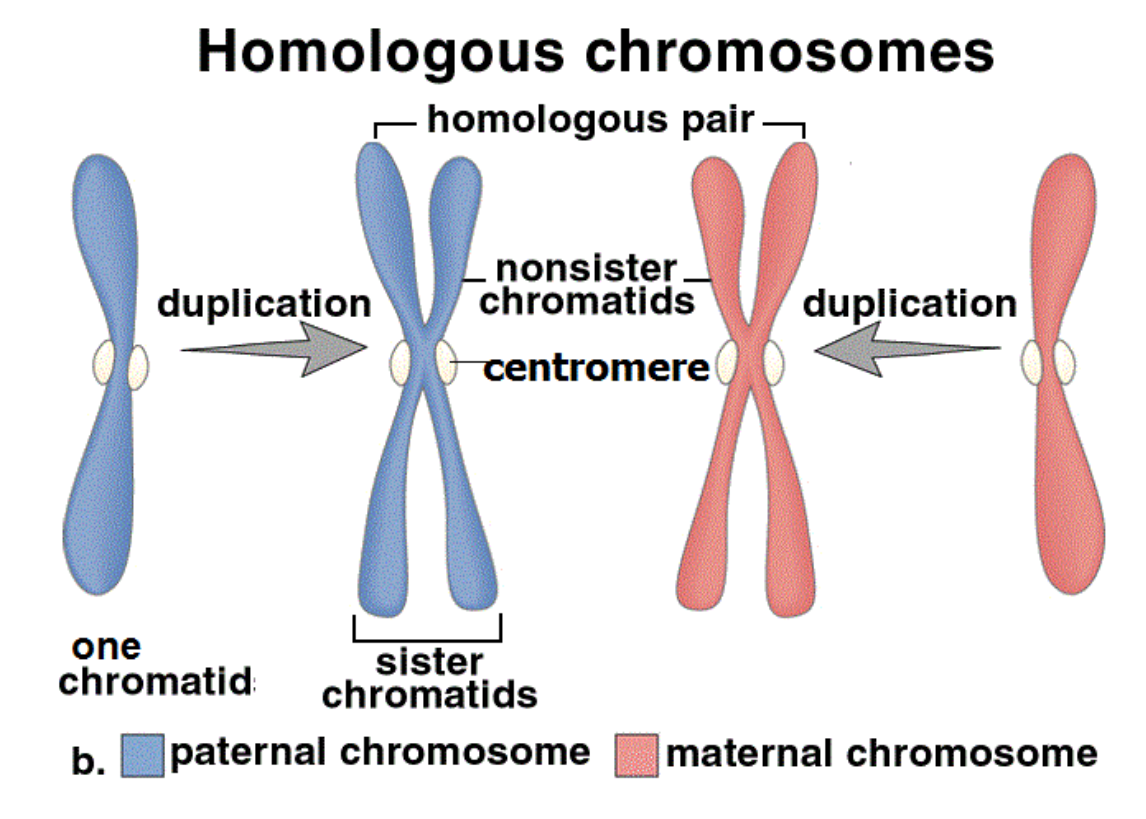
Homologous Pairs
Chromosomes that carry the same genes but possibly different alleles; one homologue comes from mom and one comes from dad
Arranged according to length, centromere location and banding pattern
Two Types of chromosomes
Autosome - Chromosome that is not involved in determining the sex of an organism (In humans, pairs 1 - 22 are autosomes)
Sex Chromosome - An X or Y chromosome, which determines the genetic sex of an organism
Cell Division and Chromosomes
When new cells are required in the body, chromosomes must be duplicated to ensure each new cells receives a complete set of instructions
Each chromatid contains a complete set of genetic information
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Polymer
The individual units (monomers) of DNA are called nucleotide
A nucleotide is made up of 3 parts:pentose sugar (deoxyribose)
nitrogenous base:
adenine (A)
guanine (G)
cytosine (C)
thymine (T)
phosphate
purines
Adenine and guanine are double ring structures
pyrimidines
Thymine, uracil, and cytosine are single ring structures
DNA Shape/Structure
DNA is a double helix (looks like a twisted ladder)
Two strands of DNA bond together through “complementary base pairing”, dependent on:
Base size (purine-pyrimidine)
Number of hydrogen bonds