Physics - Ch. 5 Imaging Motion and Flow With Principle 1
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Which state of matters classify as fluids?
liquids and solids
Which states of matter "flow"?
gases and liquids
Viscosity units
poise or kg/m-s
Volumetric Flow Rate (Q)
The volume of blood passing a point per unit of time
Volumetric Flow Rate units
milliliters per second (mL/s)
Volumetric Flow Rate formula
Q (mL/s) = Pressure difference (dyne/cm²) / Resistance to flow (poise)
What situation is Poiseuille's Law used for?
calculate steady flow in long, straight tubes
If pressure difference increases, flow rate ____________.
increases
If diameter of the tube increases, flow rate ____________.
increases
If viscosity of the tube increases, flow rate _____________.
decreases
If length of the tube increases, flow rate _____________.
decreases
Poiseuille's Equation:
Q = ΔPπr^4/8Lη
Q(mL s) = ∆P(dyne /cm2) × π × d4 (cm 4) / 128 × L (cm) × η (poise)
The volumetric flow rate in a tube is determined by ______________ difference and _____________.
pressure; resistance
With parabolic flow, the average flow speed across the vessel is equal to....
one half the maximum flow speed (center)
Is forward net flow still maintained with turbulent flow?
yes
Continuity Rule
Blood is neither created nor destroyed as it flows through a vessel SO... volumetric flow rate must be constant proximal, within, and distal to a stenosis
Bernoulli Effect
A drop in pressure associated with high flow speed at a stenosis
Absolute Doppler effect
for light
Relative Doppler effect
sound waves
f Dop =
f received - f transmitted
or
1/c
Doppler effect is caused by a change in ______________, caused by motion relative to the observer.
wavelength
As relative motion increases the Doppler effect _____________.
increases
What is the relationship between velocity and distance traveled for the doppler effect?
proportional: higher velocity implies a greater distance traveled
The relative distance change is a percentage of the ________________.
wavelength
Anything which results in a greater distance will result in a greater....
percent change in wavelength
Which three situations can affect the Doppler effect?
moving source
moving receiver
moving reflector
The change in frequency of the Doppler shift is caused by....
motion
If scatterer speed increases, the Doppler shift ____________.
increases
If source frequency increases, the Doppler shift _____________.
increases
Are Doppler shift and flow speed proportional?
yes
What type of flow information can Doppler Ultrasound provide?
presence of flow, direction of flow, speed of flow, character of flow
Form of presentation of Doppler information:
audible sounds, strip-chart recording, spectral display, color Doppler display
What happens to our velocity values as we get closer to 90 degrees?
they get less accurate
Signal processor uses a mathematical technique called __________________ to produce color Doppler.
autocorrelation
Is color Doppler angle dependent?
yes
The power of the Doppler shift is determined by the __________________ of the moving scatterers.
concentration
Is power Doppler angle dependent?
nope
Does power Doppler alias?
nope - but that also means there's no flow speed or character information
Which is more sensitive to flow, color or power Doppler?
power
What separates forward and reverse Doppler shift voltages?
A phase quadrature detector
Fast Fourier Transformation
digitization of spectral sample
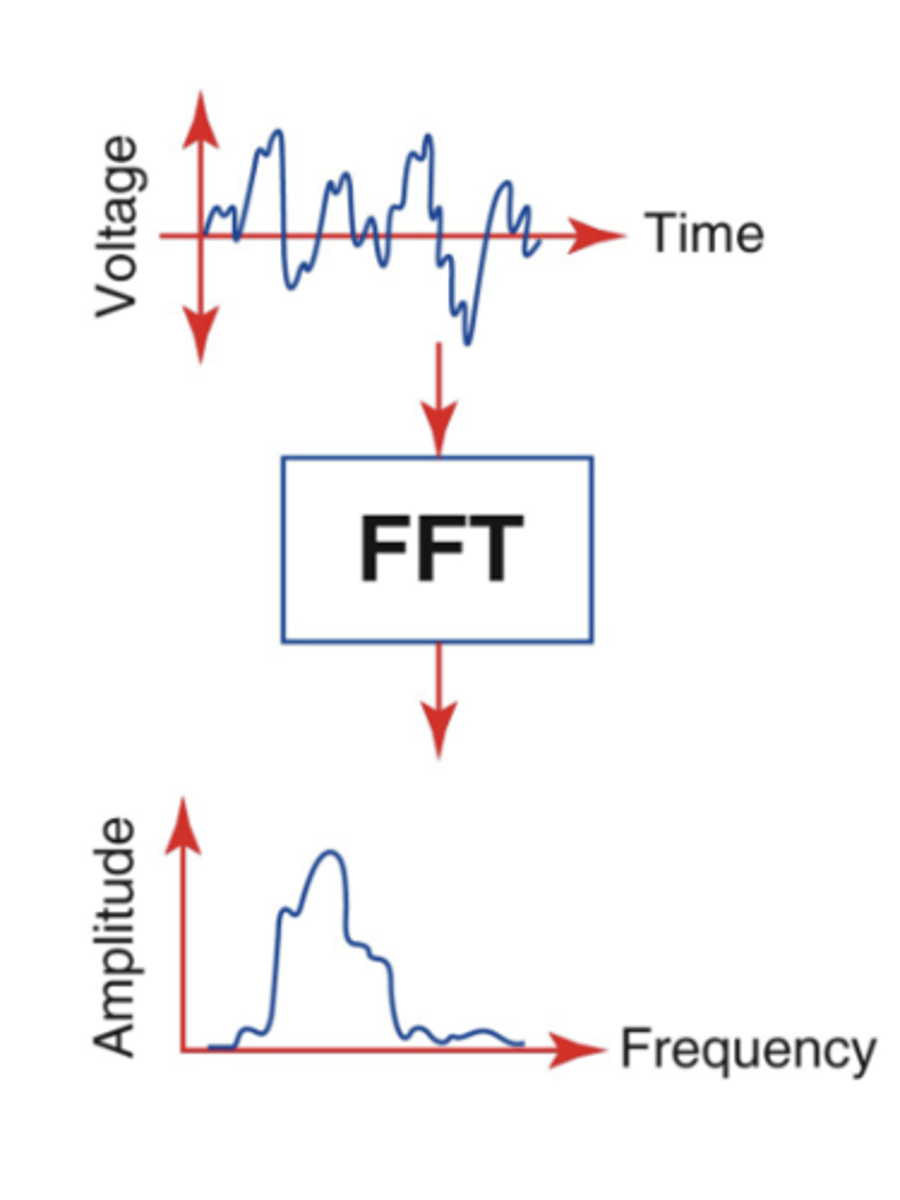
The vertical axis on spectral display represents...
Doppler shift frequency
The horizontal axis on spectral display represents...
time
What indicates flow conditions downstream?
the relationship between peak systolic and end diastolic flow speeds
What does the Pulser determine:
PW, CW, or high PRF
PW -> gate size and depth
Doppler scale -> low PRF or high PRF
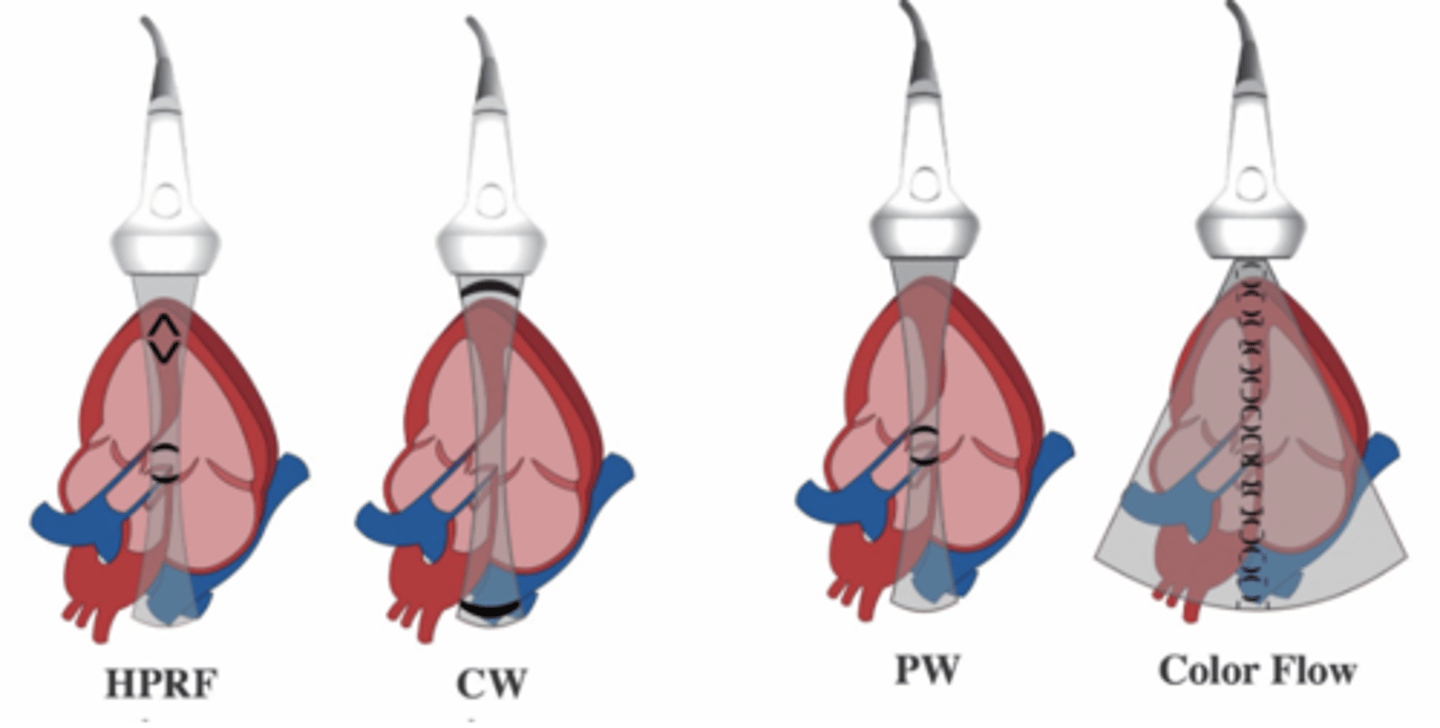
Can we steer with CW?
Naur unless it is pulsed
Do RBC's travel at the same speed and at the same angle?
no - so the machine calculates and entire RANGE of frequency shifts known as a SPECTRUM
How do we obtain bi-directional Doppler?
Reflectors coming back are both from stationary and moving structures -> Doppler removes the stationary ones -> Quadrature detection -> Zero-crossing detection -> Bidirectional Doppler
PW and CW Dynamic Range values:
PW = 140 dB
CW = 160 dB
there is a HUGE dynamic range
RBC's are _______ (high/low) level echos.
low
Wall Filter Theory
clutter is slower than blood resulting in low frequency shifts
___________ ___________ affects what wall filter setting should be used.
operating frequency
f Dop is proportional to f ___
fo (observer)
If the saturation of wall filters is set too low, _____________ __________ will occur.
electronic clutter
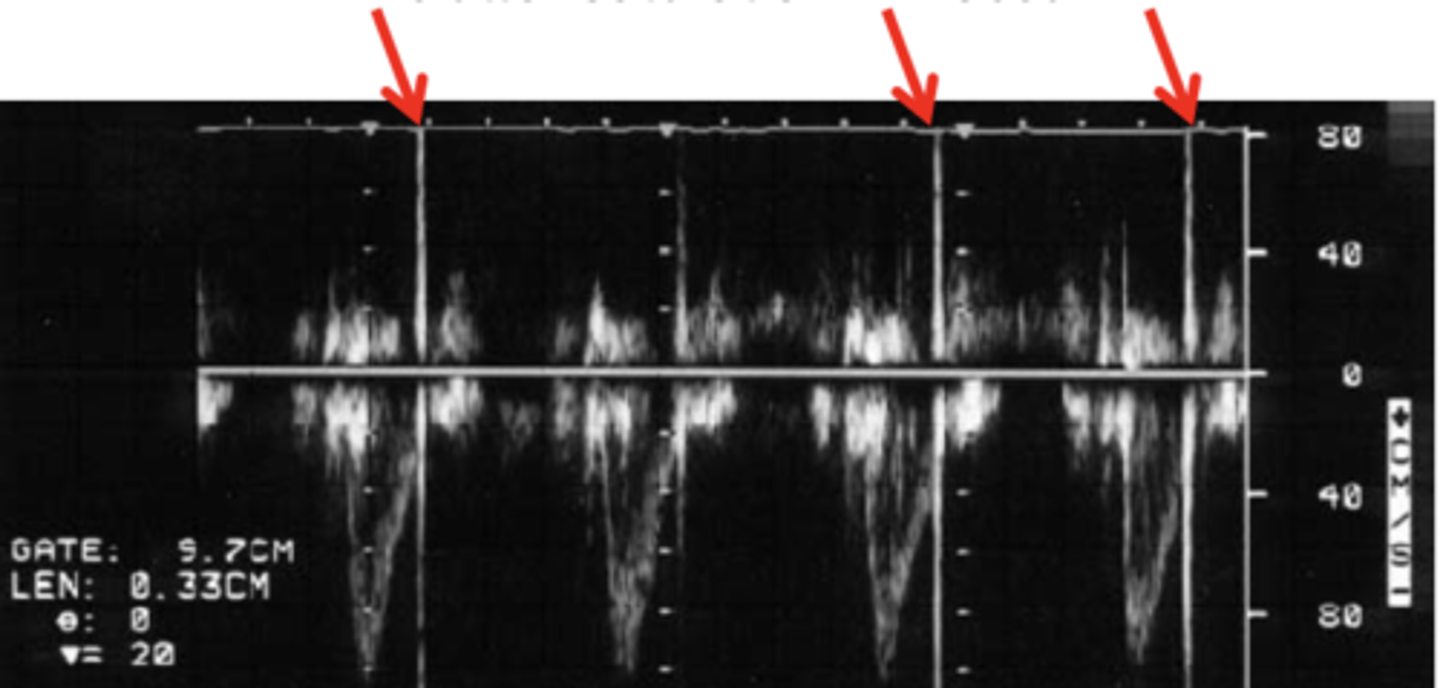
What are the 3 quantities of spectral Doppler on a 2D display?
1. Frequency on the vertical axis (converted to velocity per the Doppler equation)
2. Time on the horizontal axis (Sweep speed)
3.Amplitude/brightness
How are frequency and amplitude related?
they aren't
Frequency shift is dictated by the....
Doppler equation
Amplitude of the signal is determined by....
the scattering properties of the RBC's
Dead time
the roundtrip propagation time
When does listening start?
listening does not start until 13μsec x the depth to the gate - no earlier echoes are recorded
Does PW Doppler have any range ambiguity?
yes - it has some range ambiguity bc its not perfect
Can CW Doppler alias?
no
Nyquist criterion formula
(f Dop max) = PRF / 2
aka aliasing occurs when the frequency shift is greater than PRF / 2
__________ (high/low) frequency Doppler shifts cause aliasing.
High
Using the Doppler equation, what does high frequency Doppler shift do?
higher velocity flow, higher fo, lower, propagation velocity and angles closer to 0 and 180 degrees, deeper imaging, longer PRP, lower PRF
"True" or "Doppler" aliasing
you can not increase the scale high enough, "wrapping" around
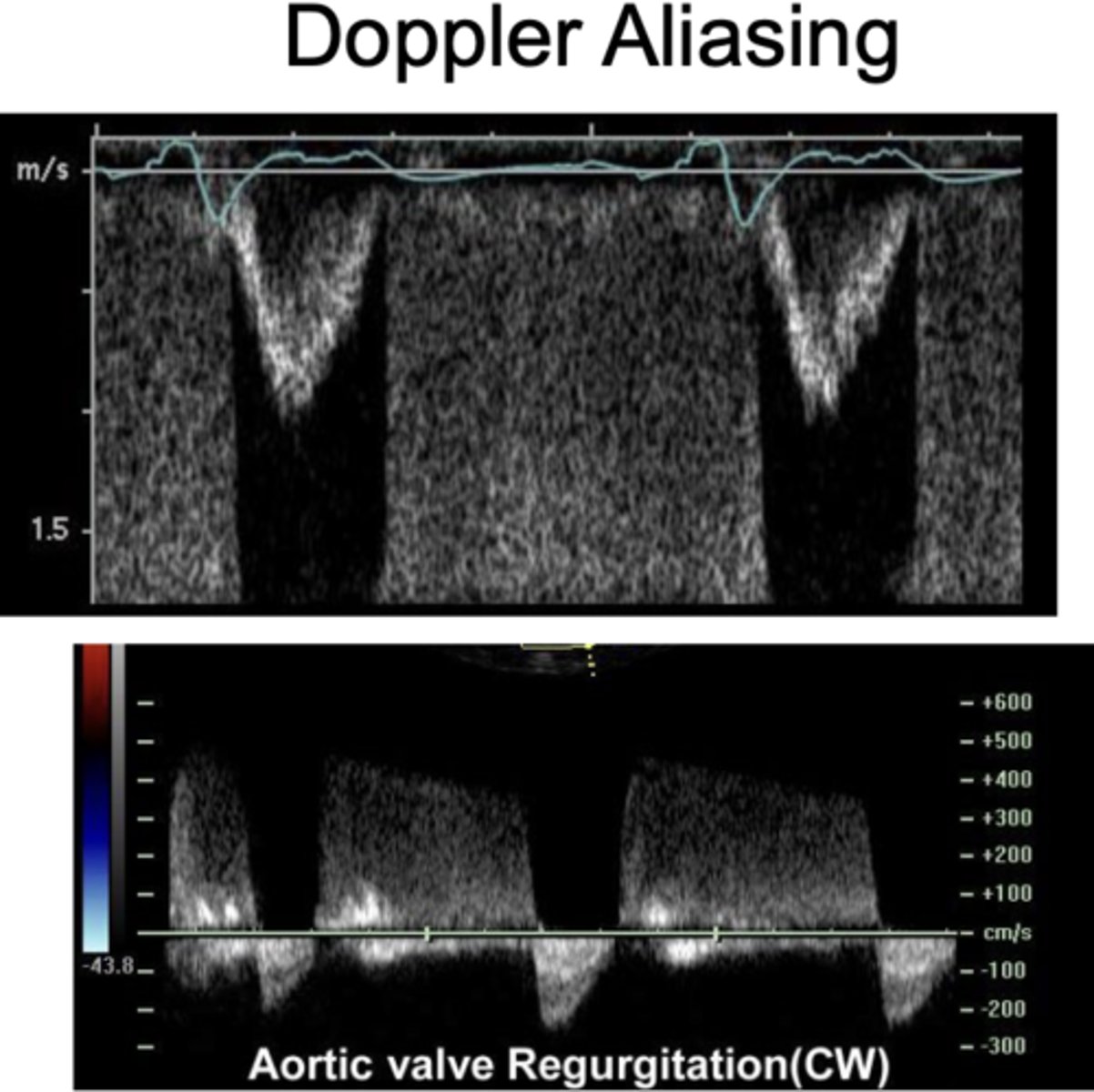
Aliasing units
cm/s and m/s
Display aliasing
can be unwrapped by changing the baseline, not true alias but display alias
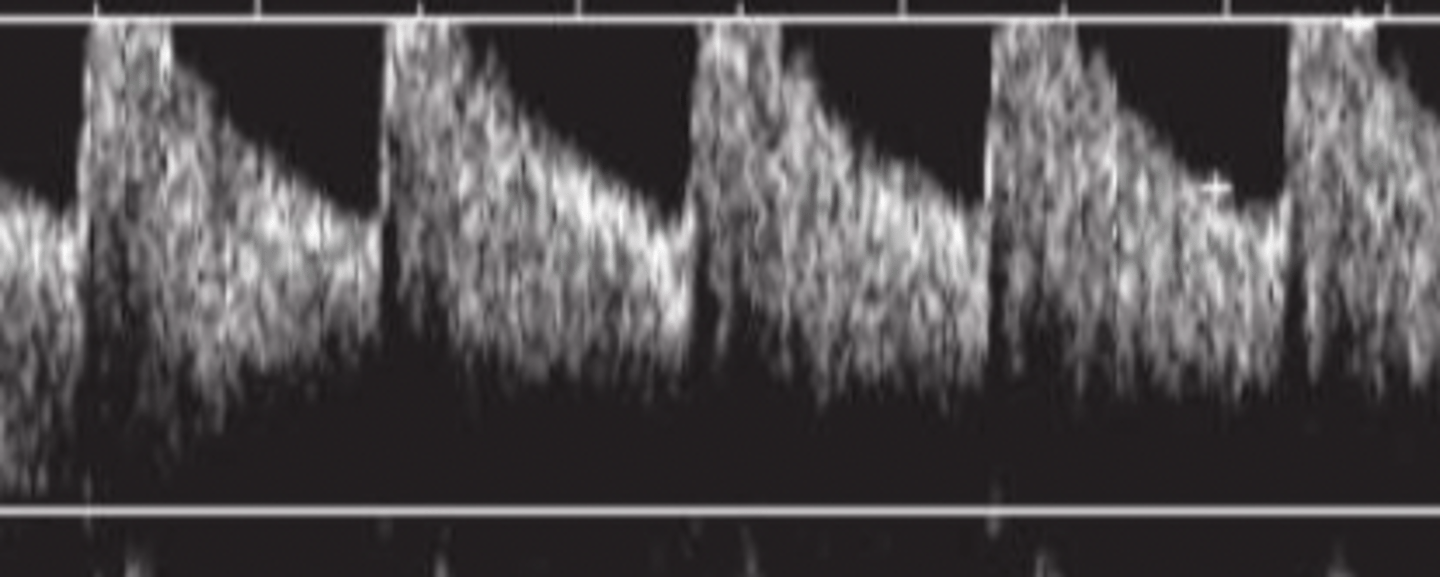
Decreasing the scale _____________ (increases/deceases) PRF and _______________ the PRP adding "dead time"
decreases; increases
What to do if aliasing continues after the scale is increased?
1. Use a lower frequency transducer
2. Find a view that has a shallower depth for the gate
3. Use CW Doppler
4. Use HPRF
Maximum Detectable Velocity equation
Rearranging the Doppler equation and adding the Nyquist
V (max) = c X PRF / 4 X f o cosθ
Nyquist Sampling Limit
Require PRF = 2 x Doppler Frequency
If there is a 3kHz Doppler signal, need _____ kHz PRF to sample.
6
The Maximum Doppler frequency that can be sampled is...
1/2 the PRF - more than that aliasing will occur
If PRF = 8 kHz, the max Doppler frequency is _____ kHz
4
Ambiguous gate location characteristics:
may be no blood flow there, signals are weaker, more attenuation from deeper depths, phased transducers are focused at the gate, decreasing the intensity for the ambiguous gate locations
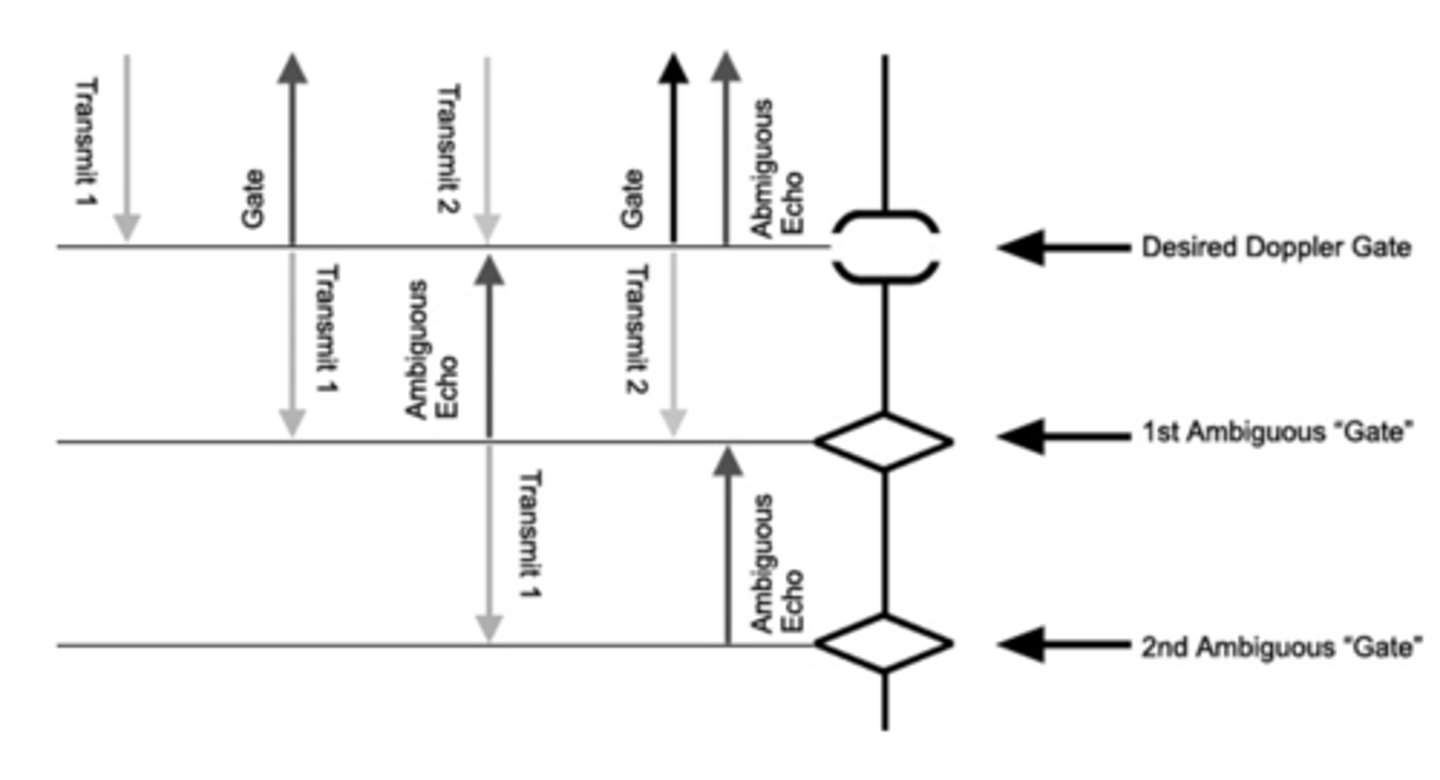
HPRF
Compromise of both PW and CW - uses ambiguous gates above and below to pick up signals - used for DEEP structures and to prevent aliasing velocities
How does HPRF use range ambiguity?
to increase the max detectable velocity without aliasing, at the expense of some range resolution
samples above and below
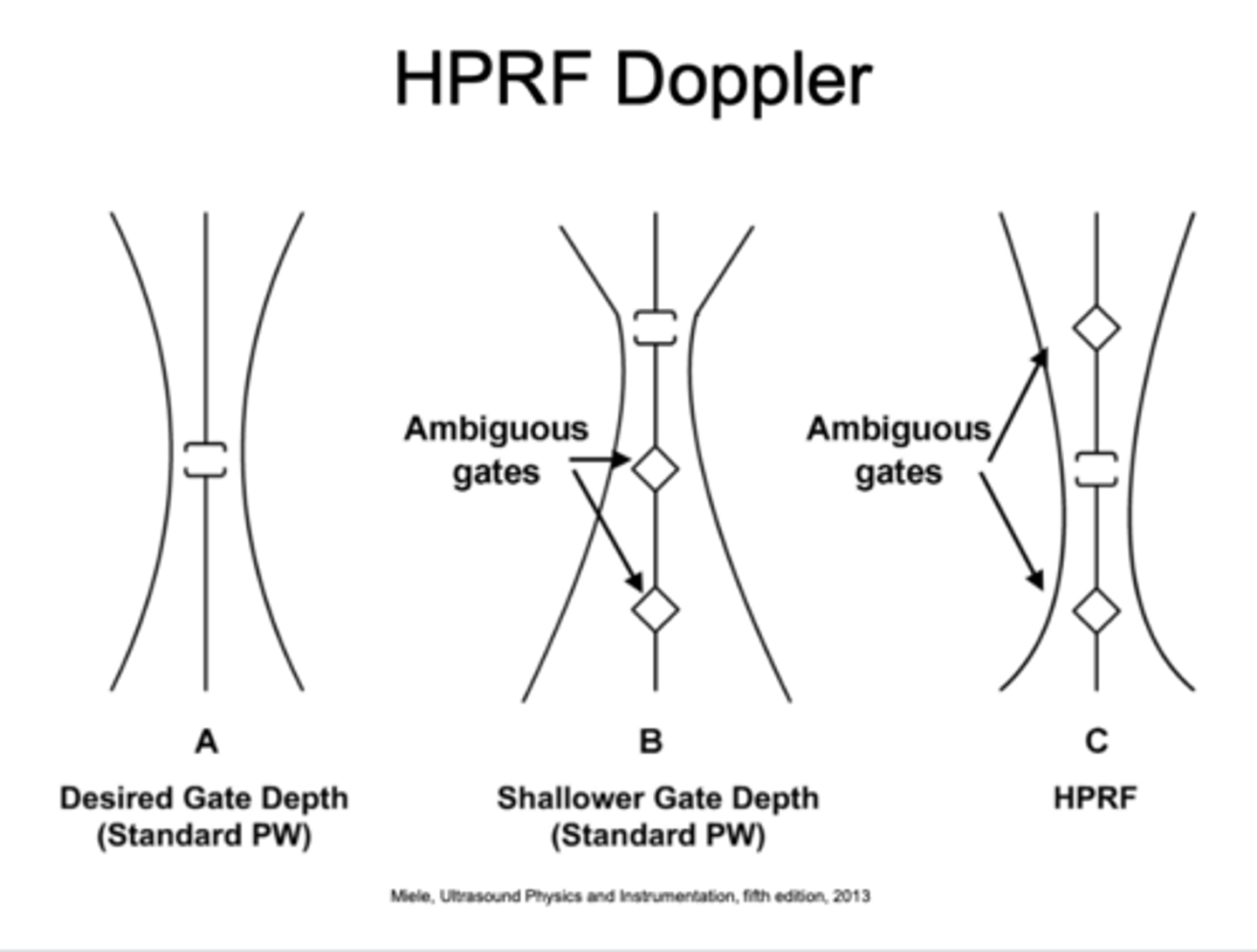
Doing what automatically activates HPRF?
increasing the Doppler scale high enough or the depth deep enough
Differenced in gating technique: HPRF, CW, PW, color Doppler
Do most systems have separate controls for the color wall filters?
no, most set the color wall filters as a percentage of the color scale (10%)
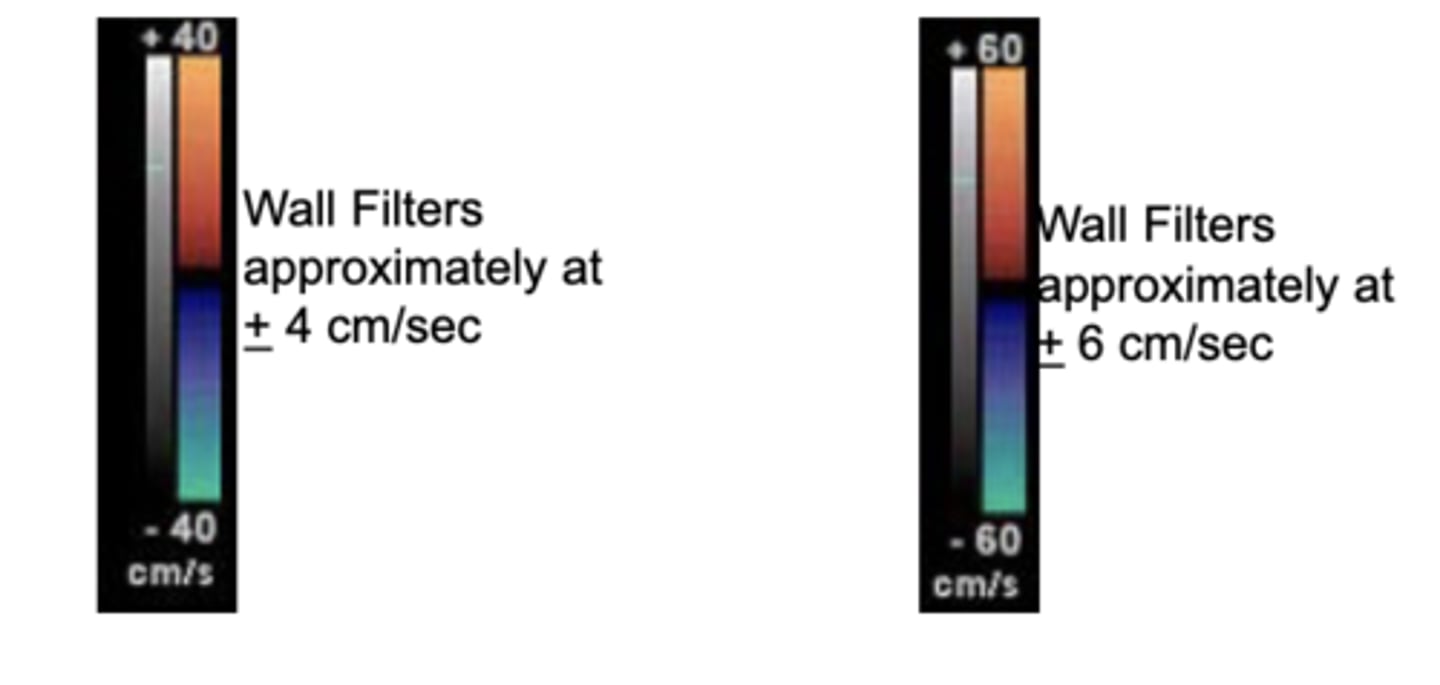
As a result of increasing the color scales, the wall filters also increase, resulting in less ability to visualize _______ (higher/lower) velocity flow.
lower
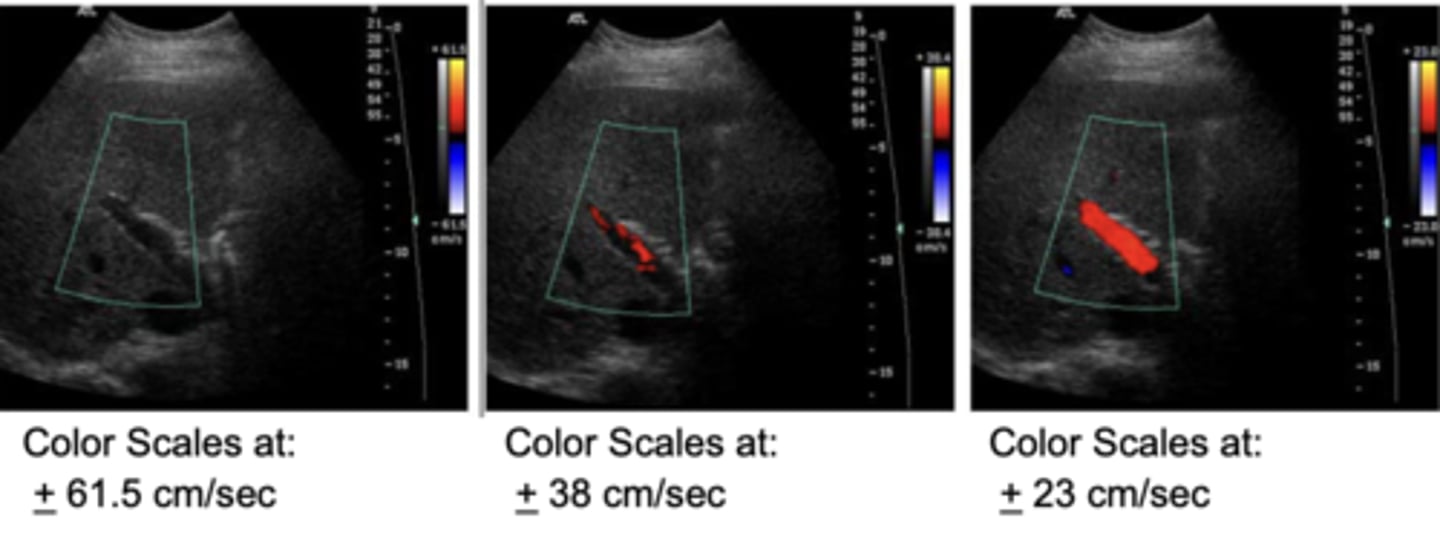
What does the number at the top of the color bar indicate?
The highest detectable mean velocity towards the transducer is 63.6 cm/sec - encoded as red towards yellow
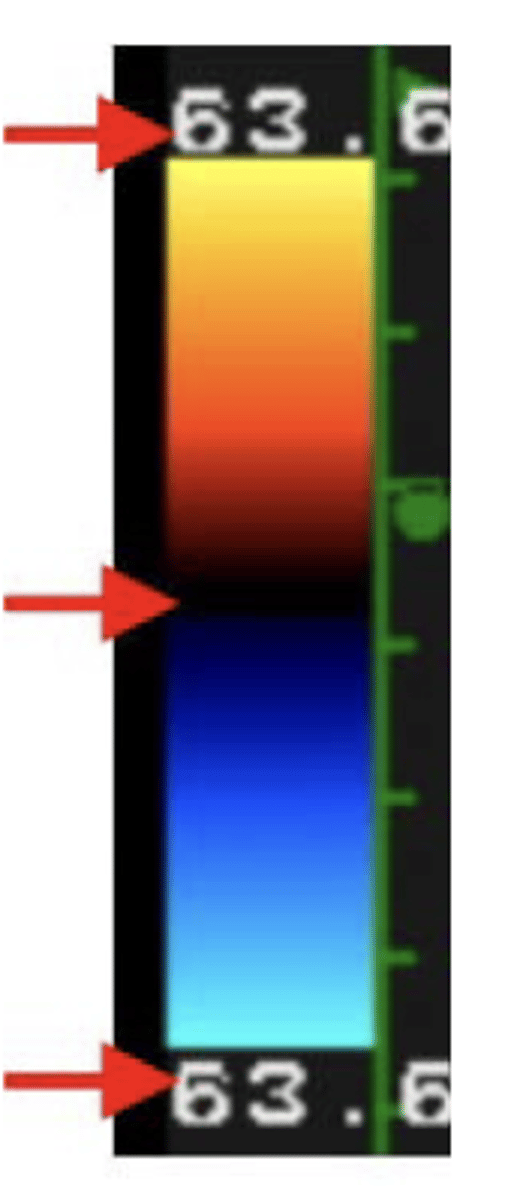
What does the number in the middle of the color bar indicate?
The black band vaguely represents that signals detected in this range are not likely to be visualized as a result of wall filtering
What does the number at the bottom of the color bar indicate?
The highest detectable mean velocity away from the transduceris 63.6 cm/sec - encoded as blue towards aqua
Color persistence
a technique in which frames are "averaged"over time
Is color averaging an equal weighting of each frame? If not, what is it an average of?
no - rather a heavier weighting of the latest frames, and less weighting of earlier frames (increases sensitivity)
How does color persistence affect short duration events vs long duration?
can make short duration events completely disappear, while making longer duration events persist even longer than reality
Color priority
a thresholding technique which allows the user to determine above what grayscale level 2-D data is presented and below which color data is presented
Round Trip Effect
the structure is moving as it reflects the wave back to the transducer, there is a doubling effect -> we should expect to see a factor of 2 in the Doppler shift equation
Doppler equation with no angle effects (yet)
f Dop = 2 f o v / c
Doppler equation assuming 1540 m/s
f Dop = 2 f o v / c = f o v / 770 m/s
cos (90)
0
DO we want to interrogate small RBC's with a high or low frequency probe?
high
Do we really even image BRC's?
no, we image constructive interference of spherical waves from multiple blood cells (increasing signal strength)
What is responsible for blood reflection?
changes in cell concentration
Rouleaux flow
occurs when RBC's aggregate -> low flow state
Doppler angle is critical to determine:
1. Flow direction
2. Assess Doppler measurement accuracy
3. Minimize Doppler error sources
4. Assess likelihood of artifact related issues, like spectral broadening
Insonification angle
measure between flow and line of observation
Which insonification angle will produce high frequency reflections? Low?
0 degrees; 180 degrees