Soils 323 Exam 2
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Nitrogen is important because __.
it’s a key component of amino acids and nucleic acids.
The key processes of the nitrogen cycle include nitrogen __, ammonification, immobilization, nitrification, denitrification, and fixation.
mineralization.
Atmospheric nitrogen exists in the form of __.
nitrogen gas (N2)
Nitrates are represented chemically as __.
NO3-
The main steps of microbial nitrogen utilization begin with the breakdown of polymers into __.
small, soluble organic molecules
The process of ammonification converts organic matter into __.
ammonium (NH4+)
In the nitrogen cycle, __ is the process through which ammonium is converted into nitrites and then nitrates.
nitrification
Denitrification ultimately reduces nitrates to __ in anaerobic conditions.
nitrogen gas (N2)
How expensive is the process of biological nitrogen fixation?
12 ATP for 2 NH4+
Leghemoglobin is important in symbiotic nitrogen fixation because it absorbs __ out of the root nodule.
oxygen (O2)
Free living nitrogen fixation can be carried out by microorganisms such as ____.
Cyanobacteria
Inoculation with rhizobia in soybean agriculture is recommended for __.
new fields or old ones that haven’t had soybeans in at least 4-5 years
The enzyme responsible for the conversion of urea into ammonia is __.
urease
N2 is relatively abundant in the atmosphere, but biological nitrogen fixation is limited because it is __ and requires specific conditions.
energy-intensive.
The resulting carbon sources from the nitrogen fixation process can result in __ or ammonification.
mineralization
What is ammonification?
Organic nitrogen compounds converted into ammonia by microbes (part of the decomposition of organic matter)
What is nitrification?
Ammonium converted into nitrites and then nitrates by soil bacteria
What is denitrification?
Reducing nitrates to nitrogen gas in anaerobic conditions
What is nitrogen fixation?
Converting atmospheric nitrogen gas into ammonia
How do legumes attract Rhizobium?
By releasing flavonoids into the soil
What factors are synthesized by Rhizobia to begin the infection process?
Nod factors
What does Rhizobium attach to to start infection?
Root hairs
What triggers leguminous plants to release the signaling chemicals for Rhizobium?
Nitrogen starvation
What is the name of the tubular structure used by Rhizobium to infect the roots?
Infection thread
What do Rhizobium bacteria turn into after entering the plant’s roots?
Bacteroids
How do root nodules form?
The proliferation of Rhizobium bacteroids
What enzyme does Rhizobium use to fix nitrogen?
A complex called nitrogenase
What is the symbiosis between Rhizobium and leguminous plants?
Rhizobium gets nutrients and a habitat, while legumes get nitrogen in return
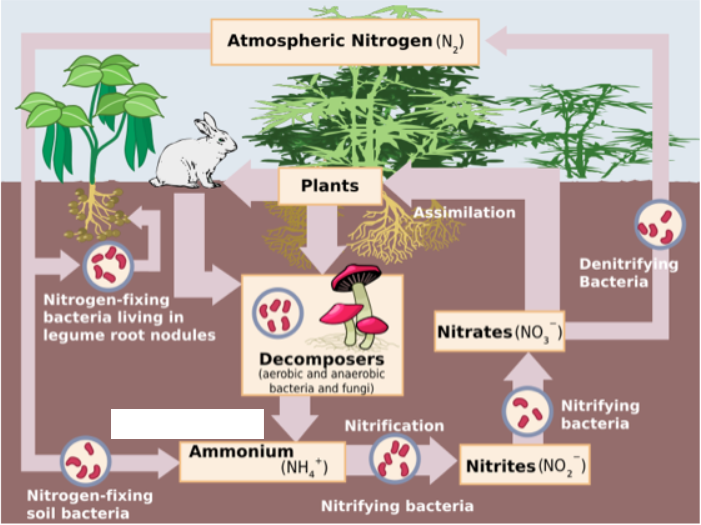
What step is missing?
Ammonification
Which of these is not a function of roots?
Anchor the plant
Absorb water and nutrients
Undergo nitrification
Exude compounds into the soil
These are all functions of roots
Undergo nitrification
The __ is where new root cells are made.
apical meristem
The __ falls off as it grows through soil.
root cap
What is one benefit of fibrous root systems?
They prevent erosion
What is one benefit of taproot systems?
They penetrate deep into the soil for more nutrients
Which root shape is ideal for very moist conditions?
Flat, shallow roots
True or false: roots can adapt their growth pattern based on the specific nutrient availability of the soil.
True
Name the three major microbiomes in soil.
Bulk soil, rhizosphere, and endophytic
What is rhizodeposition?
When roots release organic compounds, such as sugars and proteins, into the rhizosphere
True or false: Lignin-rich plant litter decomposes more quickly than other plant litter.
False, lignin is harder to break down
What is mutualism?
When two species have an arrangement that benefits both
What is predation/parasitism?
When two species exist in community but one feeds on the other
What is competition?
When two species exist together but both need the same limited resources
__ fungi form __ between root cells.
Ectomycorrhizal, hartig nets
__ fungi form little trees within a root cell.
Arbuscular mycorrhizal
Most crop species have symbiosis with __ fungi.
arbuscular mycorrhizal
What is an organic vs inorganic nutrient?
Organic nutrients are derived from living organisms and contain carbon, while inorganic nutrients are mineral-based and are more readily available to plants
__ fungi are more related to systems with rapid breakdown of leaf litter (low C compared to N).
Arbuscular mycorrhizal
__ fungi are more related to systems that have a lot of lignin in the leaf litter (high C, relatively low N).
Ectomycorrhizal
__ fungi-associated systems have a lot of leaching of nitrates.
Arbuscular mycorrhizal
Plants interact with soil bacteria via __.
root exudate
What is a holobiont?
The combination of a host and its associated microbial communities, which together form a single ecological unit
Similar to how most nitrogen is locked in the atmosphere, most sulfur is locked in __.
rocks (lithosphere)
The most readily available form of sulfur for plants is __.
sulfate (SO42-)
The process that introduces inorganic sulfur to the environment is __.
rock weathering
__ sulfur comes from the decomposition of organic matter.
Organic
True or false: Similar to nitrogen, there is only one oxidation state of sulfur in the environment.
False, there are many oxidation states (forms) of both N and S
__ can become volatilized and turns into acid rain.
Sulfate (SO42-)
True or false: Ideally, the application of elemental sulfur should change in amount depending on the type of soil.
True
Unlike nitrogen, __ doesn’t have a volatile form that is released into the atmosphere.
phosphorus
Instead of accumulating in the atmosphere, phosphorus tends to accumulate in the __.
seas
Phosphorus exists primarily as __ ions.
phosphate (PO43-)
Compared to __ and nitrogen, __ has a relatively simple environmental cycle.
sulfur, phosphorus
Briefly describe the phosphorus cycle.
Inorganic phosphorus weathers from rocks, washes from the water bodies to the ocean, then waits there to become rock again
__ mycorrhizae have been seen increasing the uptake of phosphorus, zinc, and copper.
Arbuscular
__ physically breaks fungal hyphae, but causes earlier colonization.
Tilling
What effect does crop rotation have on arbuscular mycorrhizae?
Long periods without associations result in lower populations
When is it beneficial to inoculate soil with arbuscular mycorrhizae?
In tilled soil or with crop rotation
The __ family of plants do not form mycorrhizal associations.
brassica
__ fungicides wipe out arbuscular mycorrhizae but don’t kill them forever.
Systemic
__ fungicides have very little impact on arbuscular mycorrhizae.
Foliar
High phosphorus content suppresses __ mycorrhizae growth.
arbuscular
One of the most common beneficial fungi is __.
Trichoderma
What is the biggest challenge with interpreting microbial inoculant studies?
Most of them are done in the greenhouse under controlled conditions
At Arlington, which cropping system has the deepest stores of carbon?
Prairie
Farmed
Pasture
Forage
Grain
Pasture
What are some of the benefits of cover crops?
Increased organic matter, reduced erosion, reduced compaction, controlled weeds, and excess nitrogen scavenging
Which one provided more soil organic carbon: manure or fertilizer?
Manure
Legumes are challenging cover crops because they are __.
slower to establish
Legumes are great cover crops because they __ and have __.
fix nitrogen, low C:N ratio
The challenging thing about using brassicas as cover crops is that they are __.
slower to establish
The great thing about using brassicas as cover crops is that they __.
scavenge excess soil nitrogen
The great thing about using grasses as cover crops is that they __ and __.
establish and grow quickly, scavenge excess soil nitrogen
The challenge with using grasses as a cover crop is that they have __.
high C:N ratio
Which cover crops scavenge more excess nitrates in soil: legumes or non-legumes?
Non-legumes
Which cover crops result in increased crop yields: legumes or non-legumes?
Legumes
What is the challenge with agricultural drainage tiles?
They release excess nitrates directly into nearby water bodies
Does having a high C:N ratio result in high or low nitrogen mineralization?
Low or negative mineralization (microbes have to take up more nitrogen to break it down)
What does a low C:N ratio mean for decomposition rates?
A low C:N ratio will decompose quickly
A low C:N ratio results in __ nitrogen mineralization.
high
What does a high C:N ratio mean?
Lots of carbon and only a little nitrogen
Using cover crops requires more __.
applications of nitrogen fertilizer
What are the three central tenants of soil health?
Physical, chemical, biological
Two examples of chemical properties of healthy soil are __ and __.
pH, nutrient levels
What are three examples of physical properties of soil health?
Water infiltration, compaction, and soil structure
Which of these are not a key criteria for soil health indicators?
Evidence based
Logistically feasible
Cost-effective
Scalable integration
Scalable integration