Neutron Detection
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
REM sphere
polyethylene sphere with cadmium that can detect neutrons
Bonner sphere
LiI scintillator placed at center of polyethylene moderating spheres of different diameters
Fast neutrons
> 1 keV
Slow neutrons
< 1 eV
Thermal neutrons
0.025 eV (2200 m/s)
Neutron cross section
likelihood of interaction bt nucleus and neutron
Neutron dose equivalent
impact of radiation on human tissue
Physical principles inherent to thermal neutron detection
neutron capture and ionization
Thermal neutron reaction with 10B and 6Li
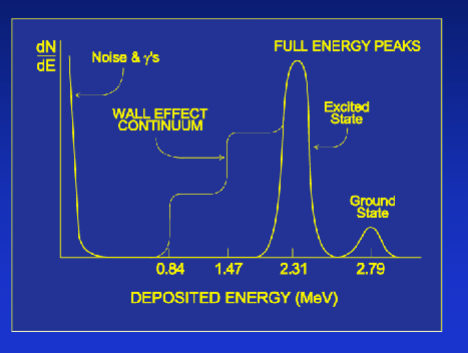
Li and alpha take turns interacting with wall; 6% of time produces Li in ground state; 94% of time produces excited Li; gamma is 48 keV
Differential pulse height spectrum of BF3 proportional counter
Relationship between dose response of REM sphere and neutron dose equivalent as a function of neutron energy
If E fixed, as radius increases it hits a max then declines; if R is fixed, as E incs it hits a max then declines
Primary fast and thermal neutron interactions in tissue
interactions and weighting factor depend on tissue type and charged particles produced
3 means of fast neutron detection
Counters based on neutron moderation
Detectors based on fast neutron-induced reactions
Detectors utilizing fast neutron scattering
Neutron shield
Neutron source then mediator (like water) then absorber (like Cd-13), then person