Genetics - NCEA level 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
Cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms
2
New cards
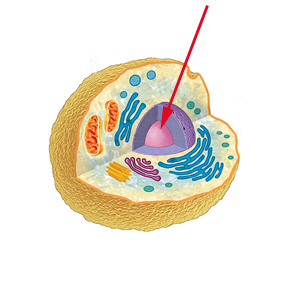
Nucleus
The part of the cell containing genetic material (DNA) responsible for growth and reproduction
3
New cards
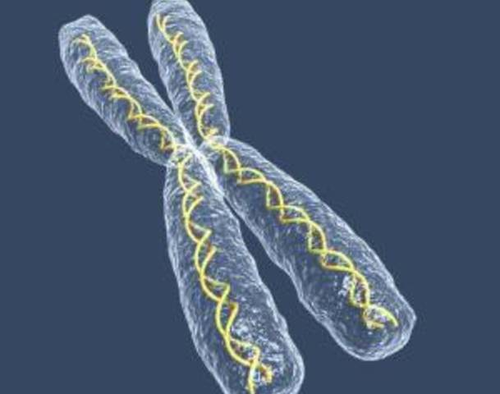
Chromosomes
Threadlike structures made of DNA found in the nucleus.
4
New cards
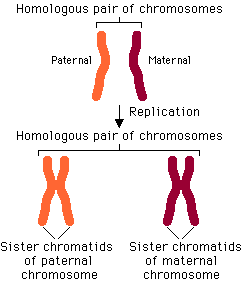
Homologous pair
A matched pair of chromosomes, one from each parent, that are identical in size, shape and the position of the genes on them.
5
New cards
Gametes
A sex cell such as an egg or sperm or pollen, containing half the normal number of chromosomes.
6
New cards
Sperm
Male sex cell in animals with half the normal number of chromosomes.
7
New cards
Ova/egg
The female sex cell with half of the DNA.
8
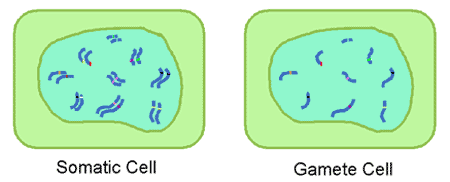
New cards
Somatic cell
Any cell in a multicellular organism except for the sex cells
9
New cards
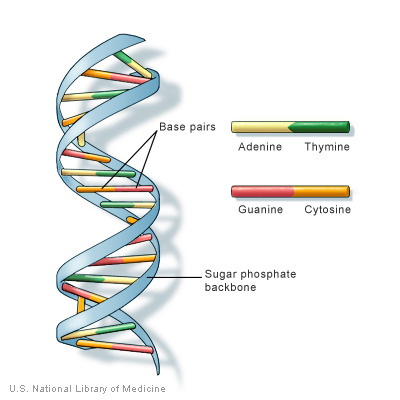
DNA
A long polymer found in the nucleus of a cell shaped like a double helix. Makes up chromosomes which contain the genetic information used in the development and functioning of an organism.
10
New cards
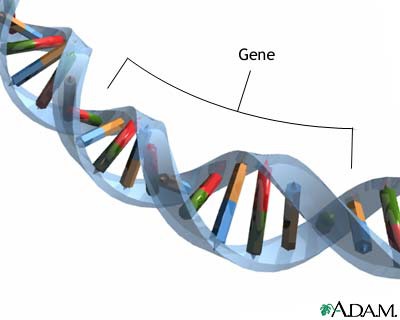
Genes
A sequence of bases on the DNA that codes for a protein, which determines a certain characteristic.
11
New cards
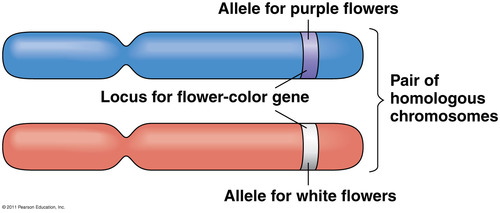
Allele
Alternate forms of a gene containing a slightly different base sequence on the DNA.
12
New cards
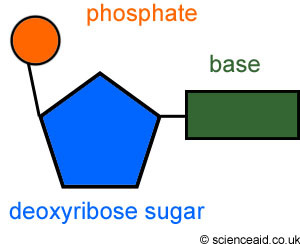
Nucleotide
The repeating units that make up DNA, consists of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base
13
New cards
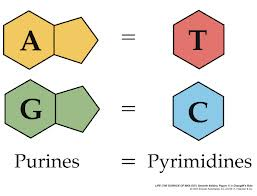
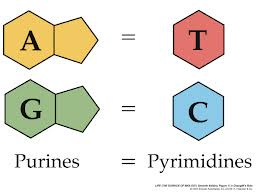
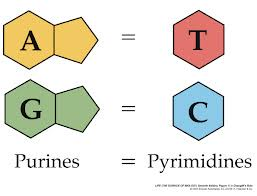
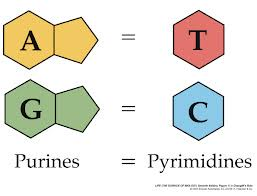
Adenine
The DNA base that pairs with (T) thymine
14
New cards
Thymine
The DNA base that pairs with (A) adenine
15
New cards
Cytosine
The DNA base that pairs with (G) guanine
16
New cards
Guanine
The DNA base that pairs with (C) cytosine
17
New cards
Amino acids
The building blocks of proteins
18
New cards
Proteins
Important molecules for life. They can be used to build the body, to control the reactions inside the cell, used for transport, to make muscles work and many other things.
19
New cards
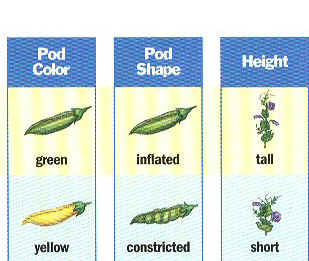
Traits
A physical characteristic controlled by the genes and can be passed on to offspring.
20
New cards
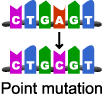
Mutation
A change in a DNA base sequence which forms a new allele and can cause a change in physical characteristics or phenotype.
21
New cards
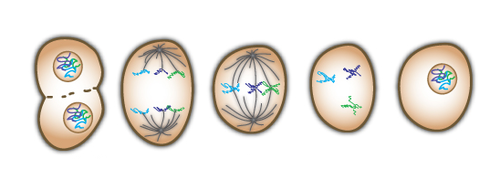
Mitosis
Cell division used for growth and repair. The cell divides to form two genetically identical cells.
22
New cards
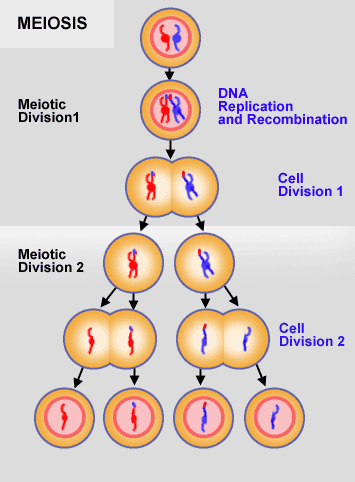
Meiosis
Cell division to produce sex cells or gametes. A cell divides to form four cells each containing the haploid number of chromosomes, each genetically different due to random assortment of chromosomes.
23
New cards
Sexual reproduction
Form of reproduction common in most animals and plants as it allows variation needed for adaptation. Involves the fusing of two gametes.
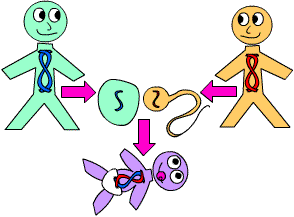
24
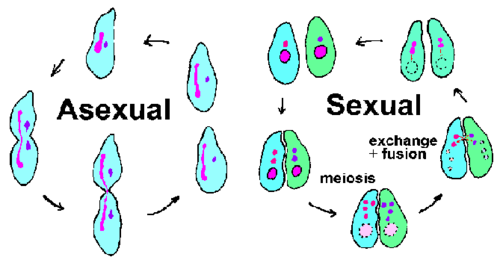
New cards
Asexual reproduction
A type of reproduction that does not involve gametes. A single individual produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent.
25
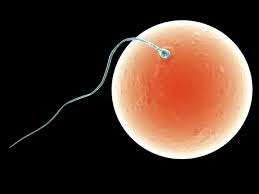
New cards
Fertilisation
Where two gametes (ova and sperm or pollen and ovule) successfuly join together to form a zygote.
26
New cards
Zygote
A fertilised egg.
27
New cards
Genetic variation
Differences among individuals in the composition of their genes. The main causes for this are mutation and sexual reproduction.

28
New cards
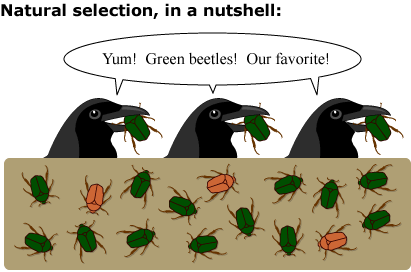
Natural selection
Process by which individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce passing on their successful alleles to their offspring.
29
New cards
Somatic mutation
A mutation that occurs in the body cells, cannot be inherited
30
New cards
Mutation in sex cells
Causes the mutation to be inheritable
31
New cards
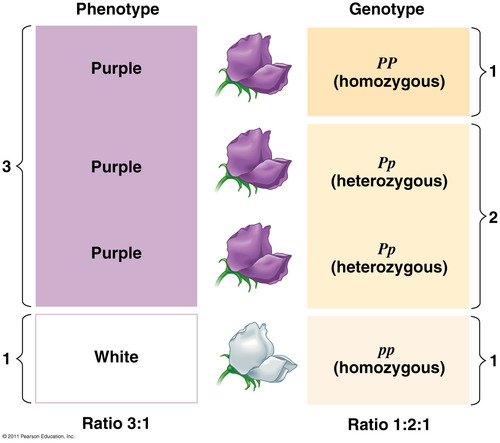
Phenotype
The physical expression of the genotype

32
New cards
Genotype
A combination of alleles for a particular gene or characteristic.
33
New cards
Homozygous
A genotype with two identical alleles for a particular trait.

34
New cards
Heterozygous
A genotype with two different alleles for a particular trait

35
New cards
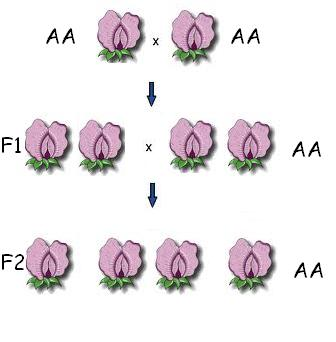
Pure breeding
Describes an organism whose genotype is homozygous for a specific trait and will always produce offspring that have the same phenotype for that trait.
36
New cards
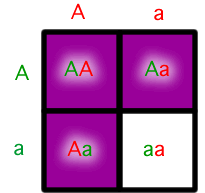
Dominant allele
An allele whose trait is always expressed when there are two different alleles in the genotype. It masks or hides the other allele.
37
New cards
Recessive allele
An allele whose trait will be expressed only if two recessive alleles are present in the genotype. It will be masked in the presence of one dominant allele.
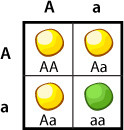
38
New cards
Punnett square
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross