BISC 133 Lab Final, Kemege
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/126
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
1
New cards
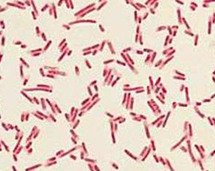
E. coli
Gram negative, rod shaped, common in digestive tract of mammals, model organism, transmitted by fecal-oral route
2
New cards
rhizobium spp.
Gram negative, rod shaped, *fix nitrogen* (N2-->NH3), important in ecosystem bc of nitrogen, can't take place in soil, live in root nodules of *legumes*, bacteria provide plant with NH3 and O2 free environment

3
New cards
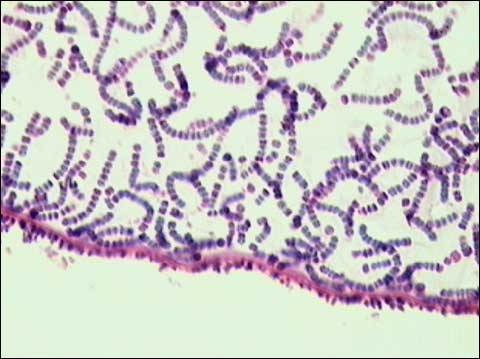
nostoc spp.
Gram negative, form long filaments, photosynthetic, macroscopic colonies, form heterocysts in low nitrogen
4
New cards
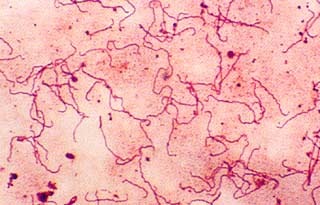
treponema pallidum
Gram negative, spirillum morphology, motile, cause syphilis
5
New cards
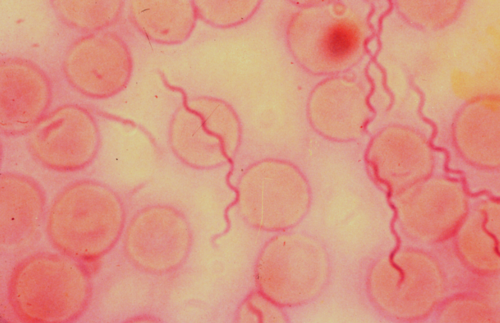
borrelia burgdorferi
Gram negative, spirillum, motile, causes Lyme disease
6
New cards
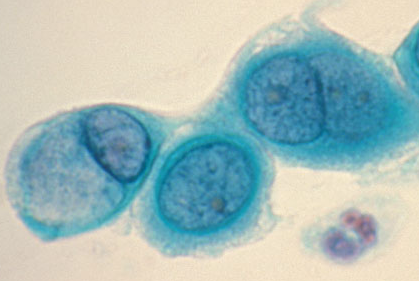
chlamydia trachomatis
Gram negative, coccus morphology, obligate intracellular parasite of humans, cause *STD chlamydia*, cause *trachoma in eyes*
7
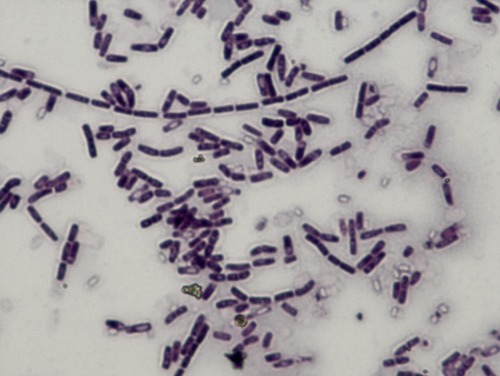
New cards
bacillus spp
*Gram positive*, bacillus morphology, can *produce endospores*, bacillus subtilis - model organism, bacillus anthracis - anthrax, found in soil
8
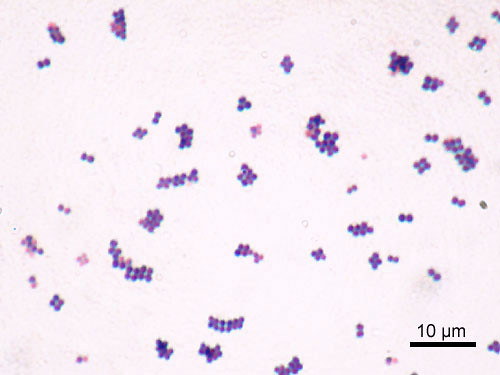
New cards
staphylococcus aureus
*Gram positive*, coccus morphology, part of normal microbial on skin, can cause pimples and boils if under skin or pneumonia or toxic shock syndrome, infections treated with antibiotics but some strains of bacteria resist
9
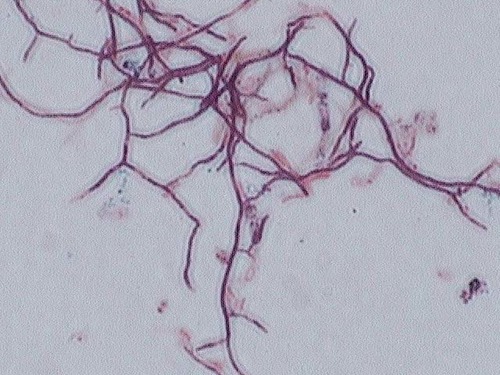
New cards
streptomyces spp
*Gram positive*, form branched structures, found in soil and decaying matter, not human pathogens
10
New cards
gram stain negative
*red*; E. coli, rhizobium, nostoc, treponium palladum, borrelia, chlamydia
11
New cards
gram stain positive
*purple*; bacillus spp, staph aureus, streptomyces spp
12
New cards
Endospores
thick-walled protective spore that forms inside a bacterial cell and resists harsh conditions
13
New cards
Nitrogen fixation
convert gaseous nitrogen (N2) to solid nitrogen (NH3); cannot take place in presence of oxygen gas
14
New cards
Haloarchea
pleomorphic (can vary in shape and size within a specific species); photosynthetic; extremophiles; *halophiles* - extreme salt conditions
15
New cards
Methanomicrobiota
chemoautotrophs; use CO2 and H2 and produce CH4; capable of living in ecosystems with *no sunlight*, form bottom of complex food chains
16
New cards
Sulfolobus spp
extremophiles; *acidophiles* (low pH) and *thermophiles* (high temp)
17
New cards
Pleomorphic
vary in shape and size within a specific species
18
New cards
Halophile
live in *high salt* environments; are haloarchaea
19
New cards
Chemoautotroph
harness energy from *inorganic chemicals* rather than from consuming organic matter or from photosynthesis
20
New cards
Acidophile
thrive in low pH
21
New cards
Thermophile
thrive at high temperatures
22
New cards
Dinoflagellates; Karenia brevis
causes red tide
23
New cards
paramecium caudatum
Cilia cover the cell surface or are clumped, reproduce asexually by *binary fission*
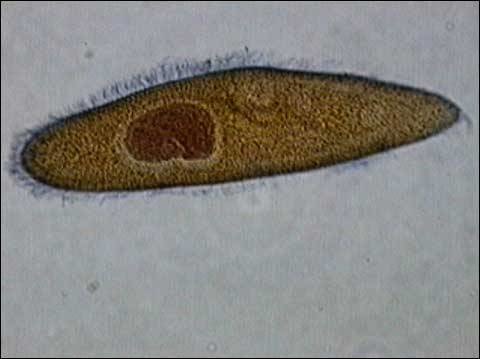
24
New cards
diatoms
protists that have intricate shells in phytoplankton; Phylum Bacillariophyta; invaded in a silica cell wall called a *Frustule*

25
New cards
red algae
Phylum Rhodophyta;
marine algae in which the chlorophyll is masked by a red or purplish pigment
marine algae in which the chlorophyll is masked by a red or purplish pigment

26
New cards
metamonads
parasite; noted for the *anaerobic metabolism* and their degenerated organelle
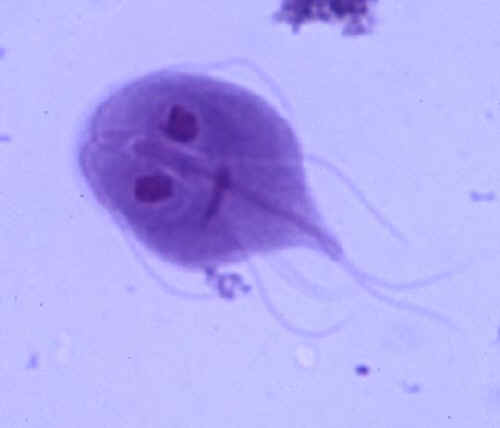
27
New cards
euglenozoa
a kind of protist, unicellular; include a variety of common free-living species, as well as a few parasites
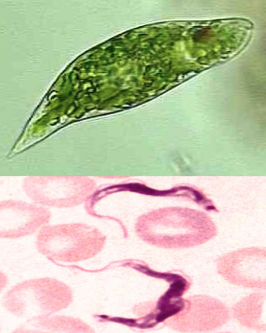
28
New cards
amoebozoa
pseudopodia, plasmodial/cellular *slime molds*
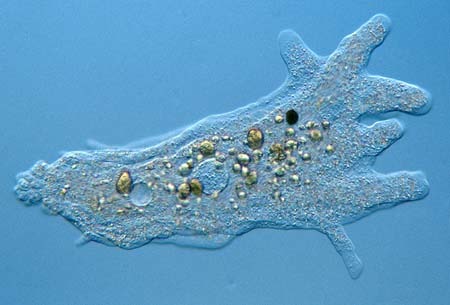
29
New cards
cup fungi

30
New cards
budding yeast
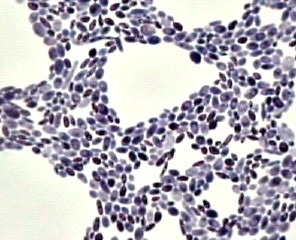
31
New cards
penicillium spp.
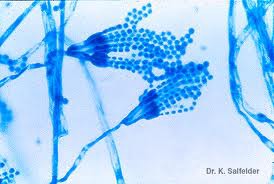
32
New cards
basidiomycota
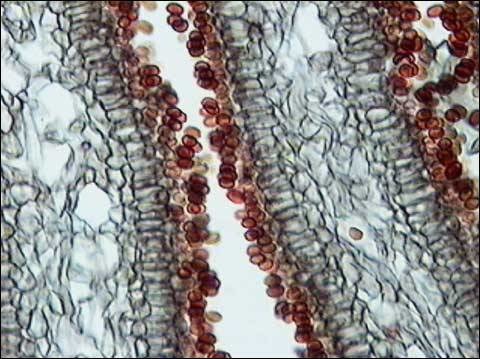
33
New cards
zygomycota
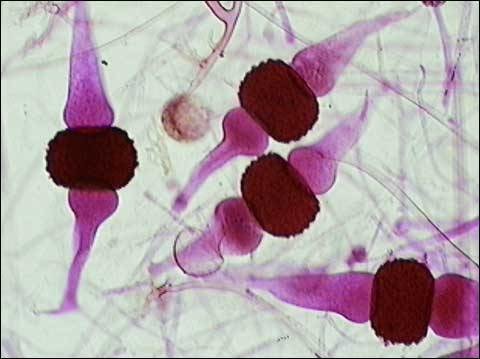
34
New cards
rhizopus spp.
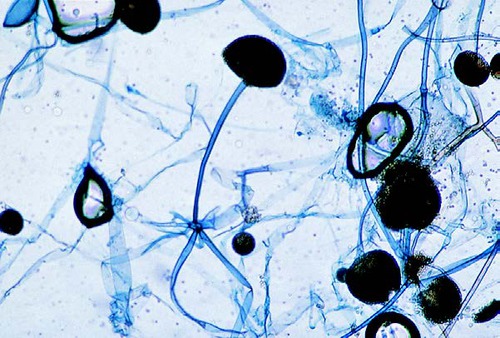
35
New cards
polyphyletic
composed of *multiple clades* organized together which are *not* evolutionarily related
36
New cards
monophyletic
part of a *single clade* & are *all evolutionarily related*
37
New cards
paraphyletic
*single clade* including *most* but *not all* evolutionarily related groups
38
New cards
fungi group is
monophyletic
39
New cards
fungi cell walls made of
chitin
40
New cards
protists and fungi are
eukaryotes
41
New cards
defining features of plants
cellulose cell walls, chlorophyll a and b, chloroplasts with two membranes
42
New cards
plants are
monophyletic
43
New cards
purpose of vascular tissue
transport water and nutrients throughout the plant
44
New cards
monocots are group within group of
angiosperms
45
New cards
difference in angiosperms and gymnosperms
angiosperms have fruit and flowers, gymnosperms don't (they have cones)
46
New cards
animals are
monophyletic
47
New cards
invertebrates are
paraphyletic
48
New cards
most ancient, simplest group of organisms
phylum porifera
49
New cards
non-vertebrates are
animals that are *chordates* but not vertebrates
50
New cards
chordates are
monophyletic
51
New cards
endothermic
spends *energy* to maintain a consistent internal body temperature
52
New cards
Which anatomical structure divides thoracic cavity from abdominal cavity?
diaphragm
53
New cards
convergent evolution
two groups of organisms evolve the *same trait* *independently* of one another
54
New cards
lamprey
chordata, hyperoartia

55
New cards
sharks
chordata, chondrichthyes (skeleton made of cartilage)

56
New cards
bony fish
chordata, osteichthyes
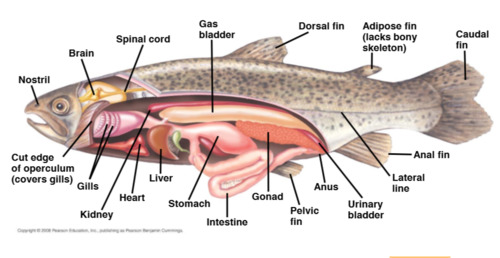
57
New cards
bullfrog
chordata, amphibians

58
New cards
turtle
chordata, reptilia

59
New cards
birds
chordata, aves

60
New cards
feather anatomy
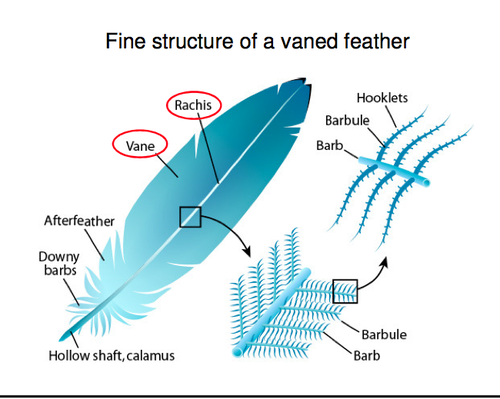
61
New cards
mammals
chordata, mammalia

62
New cards
rat dissection
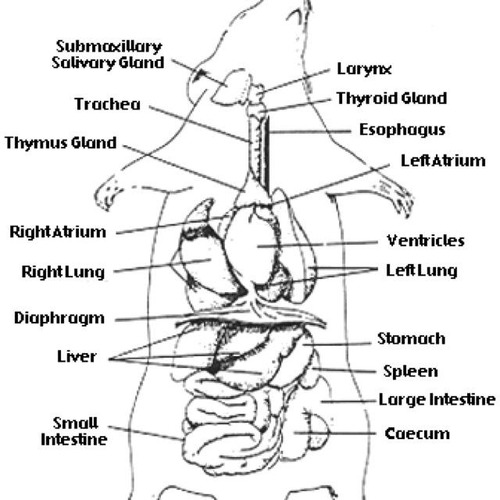
63
New cards
sponges

64
New cards
cnidarians (jellyfish, hydra, sea anemone, coral)

65
New cards
platyhelminthes
liver fluke, tapeworm, planeria aka flatworm

66
New cards
nematodes (roundworms)
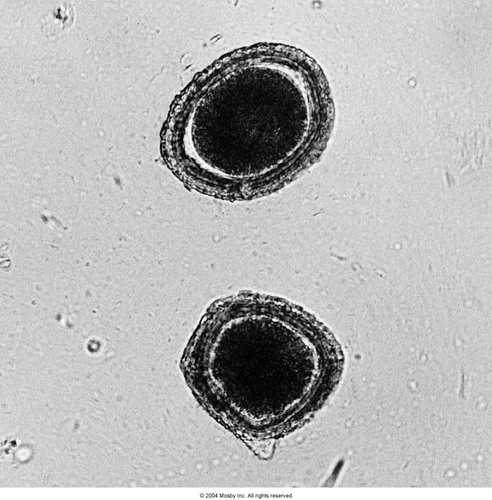
67
New cards
mollusk
cephalopods [squid, nautilus, octopus], chitons, gastropods
![cephalopods [squid, nautilus, octopus], chitons, gastropods](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2dc34f67f4494023b2d94ec2c8cd20e5.jpg)
68
New cards
arthopod
horseshoe crab, crabs, centipedes, spiders, daphnia

69
New cards
echinodermata
sea cucumber, sea urchin, sand dollar, brittle star, starfish [have radial symmetry]
![sea cucumber, sea urchin, sand dollar, brittle star, starfish [have radial symmetry]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/09b2bdd8b13b4b25917dc33172eb33ec.png)
70
New cards
invertebrate chordates
lancelets, sea peaches, sea squirts

71
New cards
phylum porifera
sponges
72
New cards
phylum cnidaria
*jellyfish*, hydra, sea anemone
73
New cards
medusa jellyfish
jellyfish
74
New cards
phylum Platyhelminthes
flukes, tape worms, *planeria (flatworms)*, rotifers, round worms
75
New cards
phylum molluscs
chitons, snails, slugs, octopus, squids, *nautilus*, clams
76
New cards
subphylum cephalopda
*squids*, octopus, nautilus
77
New cards
class bivalve
clams, mussels, oysters
78
New cards
phylum annelida
marine worm, *segmented worms*, earthworms, leeches
79
New cards
class clitellata
earthworms, leeches
80
New cards
phylum arthropoda
*horseshoe crabs*, spiders, ticks, shrimps, barnacles, daphnia, millipedes, centipedes, beetles
81
New cards
subphylum chelicerate
spiders, ticks, horseshoe crabs
82
New cards
subphylum crustacea
shrimp, barnacles, daphnia
83
New cards
subphylum Hexapoda
beetles
84
New cards
subphylum myriapoda
centipedes, milipedes
85
New cards
phylum echinodermata
starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, sea cucumbers, sea squirts, *lacelets*
86
New cards
lancelets?
no jaw/invertebrate
87
New cards
non-vertebrates
chordates that lack bones or a skeleton [fish-like (lancelets and tunicates)]
88
New cards
jellyfish (life cycle, different morphological forms)
1. egg
2. zygote (fertilization)
3. panula larva
4. hydra-like polyp
5. strobila
6. asexual reproduction
7. new medusa
2. zygote (fertilization)
3. panula larva
4. hydra-like polyp
5. strobila
6. asexual reproduction
7. new medusa
89
New cards
coral (geographical distribution, coral reef formation)
-shallow waters
-polyps produce a mineral exoskeleton, dead corals provide structural foundation for living corals, creates coral reefs
-exist where nutrients are scarce
-symbiotic relationship with *photosynthetic protists*
-polyps produce a mineral exoskeleton, dead corals provide structural foundation for living corals, creates coral reefs
-exist where nutrients are scarce
-symbiotic relationship with *photosynthetic protists*
90
New cards
annelids (segments, anatomy, skeleton)
-segmented worms (each segment has its own muscle, nerve ganglion, reproductive organs) can regenerate
-coelom forms a *hydro-static skeleton*
-has blood and blood vessels
-coelom forms a *hydro-static skeleton*
-has blood and blood vessels
91
New cards
The function of the characteristics shared by chordates
1. single hollow nerve chord
-spinal chord
-beneath dorsal surface
2. flexible notochord
-below nerve chord
3. postanal chord
-tail extends past anus
4. phalyngeal slits/ pouches
-at mouth
-can develop gills
-spinal chord
-beneath dorsal surface
2. flexible notochord
-below nerve chord
3. postanal chord
-tail extends past anus
4. phalyngeal slits/ pouches
-at mouth
-can develop gills
92
New cards
acoelomate
no coelom (body cavity in animals that exists within the mesoderm)
93
New cards
Mosses
Bryophytes, grow as carpet on moist forest floor, lack vascular tissue. Gametophytes prominent, sporophytes are composed of stalks of seta and spore-filled capsules. Seta emerge from gametophyte and release spores. Spores are not photosynthetic.
94
New cards
Liverworts
Marchantiophyta. gametophyte prominent; look-like structures called thalli;
Female thalli: archegonia;
Male thalli: anterdia;
Perform asexual reproduction through Gemma cups. No roots; use *rhizoids* to anchor themselves.
Female thalli: archegonia;
Male thalli: anterdia;
Perform asexual reproduction through Gemma cups. No roots; use *rhizoids* to anchor themselves.
95
New cards
Whisk ferns
Class psilotopsid; lack roots and leaves; synagia produce haploid spores
96
New cards
Horsetails
Class equistopsida. AKA scouring rushes. Stems coated in *rough silicon compounds*. Haploid spores are produced in cone-like structures at tips of stems called *Strobili*.
97
New cards
Hornworts
Bryophytes. Division Anthocerotophyta. "Horn" refer to sporophytes that stick out from leafy gametophyte. Lack vascular tissue; don't grow large; need moist environment. Haploid spores are released from slit near top of sporophytes
98
New cards
"true ferns"
Class pteridopsida. Leaves called fronds. Grow as curled "fiddleheads". Undersides of fronds have *sori*: clusters of sporangia. Haploid spores grow to gametophyte- separate fern: *prothallus*. Prothallus gametophyte produce egg and sperm in separate structures.
Sporophyte is predominant form.
Sporophyte is predominant form.
99
New cards
Ginkgoes
Gymnosperms. Under class ginkgoopsida. Only one living species Ginkgo biloba. *Dioecious* (each tree is either male or female)
Have fruit-like structures that house seeds called sarcotesta, not true fruits that are not edible, seeds are edible.
Have fruit-like structures that house seeds called sarcotesta, not true fruits that are not edible, seeds are edible.
100
New cards
Monocots vs. eudicots
Monocots: one cotyledon (first leaf) flowers with 3 or 6 petals (multiples of 3), leaf veins run *parallel* to one another, vascular bundles (in stem) that are spread out.
Eudicots: two cotyledons, flowers with 4 or 5 petals, leaf veins *branched*, vascular bundles (in stem) that are localized outside edges
Eudicots: two cotyledons, flowers with 4 or 5 petals, leaf veins *branched*, vascular bundles (in stem) that are localized outside edges