Pre-Labs
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
How much media is needed to prepare each of the following?: agar slant, agar plate, broth tube, agar deep
Slant: 7 mL
Plate: 20 mL
Broth: 7 mL
Deep: 50% of the test tube
Complex/undefined media
General growth media in which the exact chemical composition is not known
Broths
Used to grow microbes when a large number of cells are required
Agar slants
Used mainly for growing stock cultures
What four factors affect microbial growth?
Type of growth medium
Incubation time
Incubation temperature
pH of the medium
What are the three fundamental skills needed in a microbiology lab?
Good hand-washing technique
Good aseptic transfer technique
Good media-preparing technique
Name two ways you can isolate a colony on an agar plate.
Spread plate (pour plate)
Quadrant streak plate
Mutualism
The symbiotic organism and the host both receive benefit(s) from the relationship
Free-living organisms
Organisms that do not live in or on a host
Opportunistic organisms
Capable of producing a diseased state, if introduced into a suitable part of the body
Saprophytic
Living off dead, decomposed organic matter
Pathogens
Organisms that do cause disease and damage the host
Most organisms do not cause infections in humans (T/F?)
True
What are the appropriate settings to autoclave sufficiently?
121 Celsius ; 15 psi (pressure); 15 min
A pure culture is necessary to perform tests for identification purposes; and, it is usually grown in a broth or slant medium (T/F?)
True
Mixed cultures only have one type of organism (T/F?)
False
Identify the growth in media to the media type: pellicle
Broth
Identify the growth in media to the media type: filiform with a smooth edge
Agar slant
Identify the growth in media to the media type: turbid
Broth
Identify the growth in media to the media type: smooth, entire
Agar plate
Identify the growth in media to the media type: sediment
Broth
Define the term for growth in broth culture: flocculent
Suspended chunks or pieces
Define the term for growth in broth culture: sediment
Growth on the bottom
Define the term for growth in broth culture: ring
Growth at top around the edge
Define the term for growth in broth culture: pellicle
Membrane at the top
Define the term for growth in broth culture: uniform fine turbidity
Evenly cloudy throughout
Define the term for growth on slant culture: filiform
Smooth texture with solid edge
Define the term for growth on slant culture: spreading edge
Solid growth seeming to radiate throughout
Define the term for growth on slant culture: transparent
Almost invisible or easy to see light through
Define the term for growth on slant culture: friable
Rough texture with a crusty appearance
Define the term for growth on slant culture: pigmented
Produces a colored growth
Identify the growth in media to the media type: umbonate
Agar plate
Identify the growth in media to the media type: friable
Agar slant
Identify the growth in media to the media type: flocculent
Broth
Identify the growth in media to the media type: filamentous whole colony shape
Agar plate
Identify the growth in media to the media type: raised
Agar plate
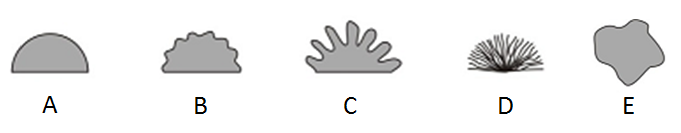
Identify the following margins:
Entire (smooth)
Undulate (wavy)
Lobate (lobed)
Filamentous (unbranched strand)
Irregular
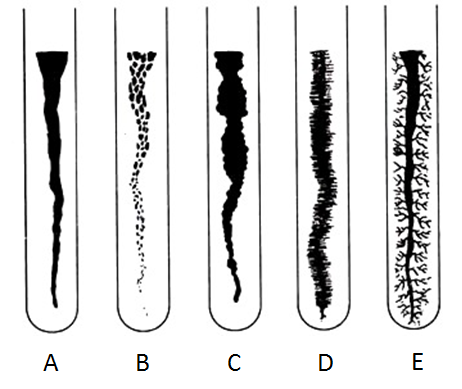
Identify the following slant growths:
Filiform (smooth, even)
Beaded
Echinulate (spiny)
Filamentous (unbranched strands)
Rhizoid (branched)
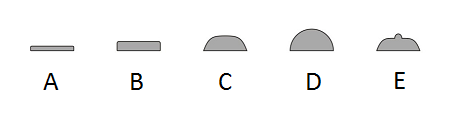
Identify the following elevations:
Flat
Raised
Plateau
Convex
Umbonate

The image below demonstrates a pellicle and sediment (T/F?)
True
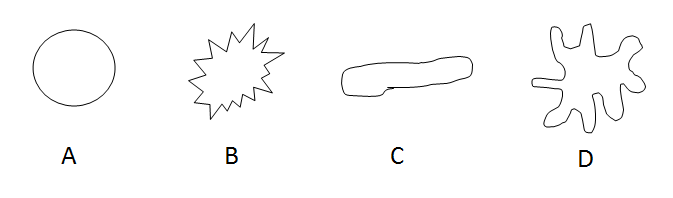
Identify the following colony shapes:
Round
Erose
Spindle
Irregular
What is the practical limit of magnification of the light microscope?
1300X
Identify the organisms to its correct common name: Clonorchis sinensis
Chinese liver fluke
Identify the organisms to its correct common name: Trichinella spiralis
Pork worm
Identify the organisms to its correct common name: Taenia pisiformis
Tapeworm
Identify the organisms to its correct common name: Fasciola hepatica
Common liver fluke
Identify the organisms to its correct common name: Enterobius vermicularis
Pinworm
Identify the structure to the group: encysted larvae
Pork worm
Identify the structure to the group: scolex and proglottids
Tapeworm
Identify the structure to the group: oral sucker and cercariae
Chinese liver fluke
Identify the structure to the group: hypostome
Tick
Micrometers can also be called microns (T/F?)
True
Identify the cellular structure of organelle to the genus that has it: cilia
Paramecium
Identify the cellular structure of organelle to the genus that has it: pseudopods
Amoeba
Identify the cellular structure of organelle to the genus that has it: kinetoplast
Trypanosoma
Identify the cellular structure of organelle to the genus that has it: chloroplasts
Spirogyra
Identify the cellular structure of organelle to the genus that has it: hyphae with conidia
Aspergillus
Identify the microbe to the appropriate category: Plasmodium vivax
Protozoa
Identify the microbe to the appropriate category: Diatoms
Algae
Identify the microbe to the appropriate category: Candida albicans
Yeasts
Identify the microbe to the appropriate category: Rhizopus
Molds
Identify the microbe to the appropriate category: Giardia lamblia
Protozoa
What is the total magnification when using the low power objective with a 10X eyepiece?
100X
Numerical aperture
The measure of the ability of a lens to “capture” light coming from the specimen and use it to make the image
Condenser
Structure of a microscope concentrates the light onto the specimen
Resolving power
Actual measurement of how far apart two points must be for the microscope to view them as separate points
Parfocal
Ability of the microscope to stay in relative focus as the objective lenses are changed from one to another
Field/field of vision
The round lit area you see when looking through the microscope
A phase contrast microscope illuminates the specimen and its parts at various levels of light intensities (contrast) because the light waves are both in phase and out of phase (T/F?)
True
What is the resolution of a compound, binocular, bright-field microscope?
0.2 µm
Acidic stains can also be called negative stains (T/F?)
True
Methylene blue is a basic stain (T/F?)
True
Safranin is an acidic stain (T/F?)
False
A pair of two rods linked end-to-end are called:
Diplobacilli
The counter stain for the Gram stain is safranin (T/F?)
True
Heat-fixing can distort cell shape, arrangement, and size (shrinkage) (T/F?)
True
Acidic stains
This type of stain is negatively charged and repels the negative charge of the bacterial cell, thus leaving the organism unstained with a colored background
Auxochrome
This is the charged portion of the chromogen
Basic stain
This type of stain is attracted to the negative charge of the bacterium and will dye the bacterium a certain color and leave the background white
Chromophore
This is the portion of the chromogen that has color
Chromogen
This is the colored molecule of a stain (usually a benzene derivative)
A chain of round cells is called a:
Streptococci
Nigrosin is an acidic stain (T/F?)
True
Congo red is a basic stain (T/F?)
False
The acid-fast stain is a differential stain (T/F?)
True
The basic stain that stains the bacterium inside the capsule in the capsule stain procedure is:
Maneval’s stain
What color are the vegetative cells in the endospore stain?
Red or pink
Central endospore
The endospore is in the middle of the cell
Terminal endospore
The endospore is on the end of the cell
Subterminal endospore
The endospore is between the middle and end of the cell
The Kinyoun acid-fast staining method requires heat for at least five minutes (T/F?)
False
A smear for the capsule stain requires heat-fixing (T/F?)
False
What are the two acid-fast staining methods?
Kinyoun (K) and Ziehl-Neelsen (ZN)
A counter stain for the acid-fast stain is:
Methylene blue
Peritrichous (flagella arrangement)
Flagella covering the entire cell surface of the bacterium
Monotrichous or polar (flagella arrangement)
A single flagellum found at one end of the bacterium
Amphitrichous (flagella arrangement)
Flagella at both ends of the bacterium
Lophotrichous (flagella arrangement)
Tufts of flagella at one end of the bacterium
The primary stain the endospore stain is:
Malachite green
In MSA the inhibitor is:
High salt content