Physics- all questions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
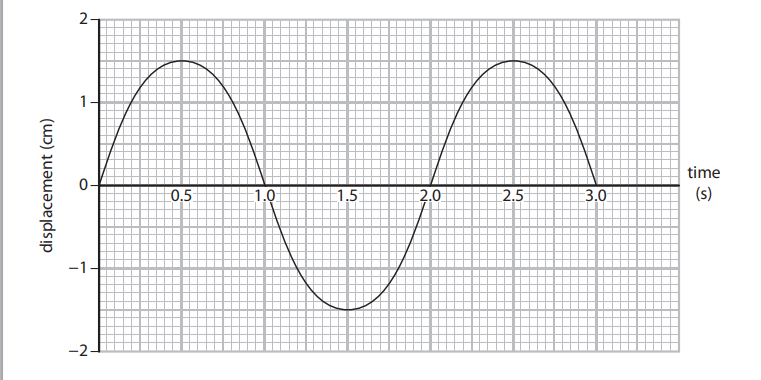
A student uses a cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO) to investigate the properties of waves produced by a signal generator. The student obtains the following output.
(a) Give the amplitude of the wave (1)
1.5cm
b) Give the periodic time of the wave (1)
2.0 seconds
The student investigates a different water wave. The wavelength is 0.05m and the wave speed is 0.075m/s. Calculate the frequency of the water wave. Show your working. (3)
substitution (1)
0.075 = f x 0.05
rearrangement (1) f
= 0.075/0.05
evaluation (1) 1
.5 (Hz)
A radio programme can be transmitted as an analogue signal or a digital signal. (a) State what is meant by the term analogue signal. (1)
Analogue: continuously variable (signal) / (signal) can have any value (1)
State what is meant by the term digital signal. (1)
Digital: two values only / on or off / 0 and 1
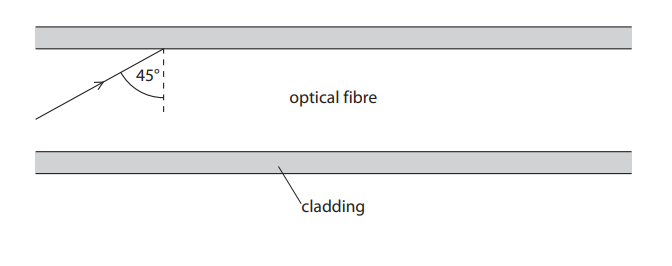
Light travels through optical fibres by total internal reflection. The diagram shows a ray of red light in an optical fibre. The diagram is incomplete. Complete the path of the red light through the optical fibre. (2)
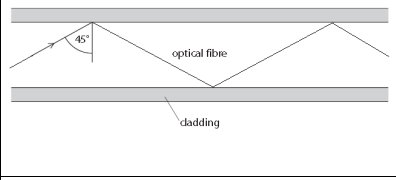
Television programmes can be transmitted through optical fibres using digital signals. Explain two advantages of using digital signals instead of analogue signals to transmit television programmes. (4)
the signal can be regenerated (1) so it can travel greater distances/further without any degradation / attenuation (1)
OR
the signal can {carry more information (in the same time)/can carry many television channels (at the same time)/need less bandwidth} (1) so cables can be thinner(1)
OR
noise can be removed from the signal/less interference (1) so that a clearer output / better quality is produced compared to an analogue signal (1)
OR
signals can be used directly by computers /digital signals do not need to be converted (1)
OR
A so processing time is lower(1)
Visible light transfers energy as a transverse wave. Sound transfers energy as a longitudinal wave. Visible light moves faster than sound. Give two other differences between visible light waves and sound waves. (2)
visible light is electromagnetic but sound is {vibration / mechanical} (1) visible light travels in a vacuum but sound needs a material medium (1) sound has a lower {frequency / higher wavelength} / ORA (1)
visible light can be polarised but sound cannot (1)
visible light carries much more energy (1)
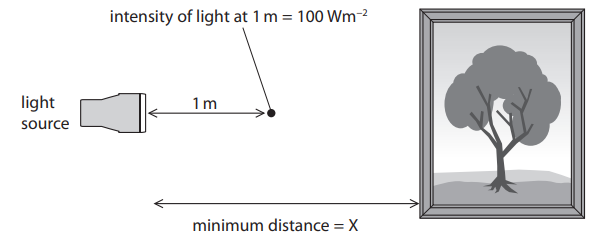
A painting is displayed in a dark room. An electrician fits a single light source to illuminate the painting. The intensity of the light 1m from the light source is 100Wm−2. The intensity of the light falling on the painting must not be greater than 30Wm−2. Calculate, using the inverse square law, the minimum distance the light source must be placed from the painting. Show your working. (3)
Substitution (1)
30 = 100 / r2
or
30r2 = 100
Rearrangement (1)
r=√ 100/ 30
Evaluation (1)
1.83 (m)
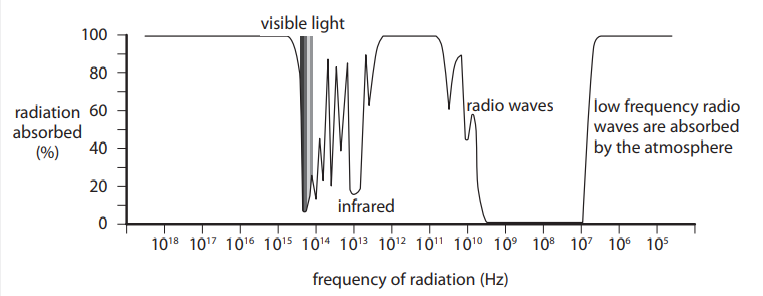
A satellite, orbiting the Earth, collects information about asteroids that might hit the Earth. A research team needs to collect a large amount of data from the satellite very quickly. This means that the data has to be transmitted rapidly. The chart shows how the regions of the electromagnetic spectrum with different frequencies are absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of using radio waves instead of light waves to send large amounts of information from the satellite to the surface of the Earth. (4)
some of the radio waves (with frequencies between 5x 109 and 3 x 107 Hz) reach the Earth’s surface (1)
so (radio waves) lose no information in transmission/a clear signal is received (1) OR not all visible light (with a frequency of about 4 to 7 x 1014Hz) reaches the Earth’s surface (1)
so (visible light) loses some information in transmission / signal is not clearly received (1)
radio wave frequency is much lower (than that of visible light) ( 5 x 109 to 3 x 107 Hz compared with 4 to 7 x 1014 Hz for light ) (1)
so (radio waves) would take longer (than light waves) to transfer the same amount of information (1)
The satellite transmits two signals, A and B, to another satellite in orbit around the Moon, using different electromagnetic waves. The signals are transmitted over the same distance. Signal A has a frequency of 3.0 × 1013 Hz and takes 1.28 seconds to travel between the two satellites. Signal B has a frequency 4.0 × 109 Hz. Explain how much time is taken for Signal B to travel between the two satellites. (2)
1.28 seconds (1)
because all electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed (in a vacuum/space) (1)
A home cinema system can be controlled either by an infrared remote control or a remote control that uses a Bluetooth© connection.
Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of using:
• an infrared remote control
• a Bluetooth© remote control
to control the home cinema system. (6)
Infrared
Strengths
does not interfere with other devices as the frequency is higher than Bluetooth©
better quality and clearer communication between devices due to higher frequency /lower wavelength used
Weaknesses
needs line of sight /not able to transmit through most materials
will only work over short distances because infrared is absorbed/scattered by the air
works with one device at a time
sunlight and other sources of infrared interfere with the signal
transmitter and receiver have to be stationary, so cannot be used when moving around
Bluetooth©
Strengths
does not need to be in direct line of sight /works through walls
Bluetooth can be used on more than one device at the same time
can be used from a mobile deviceB
Weaknesses
low bandwidth because of frequency of transmission
interference with other Bluetooth devices on similar radio frequencies if close by
Identify the region of the electromagnetic spectrum with the lowest frequency. (1)
A- microwaves
B- radio waves
C- ultraviolet waves
D-visible waves
B
Explain one advantage of using microwave radiation in mobile phone communications. (2)
they can carry a lot of information/data (1)
(because microwaves have a) high frequency / {high/wide} bandwidth (1)
they can travel {long distances /to satellite} (1)
(because microwaves are) not absorbed by/pass through the (Earth’s)atmosphere/ionosphere
Explain one disadvantage of using microwave radiation in mobile phone communications. (2)
disruption of signals/signal lost/signal attenuated /signal blocked (1)
(because of) buildings/hills/mountains/obstacles/underground or they diffract less or rain /water (vapour) in the atmosphere or not in line of sight (1)

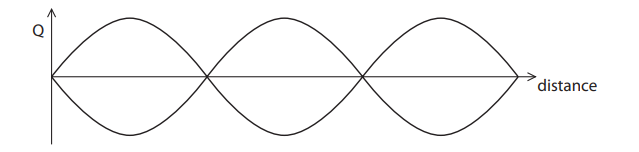
The picture shows a guitar. A standing wave is produced when a guitar string is plucked. The standing wave is represented on the graph. Give the missing label, Q, for the y-axis on the graph. (1)
displacement
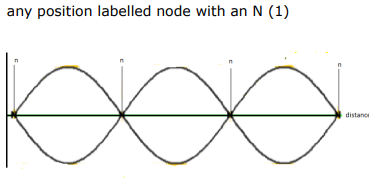
Label with the letter N the position of one node, on the graph. (1)
A guitar string is tuned by changing the tension. The speed of a wave in the string is 16.2ms−1. The mass per unit length of the string is 0.3kgm−1. Calculate the tension in the string. Show your working. (4)
Substitution (1)
16.2 = √ T/ 0.30
Squaring both sides (1) 262 = T 0.30
Rearrangement (1)
(T =) 262 x 0.30
Evaluation (1)
(T =) 78.7 (N
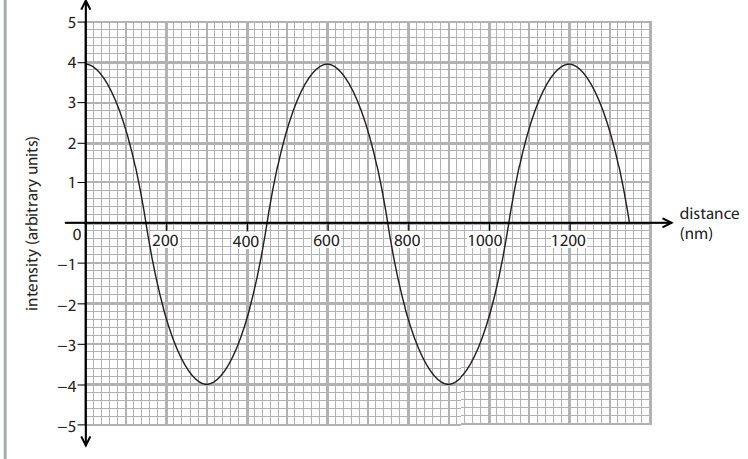
Diffraction gratings allow light waves to be split into beams that travel in different directions. (a) The graph shows a representation of a light wave. Give the wavelength of the light wave in the graph. (1)
600 (nm)
A diffraction grating is used to analyse sunlight. The pattern produced has a bright central white line. On either side of the white line there are bands of different colours. The bands of different colours become increasingly blurred the further away they are from the central white line. (i) Explain why the central white line is bright. (2)
There is constructive interference/ superposition for all the wavelengths or frequencies. So the path difference from the diffraction gratings are identical. All the wavelengths are in phase.
Explain why the diffraction grating produces a pattern of coloured bands. (4)
at the diffraction grating;
- (sunlight is made up of colours/waves with) different frequencies or wavelengths (1)
the angle through which the light {diffracts/changes direction/bends} depends on {wavelength / frequency} (1)
on the screen a pattern of coloured bands is produced because:
- constructive interference occurs when the path difference is a whole number of wavelengths (1)
so each colour will meet/form a bright line at the screen in a different place (to each other) (1)
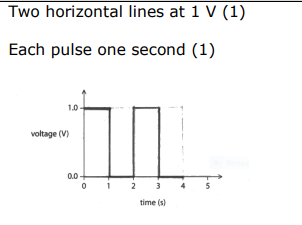
3 A digital signal has a value of 1.0V when it is on and 0.0V when it is off. The digital signal changes every second. Draw a digital signal corresponding to 1 0 1 0. (2)
Which of these processes occurs in an analogue-to-digital converter?
a- displaying data
b- randomising data
c- sampling data
d- storing data
c
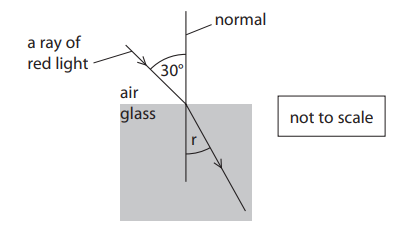
An optical fibre is made of glass. The speed of red light in air is 3.0 × 108ms−1. The speed of red light in the glass is 2.0 × 108ms−1. A ray of red light enters the glass from the air with an angle of incidence of 30°.
Calculate the angle of refraction, r, of the red light in the glass. Show your working. (3)
Substitution (1)
3.0×108 / 2.0×108 = sin30/sin r
Rearrangement (1)
(sin r=) sin30 × 2.0×108 / 3.0×108 f
so the final answer will be 19.47o
Explain the strengths and weaknesses of using optical fibres to supply broadband to homes. (6)
Strengths
signals carry more information / data because the signal can be multiplexed / multiple channels (frequencies) used /greater bandwidth
signals are resistant to hacking because they are more secure /can be encrypted
breaking the cable to eavesdrop is very hard without being detected
signal can be regenerated so there is little/no loss of information OR so it can be used over very long distances
less susceptible to noise/(electrical) interference so a better-quality output is produced /clear(er) signal
the broadband rate of information transfer (speed) of optical fibres is greater because light has great(er) range of frequencies / high(er) frequency
data can be directly used by devices because most devices use digital systems
no loss of data at the (digital) device because there is no interface / need to convert signal
less energy wasted/lost because of total internal reflection (TIR)
Weaknesses
digital signals use a greater bandwidth than analogue signals so more channels are needed to transmit data
information /data can be scrambled/lost because of sampling errors
they easily damaged /broken (if bent too much) because they are fragile/brittle
jointing/repair of optical fibres is difficult so needs specialist equipment/technician /is expensive
poor joints lead to loss of signal strength, so signal is poor
{handshaking/ synchronisation} needs to take place so that devices can {transfer information/talk to each other}