ECON200 Exam 2 (Chapters 7-14)
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Utility
A measure of the amount of satisfaction a person derives from something
Revealed preference
People’s preferences can be determined by observing their choices and behavior
Utility function
A formula for calculating the total utility that a particular person derives from consuming a combination of goods and services (called a bundle of commodity)
Marginal utility
The change in total utility from consuming an additional unit of a good or service
Principle of diminishing marginal utility
The additional utility gained from consuming successive units of a good or service tends to be smaller than the utility gained from the previous unit or service (basically the more you have of something, the more your utility goes down)
Budget constraint
Provides all possible combinations of goods and services a consumer can buy for a given income
Income effect
When consumption changes from increased effective wealth due to a lower price
Substitution effect
The change in consumption that results from a change in the relative price of goods
Altruism
A motive for action in which a person’s utility increases simply because someone else’s utility increases
Reciprocity
Responding to another’s action with a similar action.
Information asymmetry
When one person knows more than the other person in an agreement
Adverse selection
Occurs prior to completing an agreement when buyers and sellers have different information about the quality of a good or the riskiness of a situation
Market failure
The economic situation defined by an inefficient distribution of goods and services in the free market
Moral hazard
The tendency for people to behave in a riskier way or to renege on contracts when they do not face the full consequences of their actions after an agreement has been made (based on ACTIONS)
Screening
Reveals private (not personal) information
Signaling
Taking action to reveal one’s own private information
Reputation
If interactions occur multiple times, parties can use their past history to indicate that the other party has full information
Statistical discrimination
Generalizing based on observable characteristics to fill in missing information
Regulation
The government requires information disclosure or requires participation in an active market
Behavioral economics
Studies why individuals appear to act irrationally by studying insights from psychology
Time inconsistency
The tendency for individuals to change their preferences over time, and this leads to inconsistent decision-making.
Commitment device
Can be used to help fulfill a plan for future behavior that would otherwise be difficult
Sunk cost fallacy
Many times individuals remain engaged in an activity even though the benefit of continuing is less than the opportunity cost, especially if a cost was incurred to engage in the activity
Game theory
This studies how people behave strategically under different circumstances
Game
Any situation that requires two or more people who have to think strategically
Three features of games
Rules, strategies, and pay-offs
Prisoners dilemma
A one-time game of strategy in which two people in isolation make the choice to ‘confess’ or ‘don’t confess’ that together they committed a crime
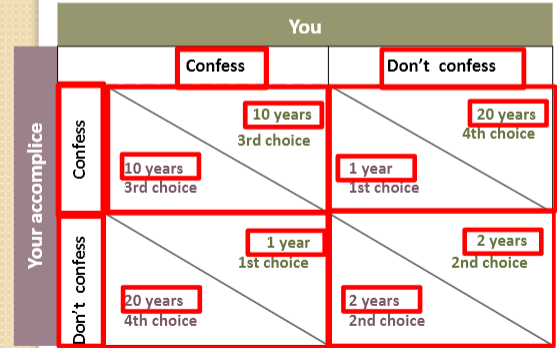
Dominant strategy
The strategy that is the best one for a player to follow, no matter what strategy the other player chooses
Nash equilibrium (non-cooperative)
A concept in game theory where no player has an incentive to change their strategy, given the strategies of the other players. It is a stable outcome where no player can improve their payoff.
Commitment strategy
An agreement to submit to a penalty for defecting to obtain a certain outcome
Tit-for-tat
One player does the same action as the other did in the previous game
First-mover advantage
The player who chooses first gets the higher payoff
Backward induction
Determining optimal strategies by working backwards, by looking at the last choices
Profit Equation
Total revenue - Total Cost
Total Revenue Equation
Price x Quantity
Total cost
The amount that a firm pays for inputs used to produce goods or services (Fixed costs + Variable costs)
Fixed costs
Does not depend on the quantity of the output produced, can be on-going payments such as rent, or a one-time cost
Variable costs
Costs that depend on the amount of outputs being produced, increase with each additional unit produced
Explicit costs
Costs that require a firm to spend money
Implicit costs
These costs represent opportunities that could have generated revenue if the firm had invested its resources in another way
Accounting profits
Total revenue - explicit costs
Economic profits
Total revenue - explicit costs - implicit costs
Production function
The relationship between the quantity of inputs and the resulting quantity of outputs
Marginal product
The increase in output that is generated by an additional unit of input
The principal of diminishing marginal product
The marginal product of an input EVENTUALLY decreases as the quantity of an input increases
Average product
Total production divided by the number of workers
Average fixed cost (AFC)
Fixed cost / Quantity
Average variable cost (AVC)
Variable cost / Quantity
Average Total Cost (ATC)
Total cost / Quantity (AFC + ACV)
Marginal cost
Change in total cost / Change in quantity
Short-run
Period of time in which at least one factor of production is fixed, resulting in limited flexibility to adjust output levels.
Long-run
A period of time in which all inputs can be adjusted, allowing a firm to change its scale of production and make long-term decisions to maximize profits.
Economies of scale
As output increases, the average total cost decreases
Diseconomies of scale
The average total cost increase when production increases
Constant returns to scale
When the average total cost does not depend on the quantity of output
Efficient scale
When the average total cost is at its minimum
Characteristics of a competitive market
Buyers and sellers are price-takers
Standardized goods
Firms freely enter and exit the market
Full information exists
Market power
When a buyer or seller has the ability to noticeably affect market prices
Demand Curve in a Perfectly Competitive Market
Horizontal Line (demand is the same as price)
Average Revenue Equation
Total Revenue / Quantity Sold
Marginal revenue
The change in revenue after selling one more unit of a good (same as price in a p.c.m)
Profit-maximizing quantity
The quantity of output where a firm maximizes its profit by producing the level of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost (MC = MR)
Competitive (socially optimal) price
Price = Marginal Cost (P = MC)
Non-competitive market
Firms in these types of markets can charge a price above the marginal cost
If P < AVC…
A firm should shut down.
If P > AFC+AVC…
A firm is making profit, keep producing
If P<AFC+AVC, but P > AVC
The loss per unit is less than the fixed cost. So the total loss is less than fixed cost. Keep producing in the short run.
Monopoly
A firm that is the only producer of a good that has no close substitutes (Perfect monopoly = controls entire market, and Monopoly power = manipulates the price)
Barriers to entry
Scare resources
Government intervention
Economies of scale
Aggressive business tactics
Natural monopoly
A market where a single firm can produce the entire quantity demanded in market at a lower cost than multiple firms
Monopoly demand curve
Downward sloping
Quantity effect
Total revenue increases after producing an additional unit (___ effect)
Price effect
Total revenue decreases after producing an additional unit
You have market power when…
Price is GREATER than marginal cost (P > MC)
Problems with monopolies
Monopolies charge a price higher than the socially optimal level
Monopolies produce less than the socially optimal level
Monopolies generate deadweight loss
Public policy responses to monopolies
Anti-trust laws
Public ownership
Vertical Split
Regulation
Do nothing
Price discrimination
The practice of charging customers different prices for the same good
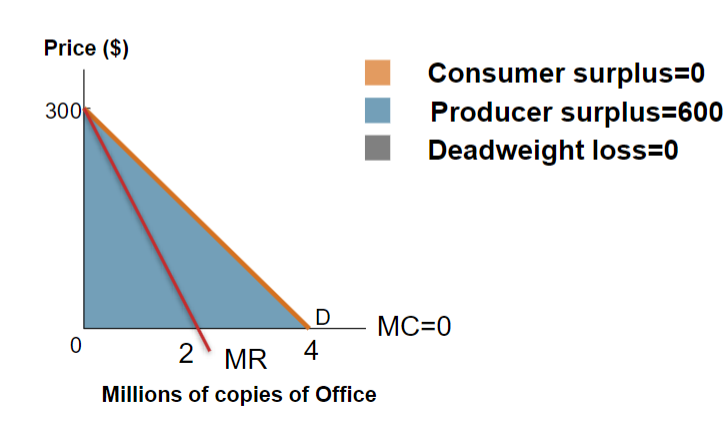
Perfect price discrimination
All producer surplus, no consumer surplus