SCI 100 Midterm Notes
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Science method
The process of gaining knowledge through testing and observation
What is the purpose of science?
To build knowledge about the world
Hypothesis
A testable statement that provides a yes or no answer to a research question.
Prediction
A description of the expected outcome of an experiment, related to the hypothesis.
Controls
Constant factors in an experiment used for comparison with the dependent variable.
Positive Control
A group treated with a known response that yields expected results.
Negative Control
A group that does not receive treatment, remaining unchanged during the experiment.
Dependent Variable
The variable being tested in an experiment, dependent on the independent variable.
Independent Variable
The variable that is changed in an experiment to observe its effect on the dependent variable.
What are the 8 water quality testing parameters?
Temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, fecal coliform bacteria, total nitrates, total phosphates, turbidity, and conductivity.
Temperature
A measure change in temperature that affects the solubility of substances in water.
pH
A scale measuring acidity (<7) or basicity (>7) from 0-14.
How big is a change in one pH unit?
A TENFOLD increase/decrease in acidity.
Dissolved Oxygen
Measures how much oxygen is dissolved in the water and is essential for aquatic organisms' survival, fluctuating due to factors like photosynthesis and temperature.
Fecal Coliform Bacteria
Gut bacteria found in warm blooded animals that indicates water contamination.
Total Nitrates
Nutrients necessary for life that come from sewage, are a limiting factor in saltwater, and can cause eutrophication if present in excess.
Total Phosphates
Nutrients that are a limiting factor in freshwater and can also cause eutrophication.
Turbidity
A measure of water clarity; can absorb sunlight that increases water temperature and can block fish’s gills and sunlight from plants.
Conductivity
A measure of water's ability to conduct electricity; more dissolved ions increase conductivity.
What is the biological importance of the Water Quality Index?
Good water quality benefits the environment and public health, protecting aquatic life and preventing dehydration and malnourishment.
Water Hardness
The concentration of dissolved minerals in water, such as calcium and magnesium.
What is the difference between hard water and soft water?
Hard water has more (dissolved) minerals; soft water is more slippery.
Watershed
A land area where water flows through on its way to a larger body of water.
What is an example of a specific watershed and a general watershed?
Herbert Run (specific) and Chesapeake Bay (general)
Estuary
A region where saltwater and freshwater mix
What is the ecological importance of estuaries?
Estuaries filter rivers, providing clean water.
Standard Curve
A graph of known concentrations of a substance vs a measurable factor.
What is the importance of standard curves?
It compares a unknown sample to known solutions to determine the unknown.
What is R2 in a standard curve?
The coefficient of determination that numerically tells how well the model fits with the data.
Eutrophication
Excessive primary production when water receives too many nutrients, leading to harmful algal blooms and fish kills.
How were dissolved oxygen and phosphate levels related to phytoplankton growth?
Dissolved oxygen levels became low while phosphate levels increased from large populations of primary producers.
Molecular structure of water diagram
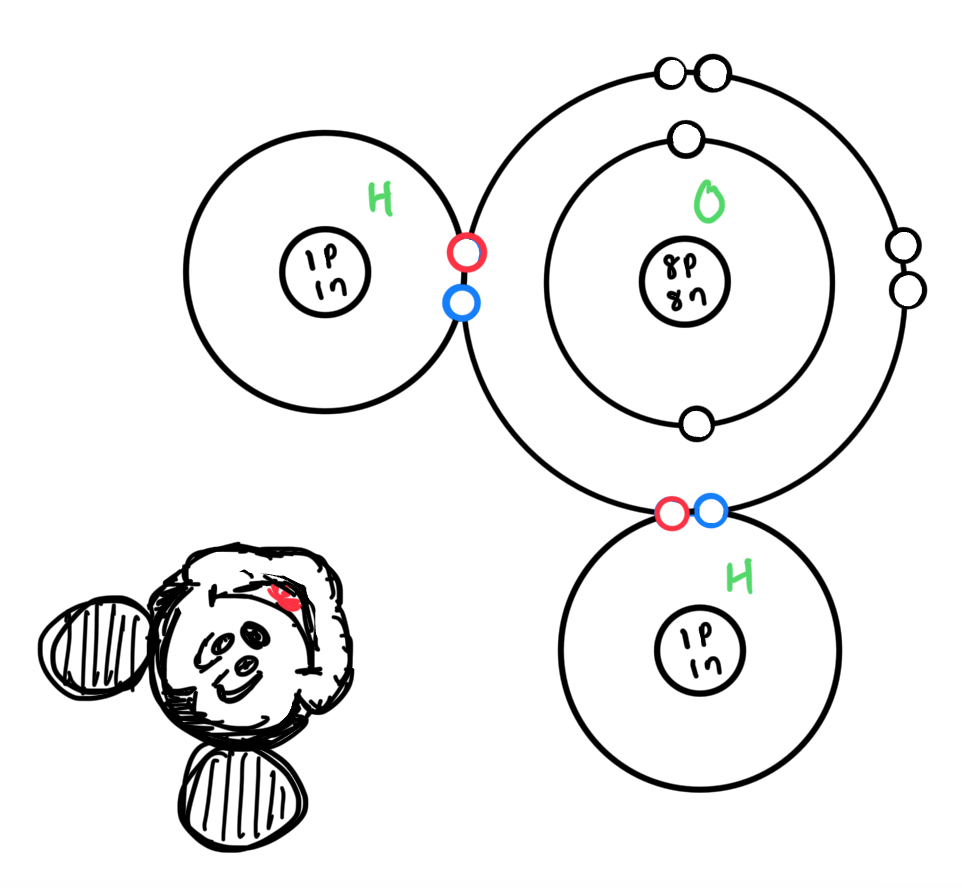
Element
A substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances.
Atom
The basic unit of matter, consisting of protons, neutrons, electrons, and a nucleus.
Ionic Bond
A bond formed by the transfer of electrons between atoms.
Covalent Bond
A bond formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms.
Polar Covalent Bond
A bond where electrons are shared unequally due to differences in charge.
Hydrogen bond
The force between the ends of molecules that are the same; one end is slightly negative and one is slightly positive.
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom; determine its chemical properties and if they lose, gain, or share an electron.
Unique Properties of Water
Water's ability to dissolve most compounds as a universal solvent
Its cohesion and adhesion
High specific heat
High heat of vaporization
Lower density as a solid compared to a liquid
What is the importance of water’s unique properties?
High specific heat: makes water a good insulator and allows oceans to regulate coastal climate
High heat of vaporization: makes water a good coolant and is depended on earth’s heat transfer
Density: allows ice to float and related to seasonal turnover
Cohesion and adhesion
Water clings to itself (co); water clings to other molecules/things (ad).
What is the relationship between temperature and water density?
Warmer water allows it to take more space, making it less dense.
At what temperature is water the most dense?
4ºC
What is the ecological importance of water density?
Colder water sinks which allows aquatic life to live during colder seasons.
Seasonal Turnover
The process in lakes where water stratifies/forms layers due to temperature changes throughout the seasons.