SYRCSE261: Electronics and Digital Systems (Combinational Logic 1 of ZyBook)
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers key vocabulary and concepts from the course on Electronics and Digital Systems.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
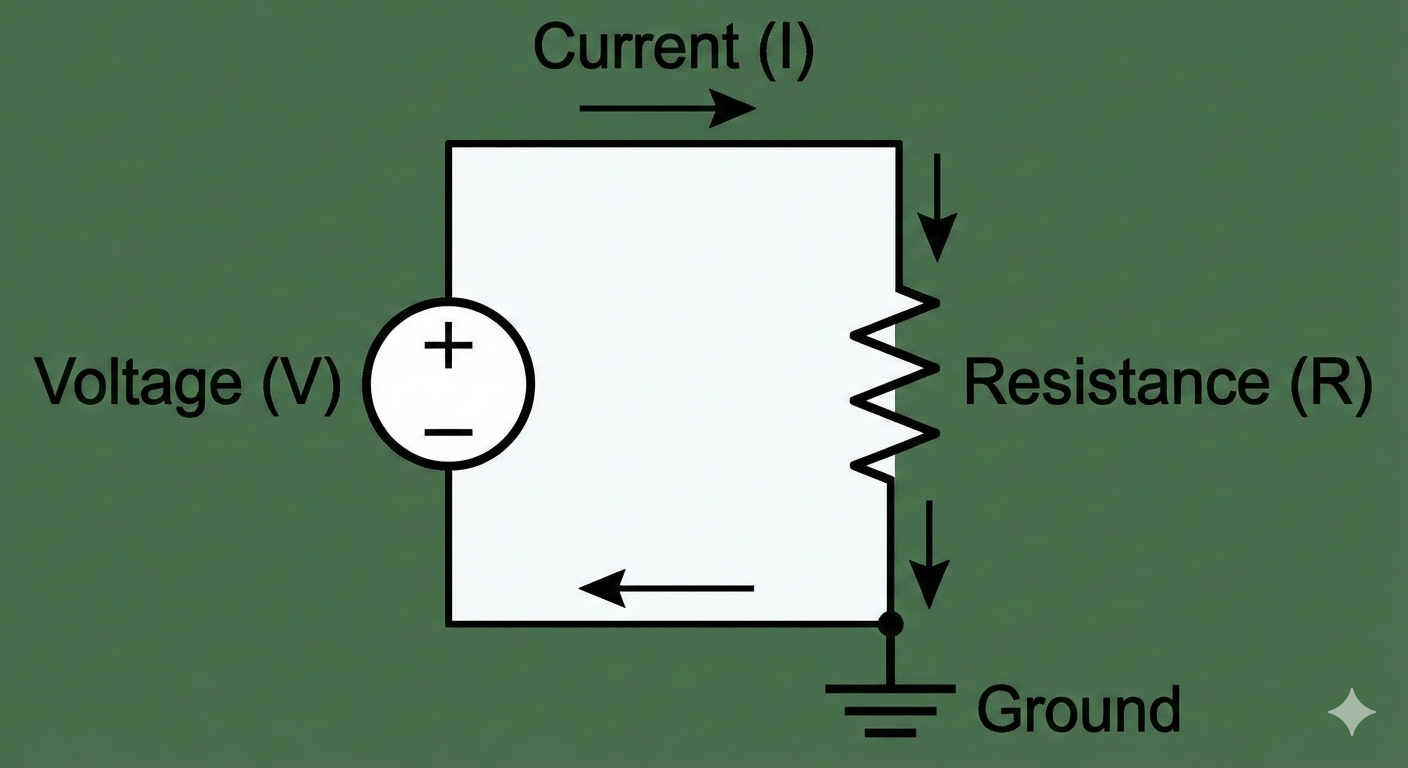
Voltage
The potential for charge to move, measured in volts (V).
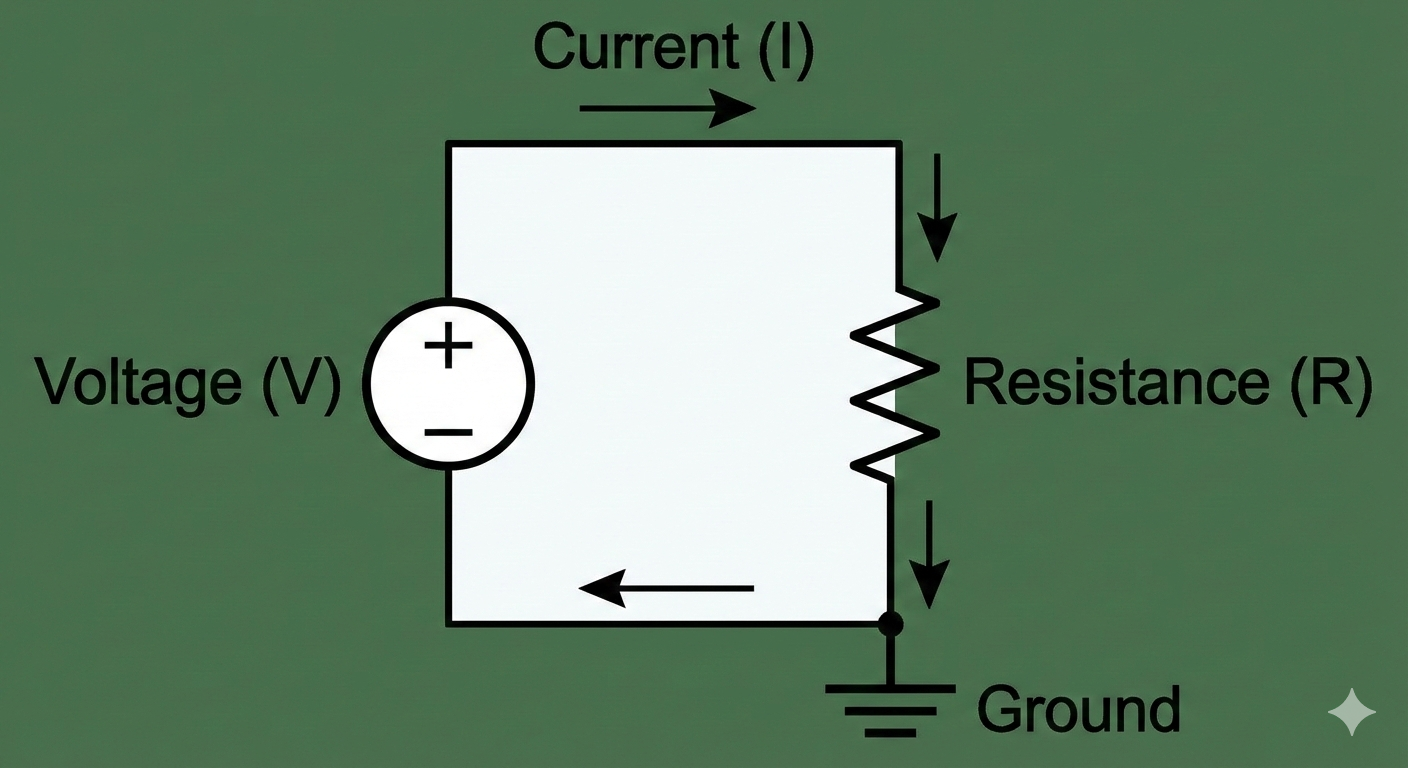
Current
The amount of charge flow, measured in amperes (A).
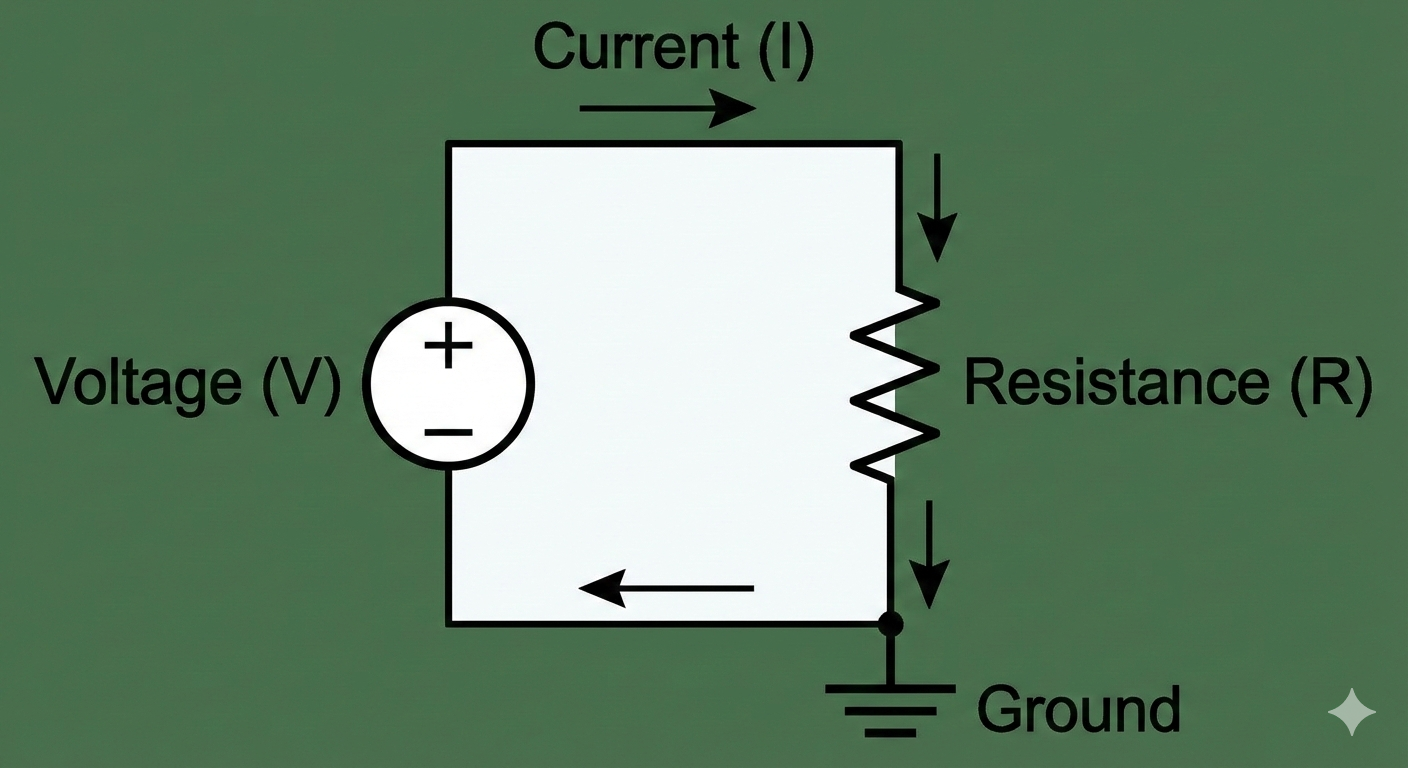
Resistance
Opposition to flow in an electrical circuit, measured in ohms (\Omega).
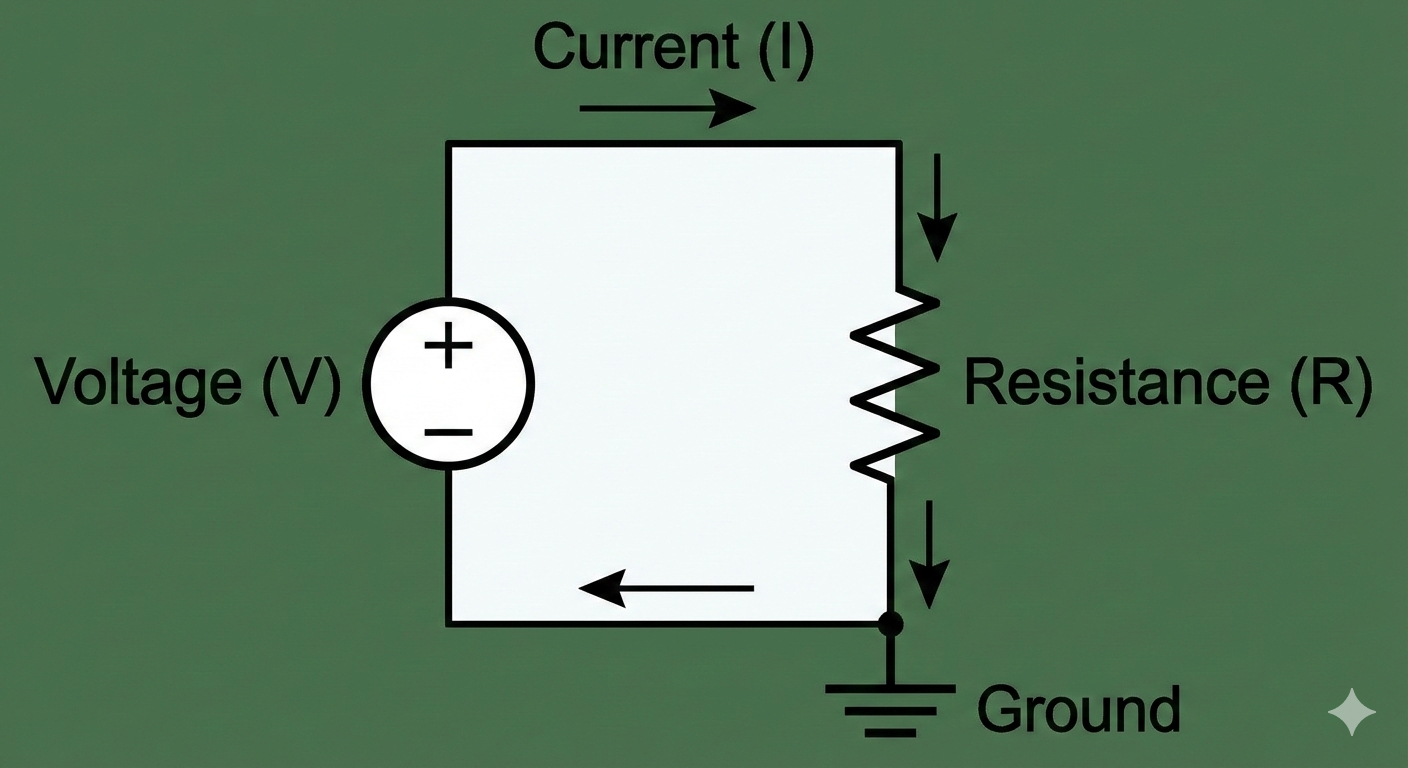
Ohm's Law
The relationship between voltage, current, and resistance, expressed as V = IR.
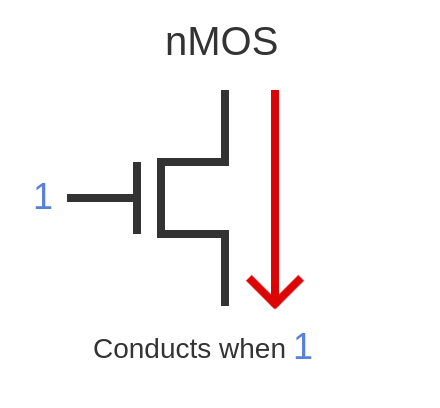
nMOS
A type of MOSFET that conducts when a positive voltage (1) is applied to the gate.
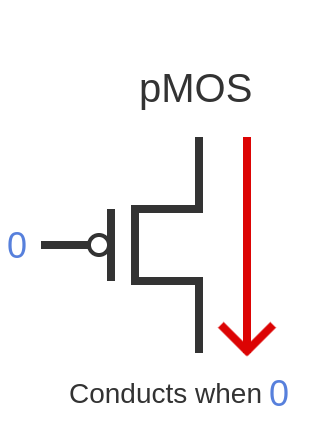
pMOS
A type of MOSFET that conducts when a negative voltage (0) is applied to the gate.
Truth table
A mathematical table used to determine the output of a logic gate based on all possible input values.
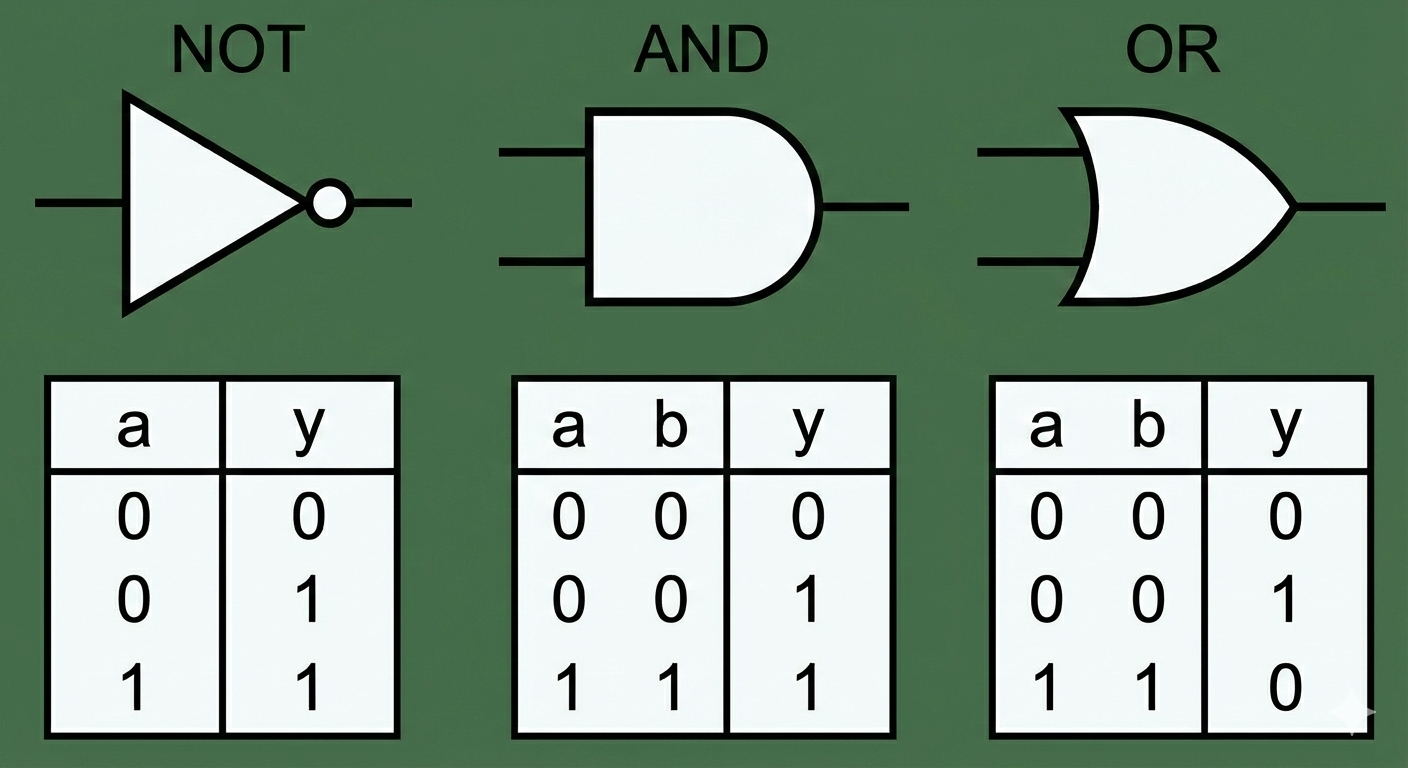
Logic gate
An electronic component that performs a logical operation on one or more inputs to produce an output.
Boolean algebra
A branch of algebra that deals with true (1) or false (0) values, used in logic and digital circuit design.
Timing diagram
A graphical representation that shows the state of a digital signal over time.
Sum-of-products form
A method of combining products (AND terms) by summing them to express a logic function.
Product-of-sums form
A method of combining sums (OR terms) by multiplying them to express a logic function.
Binary number system
A number system that consists of only two digits, 0 and 1, used in digital electronics.
Interrupt logic
The logic used to handle interrupts in a processor, determining the priority and response to events.
Maximum terms (maxterms)
The product terms in a logic expression that evaluate to false (0).
Minimum terms (minterms)
The sum terms in a logic expression that evaluate to true (1).
Digital circuit simulator
A software tool used to simulate the behavior of digital circuits.
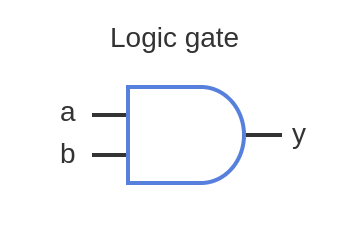
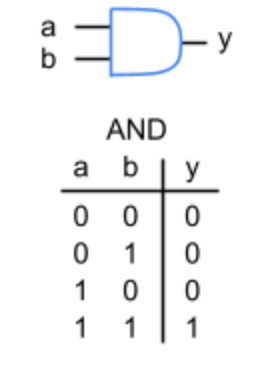
AND Gate
A logic gate that outputs true (1) only if all its inputs are true (1).
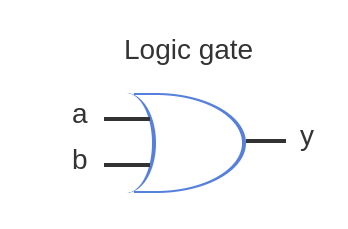
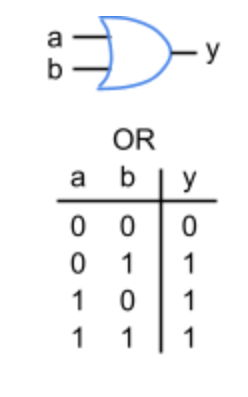
OR Gate
A logic gate that outputs true (1) if at least one of its inputs is true (1).
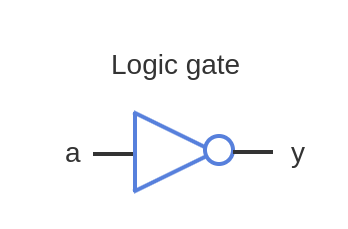
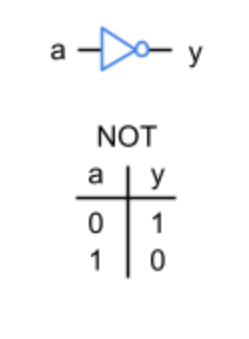
NOT Gate
A logic gate that outputs the logical complement (inverse) of its input (0 \to 1, 1 \to 0).