Microbio LAB (8.1 and 8.2) Parasitology 1-3
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
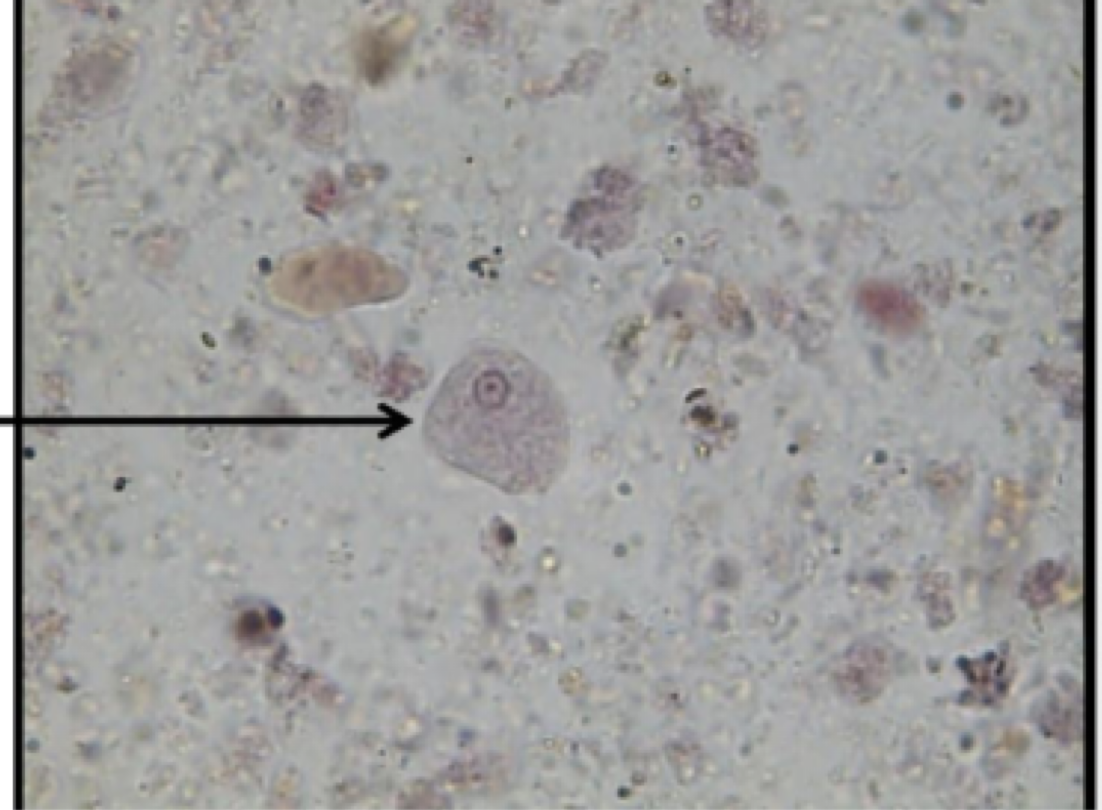
Entamoeba histolytica
Motility: pseudopod
Mode of transmission: fecal-oral
Infective stage: cyst
disease: amebiasis
parts to look for
central karyosome
bullseye nucleus
consumes red blood cells
look for RBCs inside organism
can eat through lining of GI tract and kill host
Entamoeba histolytica
Naegleria fowleri
Motility: pseudopod
Mode of transmission: travels up the nose
water enters the nose of an organism then travels up olfactory nerve to the brain
Infective stage: trophozoite
disease: primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM)
parts to look for
large karyosome that take up whole nucleus
Naegleria fowleri
Acanthamoeba spp.
Motility: pseudopod
Mode of transmission: contaminated water or soil contact
Infective stage: trophozoite or cyst
disease: keratitis (eye), amebic encephalitis
parts to look for
karyosome takes up half of the nucleus
Acanthamoeba spp.
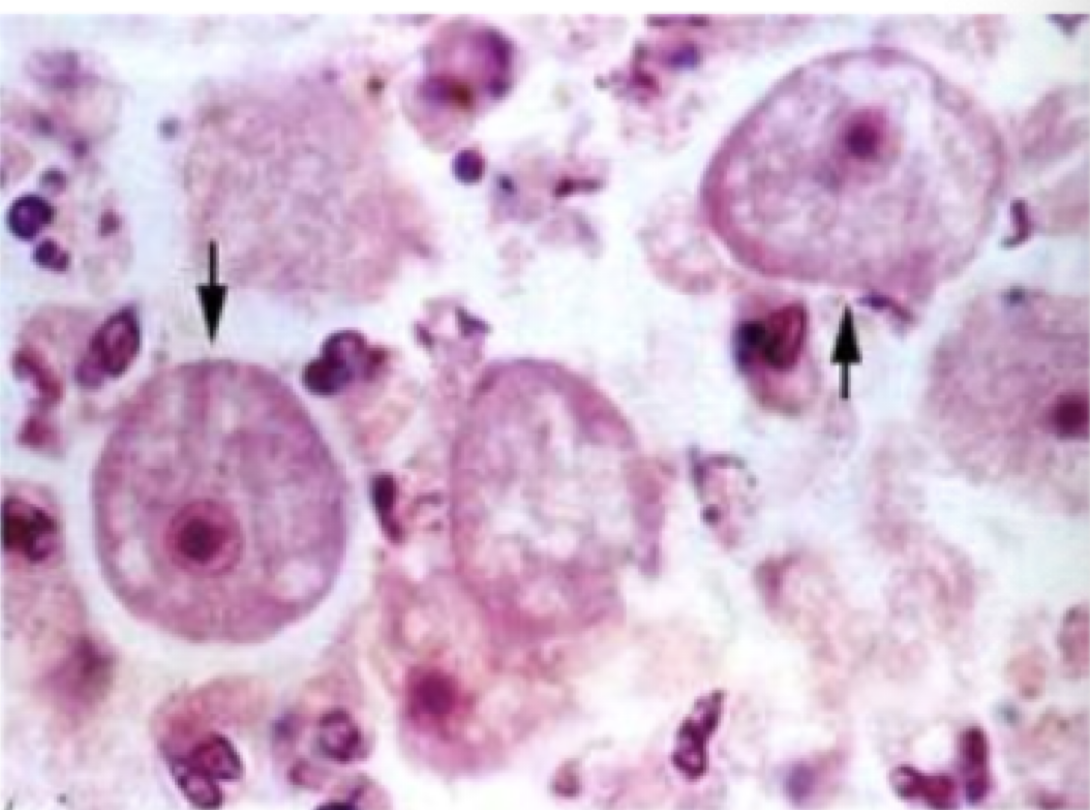
Balantidium coli
Motility: cilia
Mode of transmission: fecal-oral
Infective stage: cyst
disease: Balantidiasis
also, may people go asymptomatic
parts to look for
large kidney bean shaped nucleus
Balantidium coli
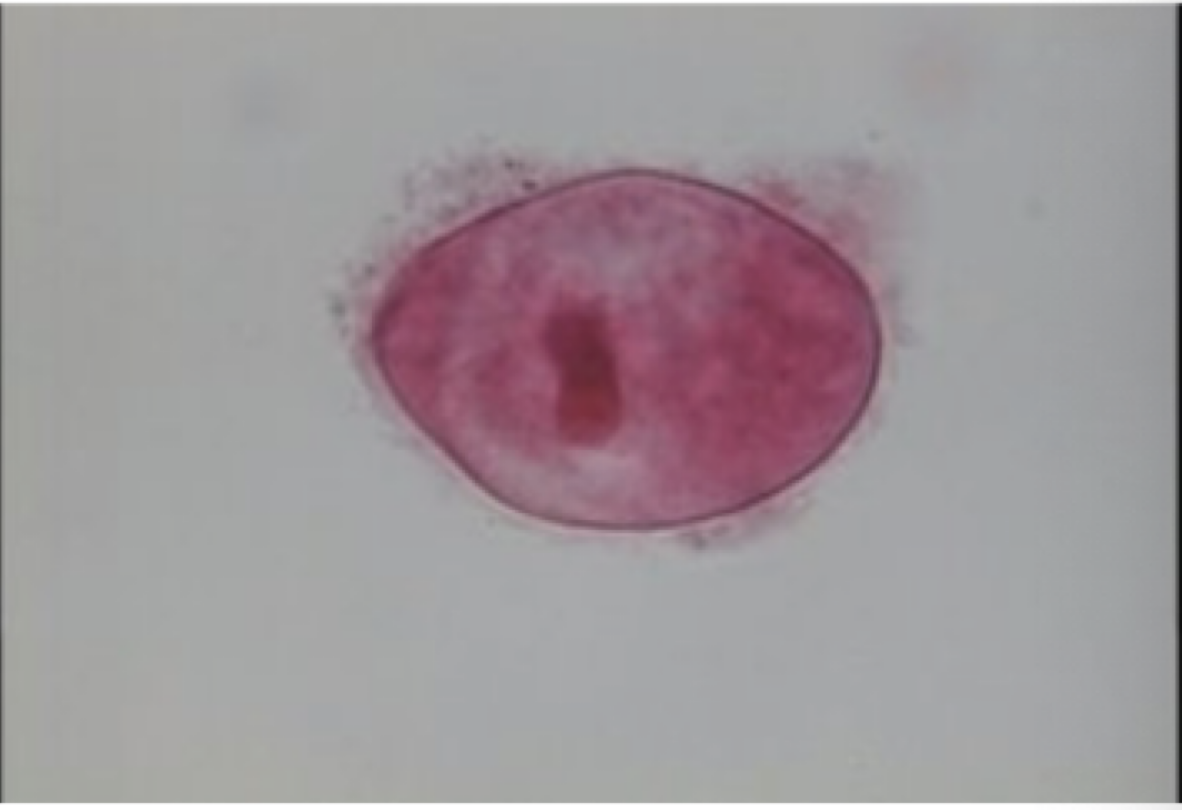
giardia lamblia
Motility: flagella
Mode of transmission: fecal-oral
Infective stage: cyst
disease: Giardiasis “Hikers’ diarrhea”
parts to look for
symmetrical heart shape
flagella
two nuclei
organelles positioned in such a way that it resembles a face
giardia lamblia
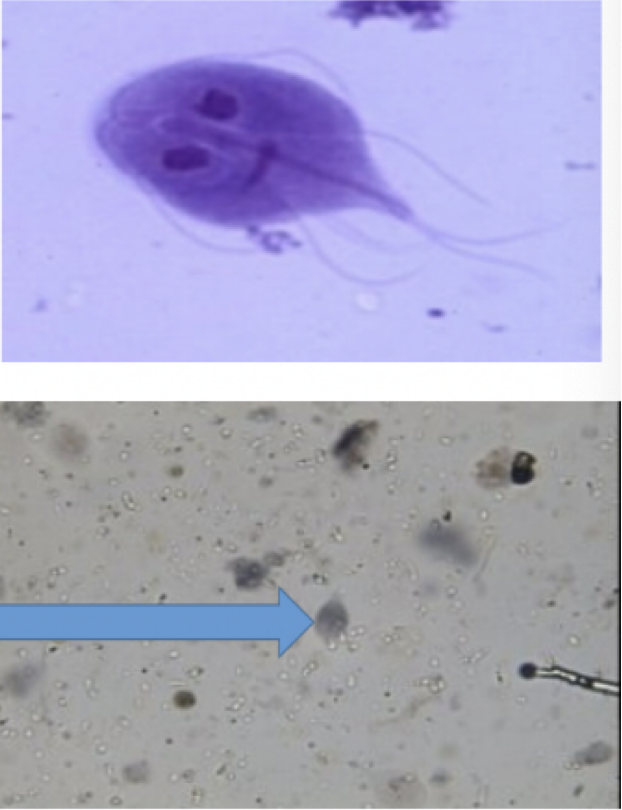
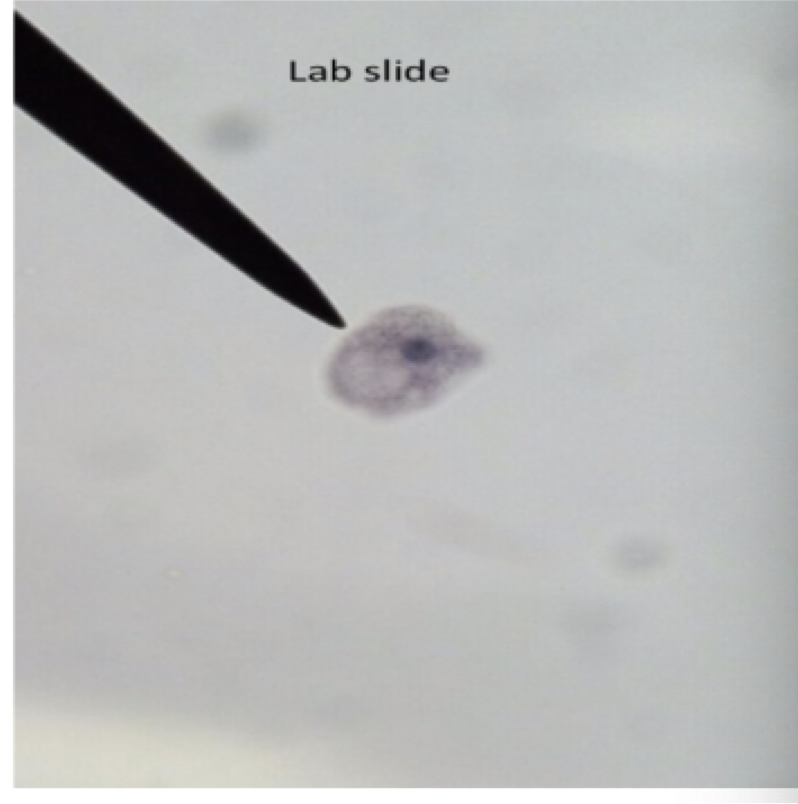
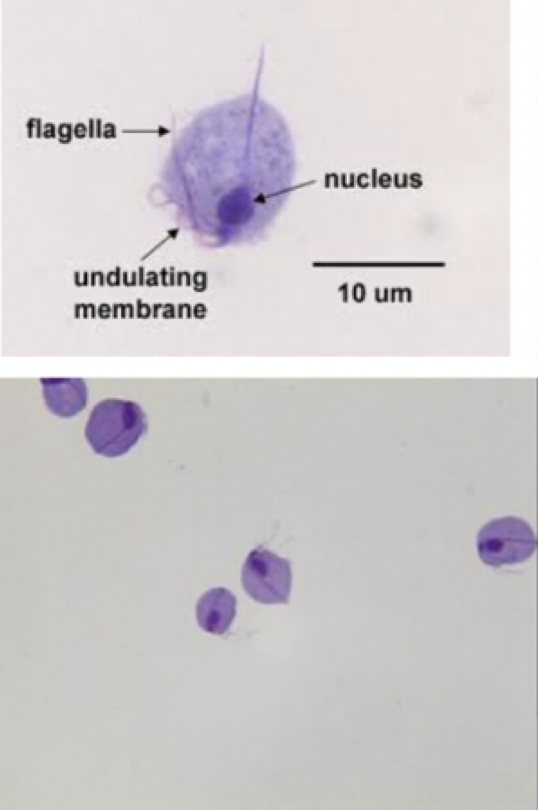
Trichomonas vaginalis
Motility: flagella
Mode of transmission: sexual intercourse
Infective stage: trophozoite
disease: Trichomoniasis
male: usually asynptomatic
female: vaginal discharge
parts to look for
pear shaped
undulating membrane
flagella
axostyle
Trichomonas vaginalis
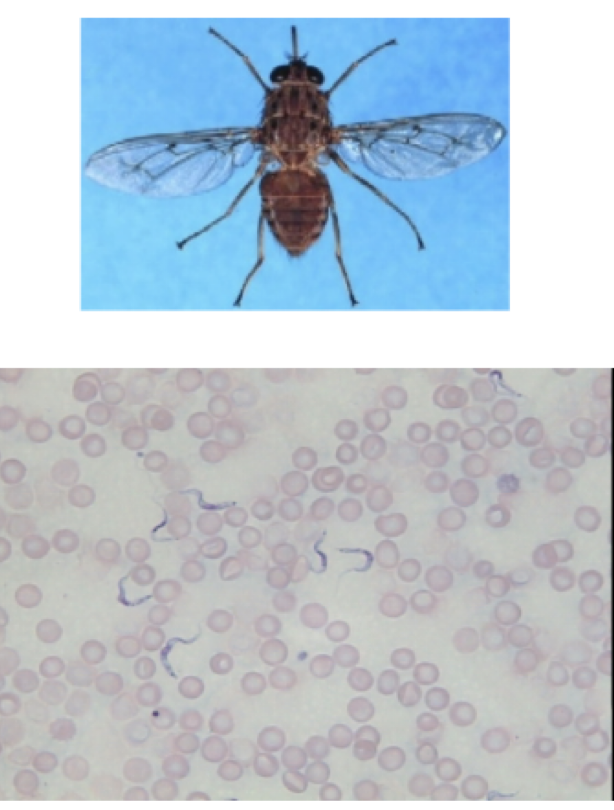
Trypanosoma brucei
motility: flagella
mode of transmission: bite from tsetse fly
infective stage: trypanomastigtoe
Host: Tsetse fly —> human
ideas; African Sleeping sickness
Trypanosoma brucei
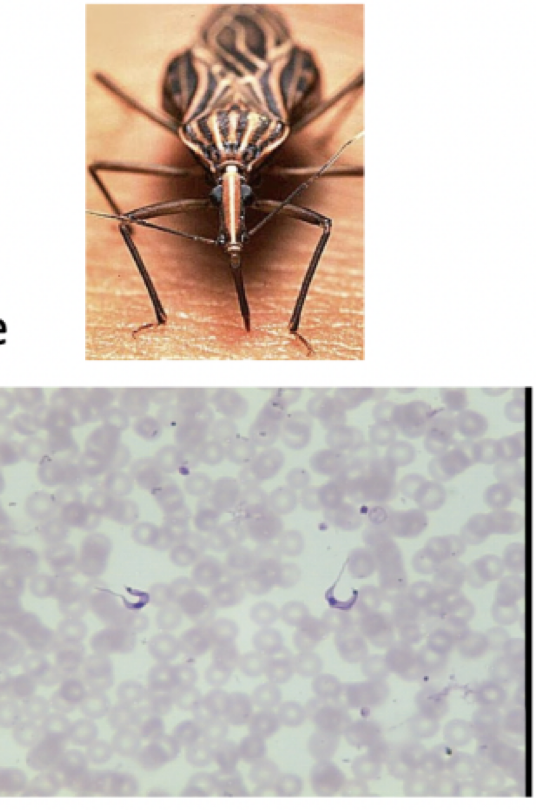
Trypanosoma cruzi
motility: flagella
mode of transmission: bite from kissing bug
infective stage: trypomastigote
Host: kissing bug —> human
Disease: Chaga’s disease
Trypanosoma cruzi
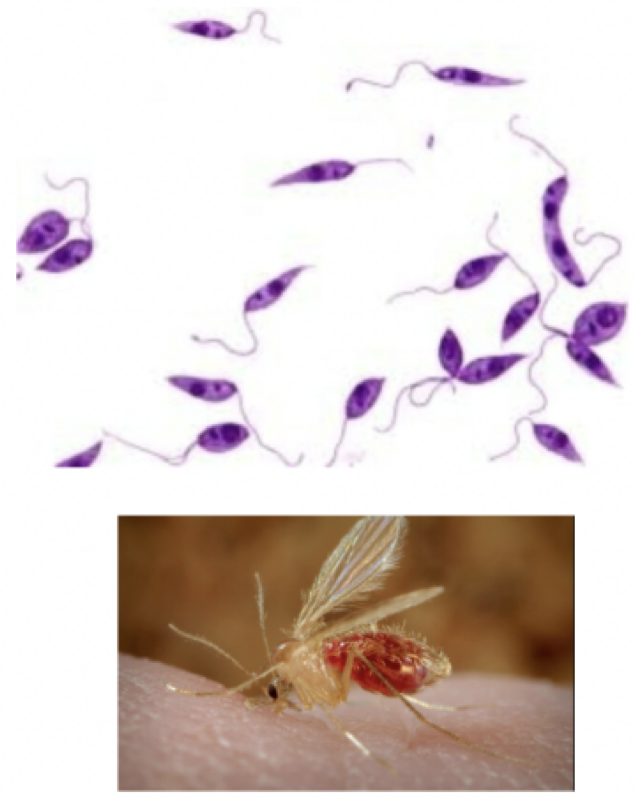
Leishmania donovani
motility: flagella
mode of transmission: bite from sand fly
infective stage: promastigote
Host: sand fly —> human
disease: Leishmaniasis
Leishmania donovani
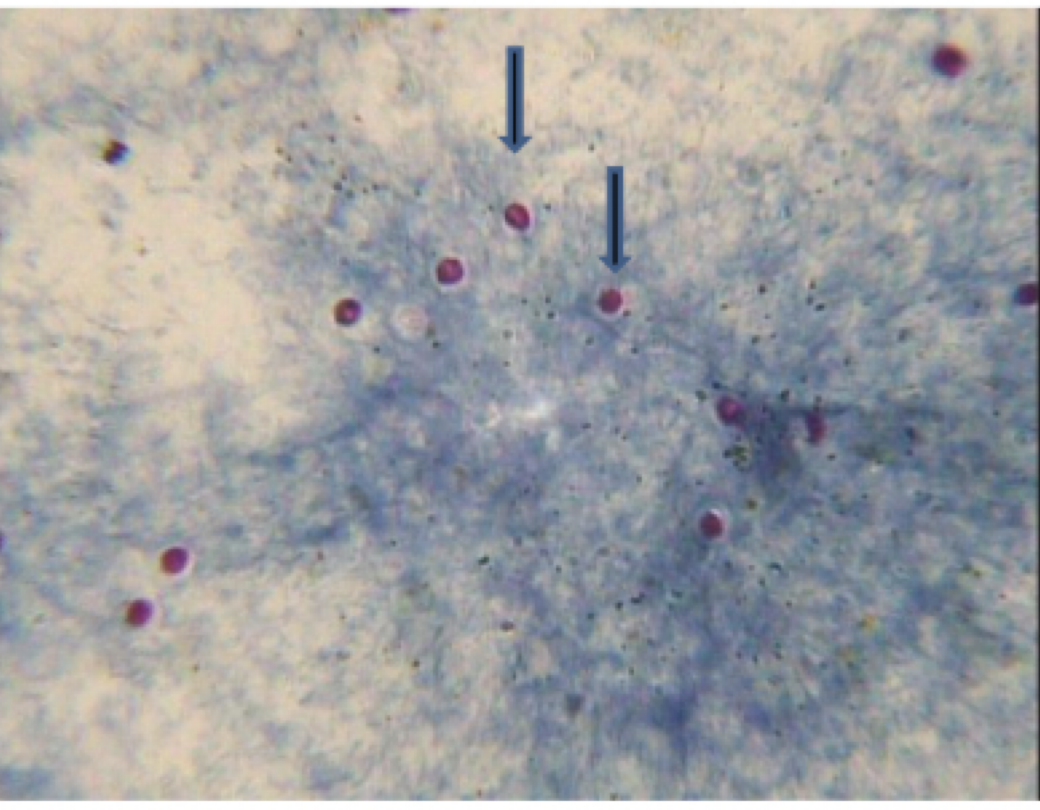
Cryptosporidium parvum
motility: none
mode of transmission: females oral, ingestion of oocyst
infective stage: oocyst
host: humans and other animals
disease: cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidium parvum
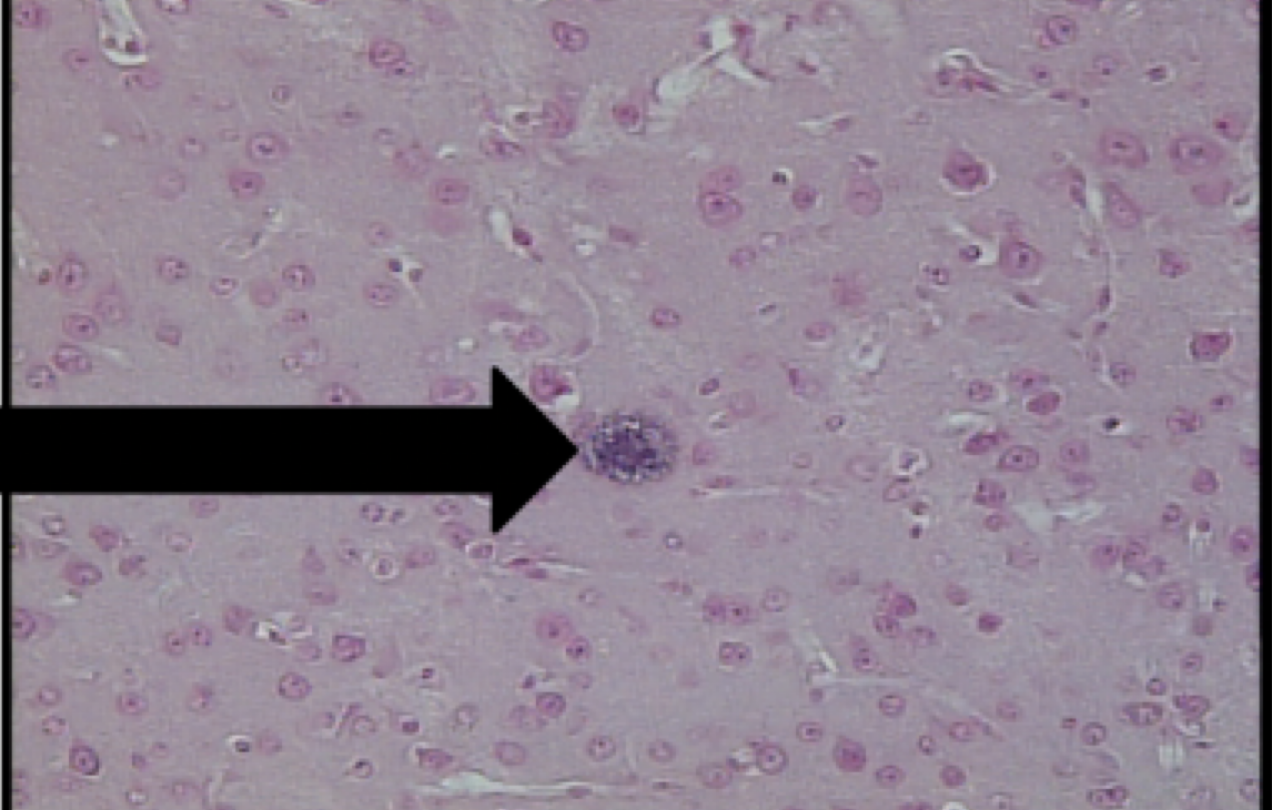
toxoplasma gondii
motility: none
mode of transmission: ingestion of oocyst
infective stage: oocyst
host: feline —> rodent, bird, human
disease: toxoplasmosis
toxoplasma gondii
plasmodium species
motility: none
mode of transmission: bite from female anopheles mosquito
infective stage: sporozoite
host: female anopheles mojito —> human
disease: malaria
plasmodium species
Specimen collection Principles
Use aseptic technique, sterile containers, and label everything properly
collect before starting antimicrobial therapy
adequate amount of material must be collected
blood cultures: require 6-8 samples
sputum samples: 2 per day for 3 days
transport media
keeps bacteria alive until it can be cultured in the lab
prevents normal flora from overgrowing the pathogen
prevents the specimen form drying out
ex: vials for tissue samples and scrapings, stool, and urine samples
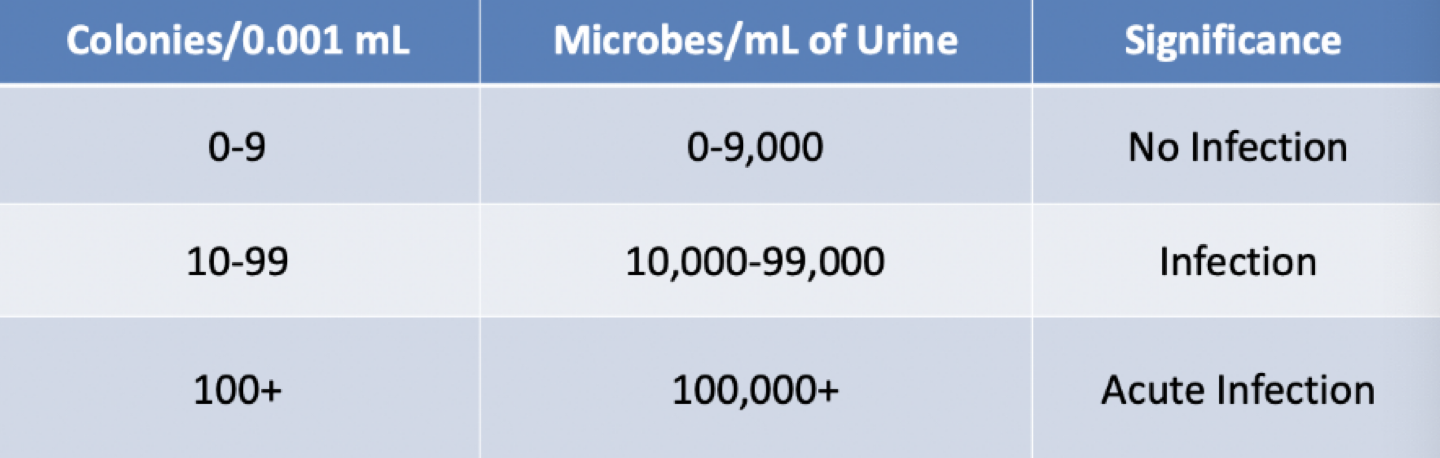
urine culture colony counts
when performing a urine colony count both the number (quantitative) of cells and the type (qualitative) of bacteria growing is important
Clean catch and Midstream method
the correct way to perform a urinalysis
1) use a sterile container, clean outer urethral orifice, catch urine midstream
2) Urinalysis- Qualitative and Quantitative
determine the identify of the bacterial infection
Qualitative urinalysis
most UTI’s are caused by E. coli
specialized media can be used to culture urine
MacConkey’s Agar: pink/ purple color
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar: metallic green
Chromagar: varies
CLED: highlighter green
Quantitative urinalysis
use a calibrated loop (0.001mL)
streak plate an dincubate
count colonies
determine number of microbes per mL
1,000 (dilution factor) x number of colonies = microbes/mL
determine clinical significance
ex: 40 colonies x 1000 = 40,000 microbes/ mL of urine
Quantitative Urinalysis Chart
Throat culture
1) swab throat (tongue depressor to only get desired region)
2) process swab
direct culture: sample is placed on growth media (small private practice)
transport media: swab is taken form patient to lab (big hospital)
3) streak on blood agar
positive result= beta hemolysis caused by streptococcus pyogenes
Enterotube II
multitest media system that identifies Gram Negative rods int he family Enterobacteriaceae
12 compartments that perform 15 biochemical tests
oxidase test used to differentiate organisms in the family Enterobacteriaceae (Oxidase Negative- from Pseudomonadaceae (Oxidase Positive)
Round worms
cylindrical, non-segmented worms
sex organs on separate worms
no hooks or suckers to attach to host
inhabit the intestinal tract, blood, organs, tissues
flat worms
flat body shape
may be hermaphrodites
have hooks/ suckers to attach to host
inhabit intestinal tract, blood, organ tissues
Ascaris lumbricoides
Mode of transmission: ingestions of ova/ egg
infective stage: egg
host: human
Disease: Ascaris or Ascariasis
Ascaris lumbricoides
Enterobius vermicularis
Mode of transmission: ingestions of ova/ egg
infective stage: egg
host: human
Disease: Pinworm
Enterobius vermicularis
Trichuris trichiura
Mode of transmission: ingestions of ova/ egg
infective stage: egg
host: human
Disease: Whipworm
Trichuris trichiura
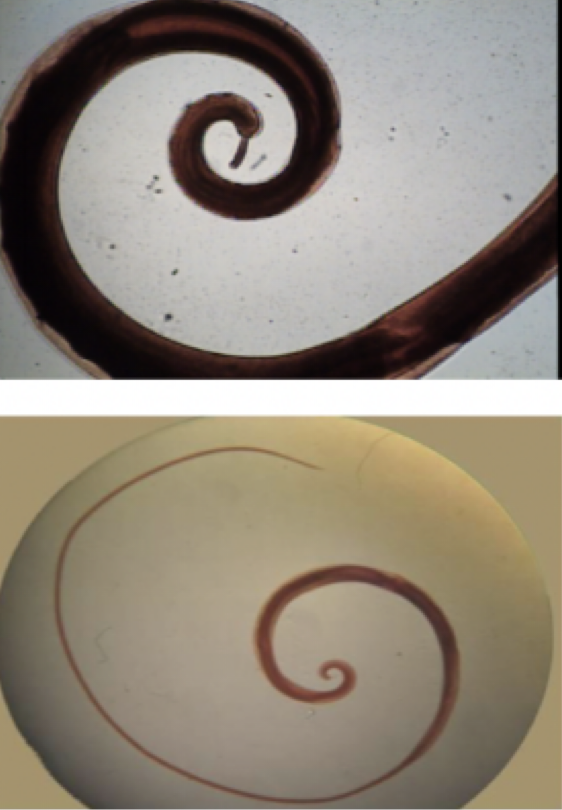

Necator americanus
Mode of transmission: larvae penetrate skin
infective stage: larvae
host: human
Disease: hookworm
Necator americanus
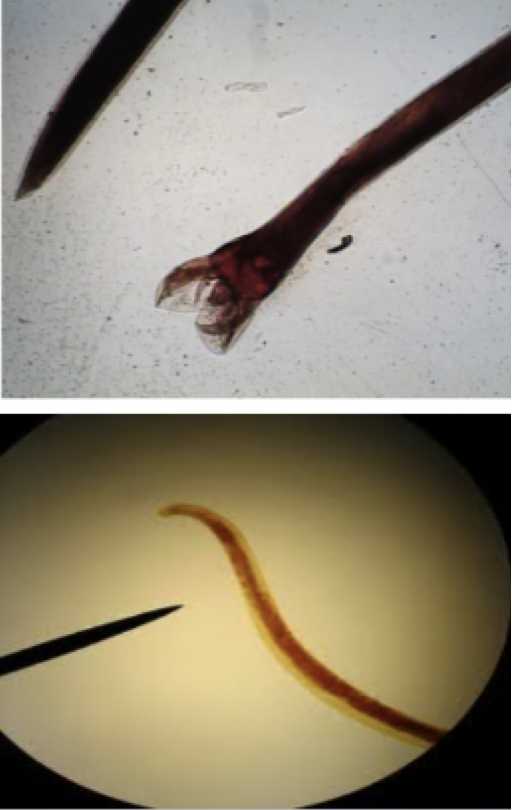

Anisakis simplex
Mode of transmission: eat uncooked infected fish
infective stage: larvae
host: marine mammal —> human, fish, squid
Disease: Anisakiasis
Anisakis simplex
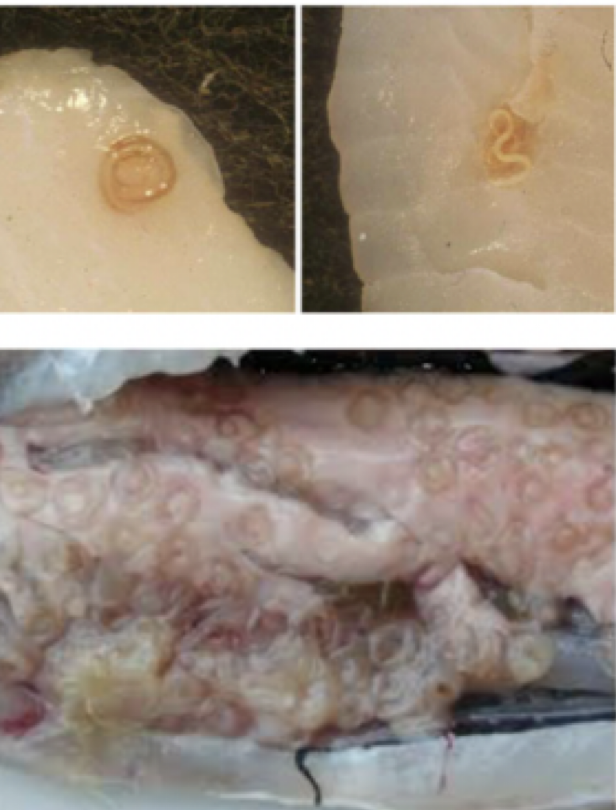
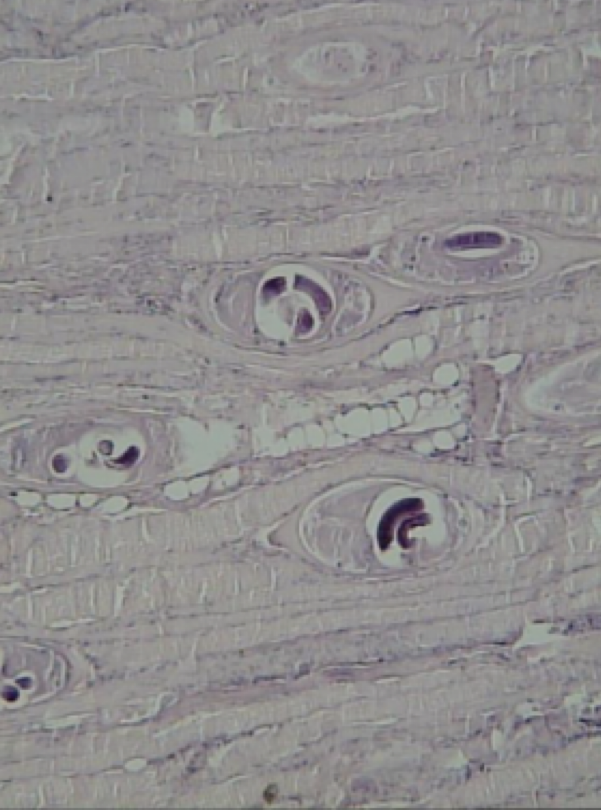
Trichinella spiralis
Mode of transmission: eat pork with encysted larvae
infective stage: encysted larvae
host: pig —> human
Disease: trichinosis
Trichinella spiralis
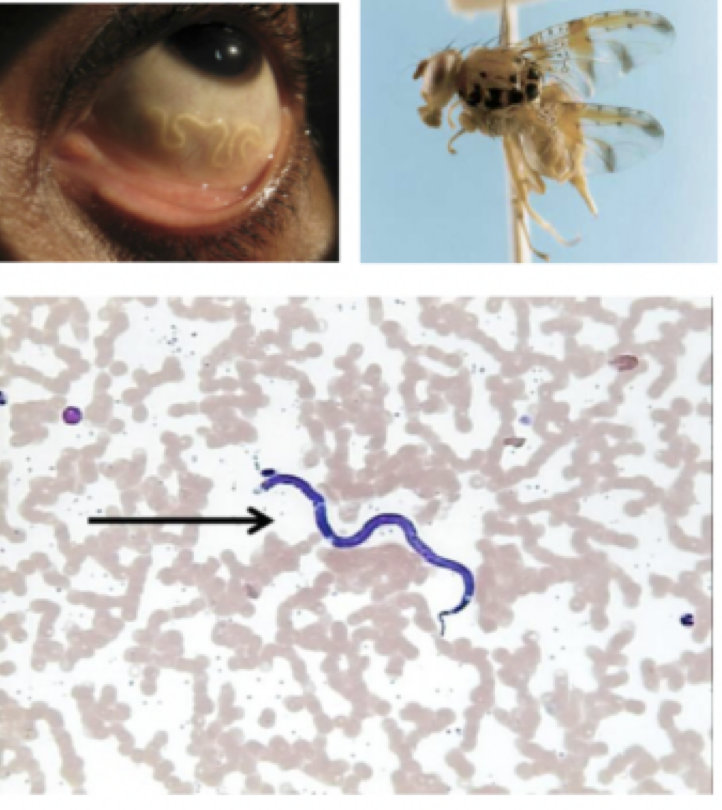
Loa loa
Mode of transmission: bite from mango fly
infective stage: microfilariae
host: mango fly —> human
vector: mango fly
Disease: African Eye worm
loa loa
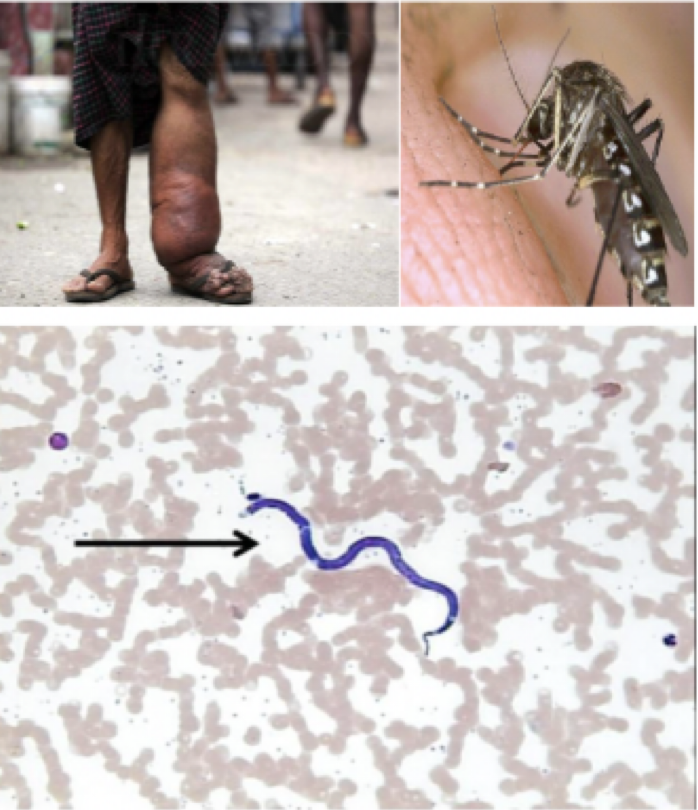
Wuchereria bancrofti
Mode of transmission: mosquito bite
infective stage: microfilariae
host: mosquito —> human
Vector: Mosquito
Disease: Elephantiasis
Wuchereria bancrofti
Onchocerca volvulus
Mode of transmission: bite form black fly
infective stage: microfilariae
host: black fly —> human
vector: black fly
Disease: river blindness
Onchocerca volvulus
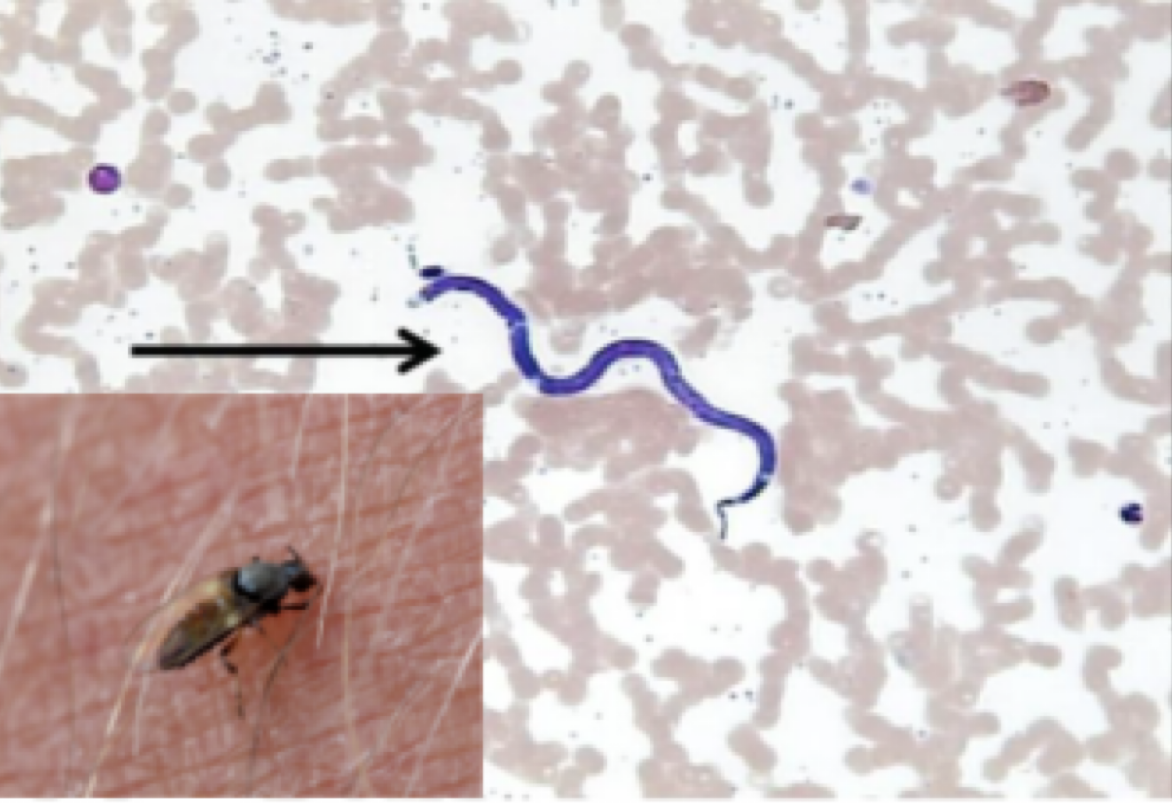
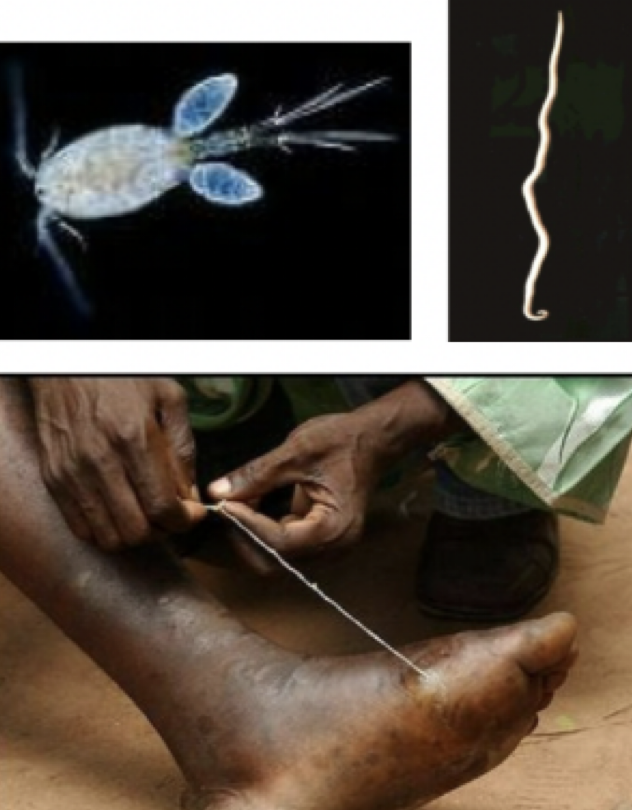
Dracunculus medinensis
Mode of transmission: drinking water with cyclops
infective stage: larvae (inside the cyclops)
host: cyclops —> human
vector: cyclops
Disease: guinea worm
Dracunculus medinensis