Unemployment
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
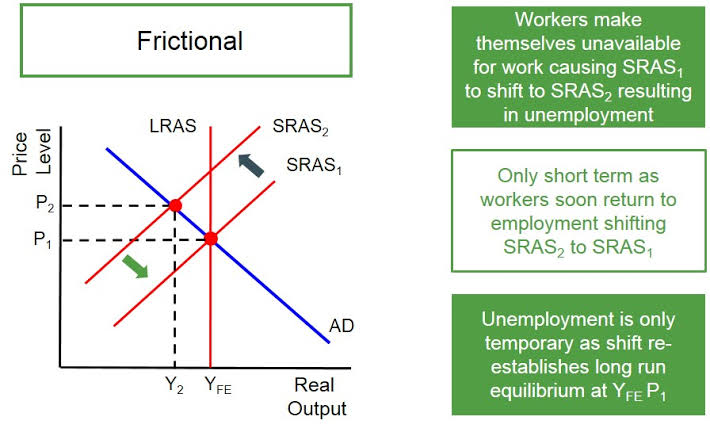
Frictional unemployment
Short-term unemployment that occurs when people are between jobs or entering the labor market for the first time.
Frictional unemployment diagram
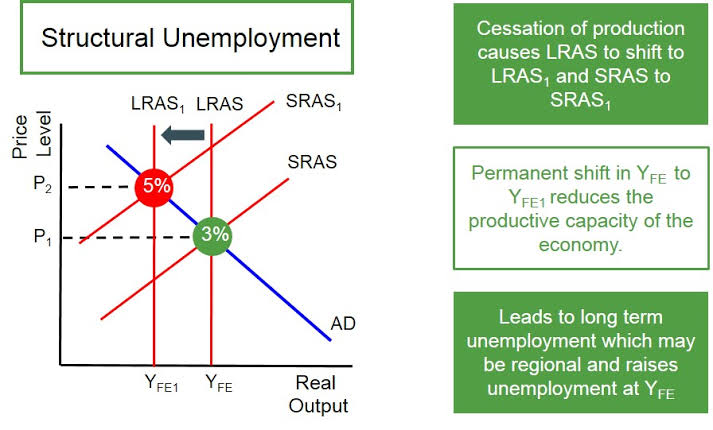
Structural unemployment
Unemployment caused by changes in the economy that reduce demand for certain skills, making some jobs obsolete. Happens when there is a miss-match between worker skills and available jobs. Some of the causes may be technological advancements, change in preference or mobility of jobs
Structural unemployment diagram
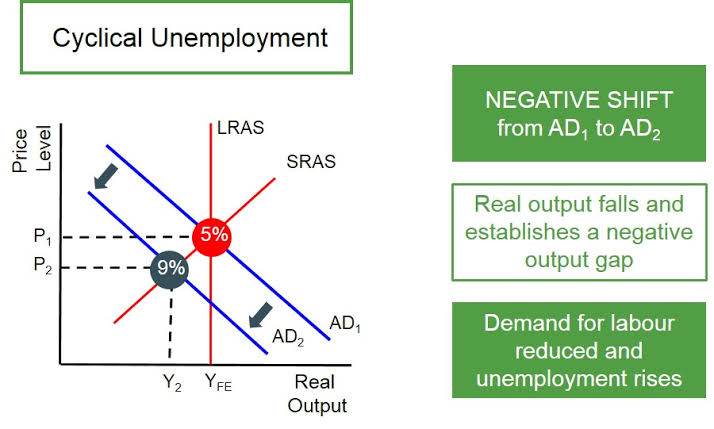
Cyclical unemployment
Unemployment resulting from a lack of aggregate demand during periods of economic downturn or recession.
Cyclical unemployment diagram
Diagram
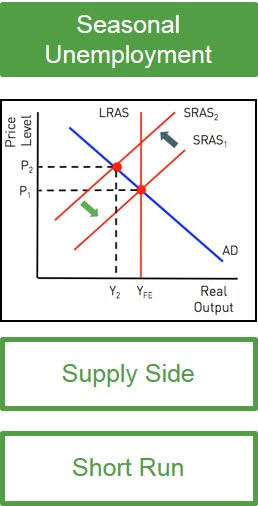
Seasonal unemployment
Unemployment due to regular and predictable seasonal changes in labor demand.
Seasonal unemployment
Diagram
Hidden unemployment
Unemployment not reflected in official statistics, including discouraged workers and underemployed individuals.
Technological unemployment:
Unemployment caused by technological advancements that replace human labor with machines or automation.
Regional unemployment
Unemployment that occurs in specific geographic areas due to regional economic decline or lack of investment.
Real-wage (classical) unemployment:
Unemployment that occurs when wages are kept above the market equilibrium, leading to excess supply of labor.