NSCI 2101 Exam 2
1/260
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
261 Terms
parts of the diencephalon
epithalamus
thalamus
subthalamus
hypothalamus
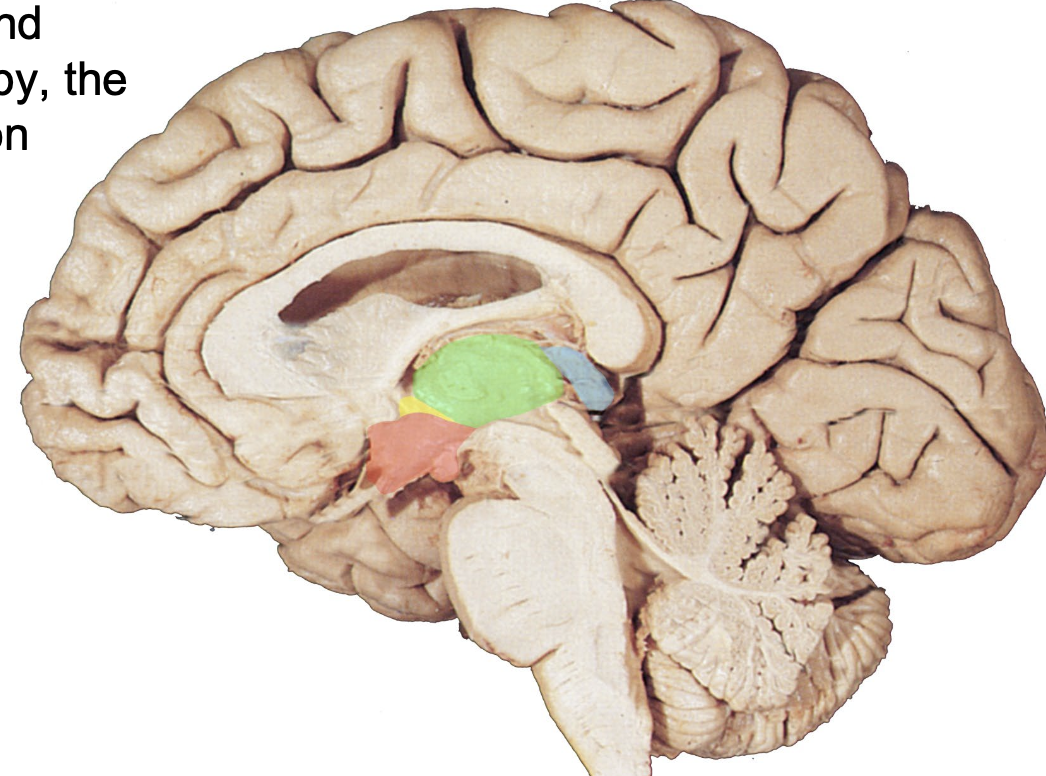
where is the epithalamus?
highlighted in blue
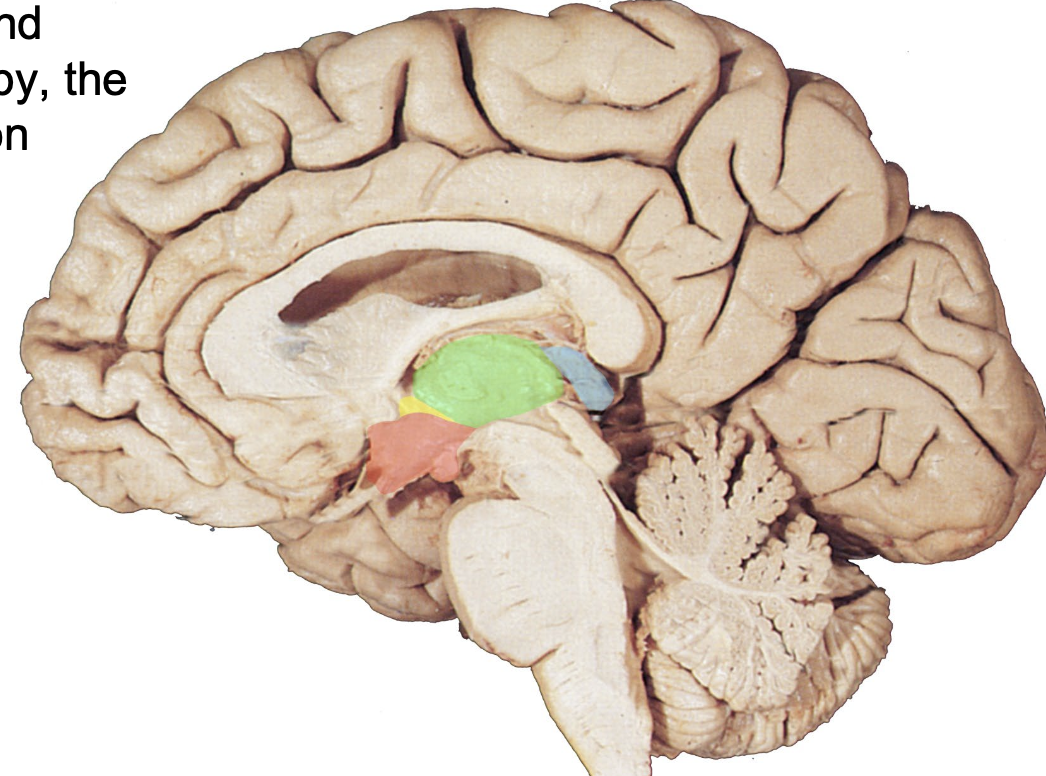
where is the thalamus
highlighted in green
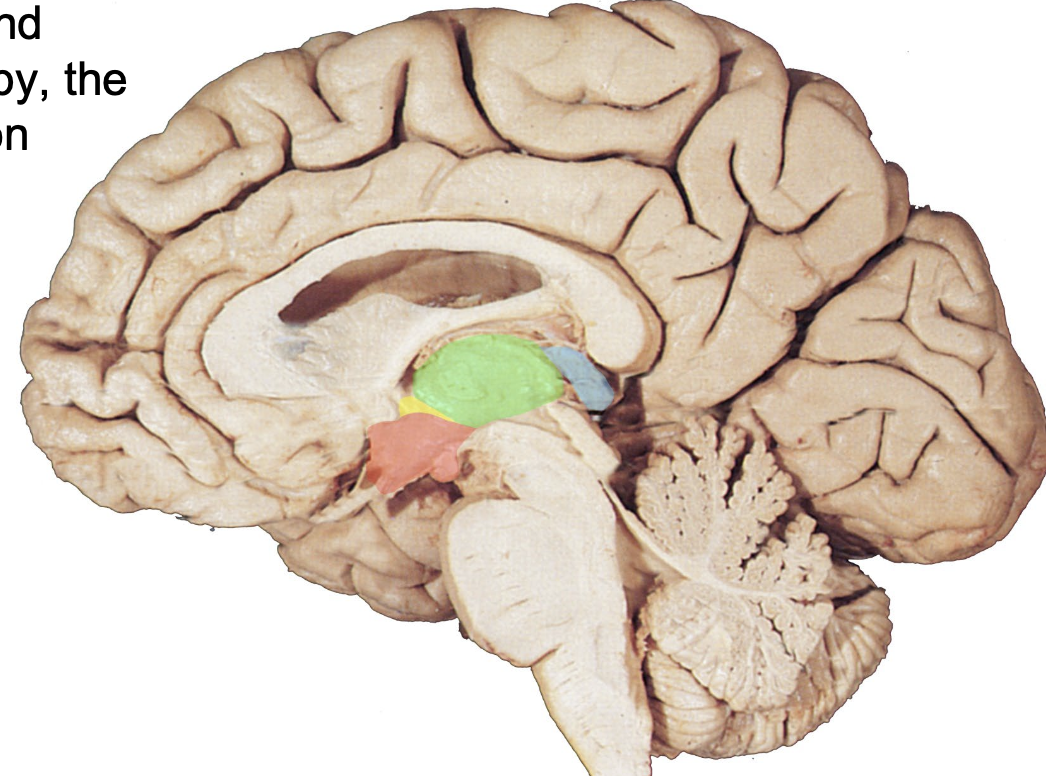
where is the subthalamus?
highlighted in yellow
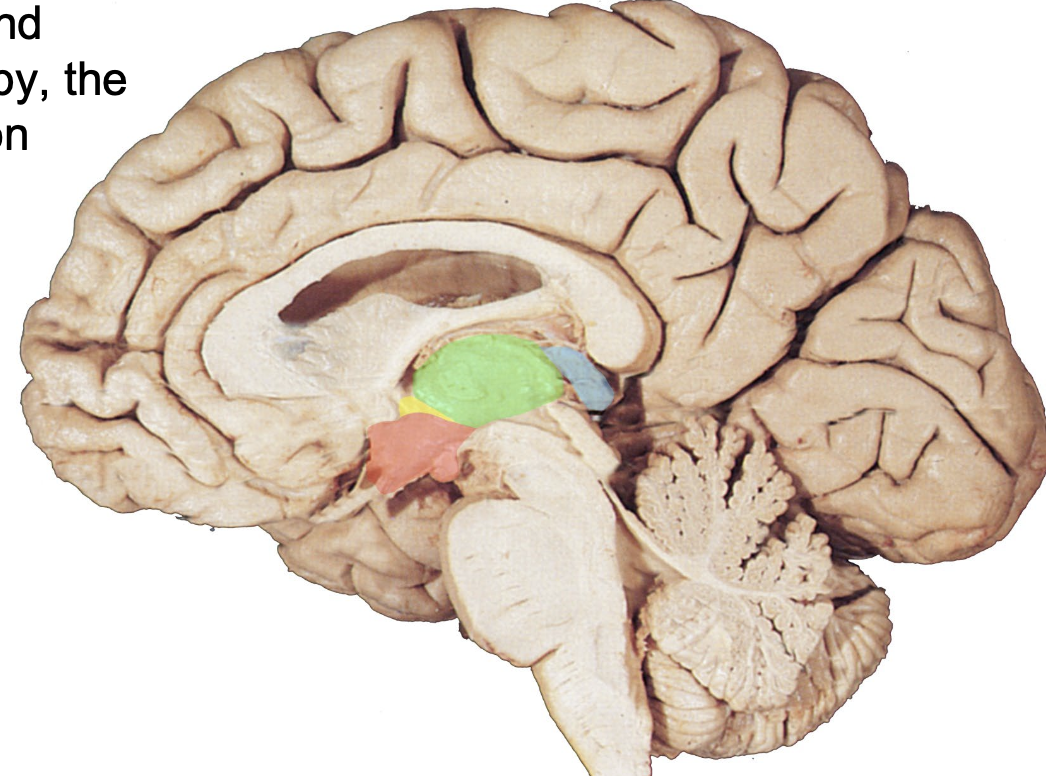
where is the hypothalamus?
highlighted in red
functions of the hypothalamus (5)
temp regulation
feeding and drinking
circadian rhythms
aggression and flight
sexual activity
hypothalamic neurons
release hormones into the blood that act on the pituitary gland
pituitary gland
neuroendocrine function. attached to hypothalamus by pituitary stalk.
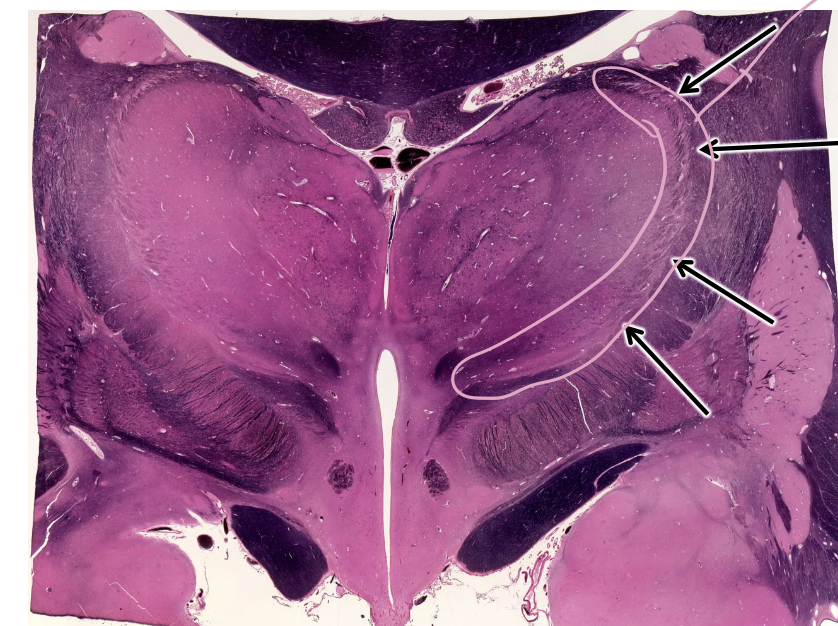
what is this structure outlined in pink?
reticular nucleus of thalamus
thalamus
every sensory input (expect smell) is relayed to the thalamus
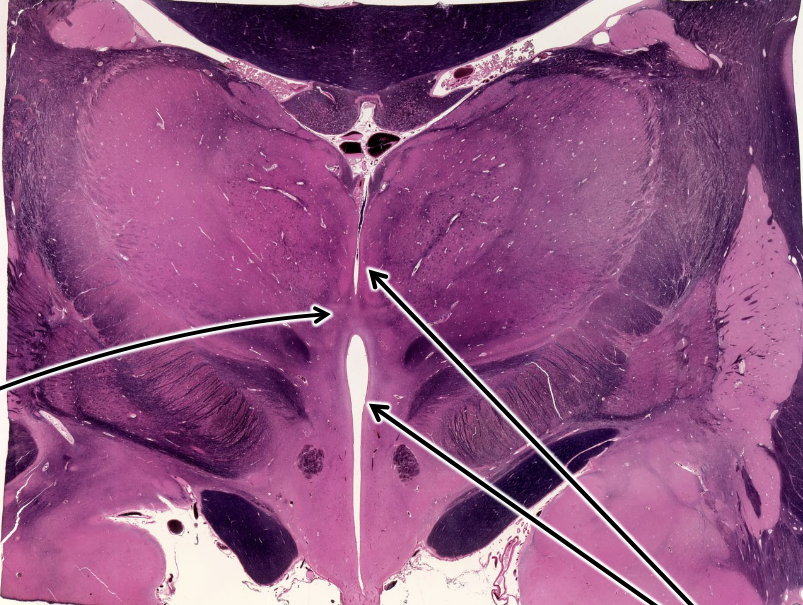
what is this whole structure?
thalamus.
myelin=black
neurons=pink
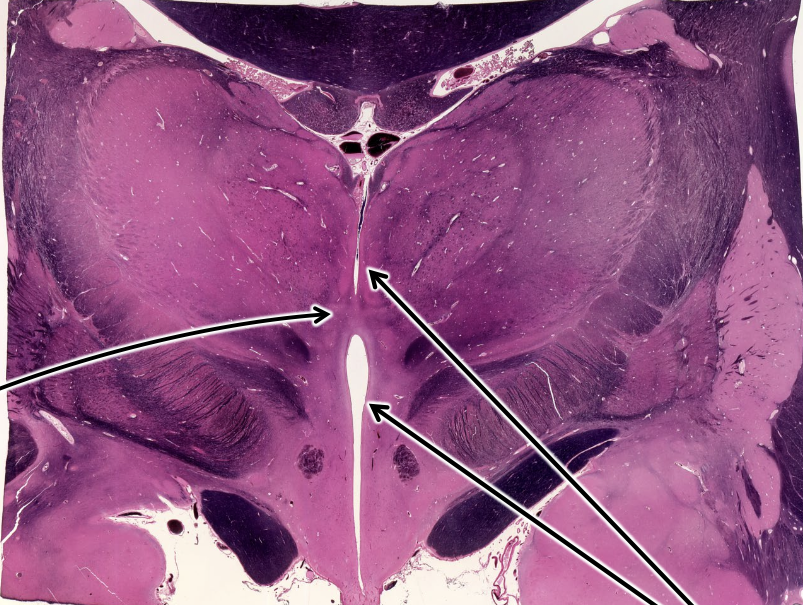
what are the right two arrows pointing at?
3rd ventricle— separates the 2 halves of the thalamus
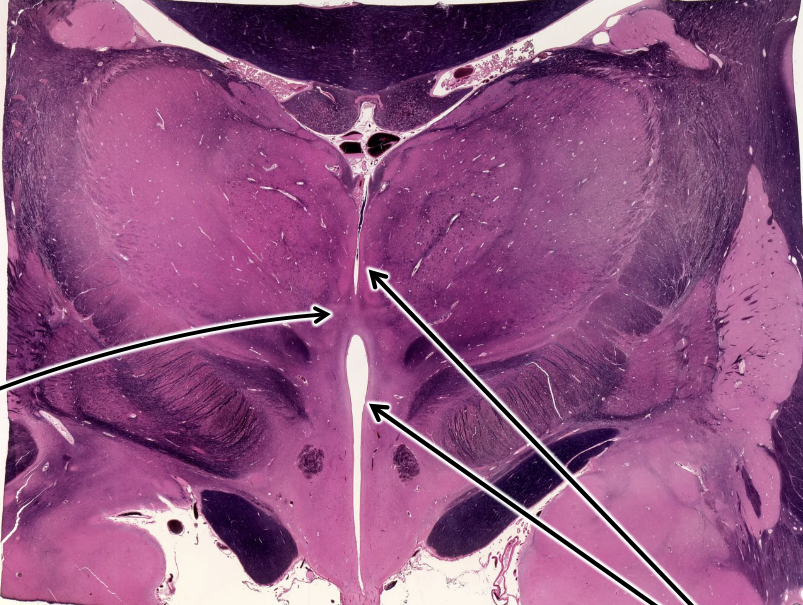
what is the left arrow pointing at?
(inter)thalamic adhesion
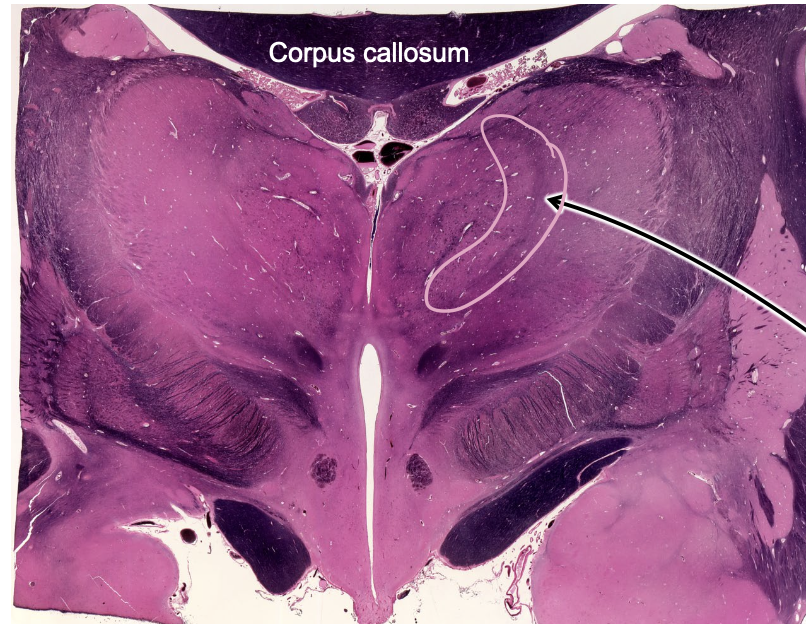
what is the structure outline in pink?
internal medullary lamina
internal medullary lamina
sheets of myelinated axons that divide thalamic relay nucleus into three regions
specific thalamic nuclei
relay specific sensory/motor info to specific regions of the cortex
eg visual thalamus projects to visual cortex
association thalamic nuclei
responds to more than one sensory input and relays info from association thalamus to association cortex
sends axons to rest of cerebral cortex aka associated cortex
non-specific thalamic nuclei
sends axons anywhere, beyond cortex, and responds to more than one sensory input
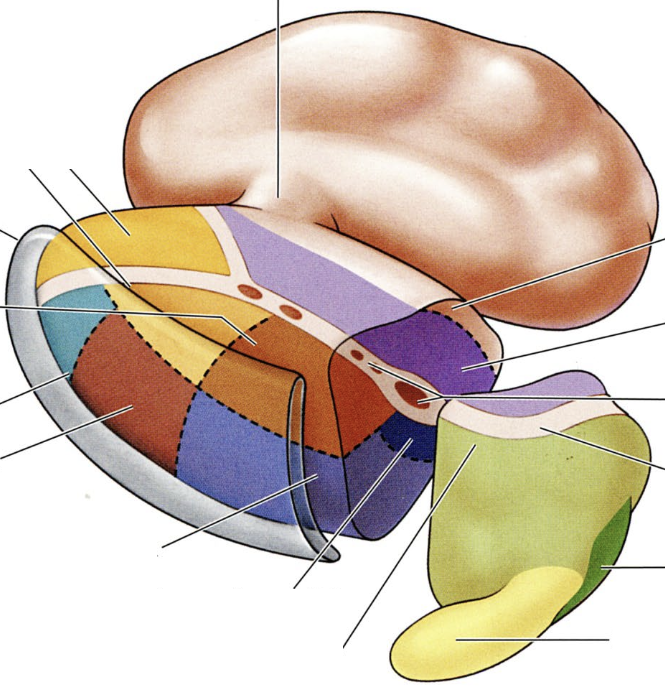
what do the colored regions represent?
specifc thalamic nuclei
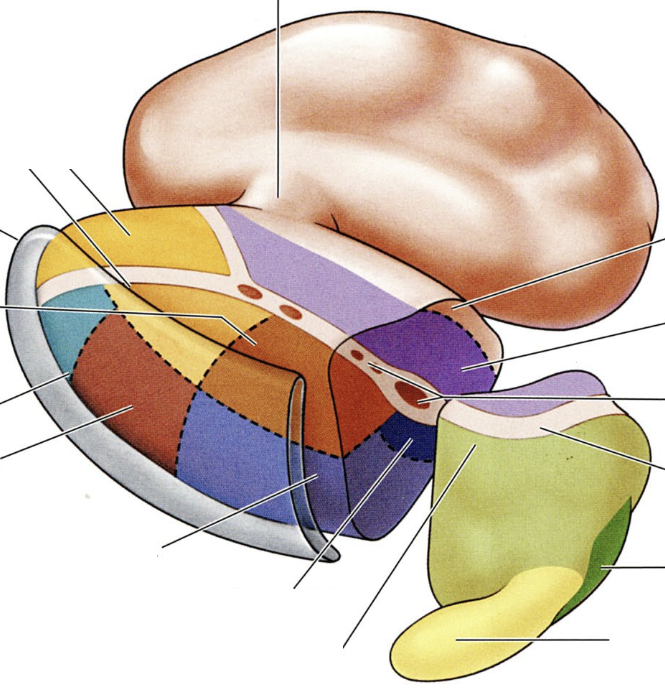
what is the dark green region?
medial geniculate nucleus, relays HEARING input
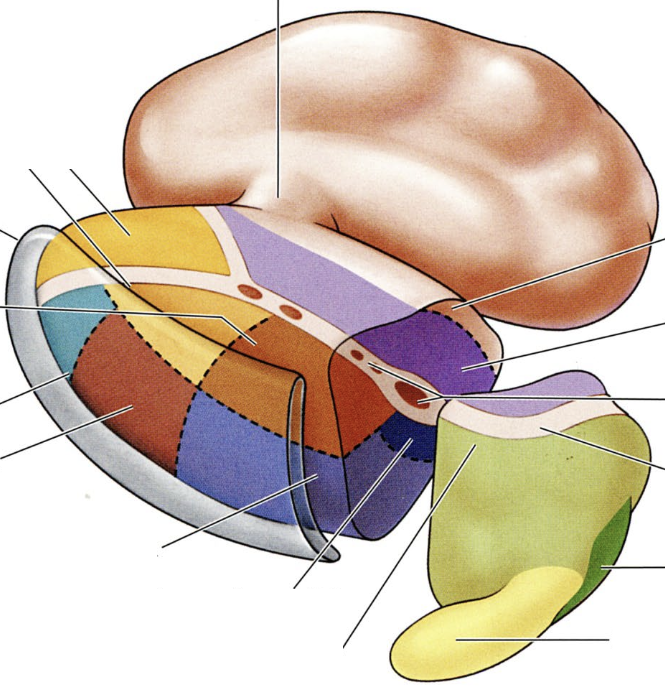
what is the red region?
ventral lateral nucleus, relays MOTOR input
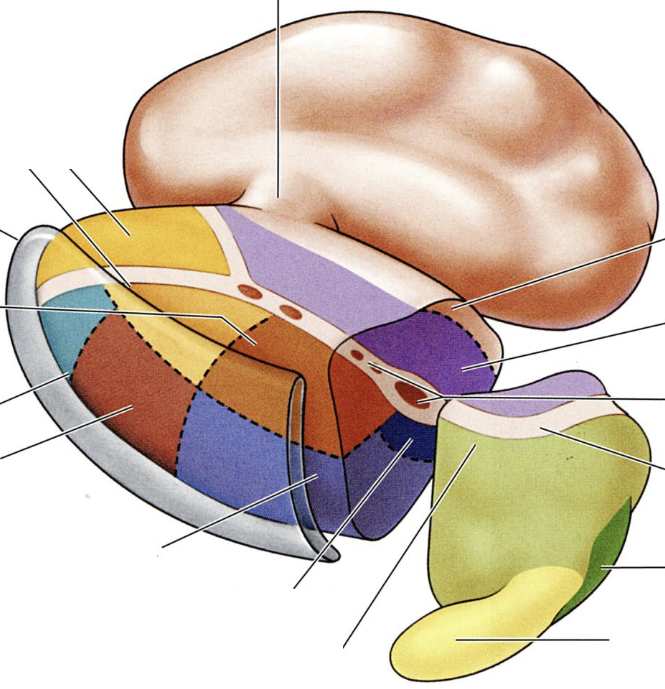
what is the teal region?
ventral anterior nucleus, relays MOTOR input
what are the dark purple regions?
ventral posterior lateral and ventral posterior medial nuclei, relays TOUCH and PAIN
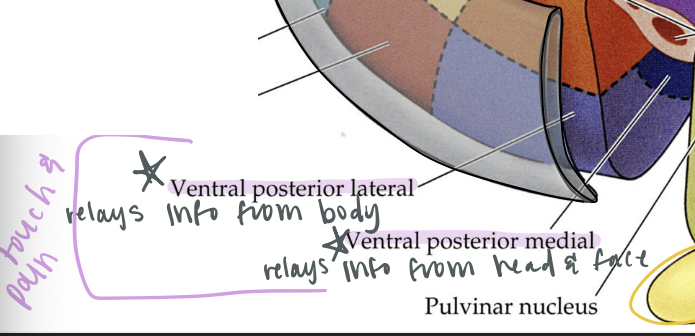
ventral posterior lateral nucleus
relays touch and pain info from body
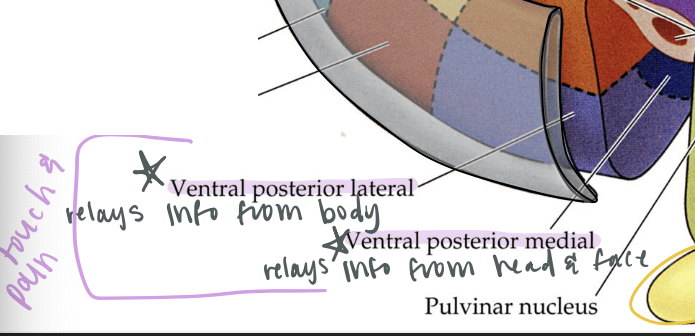
ventral posterior medial nucleus
relays touch and pain info from the head and face
relay nuclei
specific and association nuclei. project axons to cortical regions serving the same functions as their respective thalamic regions
eg visual thalamus → visual cortex
eg motor thalamus → motor cortex
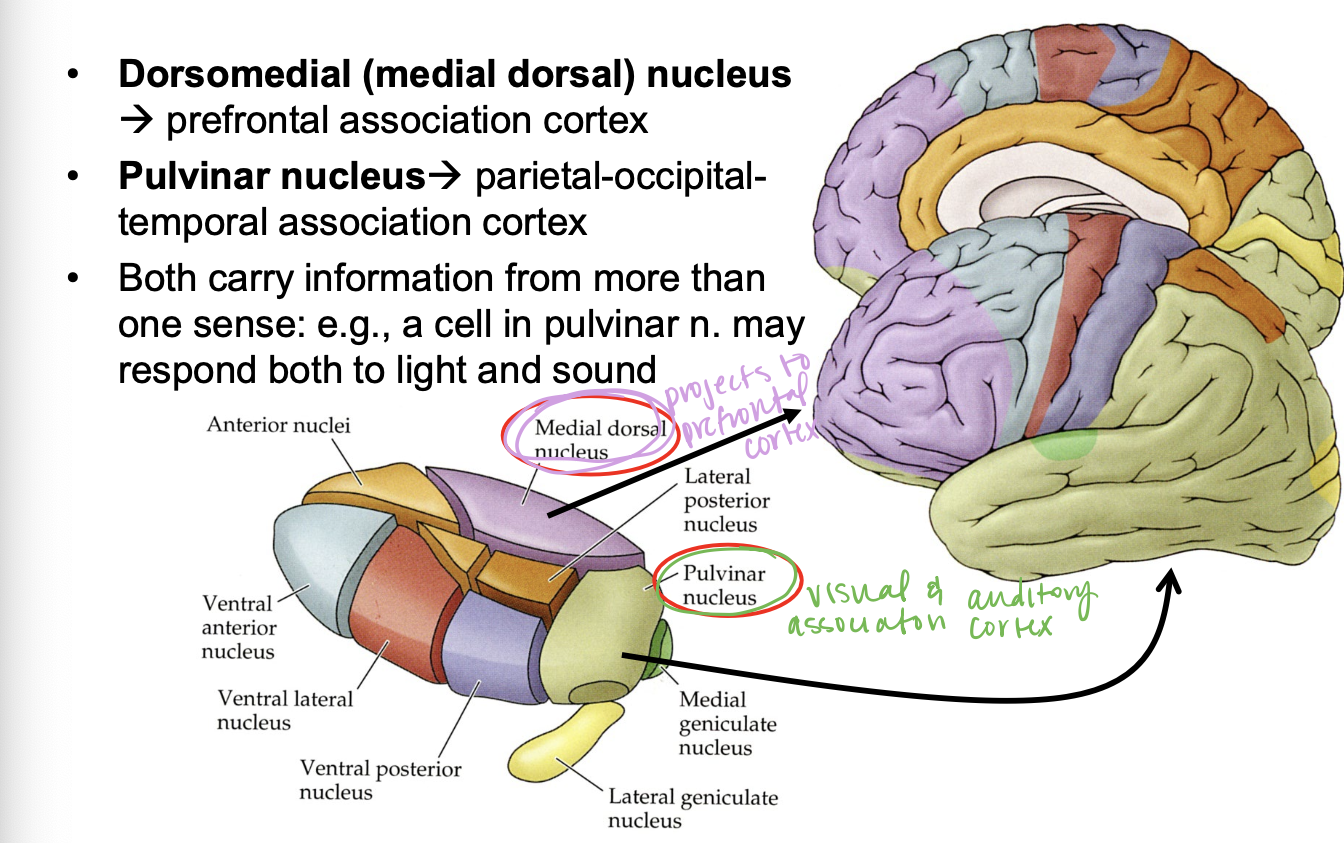
where does the dorsomedial nucleus project?
prefrontal association cortex
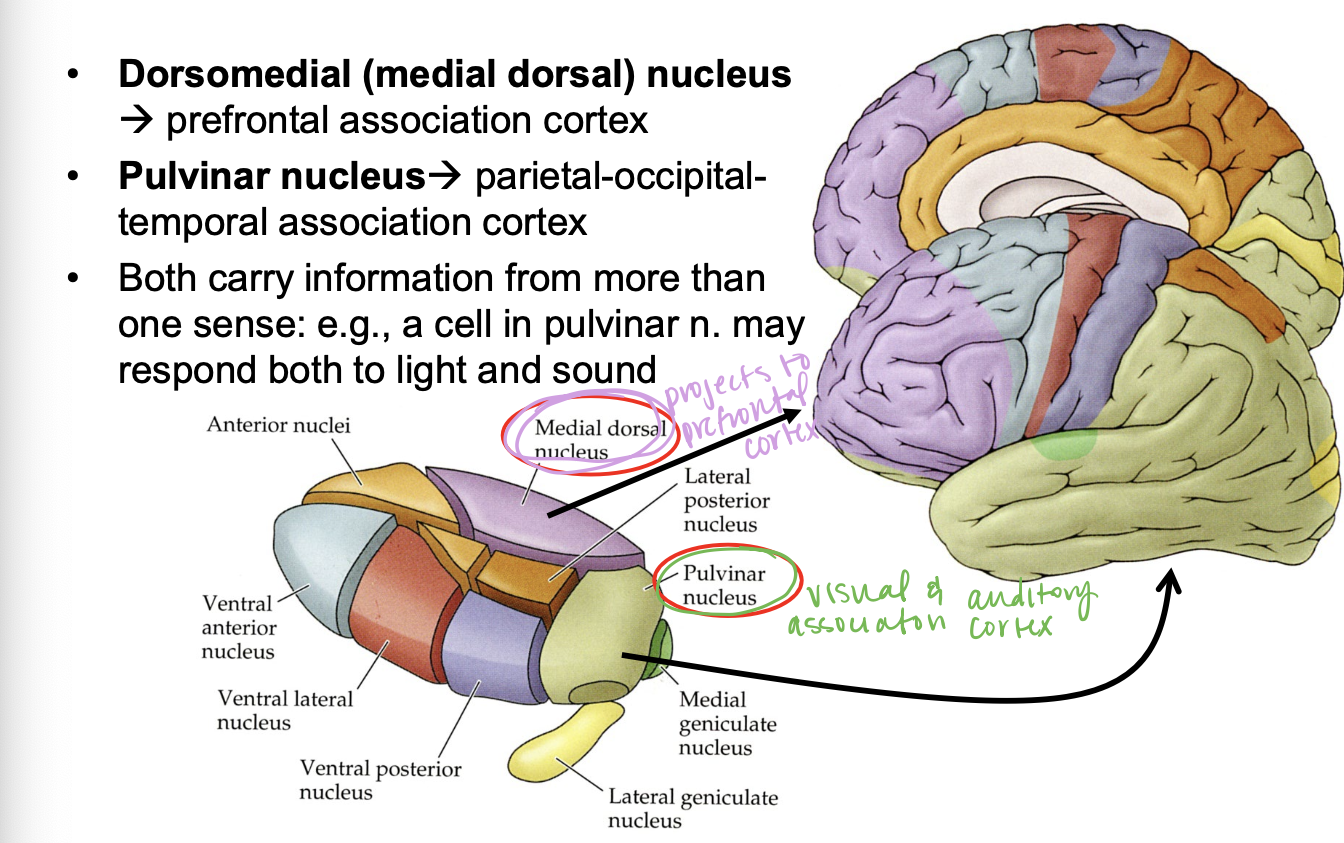
where does the pulvinar nucleus project?
visual and auditory association cortex
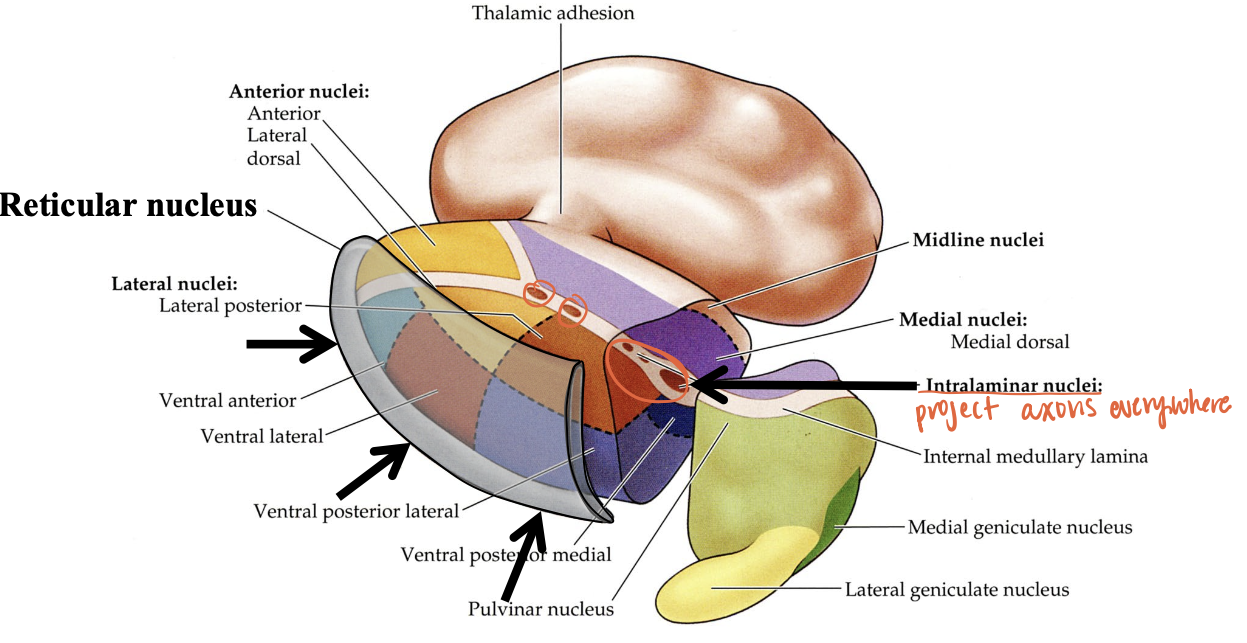
where are non-specific nuclei?
reticular nucleus and intralaminar nuclei of thalamus
input from hypothalmus/hippocampus goes to…
anterior nucleus → cingulate (limbic)cortex
input from cerebellum goes to…
ventral lateral nucleus → motor cortex
somatosensory/visceral sensory goes to…
ventral posterior (lateral & medial) → somatosensory cortex and visceral cortex
input from retina goes to…
lateral geniculate nucleus → visual cortex
input from the inferior colliculus goes to…
medial geniculate nucleus → auditory cortex
input from the cortex and other areas goes to…
other nuclei → association cortex
thalamic reticular nucleus
inhibits output of other thalamic nuclei in the cerebral cortexi
reduces info flow when it is not needed eg sleep, concentration
internal capsule
carries axons in and out of the cortex
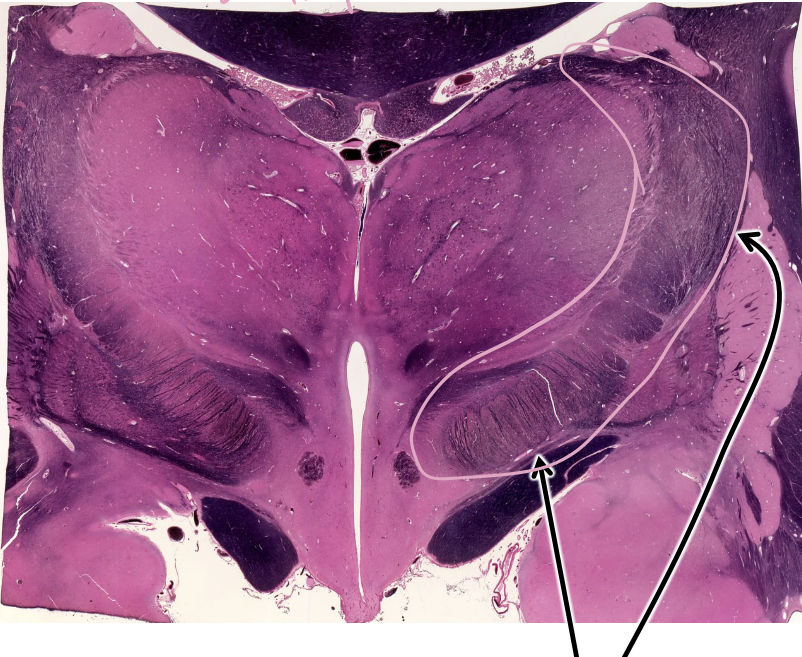
what is this region?
internal capsule
telencephalon
two hemispheres with three interrelated parts
neocortex (most of cerebral cortex)
limbic and olfactory cortex
basal ganglia
neocortex
most of the cerebral cortex, has 6 cell layers
layer IV (4)
layer of the neocortex that the thalamus projects to
projects to layers II & III
layers II & III
layers of the neocortex that interconnect with other cortical areas
layer V (5)
layer of the neocortex that projects to the brainstem and spinal cord
layer VI (6)
layer of the neocortex that projects back to the thalamus
primary sensory cortex
cortex that is innervated by specific thalamic relay nuclei for the same sense
eg lateral geniculate nucleus → primary visual cortex
primary motor cortex
cortex that innervates spinal cord or brain stem and controls motorneurons
eg corticospinal tract
association cortex
involved in the integration of sensory input where decisions have to be made about appropriate responses
cerebral commissures
discrete bundles of axons that cross the midline
region of cortex on one side of the brain communicates with the same region on the other side
what are the two main commissures of the cerebral cortex?
corpus callosum
anterior commissure (“corpus callosum” of olfactory system)
allocortex
parts of the limbic system and olfactory systems that are not in the neocortex
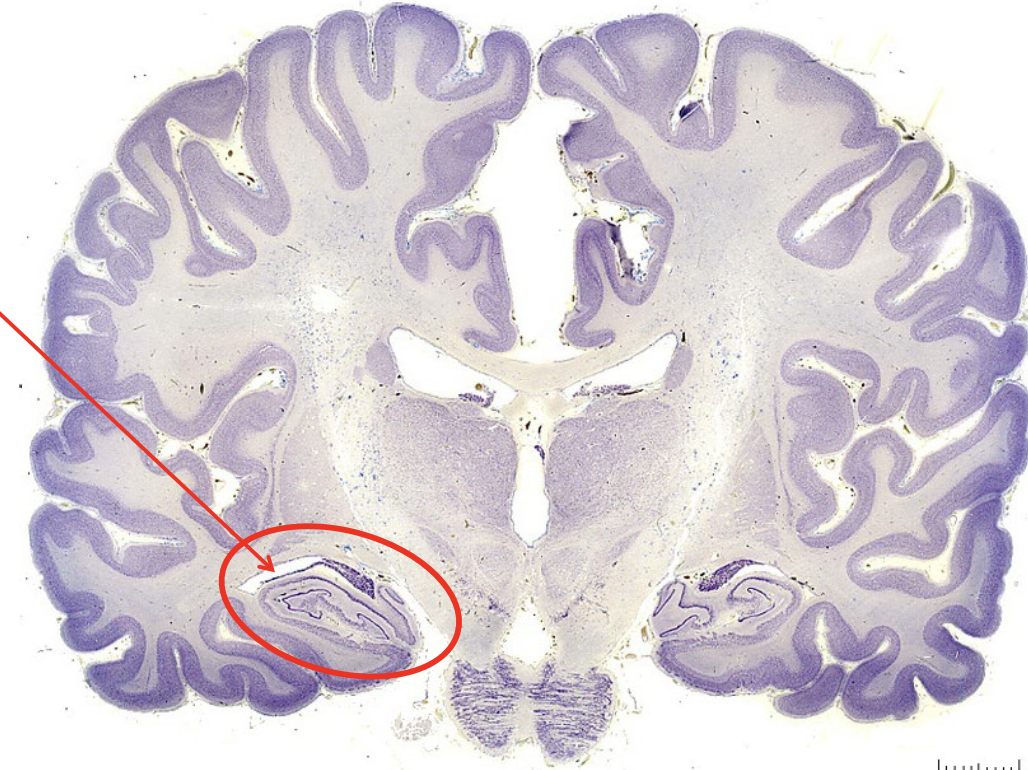
what is the structure circles in red?
hippocampus
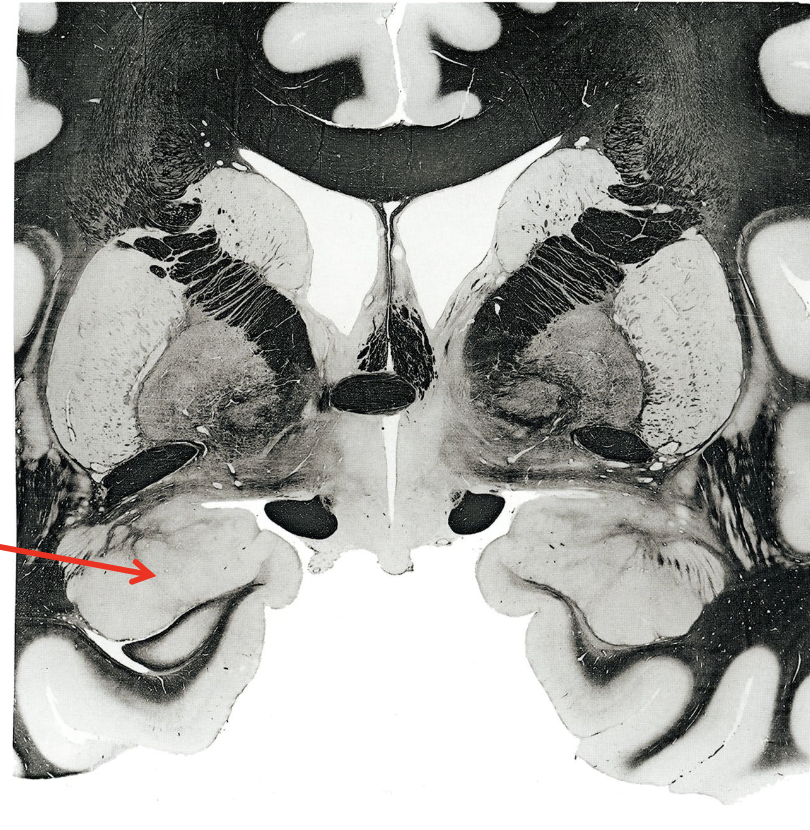
what is the arrow pointing to?
amygdala (responsible for fear responses)
limbic system
regulates emotions and behaviors, processes memories, controls thoughts and motivations
hippocampus
amygdala
fornix
tract of the limbic system that travels from hippocampus to mammillary bodies of hypothalamus
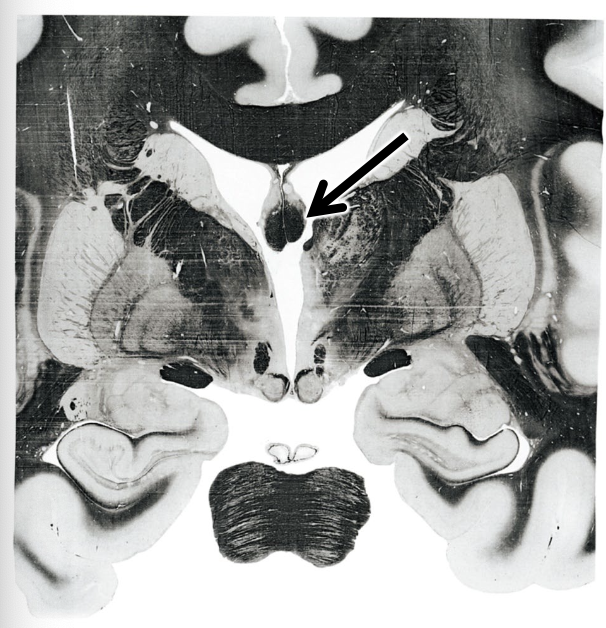
what is this arrow pointing to?
fornix
basal ganglia
group of nuclei that plays important roles in motor system and motivation (including drug abuse)
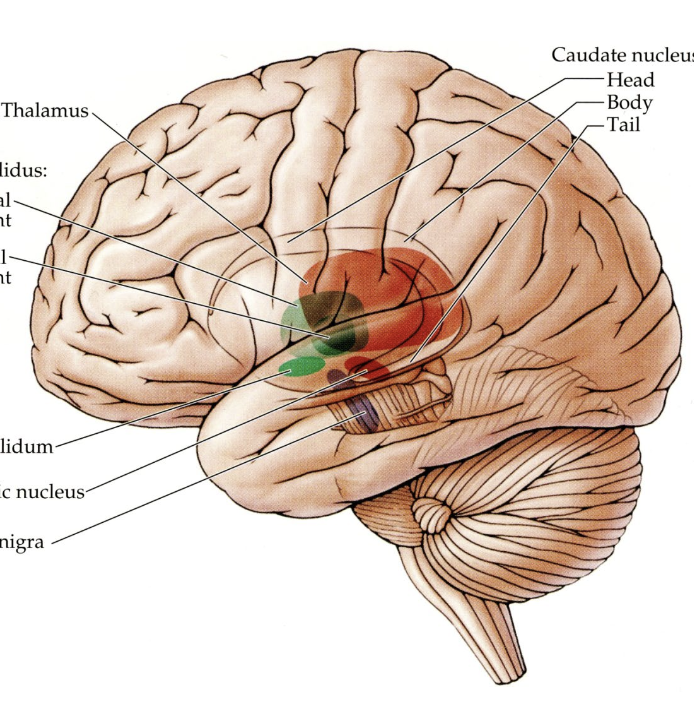
what doe the highlighted regions represent?
nuclei of the basal ganglia
all located in the midbrain, diencephalon, and basal region of telencephalon
major nuclei of the basal ganglia
striatum
globus pallidus
subthalamic nucleus
substantial nigra
striatum
in telencephalon. has three subnuclei:
caudate nucleus
putamen
nucleus accumbens
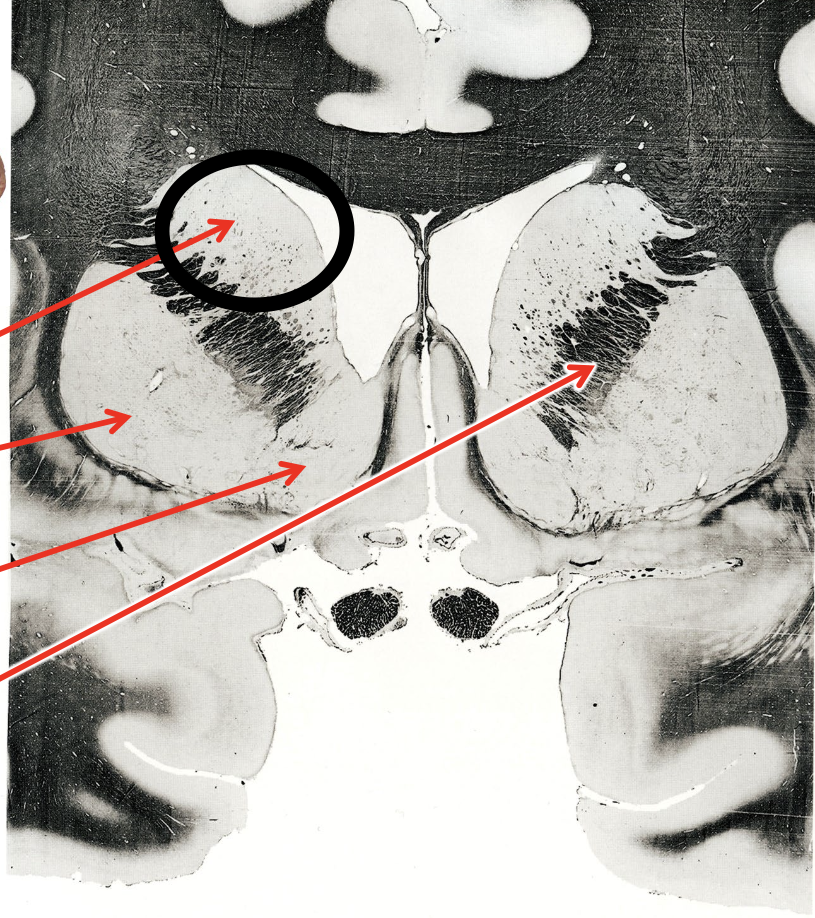
what is the circled region?
caudate nucleus
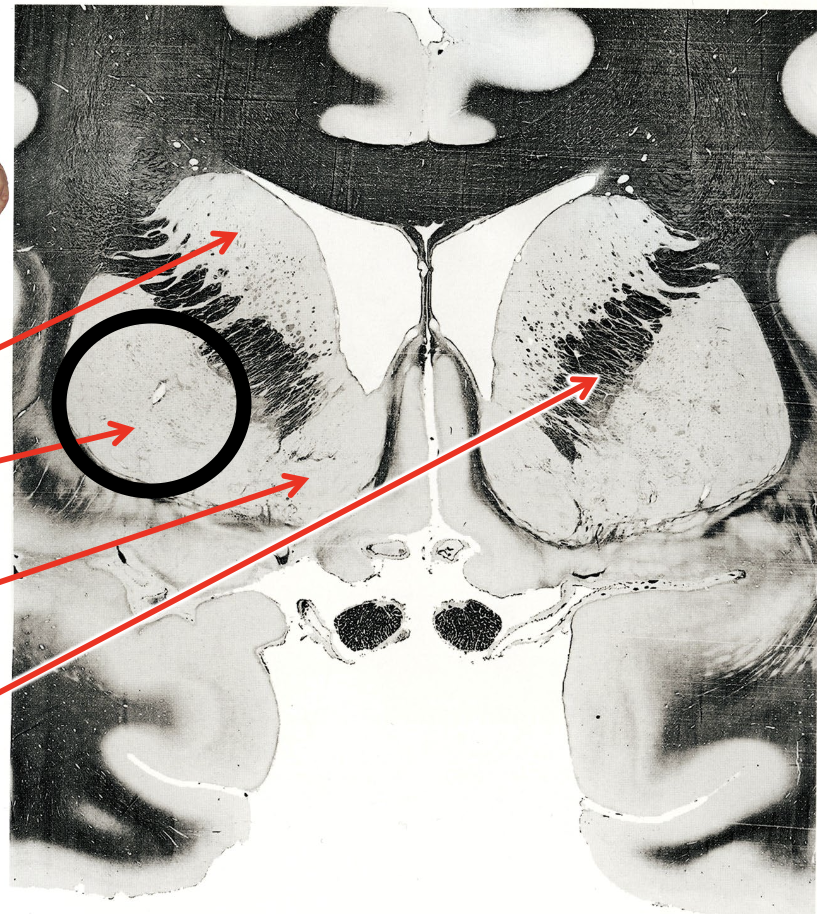
what is the circled region?
putamen
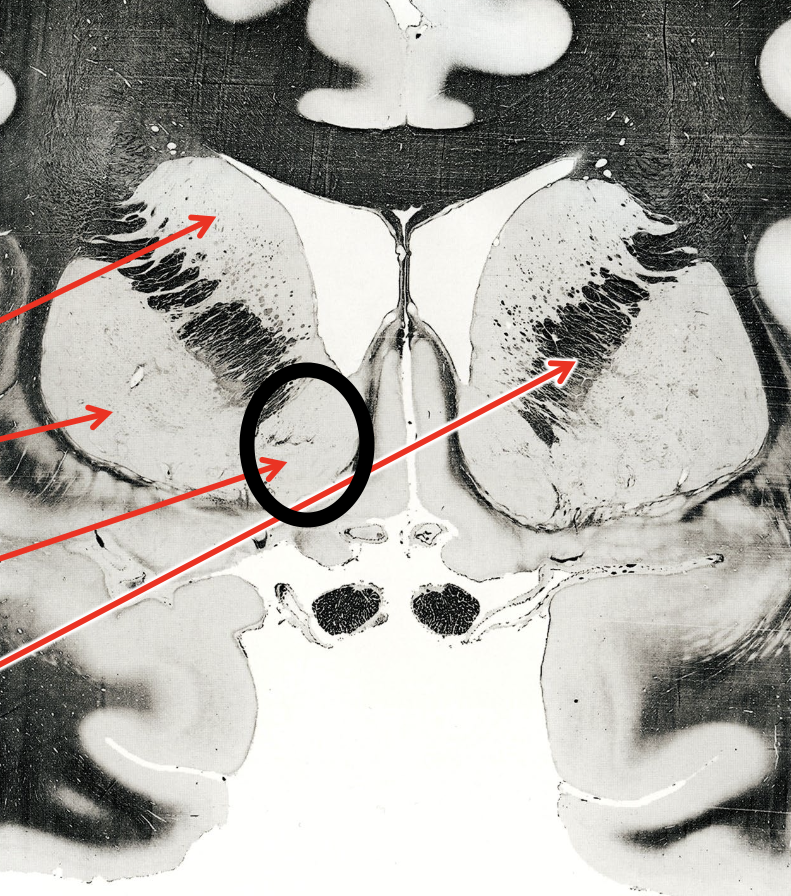
what is the circled region?
nucleus accumbens
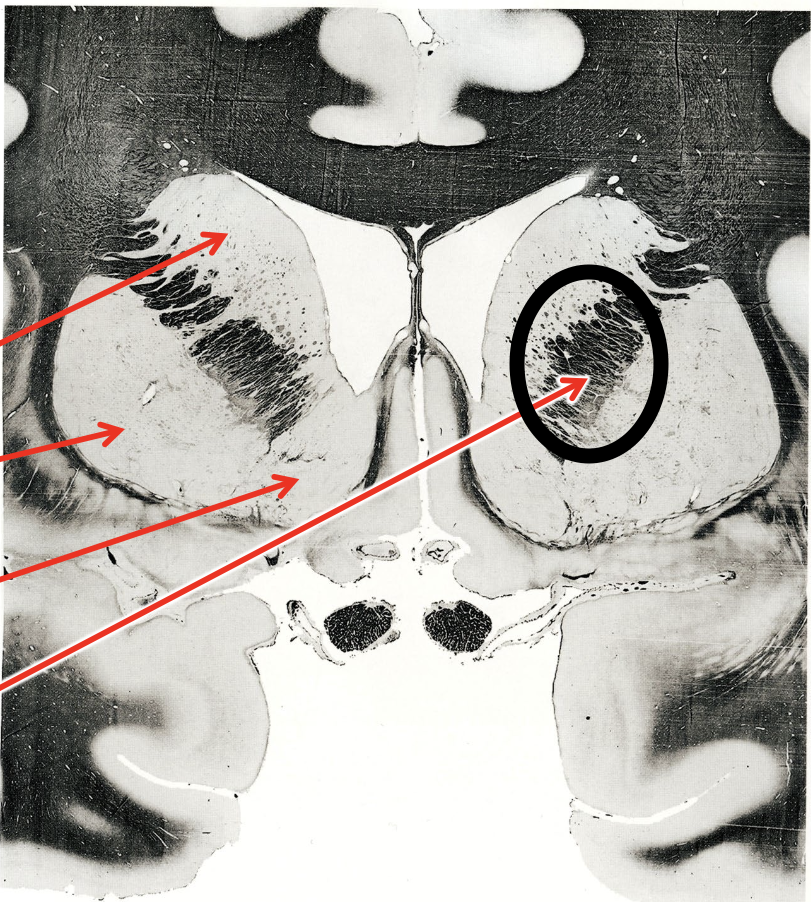
what is the circled region?
internal capsule
what are the arrows pointing to?
globus pallidus
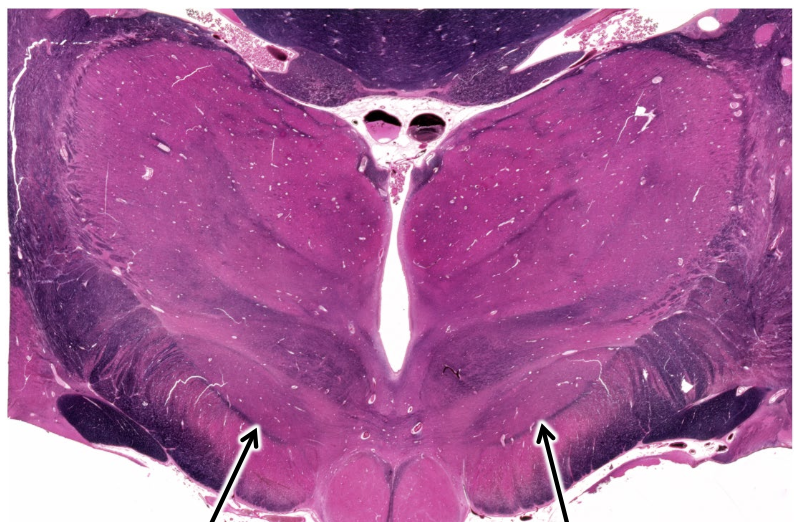
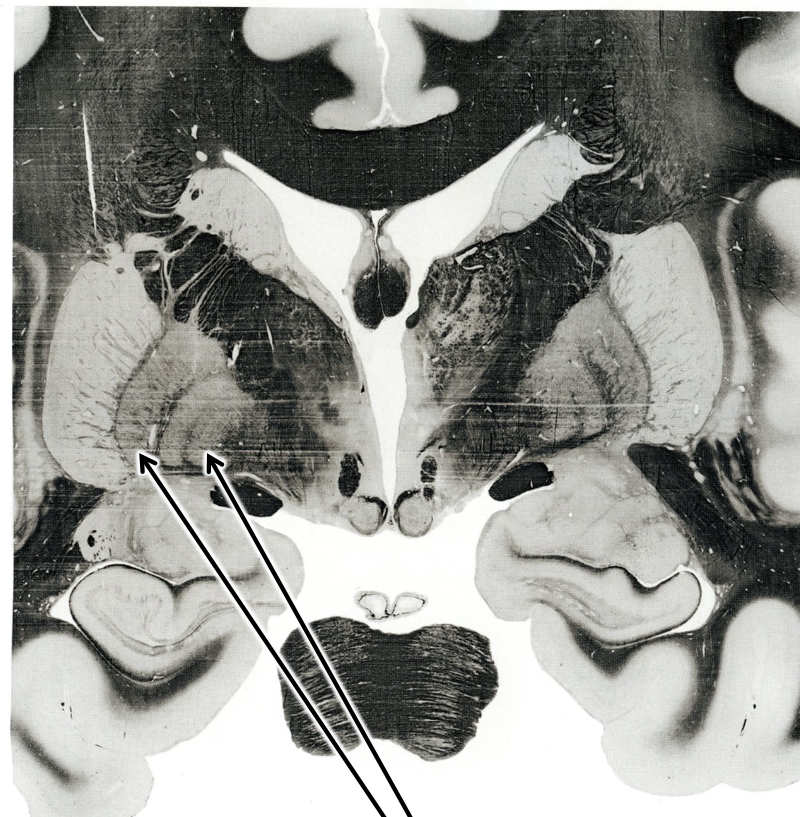
what are the arrows pointing to?
subthalamic nucleus
what are cranial nerves?
nerves that enter and exit the central nervous system through cranial foramen
spinal foramina
intervertebral openings in which spinal nerves exit
how are spinal nerves formed?
via the fusion of one dorsal root and one ventral root
afferents
sensory innervation
somatic sensory
efferents
motor innervation
skeletal muscles
cranial nerve I (1): olfactory nerves
responsible for sense of smell, located in the nasal epithelium
enters through cribiform plate
continues to cerebral cortex
where does CN I synapse?
olfactory bulbs
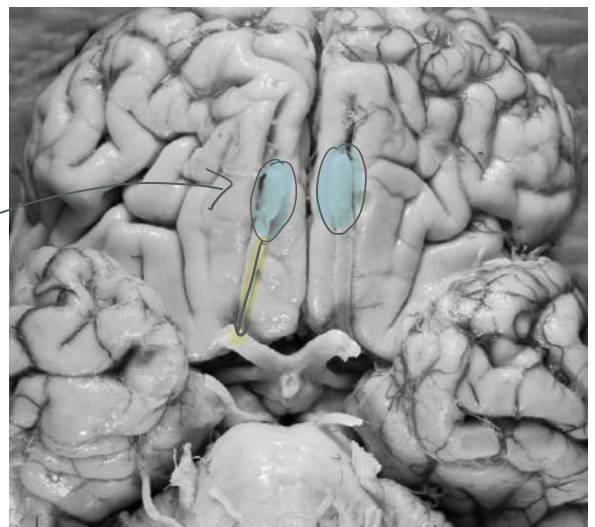
what are the blue highlighted regions?
olfactory bulbs
where do neurons in the olfactory bulb go to?
olfactory bulb neurons send their axons through the olfactory tract then to the CEREBRAL CORTEX
cranial nerve II (2): optic nerve
vison, receives input from retina cell axons
continues to thalamus
cranial nerve III (3): oculomotor nerve
innervates skeletal muscle to open eye and constricts pupil and focus lens
cranial nerves IV (4): trochlear nerve
innervates superior oblique extraocular muscle and is the only cranial nerve to exit from the dorsal surface of the brain
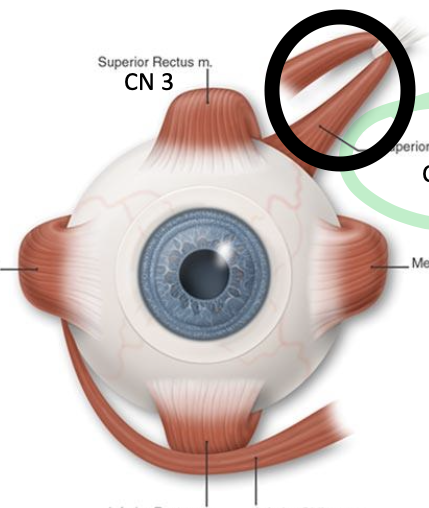
what does the circled structure?
superior oblique muscle, innervated by CN4. moves eye down and out
cranial nerve V (5): trigeminal nerve
innervates muscles of mastication and other sensation from the face and head
3 branches:
opthalmic
maxillary
mandibular
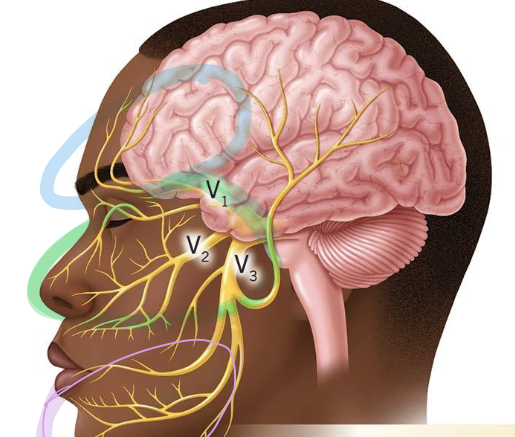
what nerve is shown here?
trigeminal nerve
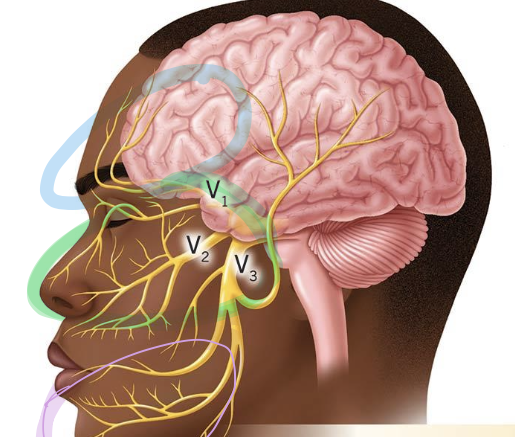
what branch is circles in blue?
opthalmic branch: receives info from the forehead
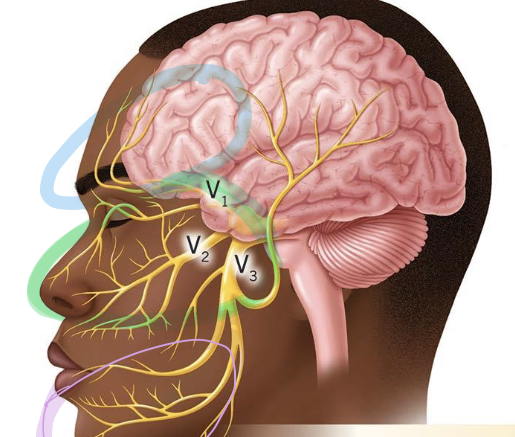
what branch is circled in green?
maxillary branch: receives info from cheek and nose
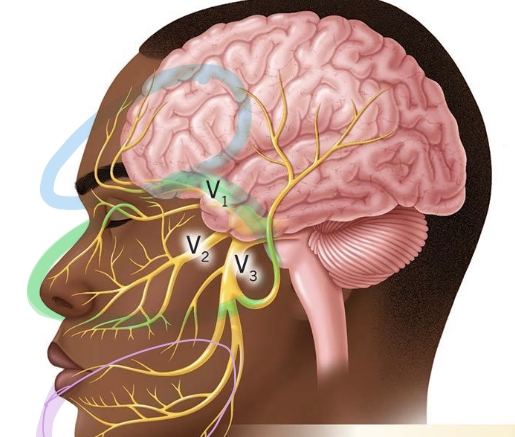
what branch is circled in purple?
mandibular branch: receives info from lower jaw
cranial nerve VI (6): abducens nerve
innervates lateral rectus extraoccular muscle
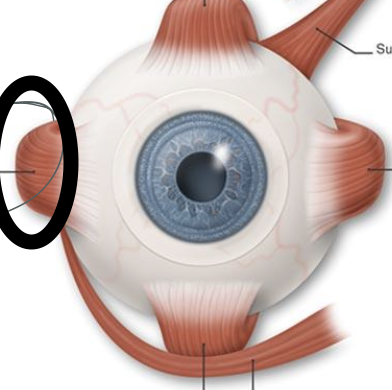
what is the circled structure?
lateral rectus muscle, innervated by CN6. pulls eye to the side
cranial nerve VII (7): facial nerve
innervates muscles of facial expression, autonomic ganglia responsible for tears, snot, and saliva, and 2/3 of tongue taste receptors
cranial nerve VII (8): vestibulocochlear nerve
responsible for hearing and balance. receives info from hair cells in cochlea
cranial nerve IX (9): glossopharyngeal nerve
innervates one skeletal muscle parotid gland, and receives sensory info from poster 1/3 of tongue
parotid gland
responsible for salvation, innervated by CN9 via autonomic ganglion
cranial nerve X (10): vagus nerve
innervates skeletal muscle, sensation, and senses blood oxygenation and CO2 levels
what skeletal muscle does CN 10 (vagus nerve) innervate?
muscles of throat and larynx for swallowing
what sensations is the vagus nerve responsible for?
taste and general sensation behind the ear and of larynx
what skeletal muscle does CN 9 (glossopharyngeal nerve) innervate?
muscles for elevating pharynx while swallowing
cranial nerve XI (11): spinal accessory nerve
innervates 2 muscles that allowing turning of head and shrugging shoulders
cranial nerve XII (12): hypoglossal nerve
innervates muscles of the tongue that allow for tongue movements
nerves that carry special senses (simplified)
olfactory, optic, vestibulocochlear
nerves that innervate skeletal muscle
oculomotor, trochlear, abducens, spinal accessory, hypoglossal
nerves that innervate muscle and carry general sensation
trigeminal
nerves that are mixed function
facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus
conjuctiva
lines inner surface of the eyelids and outer surface of the sclera
protects and excretes mucus and tears
prevents microbes from entering