L12: Learning, Memory, Amnesia
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
memory involves _________
reconstruction based on subsequent experiences
remembering ‘gist’ (over time) helps us (3)
anticipate and respond to future situations
(+) gist is adaptive
(-) may lead to erroneously recalling words or information that is semantically or perceptually related to the gist
strategies for memory consolidation (3)
Mental imagery (memory palace)
Spaced retrieval
Match study modality with test modality
memory imagery pathway (memory palace)
draw it
stimulus → sensory memory → working memory → ← long term memory
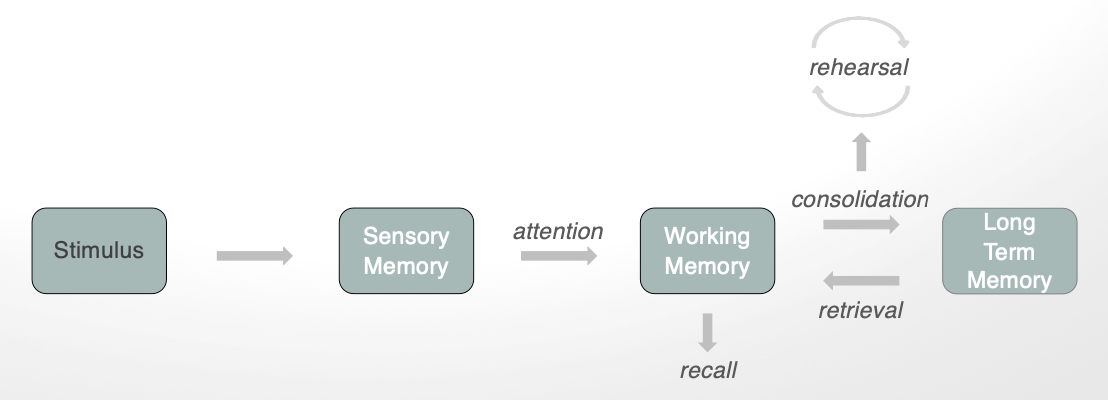
memory systems pathways (starting with sensory memory)
draw it
amnesia + 2 types (3)
partial or total loss of memory due to brain damage
retrograde
anterograde
retrograde amnesia (2)
loss of memory for events before brain damage
problem retrieving old memories
anterograde amnesia (2)
inability to form memories for events after brain damage
problem creating new memories

case study: Clive Wearing (3)
no trouble remembering details from childhood
cannot form new memories
procedural memory intact
Case study: Jason Bourne
cannot remember anything prior to two weeks ago
procedural memory is intact
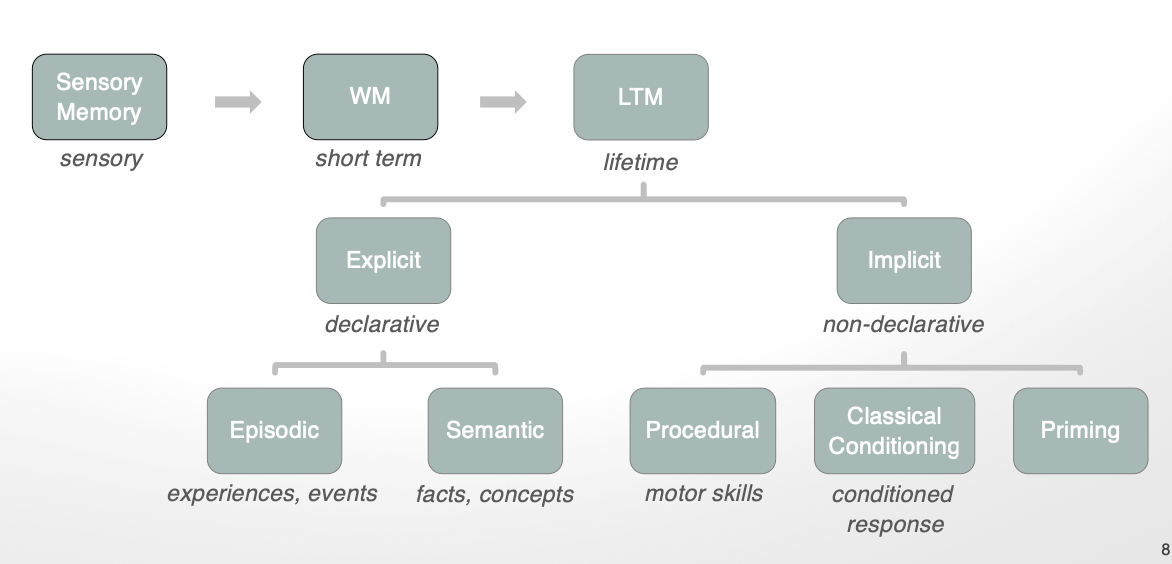
explicit memory → 2 types
what is it
2 types: episodic → experiences/events
semantic → facts/concepts
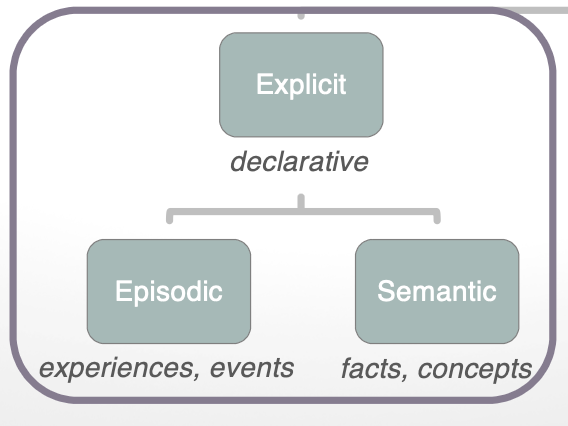
episodic/autobiographical memory (3)
recall of single episodes/events centered on the self
memory of life experiences
e.g. memory of you walking into a café for a cappuccino
semantic memory (2)
facts/concepts; knowledge of historical events;
e.g. cappuccino is 1/3 foam, 1/3 espresso, 1/3 milk
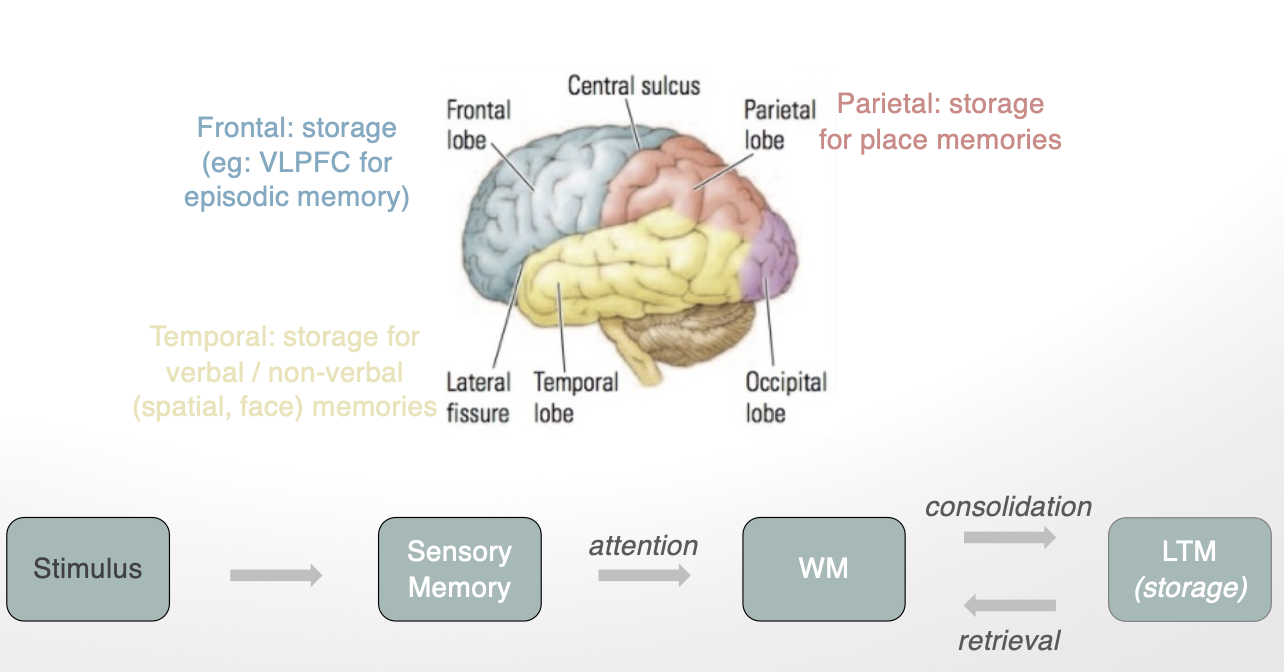
neural structures involved in explicit memory storage (3)
frontal lobe: storage (ie. VLPFC for episodic memory)
temporal: storage for verbal/nonverbal (spatial, face) memories
parietal: storage for place memories
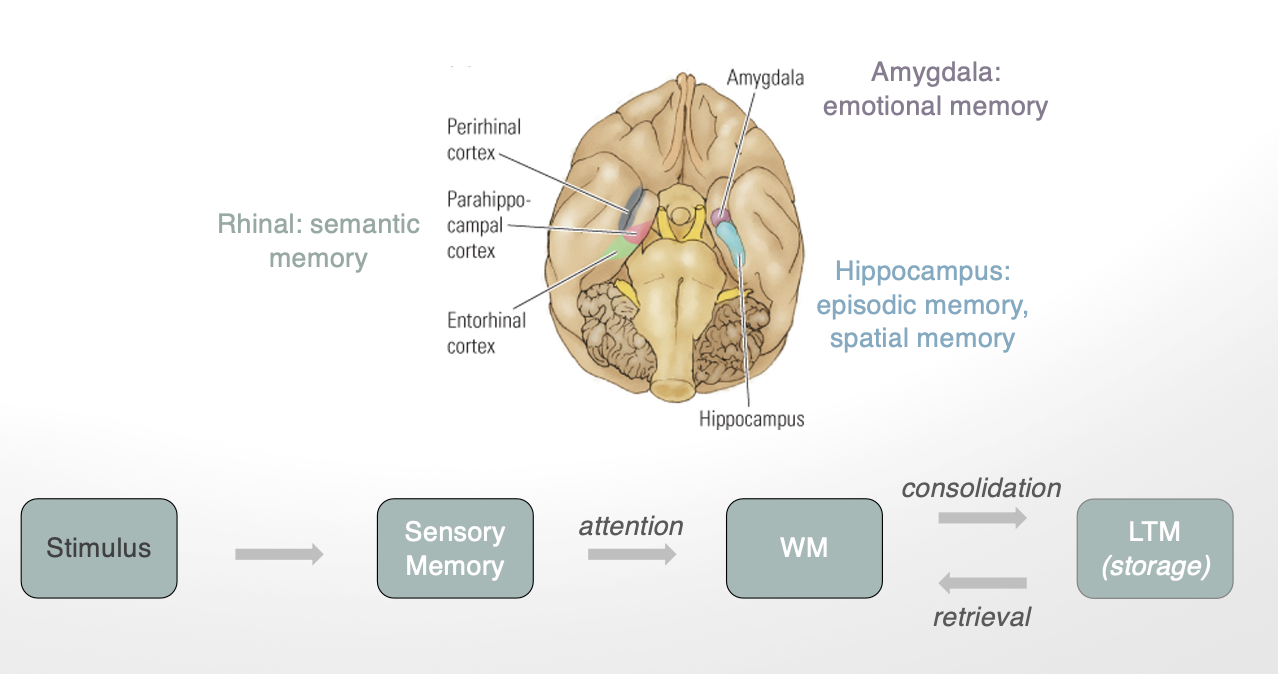
other neural structures involved in explicit memory (3)
rhinal: semantic memory
amygdala: emotional memory
hippocampus: episodic memory, spatial memory
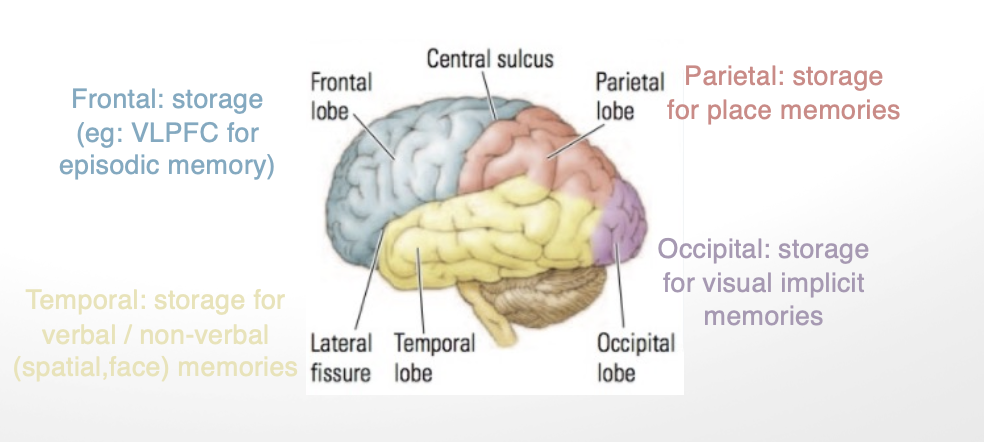
what roles do each lobe play in memory (4)
frontal lobe: storage (ie. VLPFC for episodic memory)
temporal: storage for verbal/nonverbal (spatial, face) memories
parietal: storage for place memories
occipital: storage for visual implicit memories
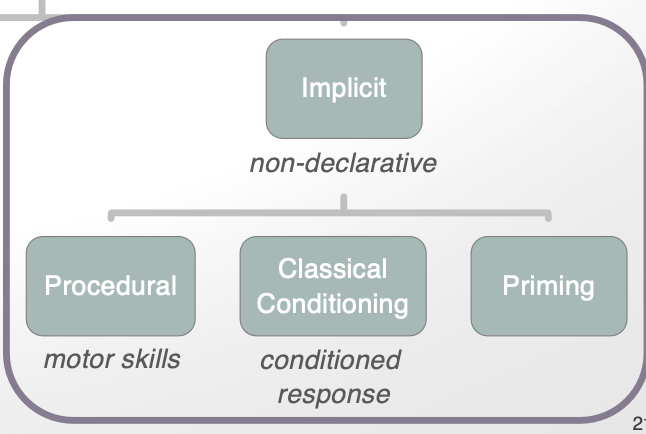
implicit memory what is it + types (4)
non-declarative memory
procedural: motor skills
classical conditioning: conditioned response
priming
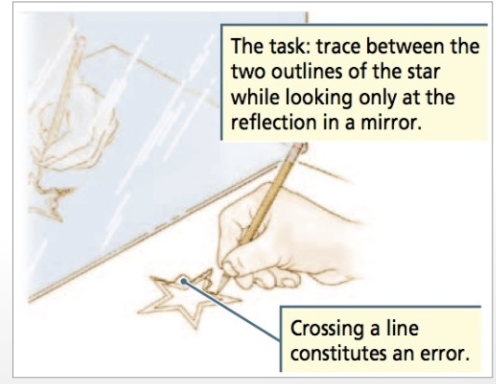
procedural learning/memory (2)
motor skills (e.g. riding a bike, snowboarding; playing the guitar)
language skills
classical conditioning
learning of pairing of neural stimulus w another stimulus that elicits bhvr
priming
initial stimulus presentation sensitizes brain to later presentation of same stimulus
neural structures involved in implicit memory
basal ganglia: habit + procedural learning
motor cortex: acquisition of implicit knowledge
cerebellum: classical conditioning
role of frontal cortex in ________
working memory → short term
working memory (aka temporal, short-term memory) (5)
memory for recent events and their order/sequence
three main types:
what = object recognition (ventral stream of sensory processing)
where = spatial location (dorsal stream of sensory processing)
when = sequence/order
🧠 What does the 2-back task measure, and how does it relate to episodic memory?
✔ Measures working memory and ability to monitor, update, and compare information over time
Involves components of episodic memory:
What = identity of the stimulus
When = its temporal position (e.g., 2 steps ago)
Where = its spatial position (in some N-back versions)
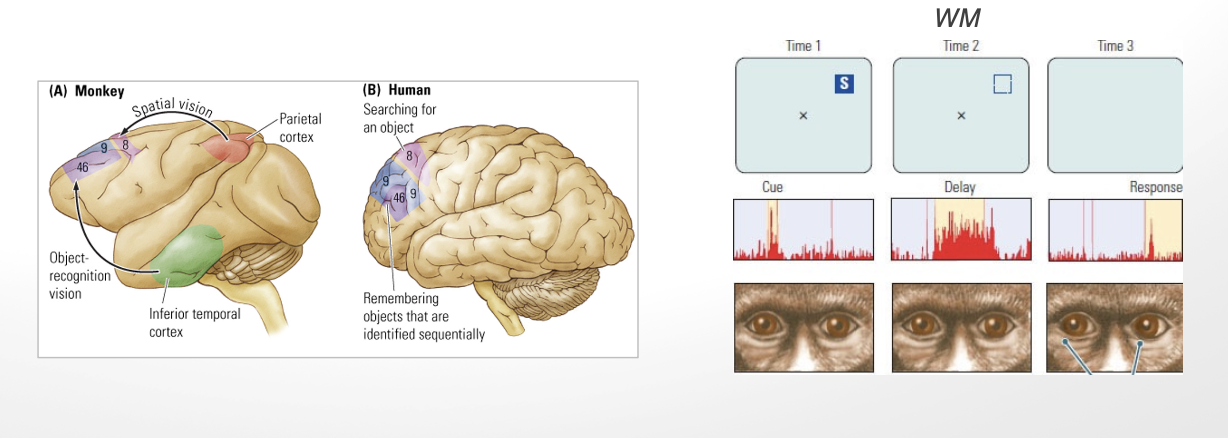
neural structures involved in working memory
frontal regions subserve working memory
hippocampus + prefrontal cortex:
work in bidirectional relationship to support working memory
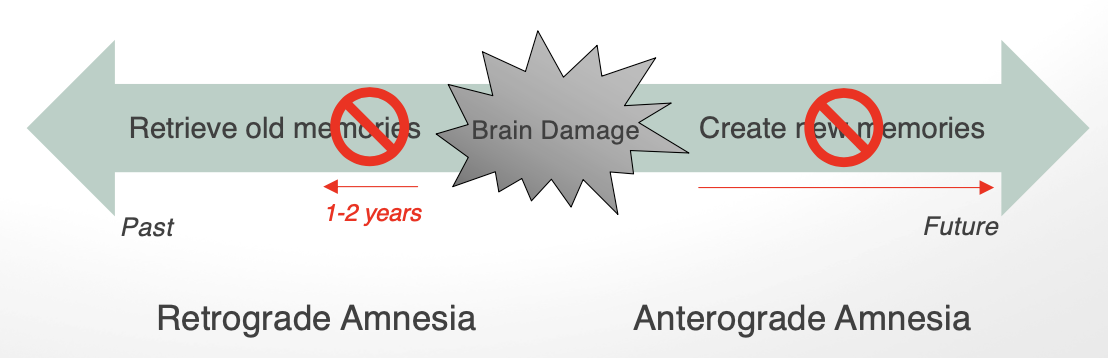
after bilateral hippocampus removal, H.M. suffered from what kinds of amnesia
severe anterograde
moderate retrograde amnesia
H.M. showed intact ___(3)___
procedural memory
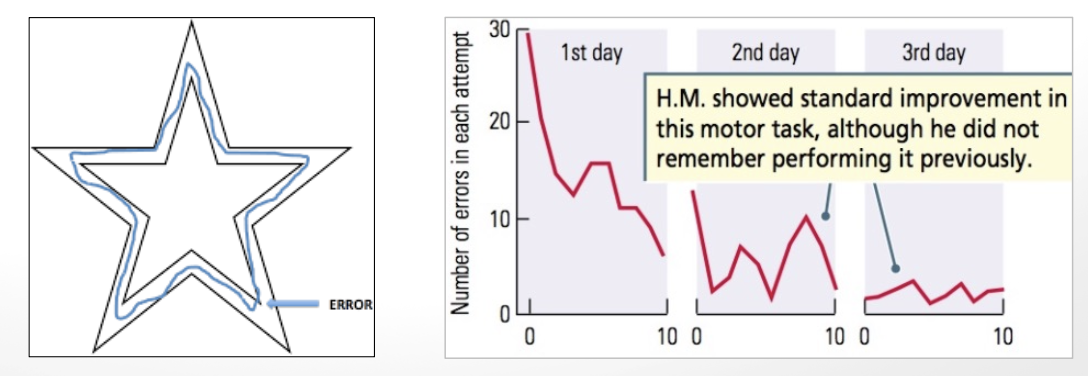
implicit memory

working memory

H.M. showed better _____ than _____ memory
implicit than explicit
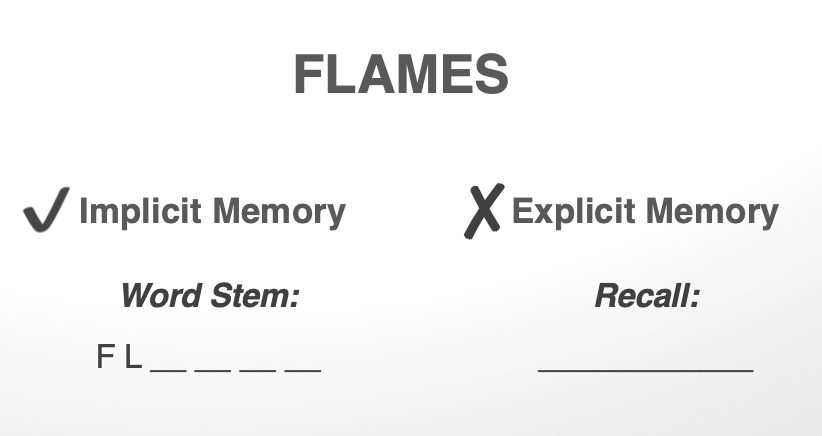
summary of patient H.M. (5)
Anterograde Amnesia: unable to learn any new information after surgery
Retrograde Amnesia: unable to remember any memories in 1 to 2 year period before his surgery
Implicit Memory: able to learn implicitly (e.g. procedural skills given intact basal ganglia/cerebellum)
Working Memory: normal functioning (intact prefrontal cortex)
Other aspects: no change in his personality, intelligence, language,
perceptual abilities
transient global amnesia (4)
Acute onset of anterograde amnesia
Usually transient (2-12 hours)
However, some evidence for permanent loss
No retrograde amnesia
chronic herpes simplex encephalitis (3)
Insula damage produces retrograde amnesia
MTL damage produces anterograde amnesia
Clive Wearing
Alzheimer’s Disease (3)
Deficits in WM (encoding)
Problems with some forms of Implicit Memory (verbal)
Intact Implicit Motor (sensorimotor)
Korsakoff Syndrome (3)
Acute onset of retrograde and anterograde amnesia
Confabulation (i.e. fabricate memories)
Ataxia and ophthalmoplegia (return to normal in chronic cases)
Korsakoff Syndrome caused by ____ (2)
Caused by severe thiamine (Vitamin B1) deficiency
typically due to chronic alcoholism or malnourishment
Alzheimer’s Disease caused by (2)
Begins with cell loss in MTL – anterograde amnesia
Subsequent damage to frontal/temporal cortex – retrograde amnesia
transient global amnesia caused by
Caused by transient ischemic attack, in rare cases migraines