Lab Animal Research
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What is the primary responsibility of laboratory animal technicians?
Controlling factors that predispose animals to certain disease
What is the goal of scientific research?
Improving humanity's knowledge of physical, chemical, and functional mechanisms of life processes and diseases
What are the "Three R's" of lab animal use? Explain each.
1. Reduction: Use the smallest amount of animals needed to achieve research goals
2. Refinement: Research must be as painless and as stress-free as possible. If this is not possible, medication should be used to alleviate suffering
3. Replacement: If possible, use non-living models for research over living models.
What are the 6 special interest groups of animal use?
1. Animal exploitation
2. Animal use
3. Animal control
4. Animal welfare
5. Animal rights
6. Animal liberation
Describe the core beliefs of animal exploitation groups.
Believe that animals were put on earth for use by humans
and they are our property
- E.g. advocates of bullfighting, cockfighting
Describe the core beliefs of animal use groups.
Believe that animals are here to be used by humans but that we must be responsible about that use
- This includes sparing an animal pain and discomfort if possible
- E.g. hunting and fishing groups
Describe the core beliefs of animal control groups.
Believe that governments should write laws that express the sentiments of most of the population
- Animal use for specific reasons like research, as long as a protocol is created and followed by everyone
- E.g. CVMA, CCAC
Describe the core beliefs of animal welfare groups.
Believe that people should treat animals as kindly as possible, and that it should be required by law to do so
- If an animal is mistreated or neglected, they have a duty to relieve their suffering
- E.g. SPCA
Describe the core beliefs of animal rights groups.
Believe that animals have intrinsic rights that should be guaranteed just as humans have rights
- Animals should not be killed, eaten, or used for sport
- Animal use in research violates the basic rights of animals
- E.g. PETA
Describe the core beliefs of animal liberation groups.
Believe animals should not be forced to work or produce for our benefit in any way
- Owning a pet is a form of enslavement
- E.g. Animal liberation front
Explain the benefits of animal welfare in the laboratory research setting.
Experimental results can be compromised when animals are not provided with suitable, appropriate enrichment activities due to increased stress response
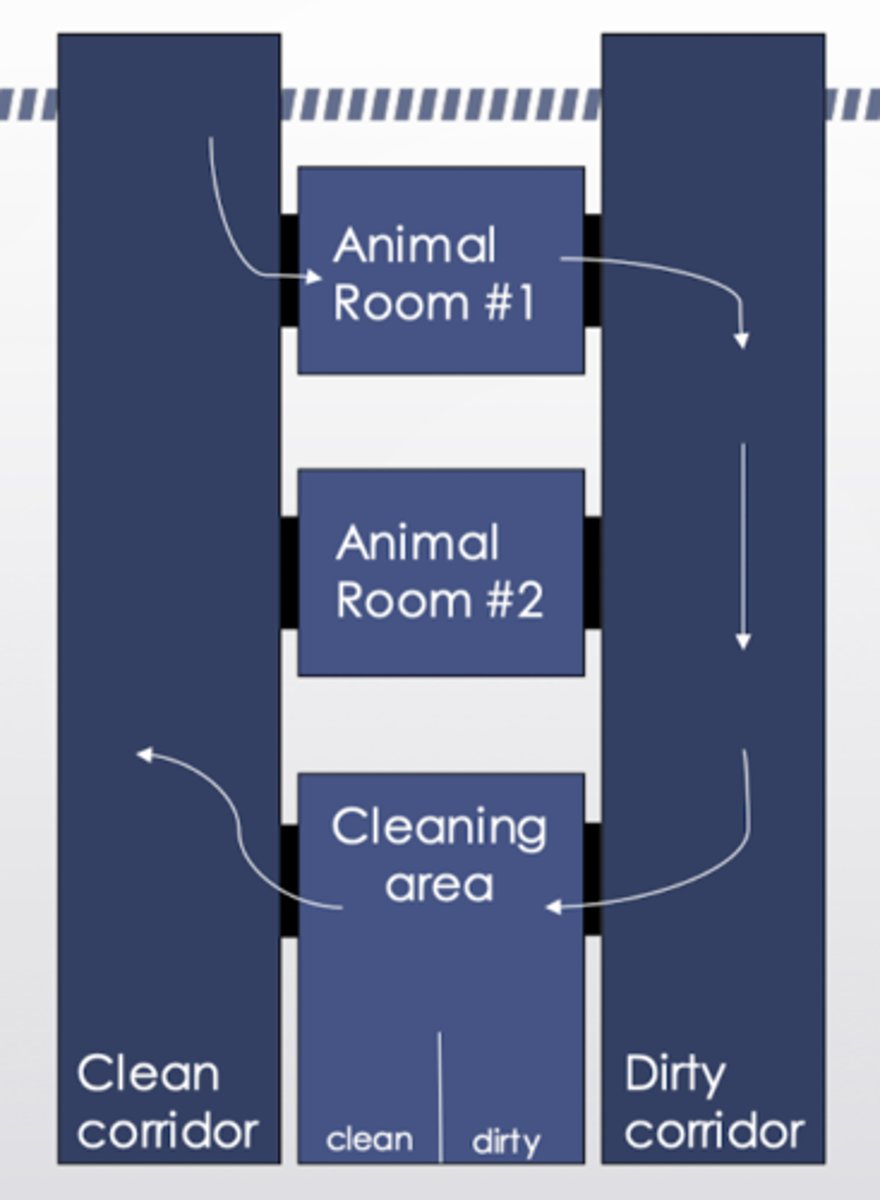
Describe a double-corridor lab animal facility. Describe the flow of traffic and the flow of air through the facility.
- Sometimes referred to as clean/dirty facility
- Rooms have two doors. One opens into the clean corridor and the other opens into the dirty corridor
- Unidirectional flow of traffic from clean to dirty
- Personnel cannot leave by the clean corridor door
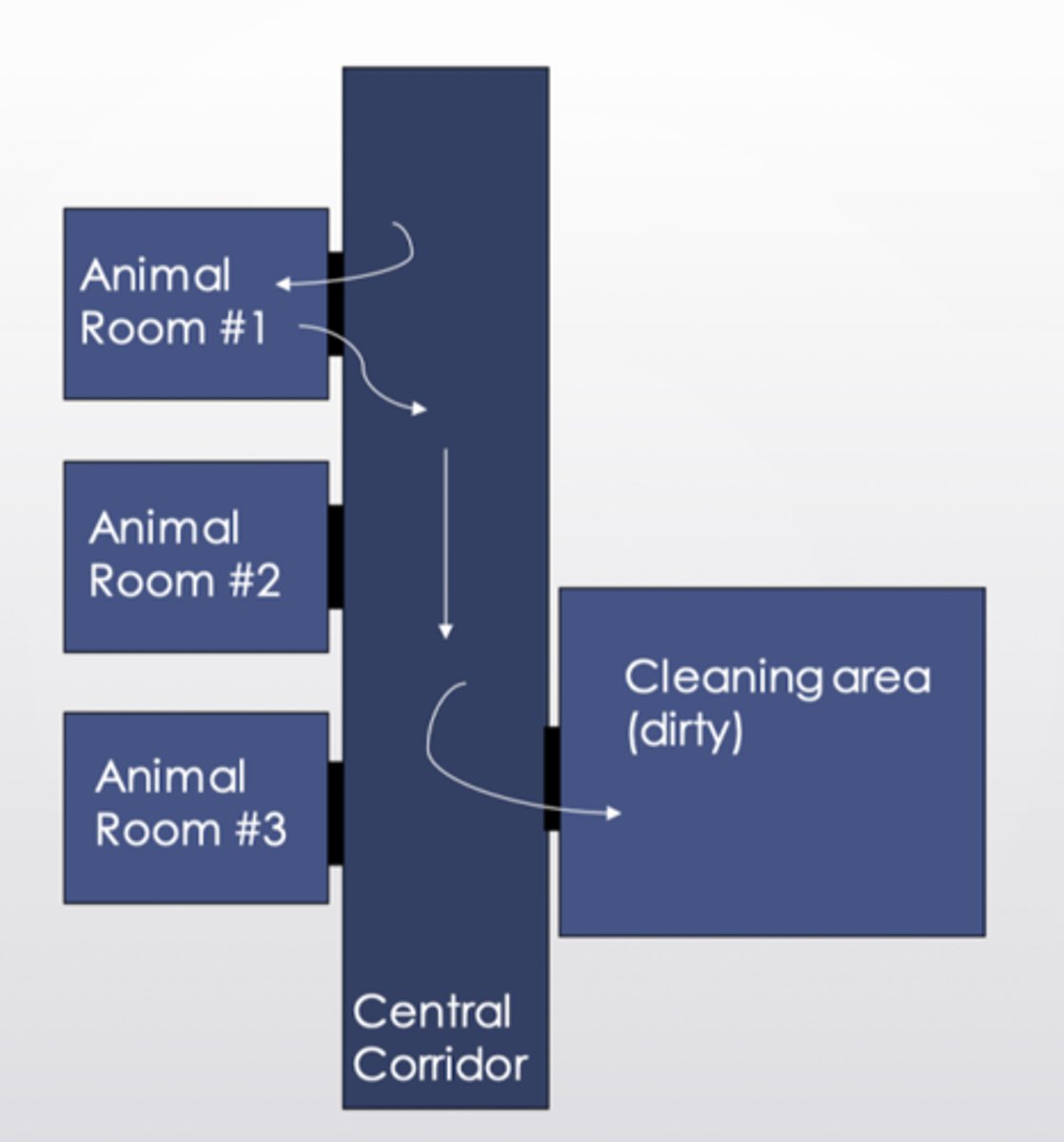
Describe a conventional facility.
- Most common in small facilities
- Rooms have single doors that open into a central corridor
- Requires extra caution to minimize disease spread (nothing dirty left in corridor)
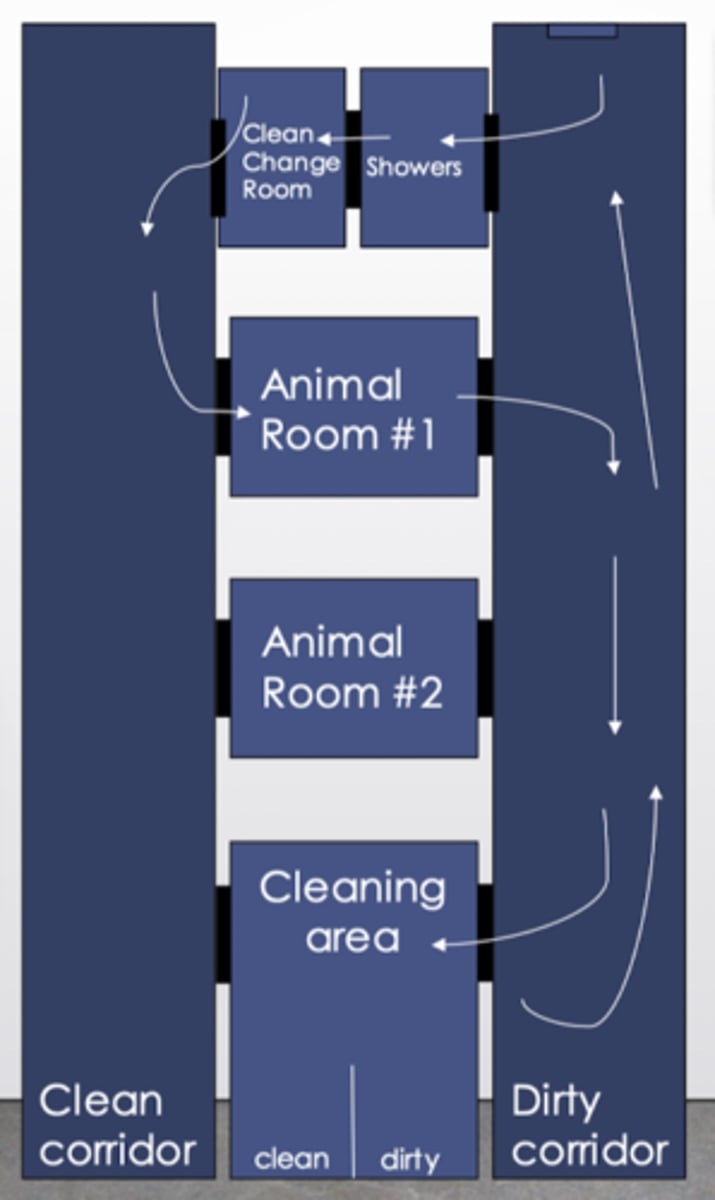
Describe a barrier facility.
- Similar to double-corridor but personnel must shower before entering animal rooms
- Often required to dress in disposable clothing
- Entry areas have an air-lock, sometimes with IV lights yo sterilize equipment. Air pressure is carefully monitored
- Used for germ-free animals
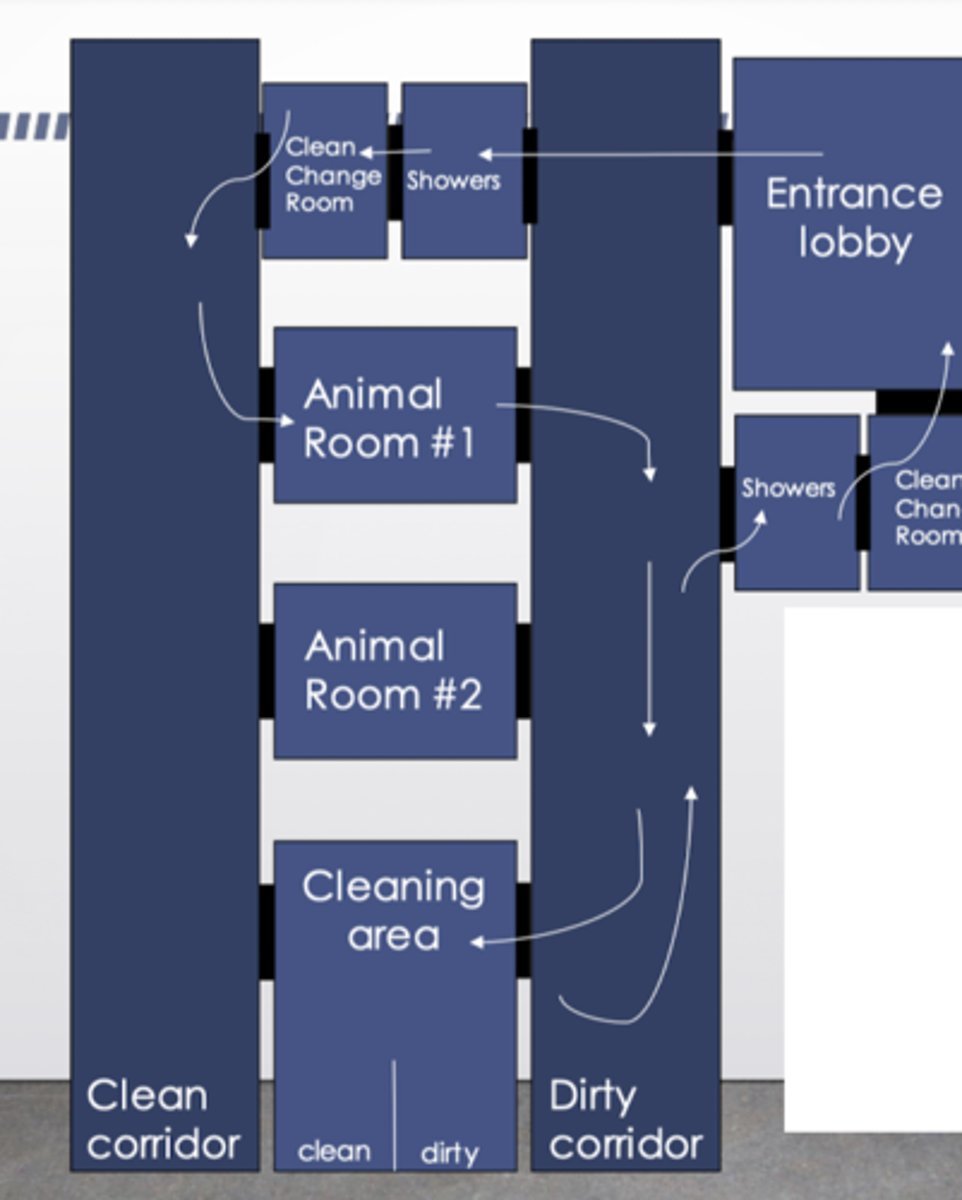
Describe a containment facility.
- Similar to barrier facility but personnel also shower upon leaving the facility
- All materials autoclaved before moved being moved in and out of the animal room
- Air passing out of facility is HEPA filtered
- Zoonotic or infectious diseases
What are the space requirements of an animal cage?
- Must be large enough to allow normal postural movement
- Provide an enriched environment to allow normal behavioral function
- Floor space requirements based on weight or body surface area
What are some methods of providing environmental enrichment for various animal species?
- Ledges
- Tubes
- Chew toys
- Activity cages
What are the different levels of gnotobiology?
- Gnotobiotic
- Specific-pathogen-free (SPF)
- Barrier-sustained
Define gnotobiology.
The study of animals with completely known flora and fauna
Describe an animal that is 'gnotobiotic'.
An animal with a well-defined microflora but all species present are known
Describe an animal that is 'specific pathogen free".
An animal that has been demonstrated to be free of certain pathogens
Describe an animal that is 'barrier sustained'.
An animal derived by c-section and then is maintained in a sterile, controlled environment. All supplies, food, water and equipment used is sterilized before entering the environment
Describe an animal that is 'cesarean derived'.
An animal delivered surgically by the removal of the uterus of the mother with delivery of the fetuses in a sterile isolation chamber
What is a sentinel animal? What is it used for?
- An animal susceptible to a certain pathogen (usually gnotobiotic)
- Used to identify any potential pathogens in the colony
Describe an animal that is 'axenic'.
An animal that is germ-free and has no evidence of microorganisms except those passed through the placenta before birth. Considered the same as barrier-sustained animals.
What are 4 factors predisposing animals to disease? Give examples.
1. Intrinsic: Species, age, sex
2. Extrinsic: Environmental parameters (temperature, humidity)
3. Dietary: Quality and quantity of food and water
4. Experimental: Surgery, restraint, drug effects
Describe a shoebox cage.
- Solid-bottom cage that is usually made of plastic
- Top is a grid of stainless steel
Describe a suspended cage.
- Rack that holds a series of cages which slide in and out of the rack on rails
- Composed of plastic or stainless steel with a plastic/wire mesh on the bottom
- Access to animals is through the top or front of cage
Describe a metabolism cage.
- Used to collect urine and feces so that the total volume can be measured and analyzed
- Food and water are located on the outside of the cage
Describe a gang cage.
- Used for housing social groupings of animals
- Has multiple sites for food and water distributed throughout the cage to discourage domination
Describe a transportation cage.
- Cages on wheels used to move animals from one room to another
- Only stay in cage for a short period of time so food and water is not required
Describe 'pens and runs'.
- Primarily used to house dogs or farm animals
- Shelter is required
- Nutritional control is lost in animals who eat grass
- Indoor or outdoor
Describe an activity cage.
Used to provide exercise areas for animals
Describe an inhalation cage.
- Enclosed chamber when strict control of environmental parameters is required
- Used for studies requiring inhalation of vaccines or antibiotic (keeps it from contaminating the room)
Describe a recovery cage.
- Provides strict control of temperature, humidity, etc.
- IV line and monitoring devices may be incorporated
What are some environmental concerns in a research facility?
- Temperature and humidity
- Ventilation requirements
- Air pressure concerns
- Illumination
- Noise
What are the types and the sources of lab animals in research?
- Purpose-bred (specifically bred for research)
- Conventially sourced (shelters)
What types of studies use metabolism cages?
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies
Describe biosafety level 1.
- Do not ordinarily cause disease in humans but may affect those who are immunocompromised
- Requires complete washing of counters, equipment & hands
E.g. E.coli
Describe biosafety level 2.
- Have the potential to cause human disease if handled incorrectly
- Need to wear gowns, gloves, face shields
E.g. Toxoplasma
Describe biosafety level 3.
- Can cause serious and potentially lethal disease
- High potential for aerosol respiration
- Personnel tested to evaluate possible exposure
E.g. Tuberculosis
Describe biosafety level 4.
- Pose high risk of causing life-threatening disease
- Shower in and shower out
- Wear full body suits with oxygen supply
E.g. Ebola
T or F: Humans are living longer and maintaining a higher quality of life because of many medical advances.
True
T or F: Animal research is inexpensive.
False
T or F: Some animal research is required by law.
True
T or F: Animal welfare is not a concern in animal research.
False
List three medical advances made as a direct result of animal testing.
- Polio vaccine
- Penicillin tested
- Discovery of insulin
List three surgical advances made as a result of animal testing.
- Open heart surgery and cardiac pacemakers
- Organ transplantations
- Hip replacement surgery
What are some adjunctive techniques that replace animal research?
- Cell and tissue cultures
- Computer simulation models
Does "cruelty-free" mean that those products are not tested on animals?
No- it only refers to the finished product not being tested on animals
Which country requires animal testing for cosmetic products by law?
China
What is the CCAC and what do they do?
Canadian Council on Animal Care
- Monitors the use of animals in research, teaching, & testing
- Allows the use of animals only if it promises to contribute to the understanding of biological principles, or to the development of knowledge that will benefit humans
What is the ACC and what do they do?
Animal Care Committee
- Responsible for all aspects of animal use, education, health and compliance with all laws and regulations
- Works with the CCAC
What is the most commonly used animal in research?
Mice, rats and fish
What are the 3 basic types of scientific research?
- Basic: Advancing fundamental knowledge. Often performed with computer models or plants
- Applied: Uses existing knowledge for solving a specific biomedical problem. Use biomedical research models
- Clinical: Always conducted on live animals, including humans
What must every study have a formal copy of before they can proceed?
Good Laboratory Practices Protocol (GLP)
- Need a formally approved written protocol
How many variables are experiments designed to test?
One
What is the difference between an experimental and a control group?
- Experimental: the variable being manipulated
- Control: receives no manipulation
What is an SOP?
Standard Operating Procedure
What is an RLAT?
Registered Lab Animal Technician
What is negative air pressure?
Air flows from outside to inside room. Required for quarantine areas
Wha is positive air pressure?
Air flows from the room to outside. Required for clean areas like the surgical suite
All animals new to a facility myst undergo a quarantine period. What is the minimum time an animal should be in quarantine?
48 hours
What are some safety hazards in an animal care facility?
- Bites
- Chemical agents
- Allergens
- Zoonosis
What are the adverse effects if the air exchange requirements are too high in an animal room?
Drafts may occur in the animal cages
Adding a resting ledge to a cage for a cat would be an example of _____.
Environmental enrichment
Define microenvironment.
Refers to environmental conditions within an individual cage
Define thermoneutral zone.
Range of temperature where an animal does not need physical or chemical mechanisms to control heat production or heat loss