Marine Systems Exam 1 - Greg
1/337
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
338 Terms
Marine Biology
Study of marine organisms and ecosystems.
Marine Science
Scientific study of oceanic environments.
Binomial Nomenclature
Two-part naming system for species classification.
Linnaeus
Developed binomial nomenclature system.
Cuvier
Pioneered animal morphology classification.
Challenger Expeditions
First scientific oceanographic research (1872-1876).
Louis Agassiz
Founded first North American marine sciences school.
Penikese Island
Location of Agassiz's marine science school.
Howard Sanders
Studied intertidal and shallow marine ecology.
Charles Darwin
Formulated theory of natural selection.
Coral Reef Formation
Process of coral growth and ecosystem development.
Cornelia Clapp
Pioneering woman in marine science, associated with MBL.
EE Just
Known for developmental biology and radiation studies.
Roger Arliner Young
Studied radiation effects on embryos.
Forbes' Error
Claimed life couldn't exist below 300m depth.
Marie Tharp
Mapped ocean floor, discovered mid-Atlantic ridge.
Heresy
Term for Tharp's groundbreaking oceanic discoveries.
Tectonic Drift
Movement of Earth's plates affecting ocean basins.
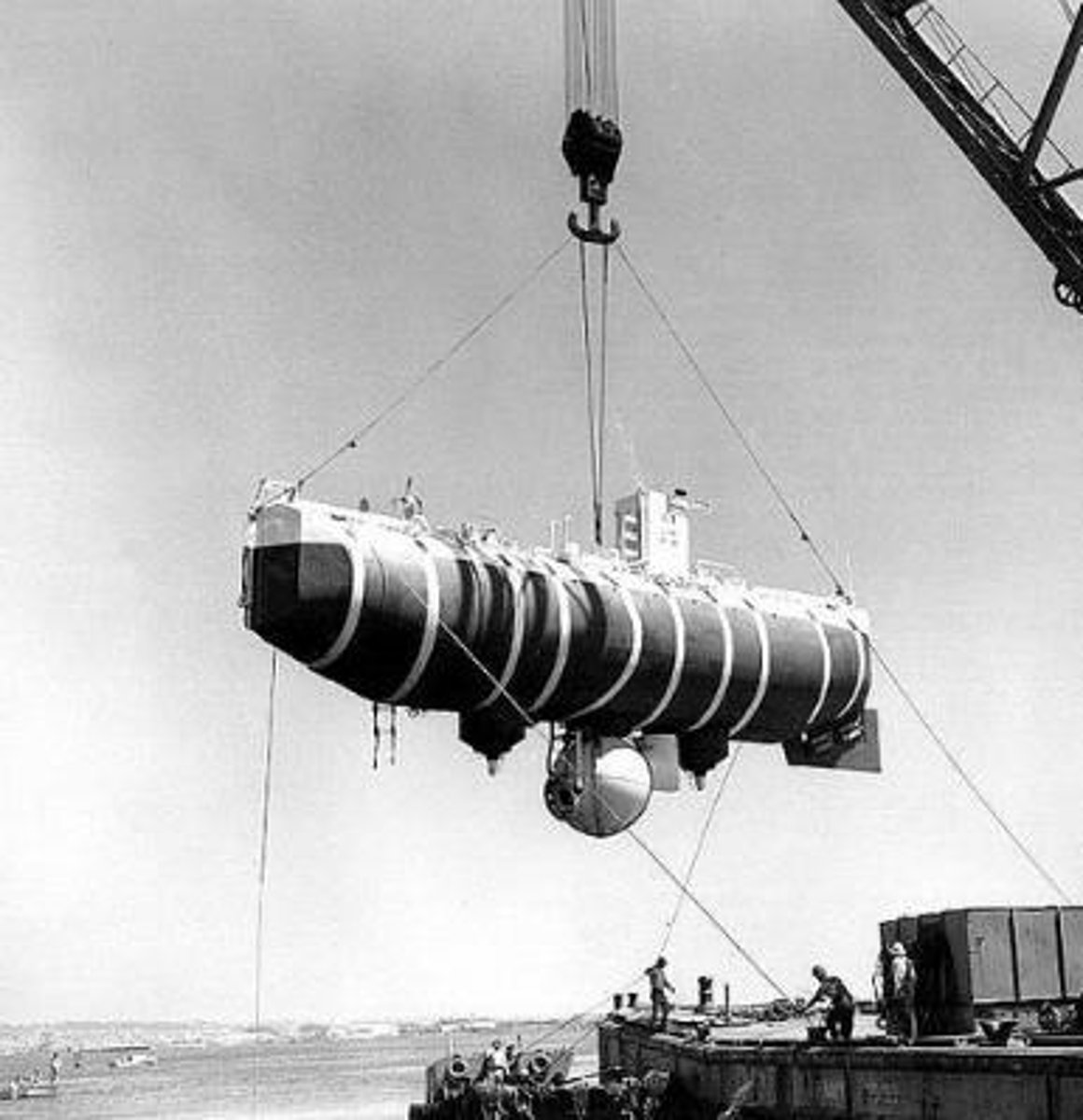
ALVIN
Deep-sea submersible for ocean exploration.

Ventana
Stationary fiber optic networks for marine research.
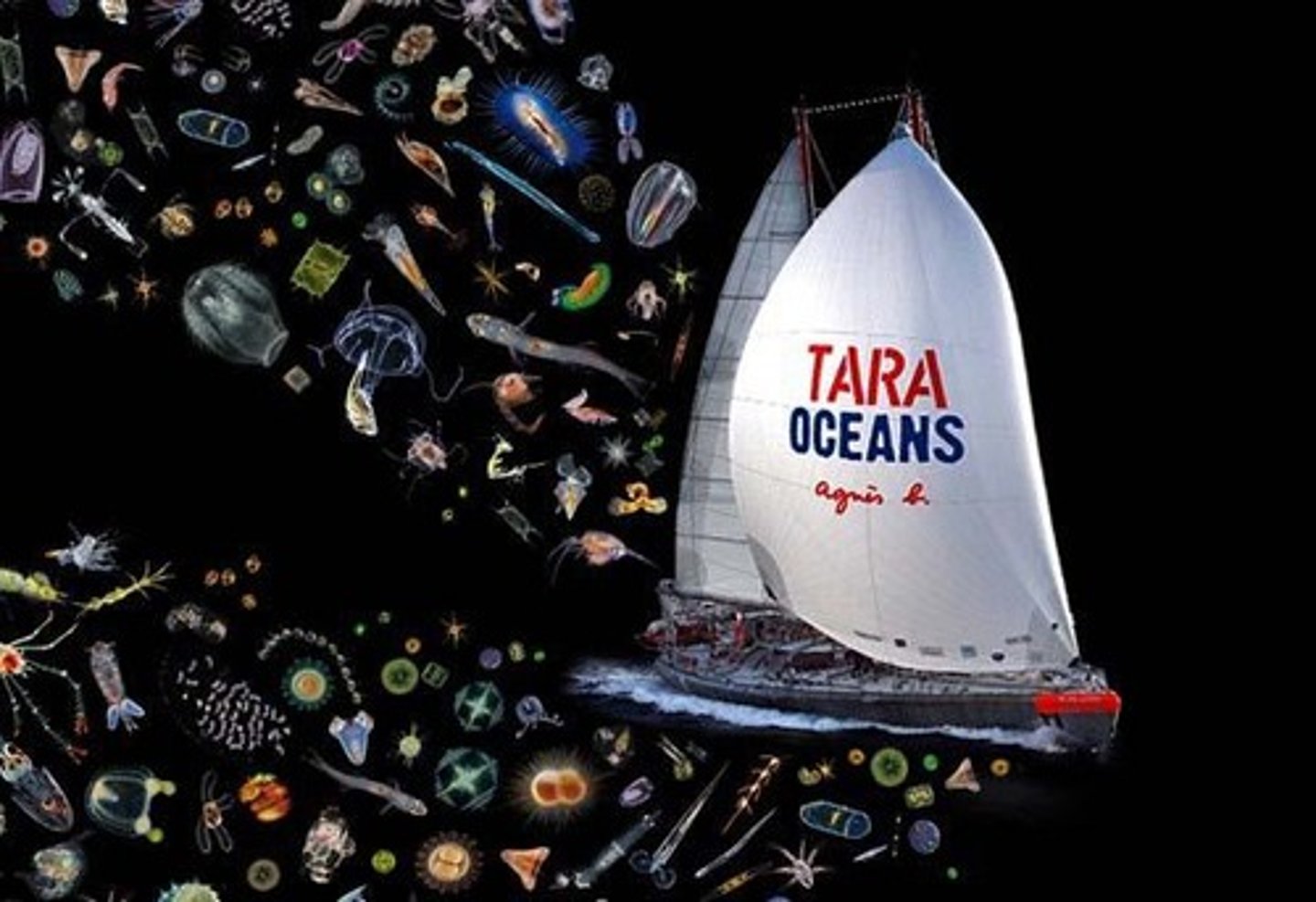
Tara Oceans Expeditions
Global scientific expeditions studying ocean ecosystems.

Scientific Method
Systematic approach to scientific inquiry and testing.
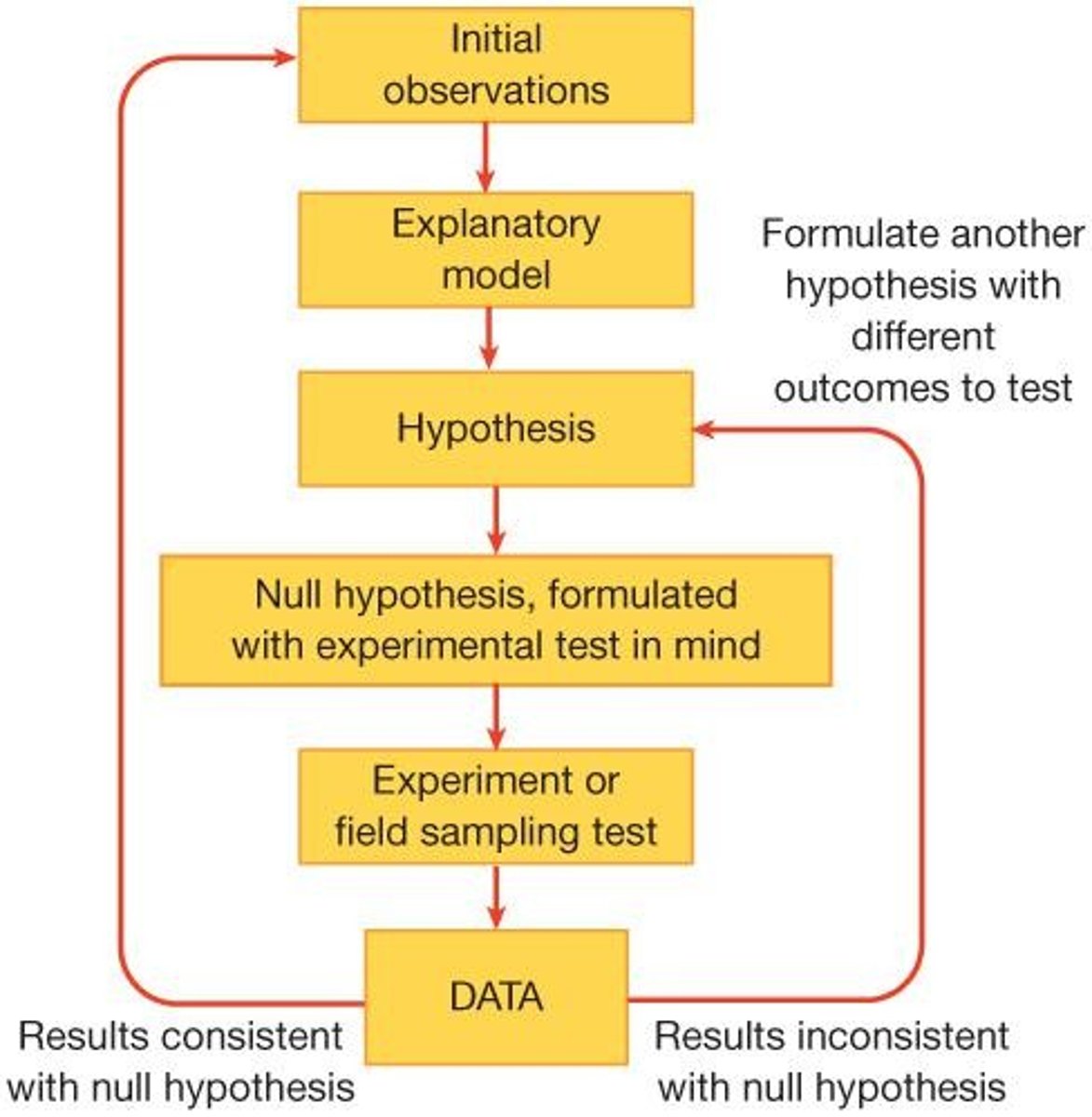
Induction
Knowledge accumulation leading to hypotheses.
Experimental Testing
Process involving observations and controlled experiments.
Ocean Coverage
Oceans cover 71% of Earth's surface.
Earth's Water Composition
Oceans contain over 95% of Earth's water.
Southern Hemisphere Coverage
Southern Hemisphere has 80% ocean coverage.
Northern Hemisphere Coverage
Northern Hemisphere has 61% ocean coverage.
Ocean Depth
84% of oceans are deeper than 2000m.
Greatest Ocean Depth
Marianas Trench reaches ~11,000 m depth.
Marginal Seas
Coastal bodies of water significantly influenced by land.
Gulf of Mexico
Example of a significant marginal sea.
Mediterranean Sea
Another important marginal sea with limited exchange.
Dynamic Water Relationships
Interactions of various water inputs in oceans.
Particulate Mineral Matter
Solid particles suspended in ocean water.
Dissolved Salts
Ionic compounds dissolved in seawater.
Particulate Organic Matter (POM)
Organic materials suspended in ocean water.
Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM)
Organic substances dissolved in seawater.
Atmospheric Precipitation
Rain and snow contributing to ocean water.
Volcanic Sources
Minerals and gases released from underwater volcanoes.
Continental Shelf
Shallow sea area adjacent to continents.
Continental Slope
Steep descent from continental shelf to ocean floor.
Continental Rise
Gentle slope leading to abyssal plain.
Abyssal Plain
Flat, deep ocean floor areas.
Oceanic Ridge Systems
Underwater mountain ranges formed by tectonic activity.
Seafloor Spreading
Process where new oceanic crust forms at ridges.
Water Molecule Properties
Asymmetrical charge enables water's solvent capabilities.
Colligative Properties
Properties dependent on solute concentration in solution.
Specific Heat of Water
Water requires 4.184 Joules to raise 1g by 1°C.
High heat of evaporation
Energy required to evaporate water, 2500 J/g.
High dissolving power
Ability of water to dissolve various substances.
High transparency
Water absorbs infrared and ultraviolet light.
Latitudinal Gradient
Variation in temperature with latitude in oceans.
Vertical Temperature Gradient
Temperature change with depth in ocean layers.
Oceanic temperature range
From -1.9 to 40 °C in oceans.
Deep ocean temperature
Typically between 2 to 4 °C.
Salinity definition
Grams of dissolved salts per 1000 g seawater.
Salinity units
Measured in o/oo, ppt, or psu.
Salinity range
Open ocean salinity is 32 to 38 o/oo.
Forchhammer's Principle
Constant ratios of elements despite salinity variations.
Residence time
Average time an element remains in the ocean.
Mixing time
Time taken for water to mix, ~1000 years.
Chloride residence time
Approximately 100 million years in seawater.
Sodium residence time
Approximately 68 million years in seawater.
Sigma-T surfaces
Measure seawater density at specific temperature.
Density of seawater
Influenced by salinity and temperature variations.
Density formula
σt = (density - 1) x 1000.
Advection
Bulk movement of fluid carrying heat and salt.
Convection
Vertical movement of fluid due to heating.
Measurement of salinity
Determined by chlorinity and chemical methods.
Gases in seawater
Dissolved gases affecting marine life and chemistry.
Vertical density gradients
Density changes with depth, affecting ocean currents.
Sigma-t
Density measure of seawater adjusted for salinity.
Seawater Density
Density influenced by salt, varies with temperature.
Vertical Density Gradients
Density changes with depth in ocean layers.
Thermohaline Circulation
Deep ocean movement driven by temperature and salinity.
Anoxia
Low oxygen condition in water bodies.
Oxygen Minimum Layer
Depth layer with lowest dissolved oxygen concentration.
Hydrogen Bonding
Attraction between water molecules affecting properties.
Salinity
Concentration of salt in seawater affecting density.
Specific Heat
Amount of heat required to change water temperature.
Density Stratification
Layering of water due to density differences.
Photosynthesis
Process converting light energy into chemical energy.
Light Intensity Decline
Exponential decrease of light with ocean depth.
Fjord Circulation
Water exchange dynamics between fjords and open sea.
Temperature Profile
Variation of seawater temperature with depth.
Chemical Characteristics
Properties influenced by solute composition in seawater.
Plate Tectonics
Movement of Earth's plates affecting geological features.
Vesuvius Eruption
Historical volcanic event destroying Pompeii in AD 79.
Density Flow
Movement of water layers based on density differences.
Western Boundary Current
Current found on western edges of ocean basins.
Gulf Stream
Warm-water current in the North Atlantic Ocean.
Eddies
Circular currents transporting organisms in oceans.
Polar Vortex
Large-scale circulation pattern affecting polar regions.
Law of Unintended Consequences
Complex systems respond unexpectedly to changes.
Coriolis Effect
Deflection of moving objects due to Earth's rotation.
Ekman Spiral
Layered water movement caused by wind and Coriolis.
Langmuir Cells
Surface currents creating parallel lines on ocean.
Upwelling
Vertical movement of water caused by wind.
Ekman Transport
Water movement due to wind and Coriolis effect.