Unit 5 - Biology
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
species
A group of similar organisms capable of breeding and producing fertile offspring
variation
Differences in any aspect of an organism
classification
A system of organising knowledge on all living things based upon their characteristics and more recently their DNA
binomial nomenclature
Naming system for living organisms using two names for each species; the genus followed by the species
sexual dimorphism
When the male and female of a species look significantly different. Often having completely different features and appearance
interbreed
Breeding between species. Produces infertile hybrid offspring
hybrid
The result of breeding between members of two different species; usually infertile
speciation
The formation of new species by the splitting of one pre-existing species into two or more new species
population
A group of organisms of one species, living in the same area at the same time
biodiversity
The variety of life on Earth, or in a particular habitat or ecosystem
Inbreeding
Breeding between closely related individuals
genetic diversity
The diversity seen in the genes (alleles) within a population of a species
species diversity
The number and types of organisms that existed during a specific amount of time
ecosystem diversity
Variety in ecosystems in a given area
community
A group of interacting species in a particular environment (for example, a forest – with its trees, plants, animals, bacteria and fungi)
dichotomous key
A tool used to identify species found in the field based on observations. A series of questions with two possible answers that leads to the correct identification of a species
DNA barcoding
A method of environmental sampling that allows for the identification of species and the determination of biodiversity from traces of DNA
anthropogenic
Relating to humans and human activity
megafauna
Very large animals that exist in a particular area, habitat or geological period
habitat
The place in which a community, species, population or organism lives
ecosystem
A community of living organisms and its abiotic (non-living) environment
biome
Communities of living organisms spread over a large geographical area. They are often named based on the dominant vegetation
biotic
The living components of an environment, such as plants and animals
abiotic
The non-living components of an ecosystem
symbiotic
A relationship between two or more organisms in which the presence of each organism helps the other organism to survive and thrive
convergent evolution
Pattern of evolution where distantly related organisms evolve similar traits in response to environmental similarities
ecological niche
The role of a species within an ecosystem or community and its interrelationships with both biotic and abiotic factors
obligate anaerobes
Organisms that can only survive in environments that lack oxygen
obligate aerobe
Organisms that can only survive in environments that contain oxygen
facultative anaerobe
Organisms that can survive in environments that contain or lack oxygen
autotroph
An organism that can produce its own chemical energy using light, inorganic compounds or other energy sources (also referred to as Producers)
heterotrophic
Organisms that cannot produce their own food, consumers; they must ingest nutrients from other organic sources (also referred to as Consumers)
holozoic
Organisms that consume food via the process of ingesting, digesting and assimilating the nutrients
mixotrophic
An organism that can use a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode on the continuum from complete autotrophy at one end to heterotrophy at the other
saprotroph
Organisms that obtain nutrients by secreting digestive enzymes followed by absorbing and assimilating the nutrients
decomposer
Organisms that break down dead matter into simpler substances
Archaea
A domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. They are known for their ability to live in harsh environments
chemoautotrophs
An organism that derives energy from the oxidation of inorganic compounds via chemosynthesis
photoautotrophs
An organism that can make its own energy using light and carbon dioxide via the process of photosynthesis
hominids
A primate of the family Hominidae that includes humans and their fossil ancestors including some of the great apes (such as gorillas, chimpanzees, and orangutans)
herbivore
An organism that obtains its nutrition by consuming plants or plant material
carnivores
An organism that relies on eating other organisms for nutrition
omnivores
An organism that is adapted to eat both plant and animal material for nutrition
predator
Organism that kills and consumes other organisms
prey
An organism that is hunted, captured and consumed by another organism (predator) as a source of food
parasitism
Relationship where one species benefits and the other is harmed
mutualism
Relationship where both species benefit
commensalism
A relationship where one organism benefits without affecting the other
competition
Interaction between organisms competing for the same limited resource
proboscis
An elongated sucking mouthpart found in insects that is typically tubular and flexible
phytochemicals
Chemical compounds produced in plants
epiphytes
Plants that grow on the surface of other plants using them only for support. For example, orchids
lianas
A climbing plant common to tropical rainforests. They have long winding aerial roots that enable them to climb trees of the rainforest
fundamental niche
The range of environmental conditions in which a particular species can live
realised niche
The environmental condition in which the species actually lives
competitive exclusion principle
States that if two species with identical niches compete, then one will inevitably drive the other to extinction
niche/resource partitioning
The process by which competing species use the environment differently in a way that helps them to coexist. This may be spatial or temporal
carrying capacity
The maximum number of individuals of a species an environment can sustain
reproductive isolation
A mechanism that prevents individuals of different species from mating and producing viable offspring
geographical isolation
The physical separation of populations of a species by geographic barriers, such as mountains, rivers or oceans, which restrict gene flow between populations
behavioural isolation
Type of reproductive isolation in which differences in behaviour, such as mating rituals or courtship displays, prevent individuals from breeding
temporal isolation
Type of reproductive isolation in which individuals of the same species have different mating seasons or times of reproductive activity, preventing them from breeding with individuals from other populations
random sampling
A method of selecting a subset of individuals from a larger population in a way that each individual has an equal chance of being selected
quadrat sampling
Sampling technique in which a quadrat, typically a square or rectangular frame, is placed in a specific area to study the distribution and abundance of organisms within that defined area
quadrat
A square or rectangular frame used for sampling in ecological studies
total abundance
The total number of organisms in all species in an area
sessile
An organism that is fixed to one location
motile
An organism that is able to move its whole body from one location to another
food chain
Feeding relationship where energy passes from producers to consumers
food web
A network of interconnected feeding relationships
keystone species
A species with a disproportionately large effect on its community
domain kingdom phylum class order family genus species
Levels of classification (name all)
Population
A group of organisms of 1 species, living in the same area at the same time
Speciation
Formation of new species by the splitting of one preexisting species into 2 or more new species
Possible causes for species splitting:
Reproductive barriers limiting/preventing interbreeding between 2 populations
Physical barriers prevent interbreeding
Change in behavior/timing around reproductive cycles
Sudden event changes chromosome number, resulting in new species (errors in cell division)
Occurs gradually (take long time after physical splitting of population), with populations slowly showing different traits from selection pressure ---> becoming more and more isolated --> less likely to gene flow --> more clear differences between the populations --> formation of new species
Possible causes for species splitting:
________ barriers limiting/preventing _______ between 2 populations
Physical barriers prevent interbreeding
Change in _____/timing around reproductive cycles
Sudden event changes chromosome number, resulting in new species (errors in cell division)
Occurs ___quickly/gradually____ (take long time after physical splitting of population), with populations slowly showing different traits from selection pressure ---> becoming more and more isolated --> less likely to _____ flow --> more clear differences between the populations --> formation of new species
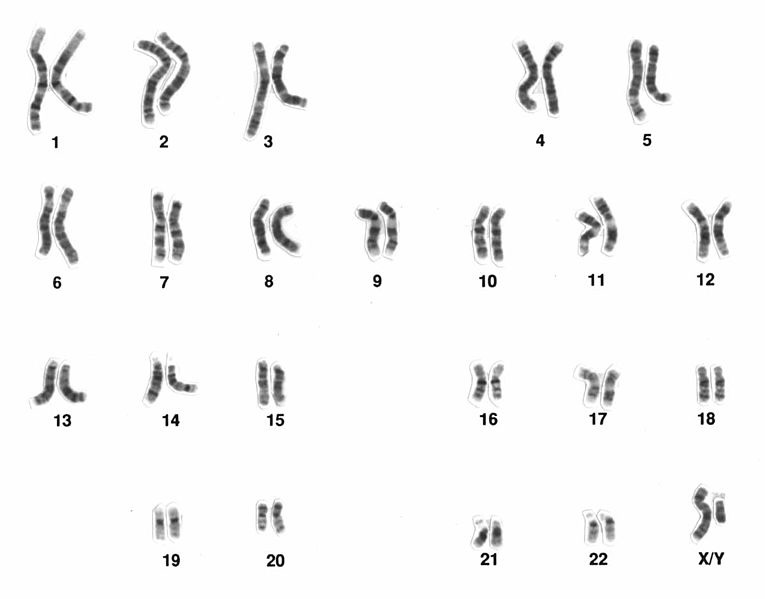
Karyotyping
Isolating condensed chromosomes taken from actively dividing cells, allowing for comparison of chromosomes
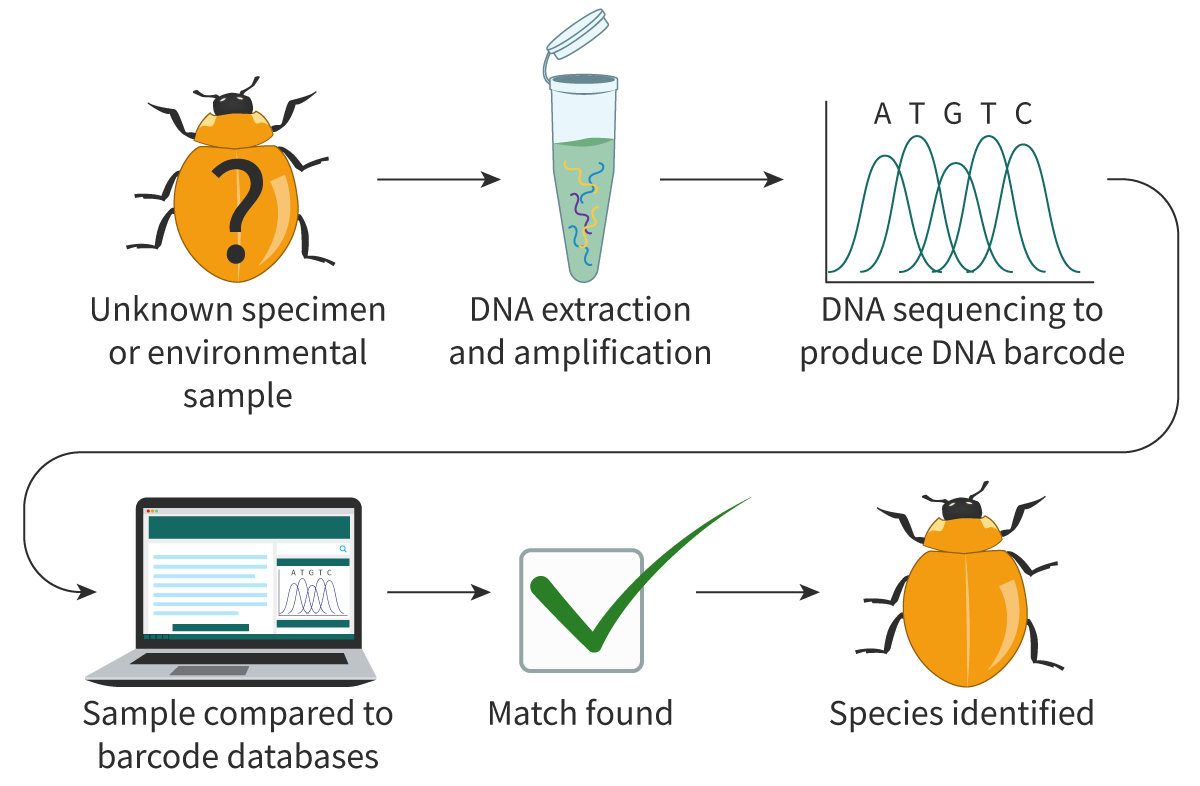
DNA barcoding
Unknown specimen/environmental sample, often water or soil, is collected and DNA is extracted. From the sample, certain specific sequences are identified, creating a unique "barcode" for the specimen
Pros and Cons of eDNA:
Pros: Non-invasive, can detect rare/cryptic species, rapid assessment of large areas cheaply
Cons: DNA degrades, inaccurate gauge of population sizes, potential contamination, won't identify any species not in the database.
Pros and Cons of eDNA:
Pros: Non-_______, can detect ____/cryptic species, _____ assessment of large areas cheaply
Cons: DNA degrades, inaccurate gauge of population _____, potential ___________, won't identify any species not in the database.
Biodiversity
Variety of living organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. Occurs in 3 levels: Genetic, species, and ecosystem.
Genetic, species, ecosystem
Levels of biodiversity: (3)
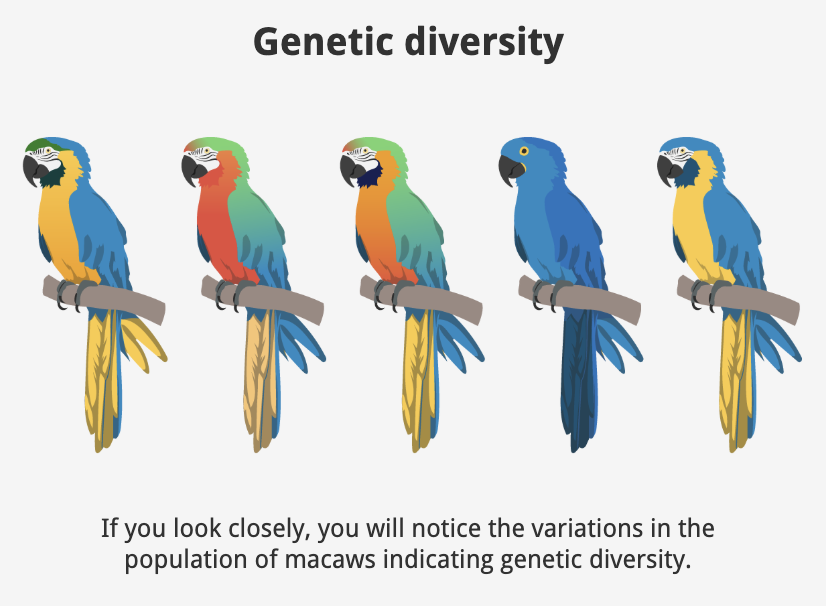
Genetic diversity
Variation of existing genes between individuals of a population, caused by variations in the genes

Species diversity
Variety of species seen in a particular habitat, which influences species diversity. Result of the community of organisms (the biotic) and their interaction with the abiotic environment
species richness and species evenness
Species diversity depends on 2 factors:

Ecosystem diversity
Variety of ecosystems (both terrestrial and aquatic) found in a given geographical area
Ecosystem
Community of organisms and their interaction with the abiotic environment, varying in size.
overexploitation from overhunting and overharvesting
habitat destruction
invasive species
pollution
climate change
Causes of anthropogenic species extinction (5)

Giant moas and carribean monk seal
2 Case studies of anthropogenic species extinction: (2)

Ecosystem Services
The processes and outputs of the ecosystem that directly or indirectly benefit humans.
Supplying resources (water, food, timber, medicine)
Providing basic services essential for survival
Keystone species
A species that plays a critical role in maintaining the structure and functioning of an ecosystem. The presence or absence can significantly impact the overall biodiversity and stability of the ecosystem
Dipterocarp trees and coral reefs
2 case studies of ecosystem services:

IPBES and IUCN
2 databases to identify biodiversity crisis:

In situ conservation
Way of conserving animals and plants in their natural habitat whilst maintaining the original biodiversity of the area
Involves designing, managing, and maintaining areas for the protection of plant and animal species
Conserves plant/animal species AND their habitat
Preserves normal behavior
Prevents disruptions of the food chains
Cost efficient
Ex situ conservation
Plants/animals conserved outside natural habitats
Include zoos, botanical gardens, aquariums
For some species, numbers are too small to sustain species, or risk of poaching is high = Gene banks to store "biodiversity" = storage of germplasm
Seed banks: Dehydrate and cool seeds prior to storage
Tissue banks: Store tissue samples from plants
ex
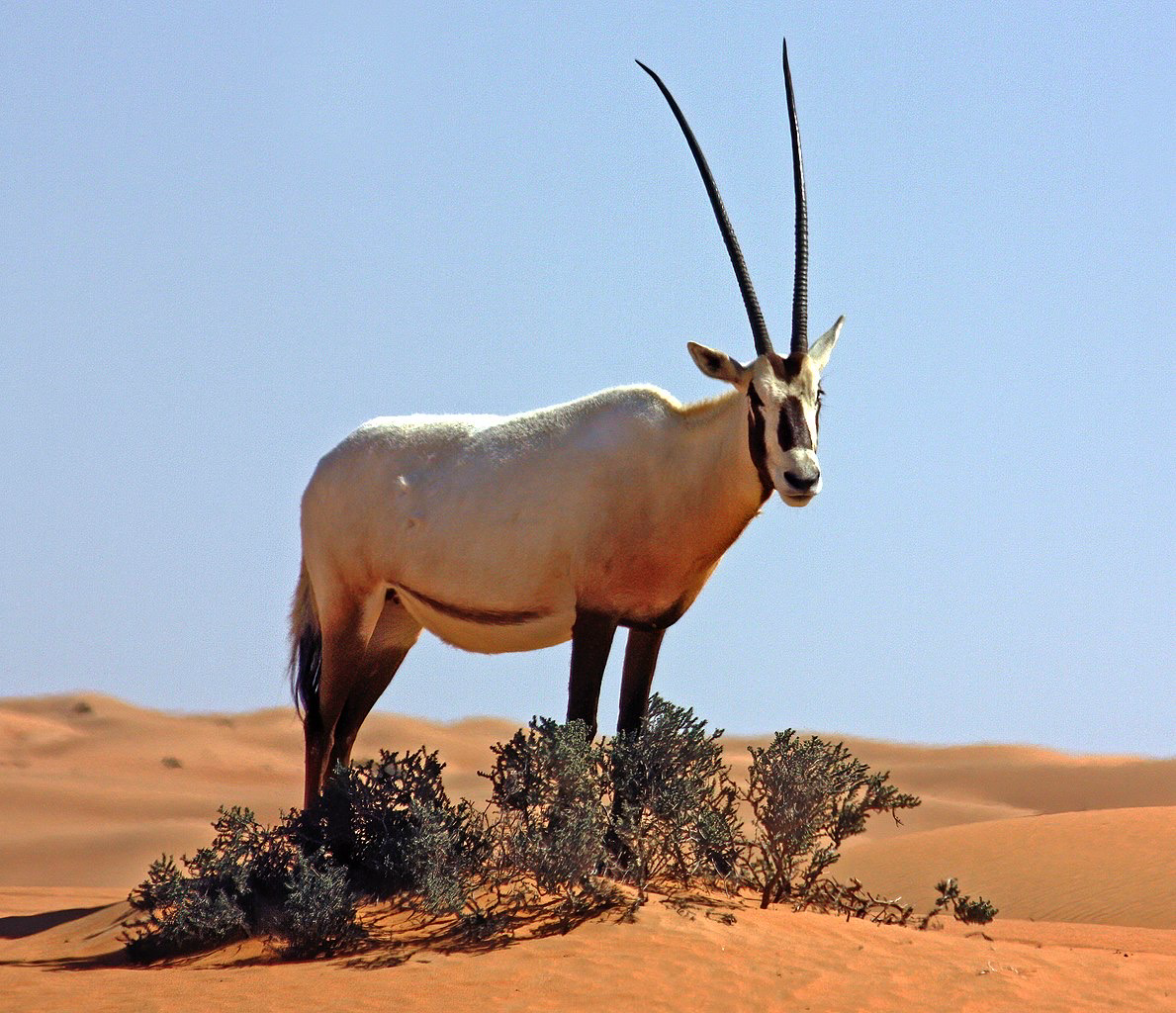
Captive breeding
○ Conservation technique for preventing the extinction of species whose populations are small, fragmented, and on the verge of extinction
○ Encouraged to breed + reintroduced into the wild
○ BUT, small populations = lower genetic diversity = Increased chance of passing on unfit genes
Ex. Arabian oryx: Antelopes existed in zoos, which captive breeding ensured species could be released into the wild

Rewilding
○ Conservation technique by which wildlife and natural processes are allowed to reclaim areas, bringing back biodiversity
○ Habitat is restored to what it would've been if human disturbance hadn't happened
Rewilding happens with human intervention, as plant/animal species that have disappeared from the habitat are reintroduced = Helps rebuild ecosystems
Reclamation of degraded ecosystems
land restoration and management with support from local communities and indigenous people yields higher results as they have a deep knowledge of the land
Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered
EDGE stands for:
Habitat
Place where an organism/group of organisms lives and interacts with its surroundings
Geographical or physical location that provides the necessary resources for an organism's survival and reproduction
Consists of biotic and abiotic factors

Adaptation
Genetic change that increases an organism's chances of survival + reproduction in a particular environment
Can occur randomly via mutation or via selective pressures
Developed to cope with physical/abiotic conditions of habitat (ex. Temp, moisture, light)
Natural selection
Mechanism that drives the spread of beneficial genetic mutations throughout a population
Individuals with advantageous traits more likely to survival and pass on genes to next generation
Over time, advantageous traits become more common in population