Immunology: Ab Genetics
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
How many protein-coding genes do humans have?
20,000
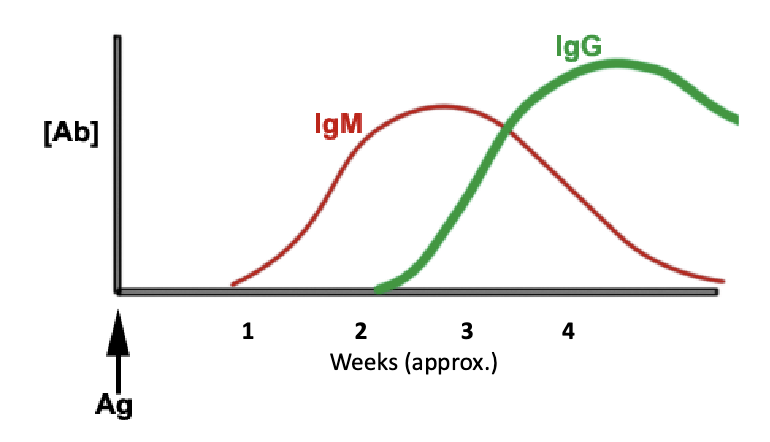
what is the first antibody to appear in a primary response to antigen?
IgM (then transitions to IgG)
recent exposure = IgM
2 months ago or 10 years ago exposure = IgG
what is V(D)J recombination?
lymphocyte-specific process that mediates the recombination of V, D, and J gene segments within antigen receptor loci to give rise to a diverse set of antigen-specific receptors.
The DNA rearrangement mechanism that creates many billions of BCRs and TCRs using relatively few BCR and TCR genes
V(D)J recombination is mediated by two proteins:
RAG-1
RAG-2
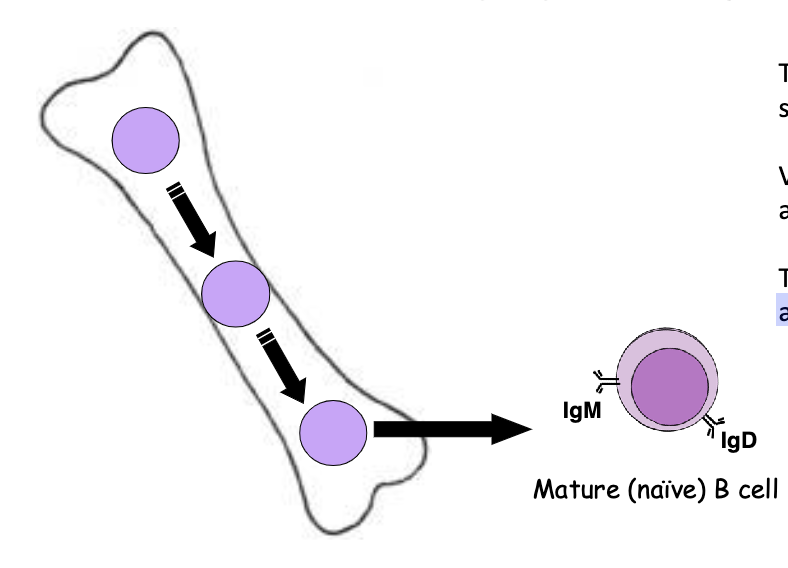
RAG-1 and RAG-2 are expressed only where?
in the 2 primary lymphoid organs:
Developing B cells in bone marrow
Developing T cells in the thymus
V(D)J takes place in the presence/absence of antigen.
absence
t/f: V(D)J is a costly process – most developing B and T cells fail to make a receptor and die
true
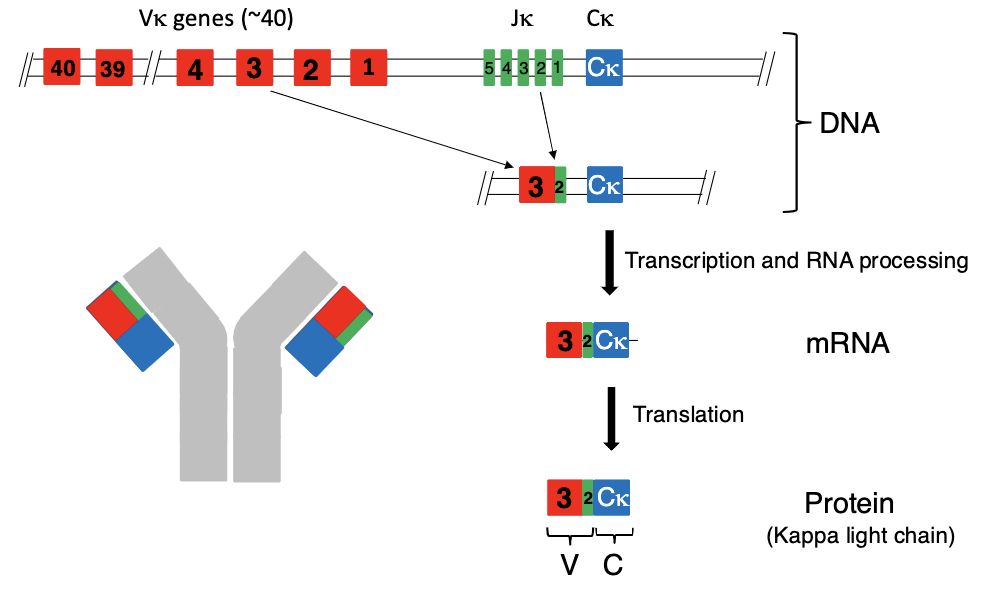
describe the process of V(D)J recombination of the kappa light chain genes
kappa light chain has ~40 V genes and several J genes
these gene randomly recombine to create combiantions then go through transcription/RNA processing and translation
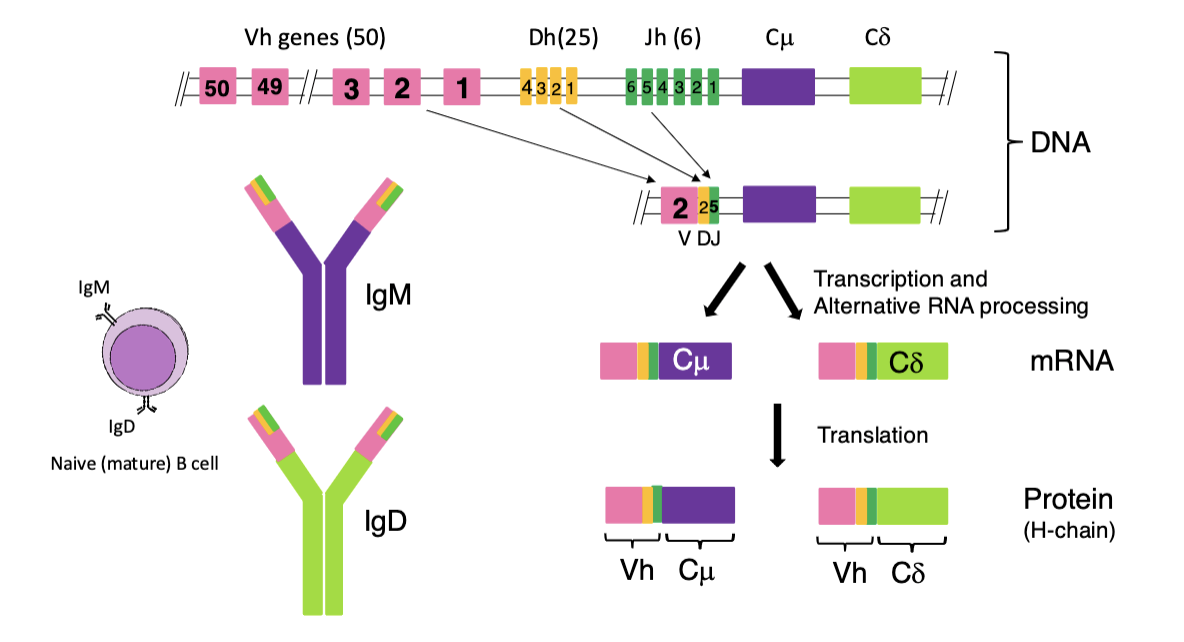
describe the process of V(D)J recombination of the Ig heavy chain genes
(similar to kappa light chain genes but a lil more complicated cuz more genes are involved)
Ig heavy chain has ~50 V genes, 25 D genes, 6 J genes which all randomly recombine to form different combinations
these combinations then go through transcription/alternative RNA processing and translation
what are the different sources of generating antibody diversity?
germline: multiple inherited V, D and J genes
Combinatorial: V + D + J and H + L
Junctional imprecise joining and TdT (TdT = terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase)
this is actually where most of the diversity comes from
WHAT WOULD HAPPEN IF RAG-1 OR RAG-2 IS MISSING?
no adaptive immunity (no B or T cells)
results in SCIDS (severe combined immunodeficiency)
V(D)J recombination takes place in…?
DNA
This means that when a B or T cell undergoes antigen selection, the randomly made receptor is retained in the clone!
in B cells, V(D)J recombination occurs where?
rearrangement of Ig loci (heavy chain) in bone marrow
Igh, and either Ig-kappa or Ig-lambda
in T cells, V(D)J recombination occurs where?
rearrangement of TCR loci in thymus (TCR-alpha and TCR-beta)
after antigen binding, B cells undergo what processes?
somatic hypermutation (SHM)
AND
class switch recombination (CSR)
both somatic hypermutation (SHM) AND class switch recombination (CSR) are mediated by what protein?
AID (activation induced cytidine deaminase)
The strength of binding between an antibody combining site and its epitope is called?
its AFFINITY (association constant)
somatic hypermutation (SHM) leads to..?
affinity maturation via point mutations in Ab variable regions AND antigen competition
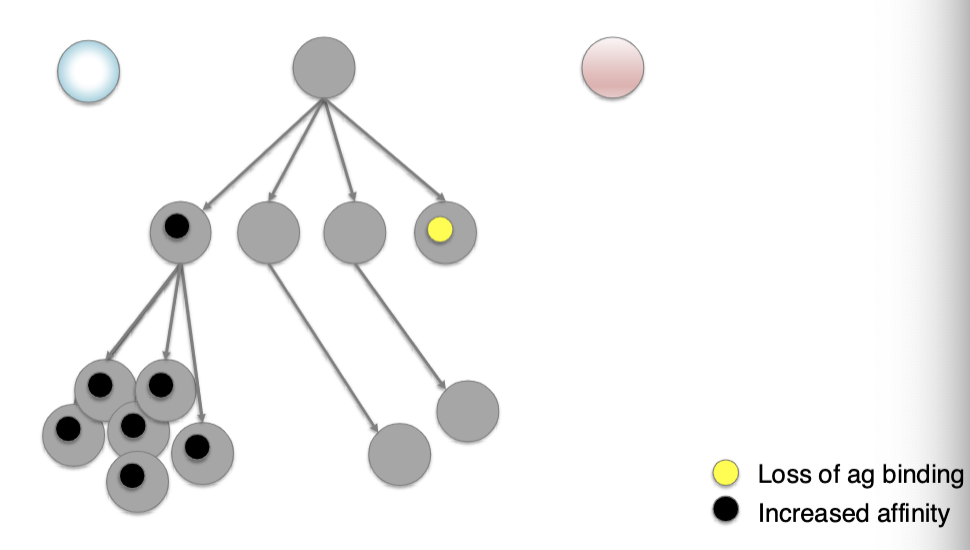
The average affinity of an antibody response can increase ____-fold over time due to SHM
and selection
100 to 1000
what is class switch recombination (CSR)?
A genetic process of changing isotypes.
CSR and SHM occur during…?
clonal expansion of B cells in germinal centers of secondary lymphoid organs
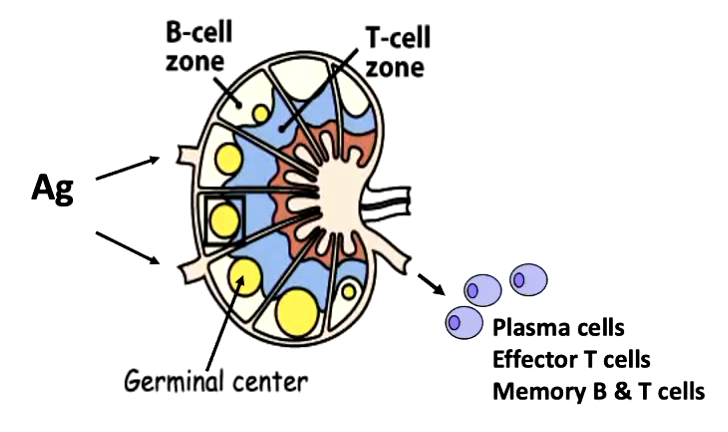
do T cells undergo CSR or SHM?
no
A defect in AID results in:
– Limited class-switching to IgG, IgA, IgE
– Limited production of high-affinity antibodies
– High IgM levels
AID deficiency represents one form of…?
hyper-IgM syndrome
describe the process of class switch recombination (CSR).
allows B cells to change the antibody class they produce (e.g., from IgM to IgG, IgA, or IgE) without altering the antigen specificity. This process is guided by helper T cells, cytokines, and the enzyme AID, which introduces DNA breaks at switch regions to remove intervening constant region genes. The result is an antibody better suited to specific immune functions, such as neutralization, mucosal defense, or allergy responses.
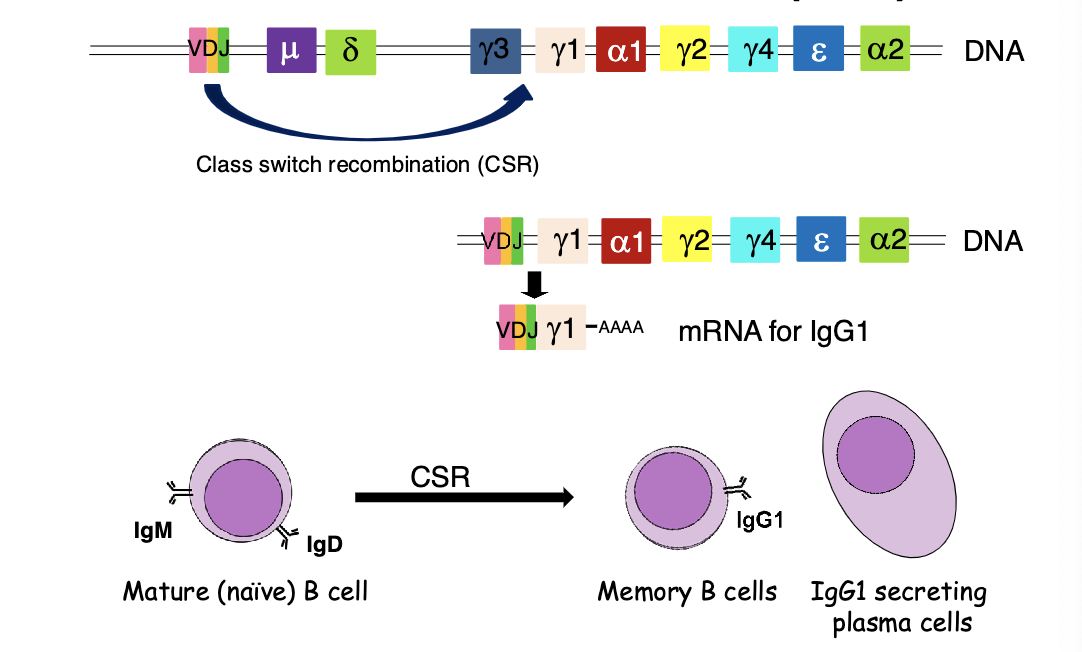
does class switch recombination (CSR). occur before or after antigen exposure?
after
WHAT WOULD HAPPEN IF AID DOES NOT WORK?
after exposure to antigen, class switch recombination (CSR) can’t happen. antibody can’t be made better/more efficient. instead, they’ll make lots and lots of what they can make (IgM) but that means they can’t perform any of the other processes that don’t work great w IgM
what is a treatment for hyper IgM syndrome?
IVIg (intravenous immunoglobulin)
The great diversity of BCRs (Ig) and TCRs is created by the process of
V(D)J recombination
what happens to B cells and T cells that are activated by antigen?
they proliferate (clonal expansion) and differentiate into effector cells and memory cells.
what type of immunity can rapidly evolve high affinity antibodies via SHM and selection (“survival of the fittest” = B cells making high-affinity BCR)
humoral
SHM and CSR occur in germinal centers only in __ cells that have been stimulated by antigen and have received signals from __ cells
B
T