R3.4.11 Electrophilic addition reactions & Markovnikov's rule
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Electrophilic Addition
Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition due to the high electron density in the C=C bond
the π bond breaks, allowing new atoms to bond, forming a larger molecule.
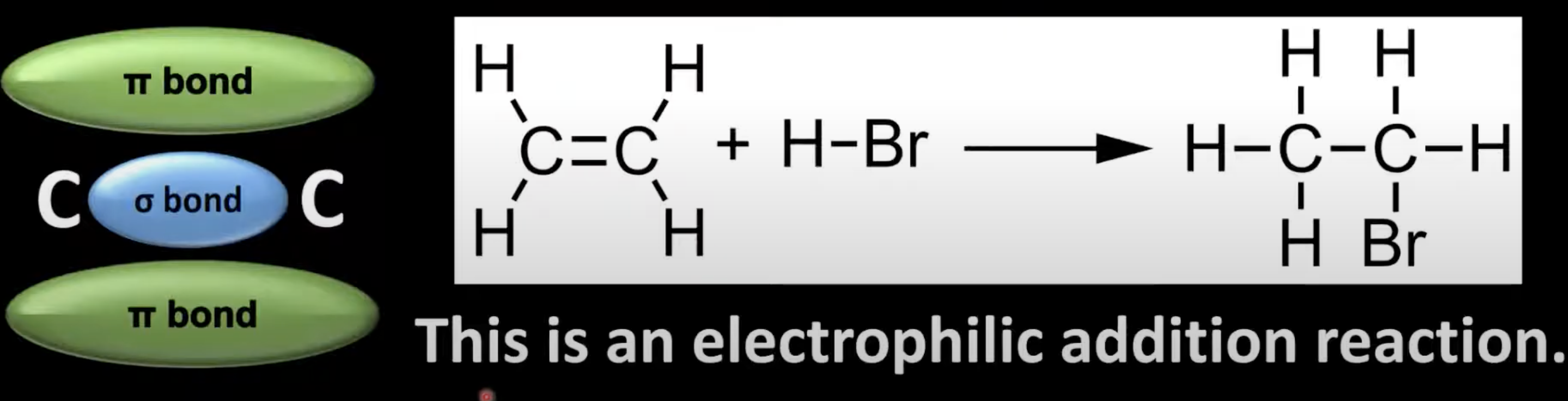
Electrophile approaches the C=C bond; heterolytic fission occurs
π electrons form a bond with electrophile, generating a carbocation intermediate.
Anion formed from fission uses a lone pair to bond with the carbocation
Product is a saturated molecule with added atoms.
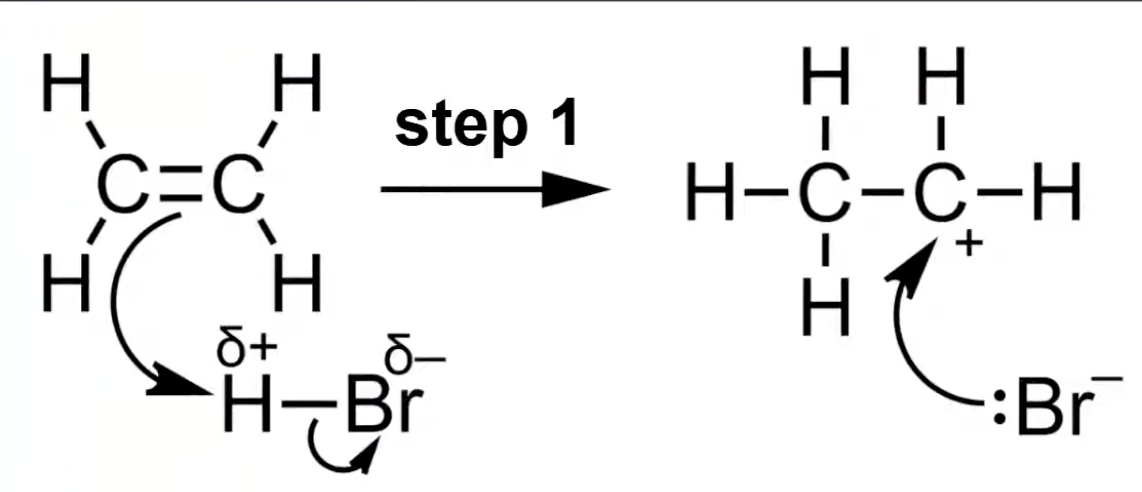
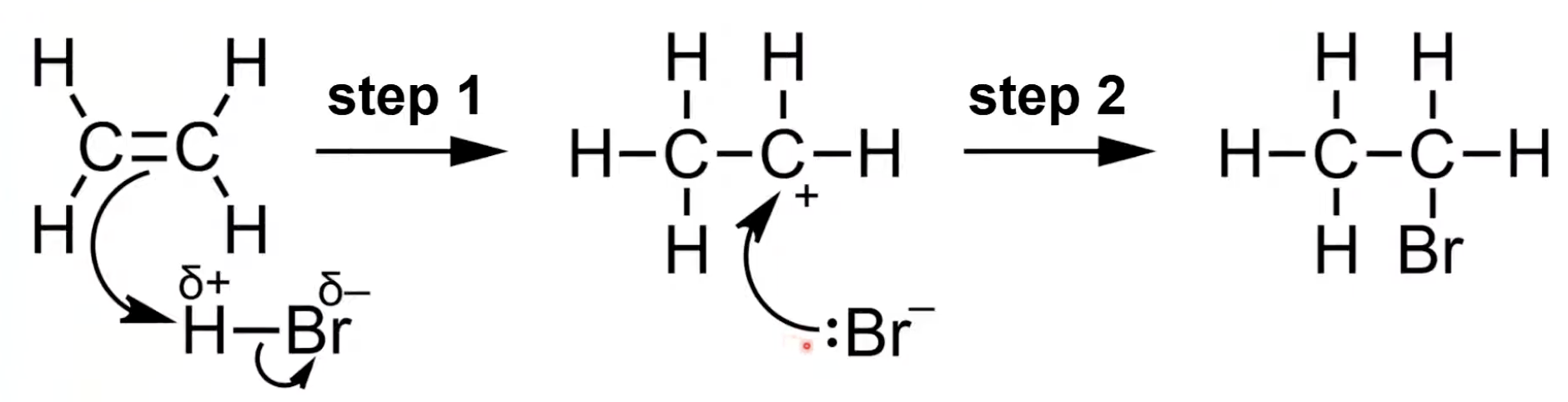
HBr is polar
H bonds with one carbon forming a carbocation
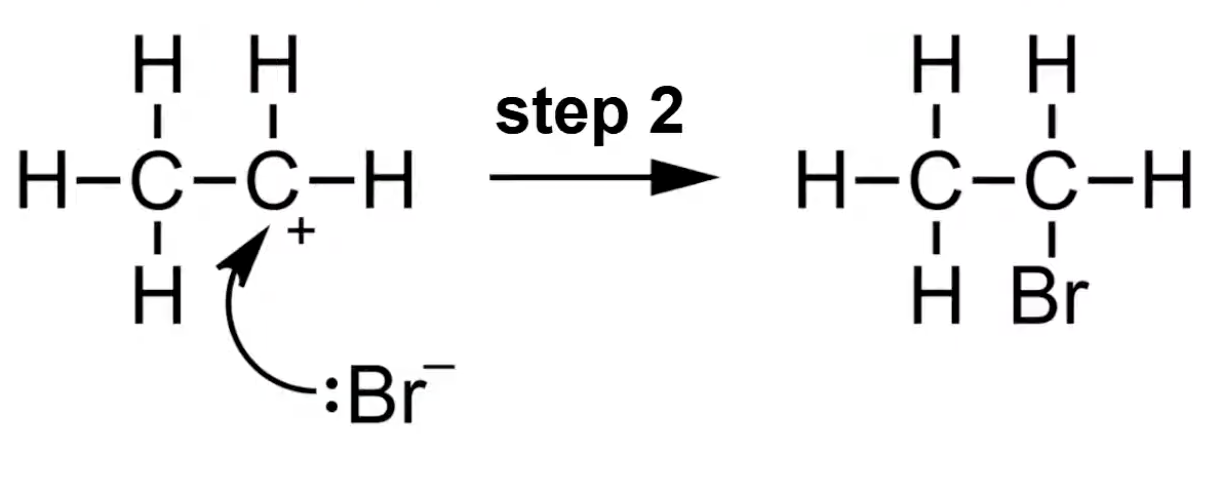
Br⁻ attacks carbocation to form bromoethane.
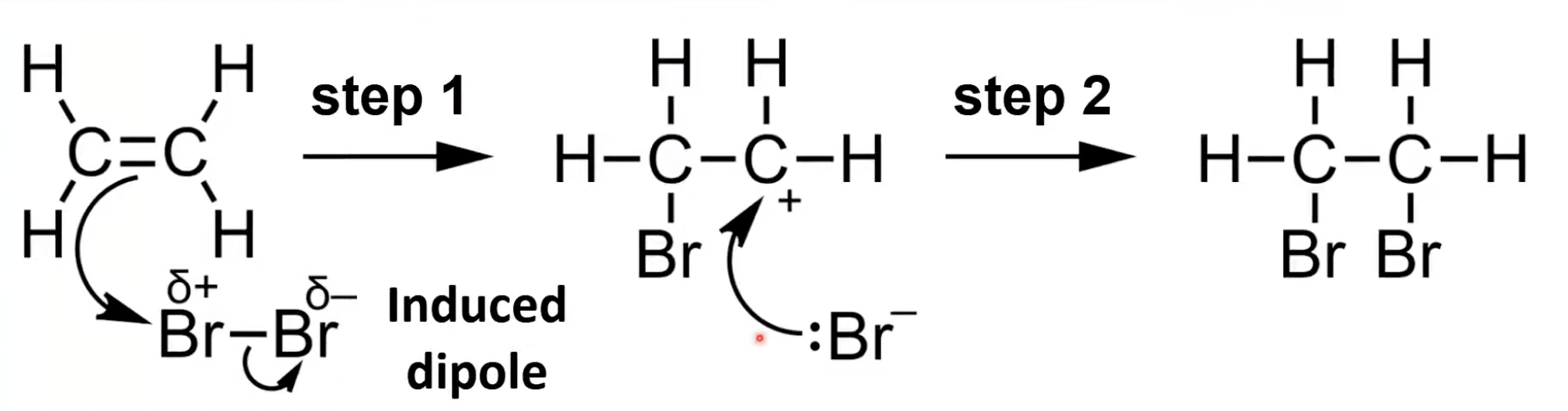
Br₂ becomes polar near C=C; Br bonds to one carbon forming a carbocation
Br⁻ attacks carbocation forming 1,2-dibromoethane.
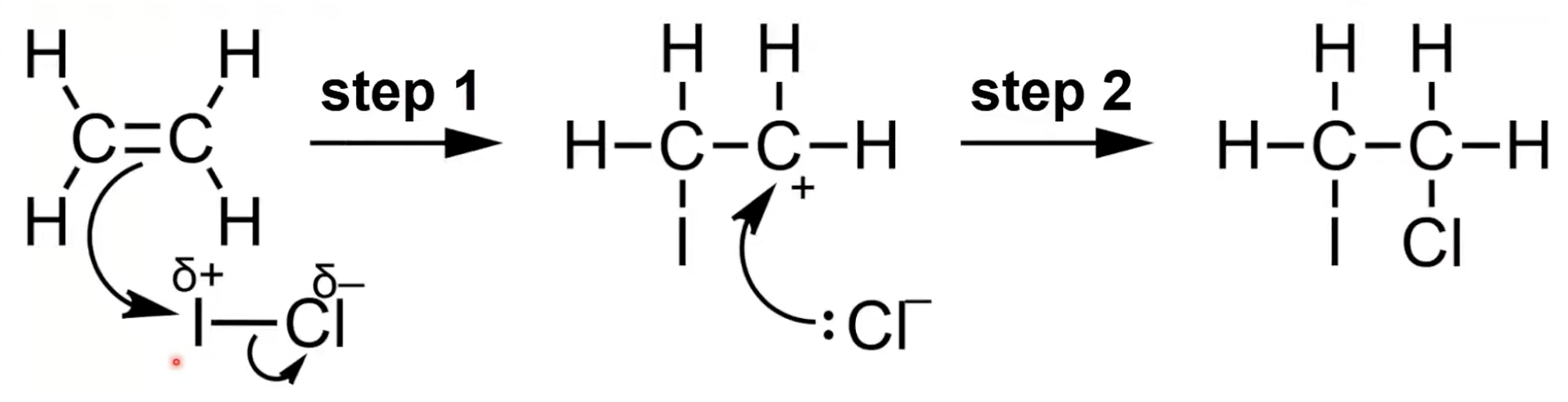
ICl is polar
I bonds to one carbon forming a carbocation
Cl⁻ bonds with carbocation forming 1-chloro-2-iodoethane.
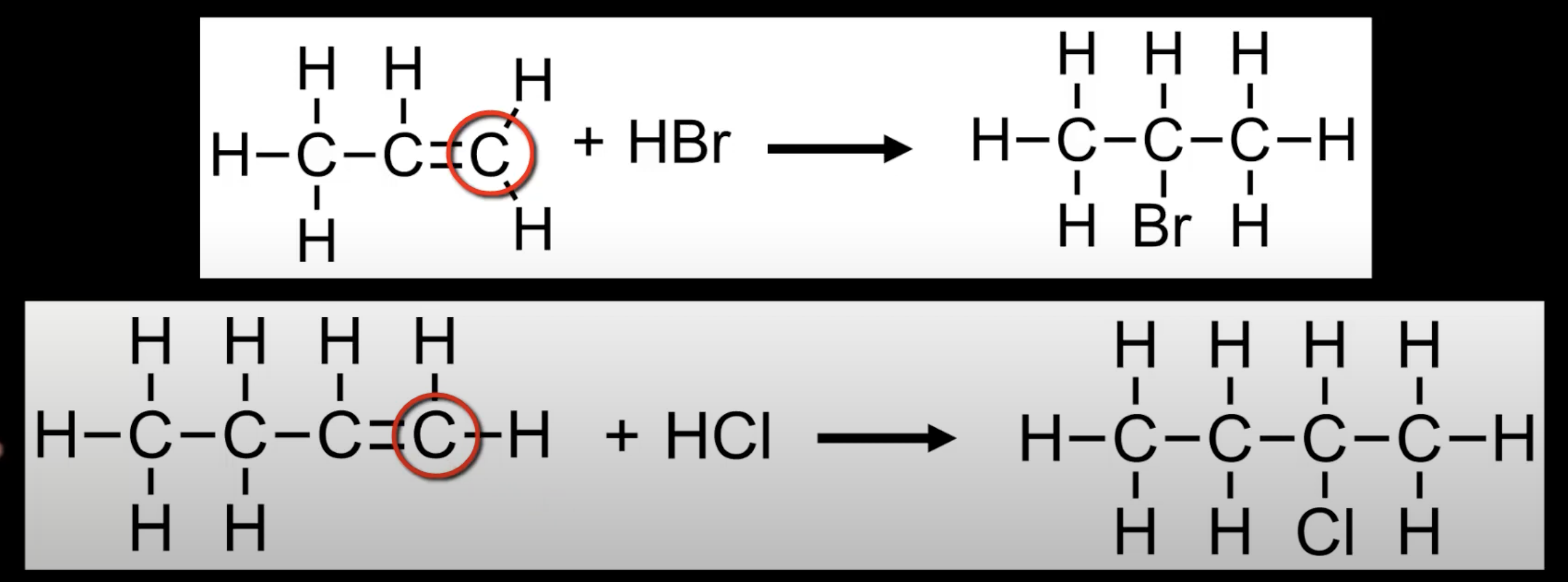
In electrophilic addition of HX to an asymmetrical alkene, the H adds to the carbon with more hydrogens.
The major product forms via the more stable carbocation intermediate.
Applies when predicting regioselectivity of unsymmetrical alkenes.
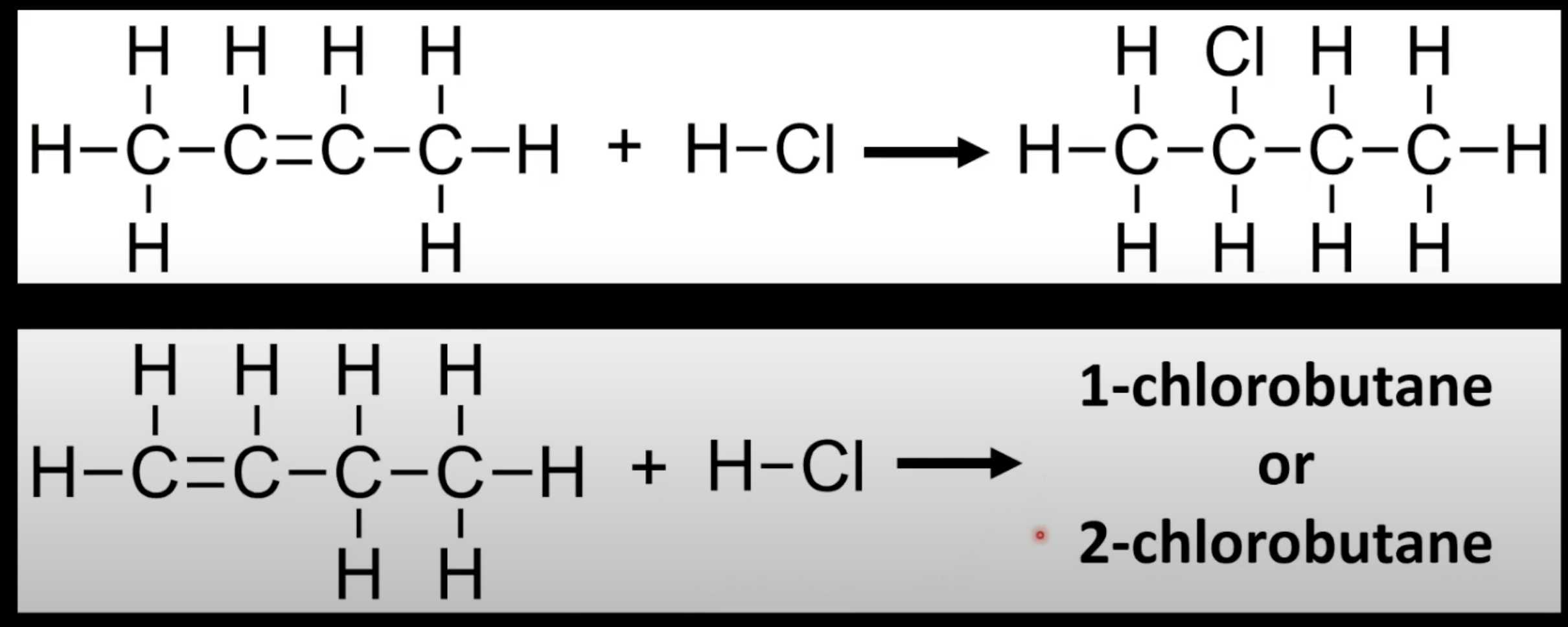
Alkenes like propene reacting with HBr can form two products.
According to Markovnikov's Rule, the major product has H on the more H-rich carbon.
Stability of the intermediate carbocation determines the major product.
More stable carbocations lead to the major product in addition reactions.
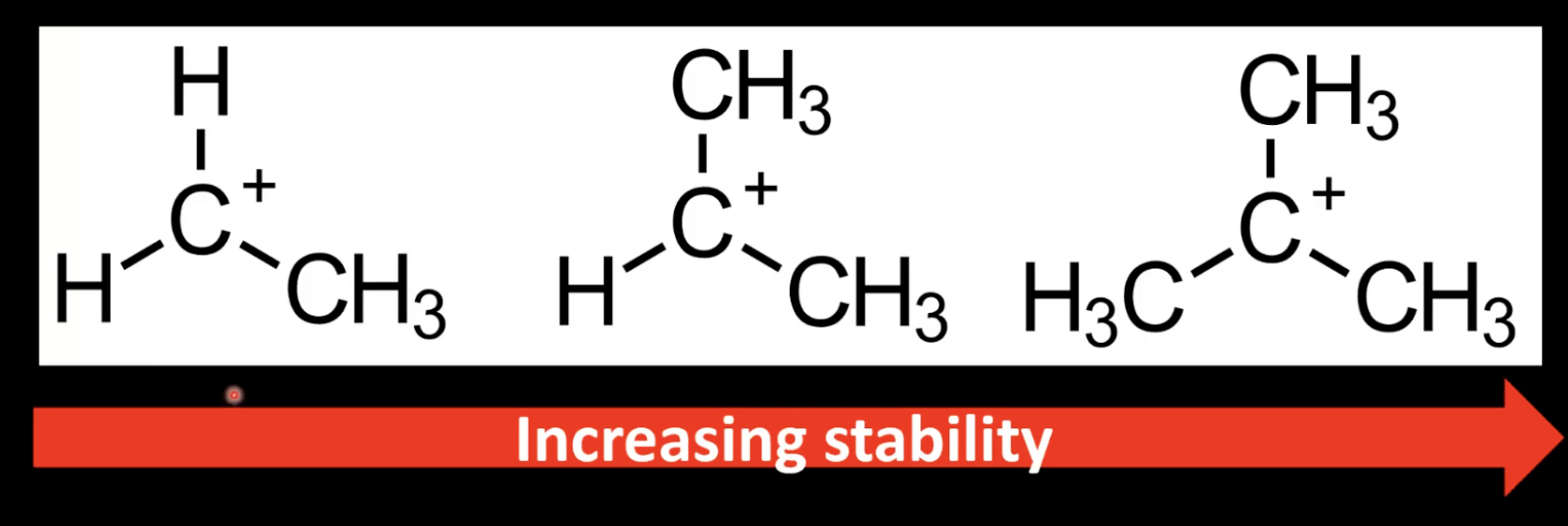
Stability order: tertiary > secondary > primary.
Electron-donating alkyl groups stabilize carbocations via inductive effect.
In electrophilic addition, the H-X bond breaks heterolytically forming X⁻
H⁺ adds to the alkene carbon forming a carbocation
X⁻ then bonds to the carbocation forming the final product.
Two possible products
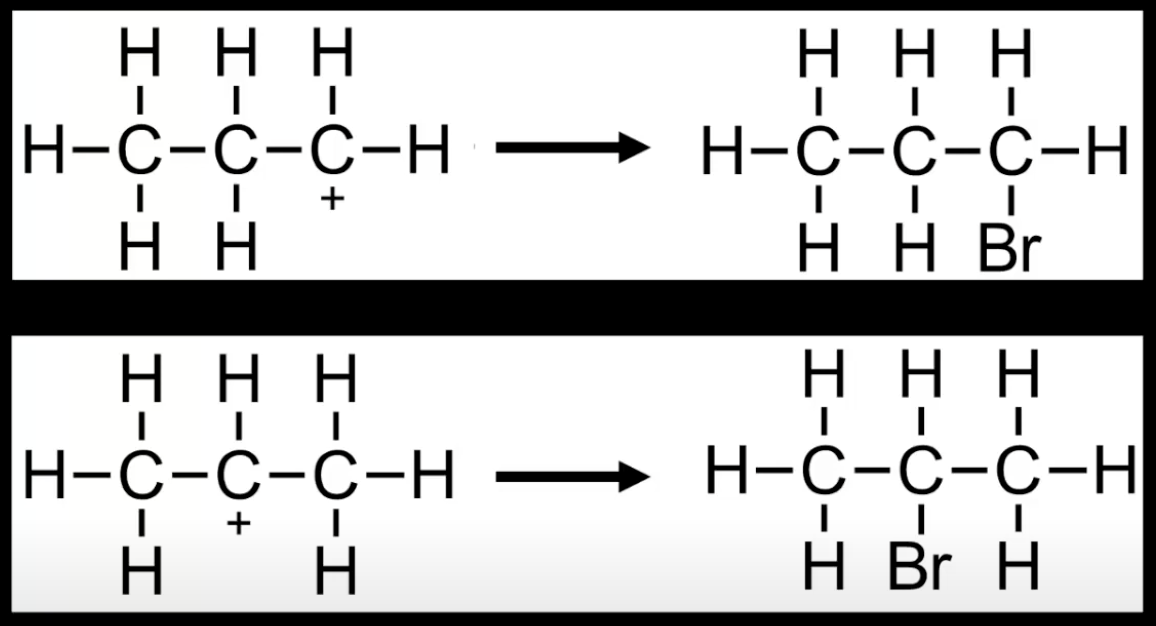
1-bromopropane (from primary carbocation)
2-bromopropane (from secondary carbocation)
2-bromopropane is the major product due to carbocation stability.
Alkyl groups donate electron density stabilizing carbocations.
More alkyl groups mean greater carbocation stability.
Explains why tertiary carbocations are most stable.