Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders Overview
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Anxiety disorder with obsessions and compulsions.
Obsessions
Intrusive thoughts, urges, or images causing distress.
Compulsions
Repetitive behaviors performed to reduce anxiety.

Hoarding Disorder
Persistent difficulty discarding possessions, leading to clutter.
Trichotillomania
Hair pulling disorder, often linked to stress.
Excoriation Disorder
Skin picking disorder, resulting in skin damage.
Lifetime Prevalence
2.5% of the population affected by OCD.
Chronic Course
Only 20% of individuals recover completely.
Early Onset
OCD often begins before age 14.
Gender Ratio
2:1 female to male prevalence in OCD.
Common Obsessions
Contamination and aggression are frequently reported.
Common Compulsions
Checking and washing are typical compulsive behaviors.
Comorbidity
75% have comorbid anxiety disorders with OCD.
Biological Etiology
Dysregulation in brain regions affecting impulses.
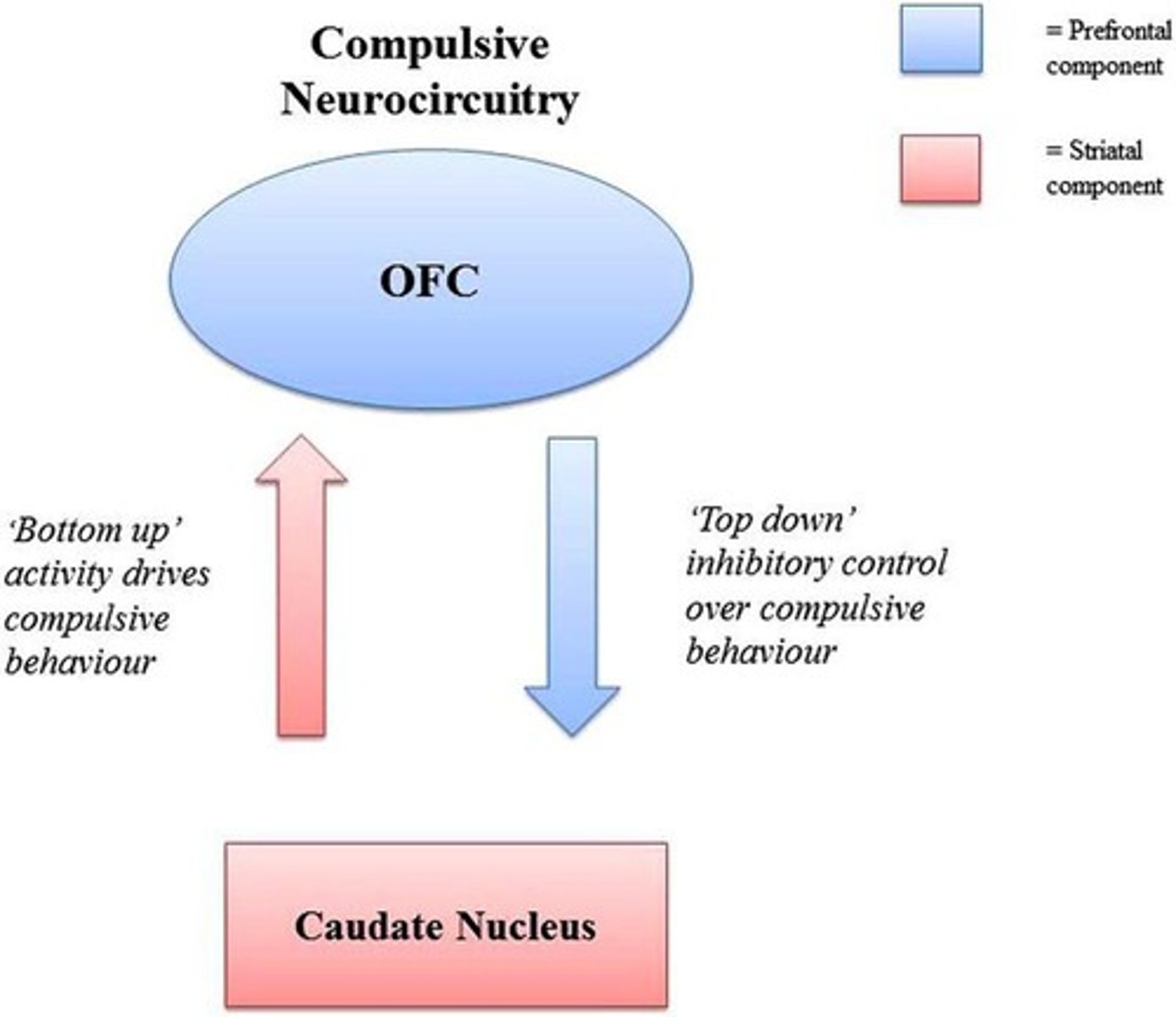
Orbitofrontal Cortex (OFC)
Brain region involved in impulse regulation.
Cingulate Gyrus
Connects OFC to the caudate nucleus.
Caudate Nucleus
Part of basal ganglia, involved in behavior.
Hyperactive Circuit
OFC to caudate loop remains active in OCD.
Serotonin Levels
May be low in areas related to OCD.
Cognitive-Behavioral Etiology
Negative thoughts persist due to rigid thinking.
Yedasentience
Subjective feeling of completion in thoughts/actions.
Thought-Action Fusion
Belief that thoughts can cause actions.
OCD
Anxiety disorder characterized by intrusive thoughts.
Suppression
Attempting to stop unwanted thoughts or actions.
SSRIs
Medications improving OCD symptoms by 25-75%.
Cingulatomy
Psychosurgery targeting OFC-Caudate circuit for OCD.
Deep Brain Stimulation
Treatment involving stimulation in basal ganglia.
Exposure & Response Prevention
Therapy combining exposure to fears and preventing compulsions.
Exposure
Gradual exposure to feared thoughts or situations.
Response Prevention
Actively preventing compulsive behaviors in therapy.
Magical Thinking
Belief that thoughts can influence reality.
Family Accommodations
Family members easing OCD fears, hindering treatment.
Relapse Rates
High likelihood of OCD symptoms returning post-treatment.
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
Preoccupation with perceived defects in appearance.
Repetitive Behaviors
Actions like mirror checking in BDD response.
Ideas of Reference
Belief others are focused on one's perceived defect.
Suicidal Ideation
Thoughts of suicide common in BDD (33%).
Epidemiology of BDD
2% prevalence, more common in women.
Onset of BDD
Usually begins in adolescence, chronic course.
Comorbidity
High overlap of BDD with OCD (33%).
Cognitive-Behavioral Factors
Decision-making deficits contribute to Hoarding Disorder.
Hoarding Disorder
Difficulty discarding possessions, regardless of value.

Accumulation of Items
Leads to cluttered living spaces in hoarding.
Prevalence of Hoarding
Affects 1.5-2.6% of the population.
Childhood Onset
Hoarding begins in childhood or early adolescence.
Squalid Living Conditions
Poor hygiene and safety issues from hoarding.
Indecisiveness
Difficulty making decisions due to perfectionism.
Poor organizational abilities
Struggles with arranging tasks or items effectively.
Categorization difficulties
Challenges in classifying objects into categories.
Memory confidence
Lack of trust in one's memory capabilities.
Hoarding Disorder
Compulsive accumulation of possessions and inability to discard.
Emotional attachment to possessions
Strong feelings tied to inanimate objects.
Identity and possessions
Objects perceived as integral to self-identity.
'Just in case' items
Keeping items for potential future needs.
Avoidance behaviors
Actions taken to evade anxiety-inducing situations.
Motivational strategies
Techniques to encourage clients to acknowledge symptoms.
SSRIs
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for treating anxiety.
Exposure & Response Prevention (ERP)
Therapy focusing on facing fears and stopping rituals.
Comorbidity
Co-occurrence of multiple disorders in individuals.
OCD
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder characterized by intrusive thoughts.
BDD
Body Dysmorphic Disorder focused on perceived flaws.
PTSD
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder from traumatic experiences.
Acute Stress Disorder
Symptoms following trauma lasting 3 days to 1 month.
Intrusion symptoms
Recurrent memories or flashbacks of traumatic events.
Avoidance symptoms
Efforts to evade distressing thoughts or reminders.
Negative alterations in cognition
Changes in thoughts or mood after trauma.
Alterations in arousal
Increased reactivity or heightened alertness post-trauma.
Clinically significant distress
Symptoms causing notable impairment in daily functioning.
Avoidance
Efforts to evade distressing reminders of trauma.
Inability to remember
Failure to recall significant aspects of trauma.
Negative beliefs
Persistent distrust in self or others.
Excessive blame
Overly attributing fault for trauma consequences.
Negative emotional state
Chronic feelings of fear, guilt, or shame.
Diminished interest
Loss of enthusiasm for previously enjoyed activities.
Detachment
Feeling disconnected from others emotionally.
Inability to experience positive emotions
Persistent lack of joy or happiness.
Hypervigilance
Heightened state of alertness and anxiety.
Sleep difficulties
Problems with falling or staying asleep.
Irritability
Frequent anger outbursts or frustration.
Self-destructive behavior
Engaging in reckless or harmful actions.
Difficulty concentrating
Struggling to maintain focus on tasks.
Exaggerated startle response
Overreacting to unexpected stimuli.
Lifetime prevalence
7% of population experiences PTSD.
Acute PTSD
Symptoms lasting less than 3 months.
Chronic PTSD
Symptoms persisting for over 3 months.
Delayed onset PTSD
Symptoms appearing more than 6 months post-trauma.
Risk factors
Elements increasing likelihood of developing PTSD.
Personality traits
Characteristics like neuroticism impacting PTSD risk.
Coping styles
Methods of dealing with stress and trauma.
Biological mechanisms
Neurological factors contributing to PTSD symptoms.
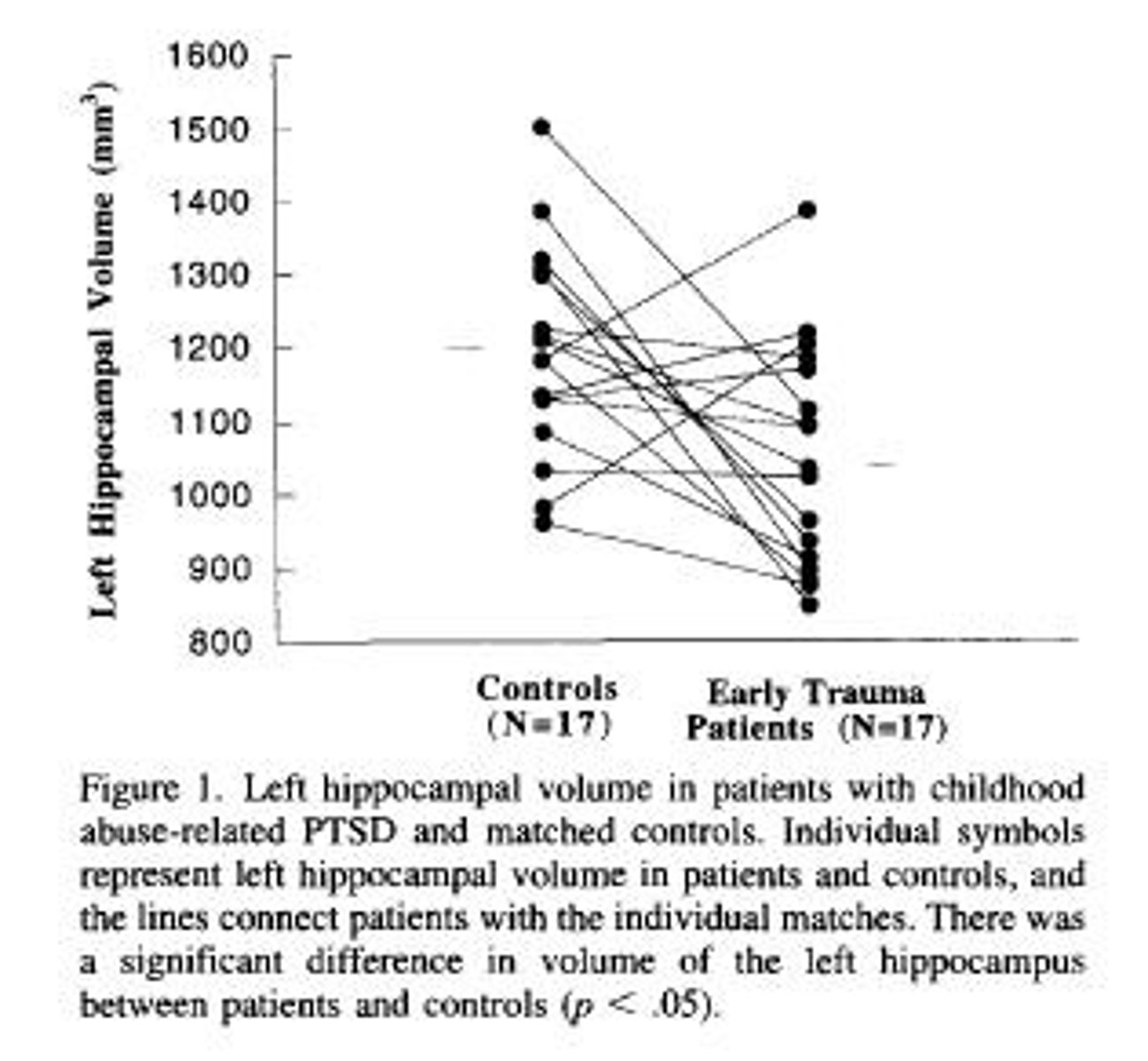
Hippocampus function
Involved in organizing autobiographical memories.
Pharmacological treatments
Medications like SSRIs used for PTSD management.
Cognitive restructuring
Changing negative thoughts to more positive ones.
Exposure therapy
Systematic desensitization to trauma-related memories.
Eye Movement Desensitization
Therapy combining eye movements with trauma processing.