Chapter 4 - Schizophrenia and Psychosis
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Paralytic Dementia Behavioural & Neurological Symptoms
Delusions
Grandiosity
Euphoria
Poor Judgement
Argyll-Robertson pupil
Syndrome Definition
Clinically significant disturbance cognitively, emotionally or behaviourally.
Psychosis
Hallucinations or delusions and the person doesnt feel anything is wrong with them
Schizophrenia Positive Symptoms
Delusions
Hallucinations
Disorgonised Thinking
Schizophrenia Negative Symptoms
Alogia
Affective Blunting
Asociality
Anhodenia
Avolition
Negative versus Positive Symptoms
Negative symptoms are a deficit and take away from an experience; positive symptoms add to an experience.
Explain the process of dopamine production
A reuptake pump transports tyrosine into the cell, and a two-step enzymatic process occurs to make dopamine. VMAT then moves dopamine into vesicles for dopamine to fuse and move into the synaptic cleft.
Explain dopamine termination
MOA A or B re-packages dopamine into vesicles, and COMT is an enzyme that can inactivate dopamine.
What does the D2 receptor do?
This autoreceptor will tell the presynaptic neuron to stop sending dopamine into the synaptic cleft.
What are the four dopamine pathways?
Mesolimbic
Mesocortical
Nigrostriatal
Tuberoinfundibular
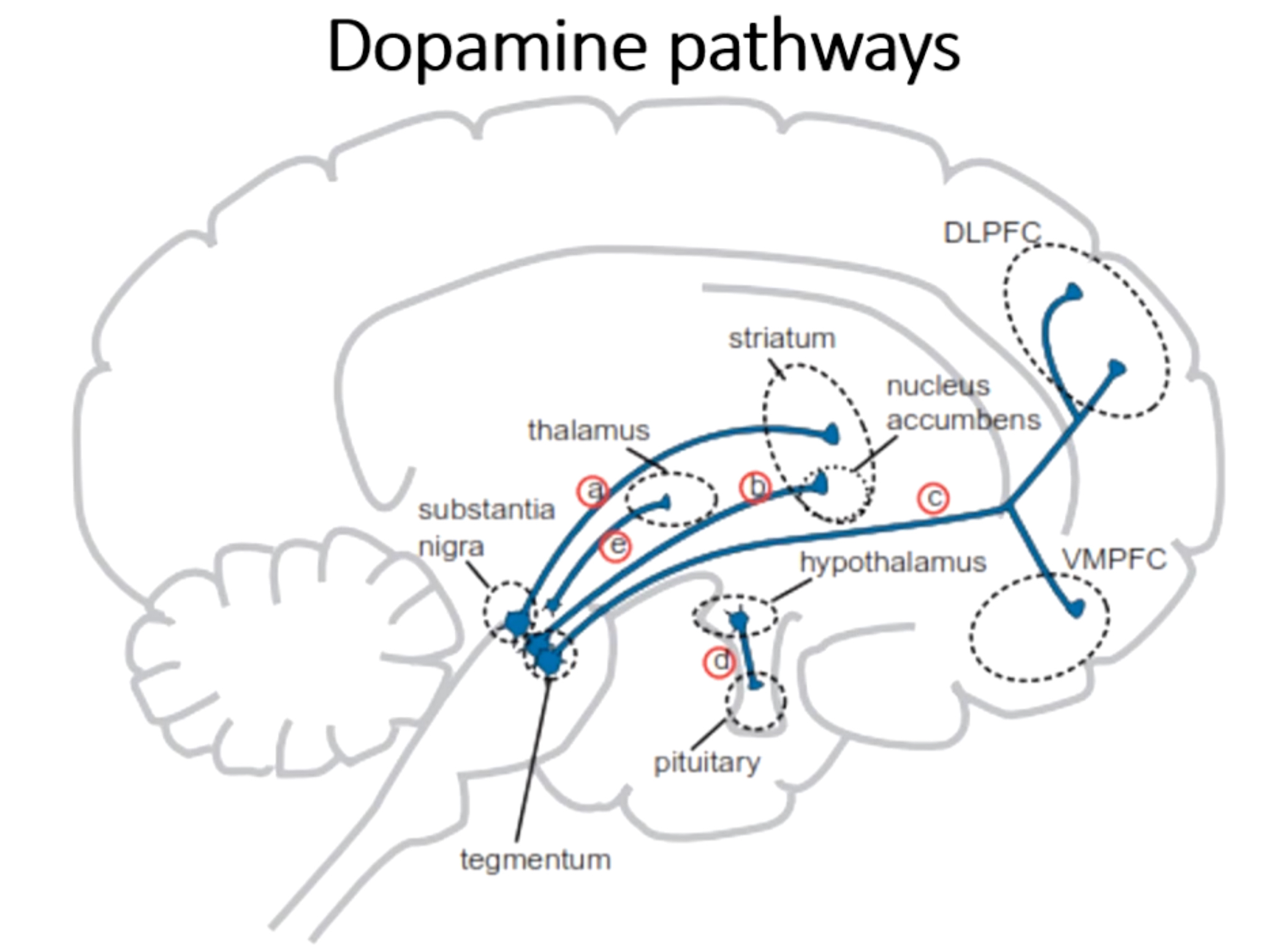
What is pathway b?
Mesolimbic pathways from the VTA → nucleus accumbeans
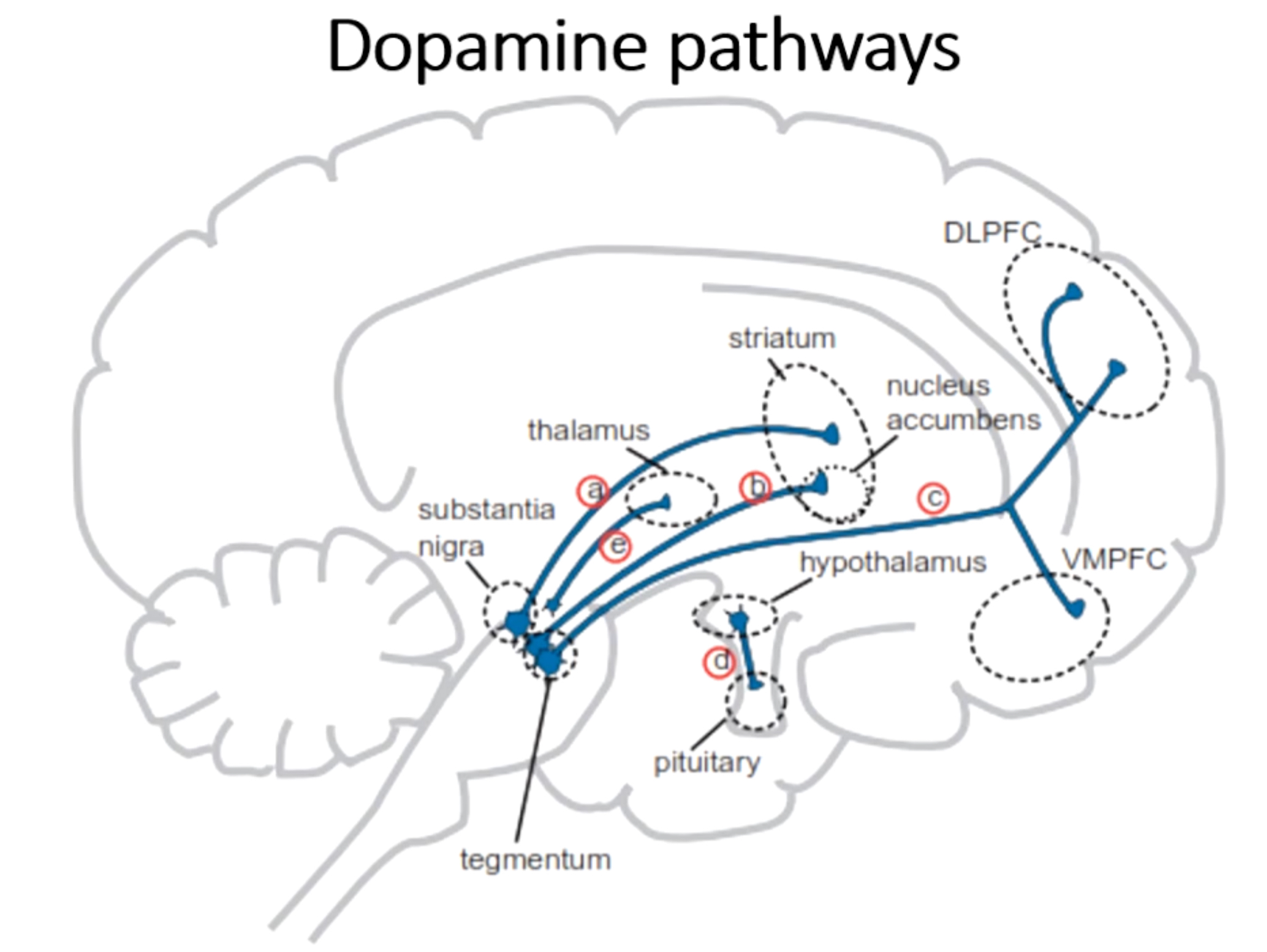
What is pathway c?
Mesocortial pathway from VTA → frontal cortex (DLPFC and VMPFC)
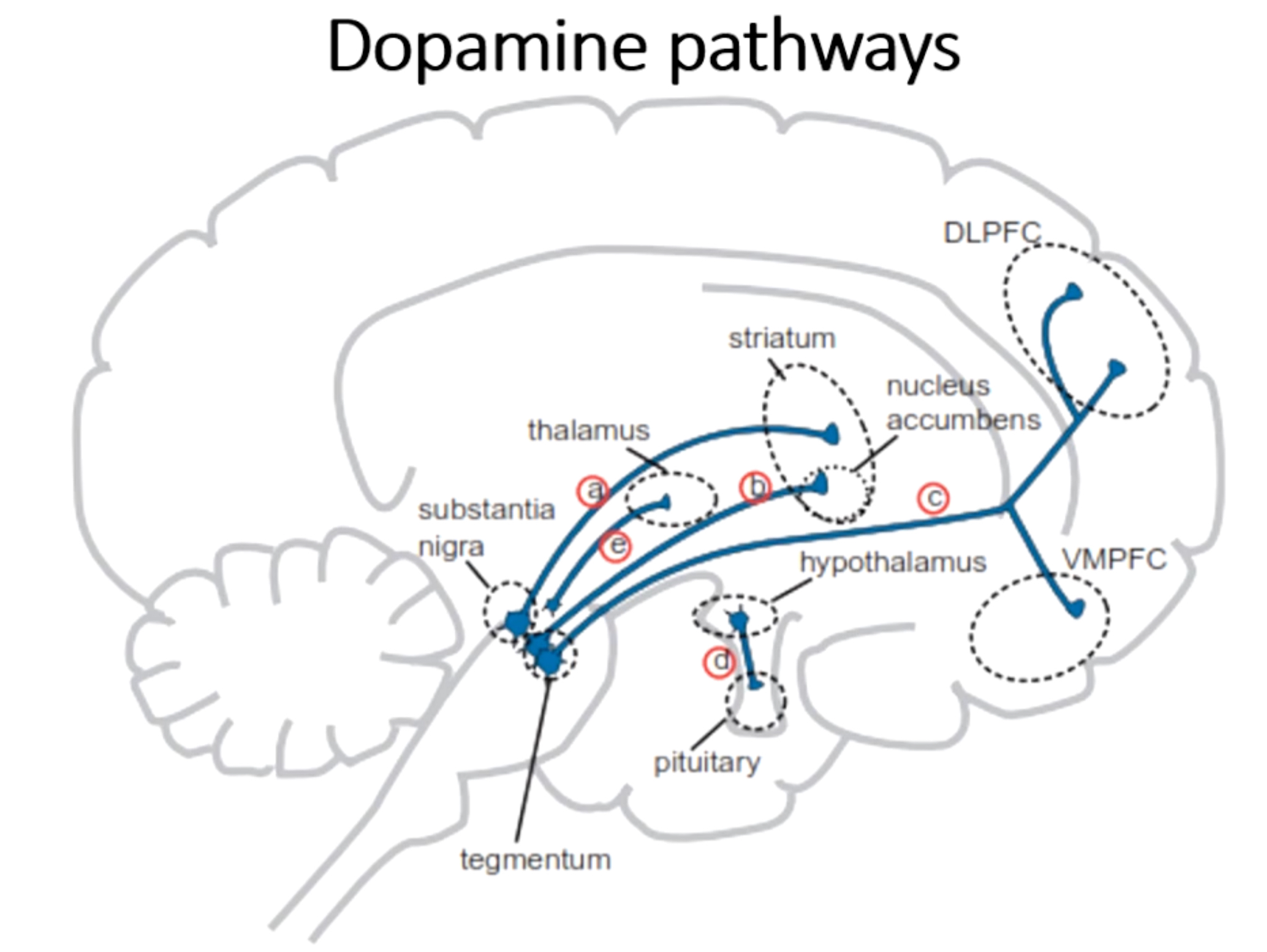
What is pathway a?
Nigrostriatal pathway
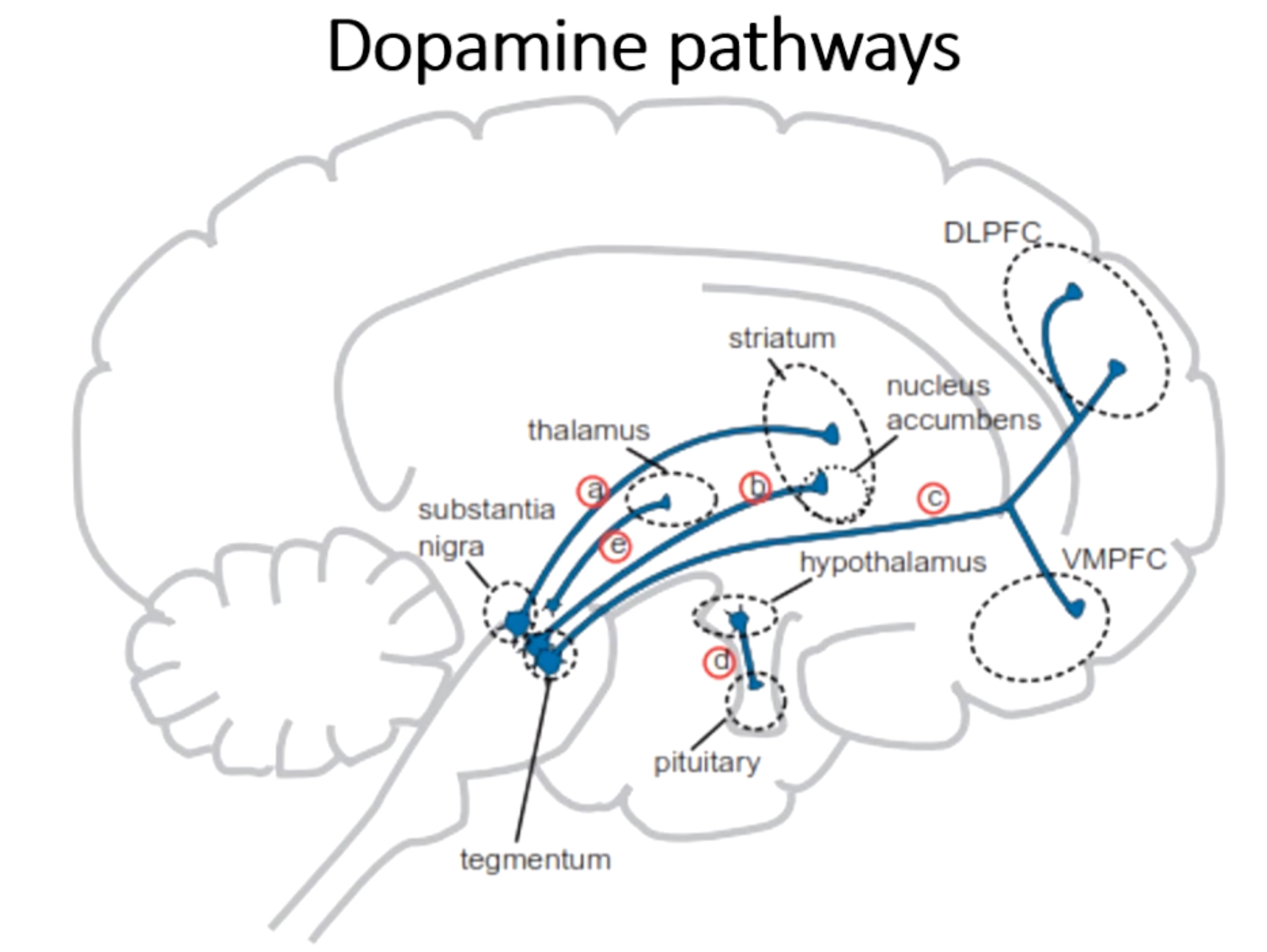
What is pathway d?
Tuberoinfundibular pathway
Explain the Mesolimbic Dopamine Hypothesis of Positive Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Too much activation of dopamine on this pathway is lead to show increased posiitve symptoms of schizophrenia
Explain the Mesocortical pathway projections for dopamine and schizophrenia.
This is from the VTA → frontal cortex, if there are difficulties in projections along this pathway, we can see negative symptoms of schizophrenia
What do low levels in the Nigrostriatal pathway and Tuberoinfundibular pathway cause?
Galactorea and Parkinsons
What is the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain?
Glutamate
What are the main receptors for glutamate in schizophrenia?
NMDA
AMPA
Kainate
Explain the NMDA recpetor.
Glutamate and an co-neurotransimtter are needed, but this isnt enough to open channel. Magneium (M++) is blocking and needs to be removed.
What causes the removal of M++ in the NMDA channel?
AMPA and Kainate receptors are activated, which depolarizes membranes and sends Na+ out, which removes Mg++
What does long term NMDA activation lead to?
Long term memeory processing and synaptogenisis
What can be a cause of NMDA hyperactivation?
This is what we believe causes the overactivation of dopamine and, therefore, positive symptoms.
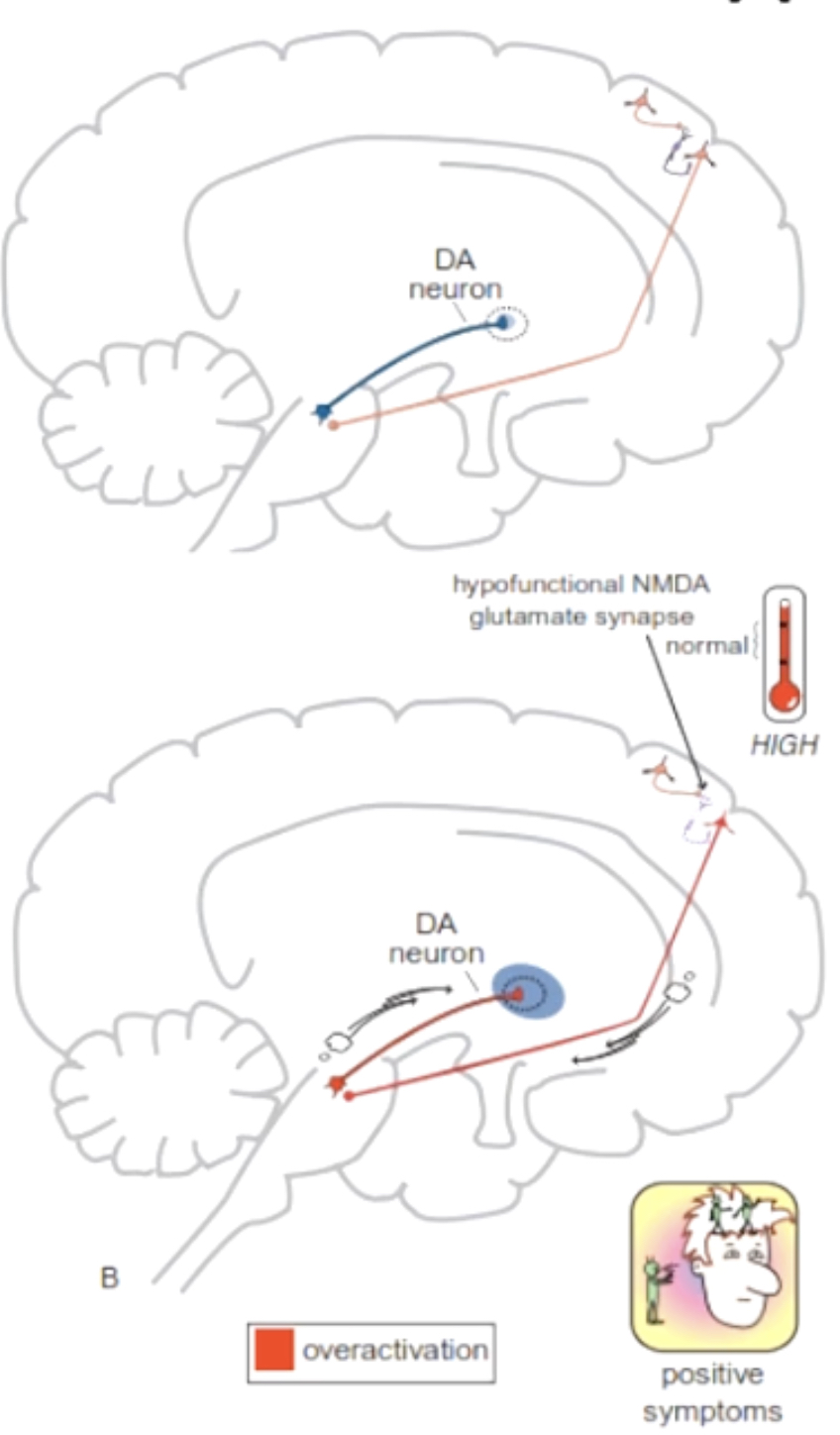
Explain this diagram
Pyramidal neurons communicate through GABAergic intermediate neurons. If the NMDA tone is altered, then the intermediate neuron can die, and this causes hyperactivation. This causes a hyperactive glutamate neuron, which leads to overstimulation of the dopamine pathway and, therefore, positive symptoms.