Lab 14: Fetal Pig Dissection 3
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Kidney
The large, kidney-bean-shaped organs located on the posterior dorsal wall of the abdominal cavity. They lie beneath a layer of connective tissue on either side of the dorsal aorta. They produce urine.
Ureter
The paired tubes that join the kidneys and the urinary bladder. They conduct urine to the bladder.
Urinary bladder
The large sack that is located between the two umbilical arteries. It is the temporary storage site of urine.
Urethra
This tube transports urine when the urinary bladder is emptied. It is relatively short in females, and just ventral to the anus. It is much longer in males and ends at the urogenital opening. It also functions to conduct semen in males.
Scrotum
The external pouch, ventral to the anus, which contains the testes.
Testes
The small, bean-shaped male reproductive organs contained within the scrotum which produce sperm and testosterone.
Epididymis
The band-shaped collection of tubules with a coiled duct that lays on the testis. It is used for sperm storage and maturation.
Ductus deferens
The ducts that transfer sperm from the epididymis to the urethra during an ejaculation. It is called the “vas deferens” in humans.
Inguinal canal
The passageway through the abdominal wall in the groin of males though which the ductus deferens and blood vessels pass to the testes.
Seminal vesicles
These small glands are located near the junction of the ductus deferens and the urethra. They produce some of the seminal fluid.
Prostate gland
A small gland located between the seminal vesicles, which surrounds the junction of the ductus deferens and the urethra. It produces some of the seminal fluid.
Bulbourethral glands
A pair of glands near the base of the penis in the pelvic canal on either side of the urethra. They produce some of the seminal fluid. They are also called “Cowper’s glands.”
Penis
The male copulatory organ located ventrally on the exterior abdominal wall, just posterior to the umbilical cord.
Urogenital Opening
The opening that is the terminal end of the male urogenital tract. Located just below the umbilical cord in the fetal pig.
Ovaries
The female reproductive organs, which are small and bean-shaped, found on the dorsal abdominal wall, just posterior to the kidneys. They produce the eggs and hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
Uterine tubes
Small ducts found between the ovaries and uterine horns. They transport eggs to the uterine horns. In humans, fertilization occurs in the uterine tubes. They are also termed the “fallopian tubes” in humans.
Uterine horns
The wider tubes located at the end of the uterine tubes and connected to the uterine body. Embryos develop within these tubes.
Uterine body
The single, wider tube formed by the union of the two uterine horns. The cervix is at its posterior end. Termed the “uterus” in humans.
Vagina
The most posterior tube of the female reproductive tract. It receives the penis during copulation.
Genital papilla
This is the female’s external genitalia located directly below the anus.
Dorsal aorta
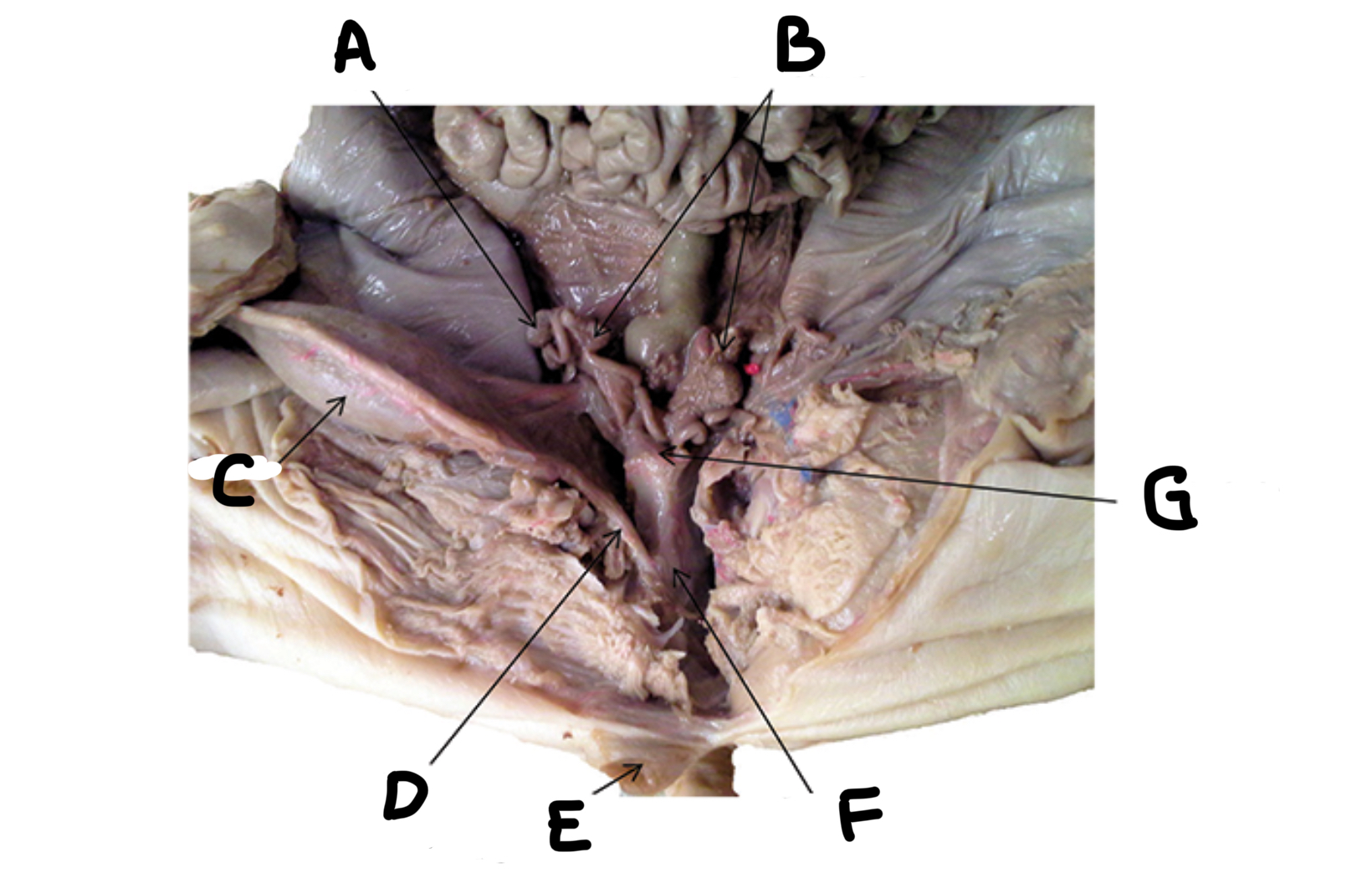
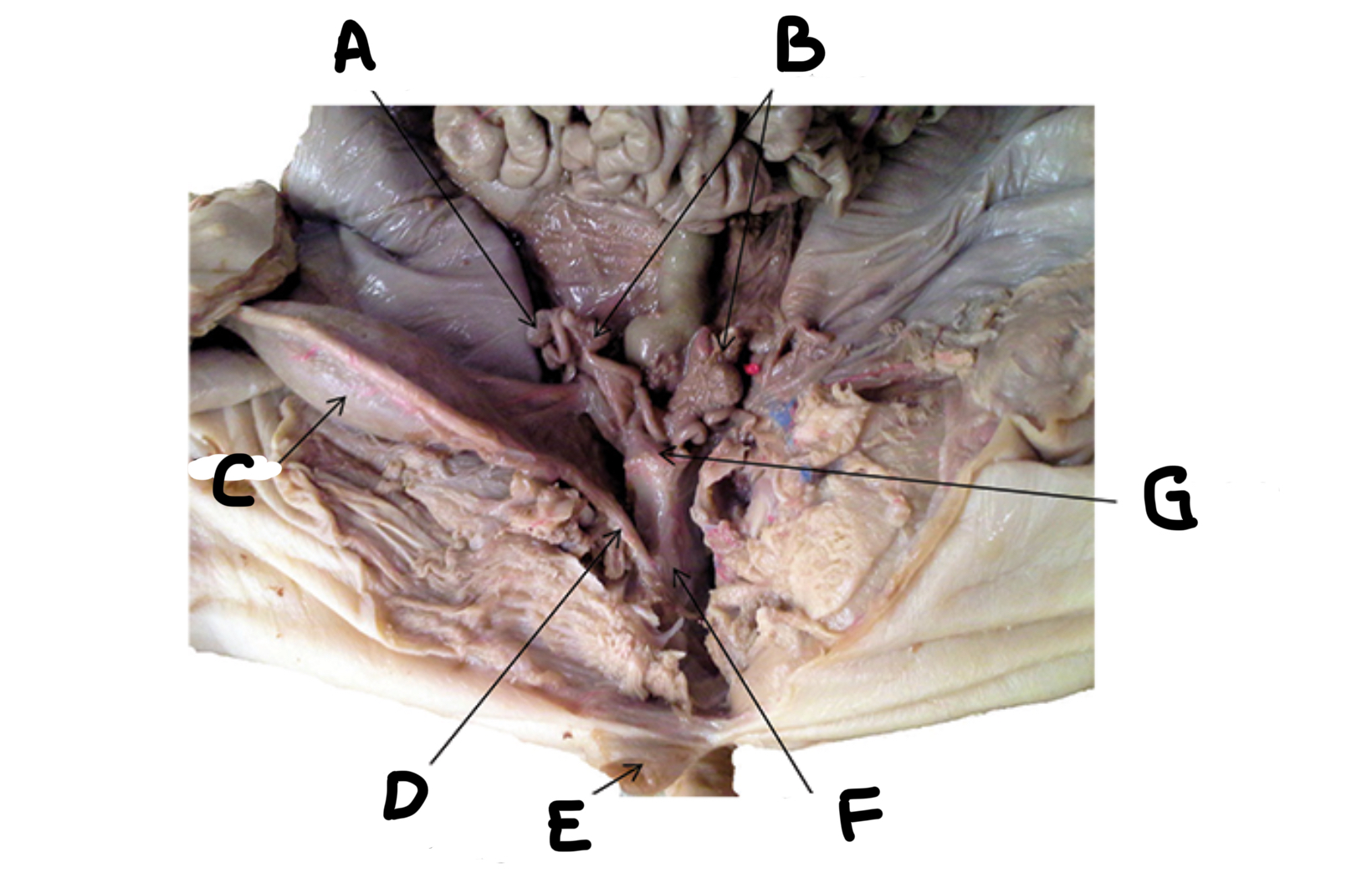
What is A
Urinary bladder
What is B
Umbilical artery
What is C
Kidney
What is D
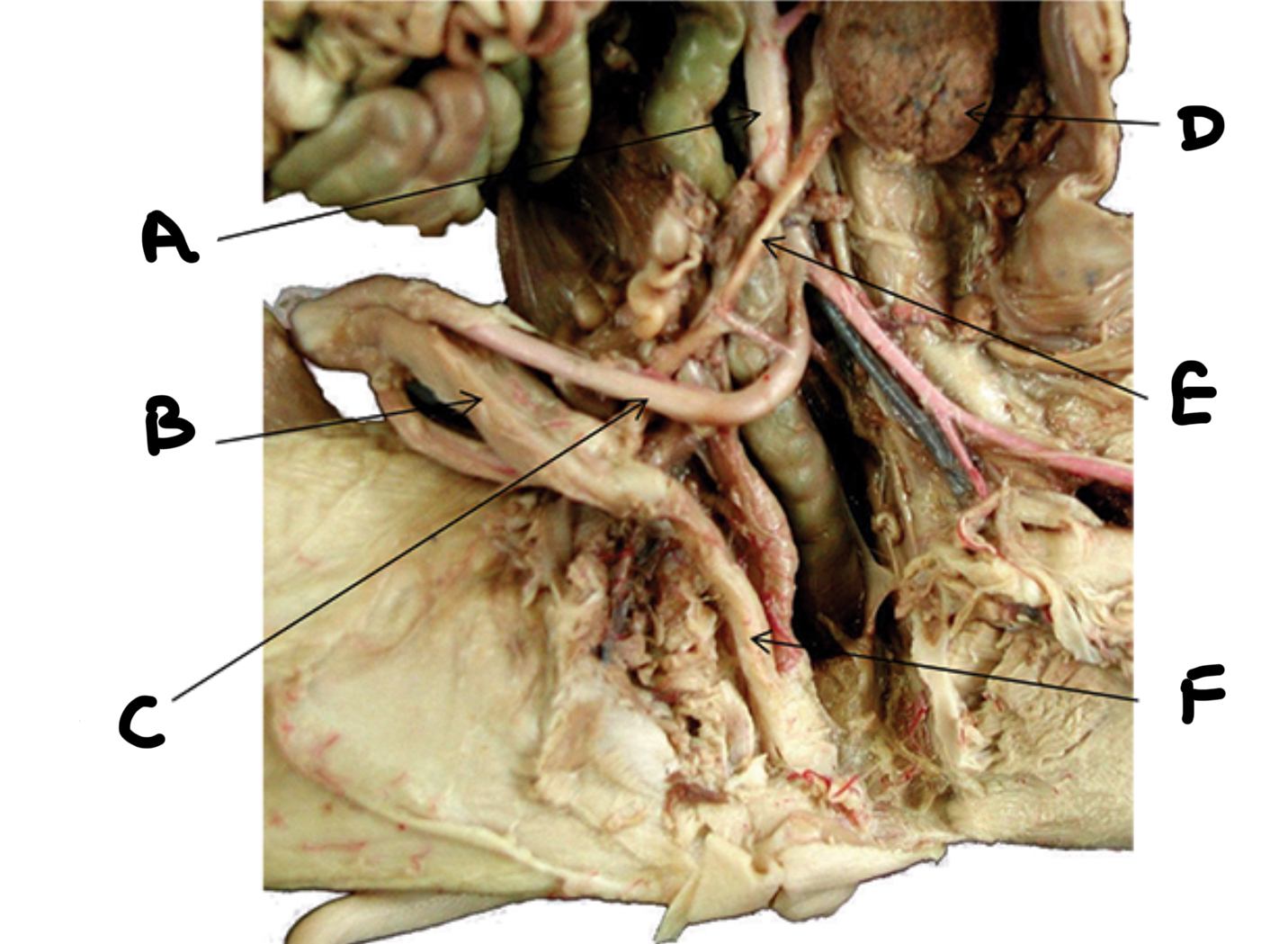
Ureter
What is E
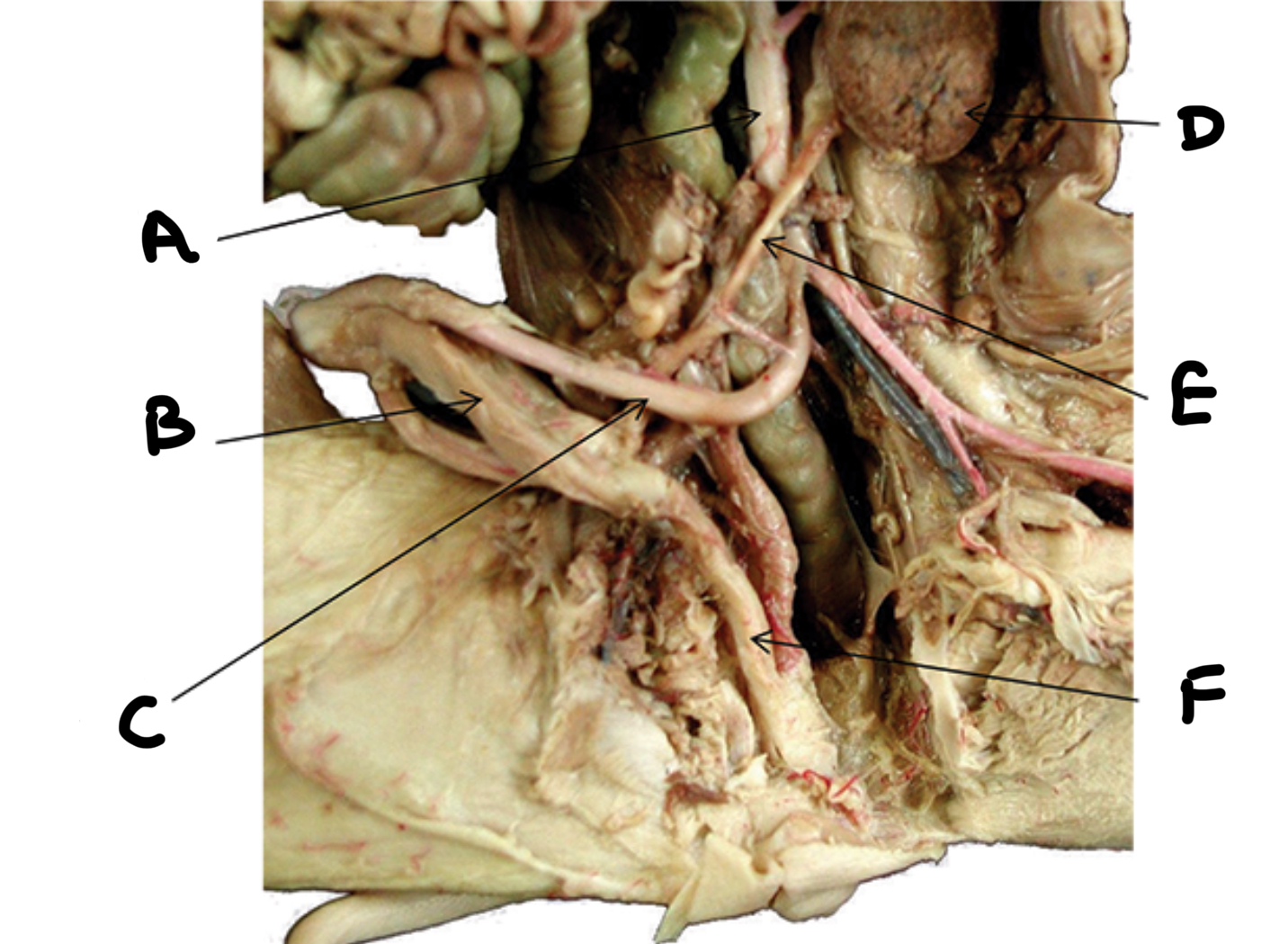
Urethra
What is F
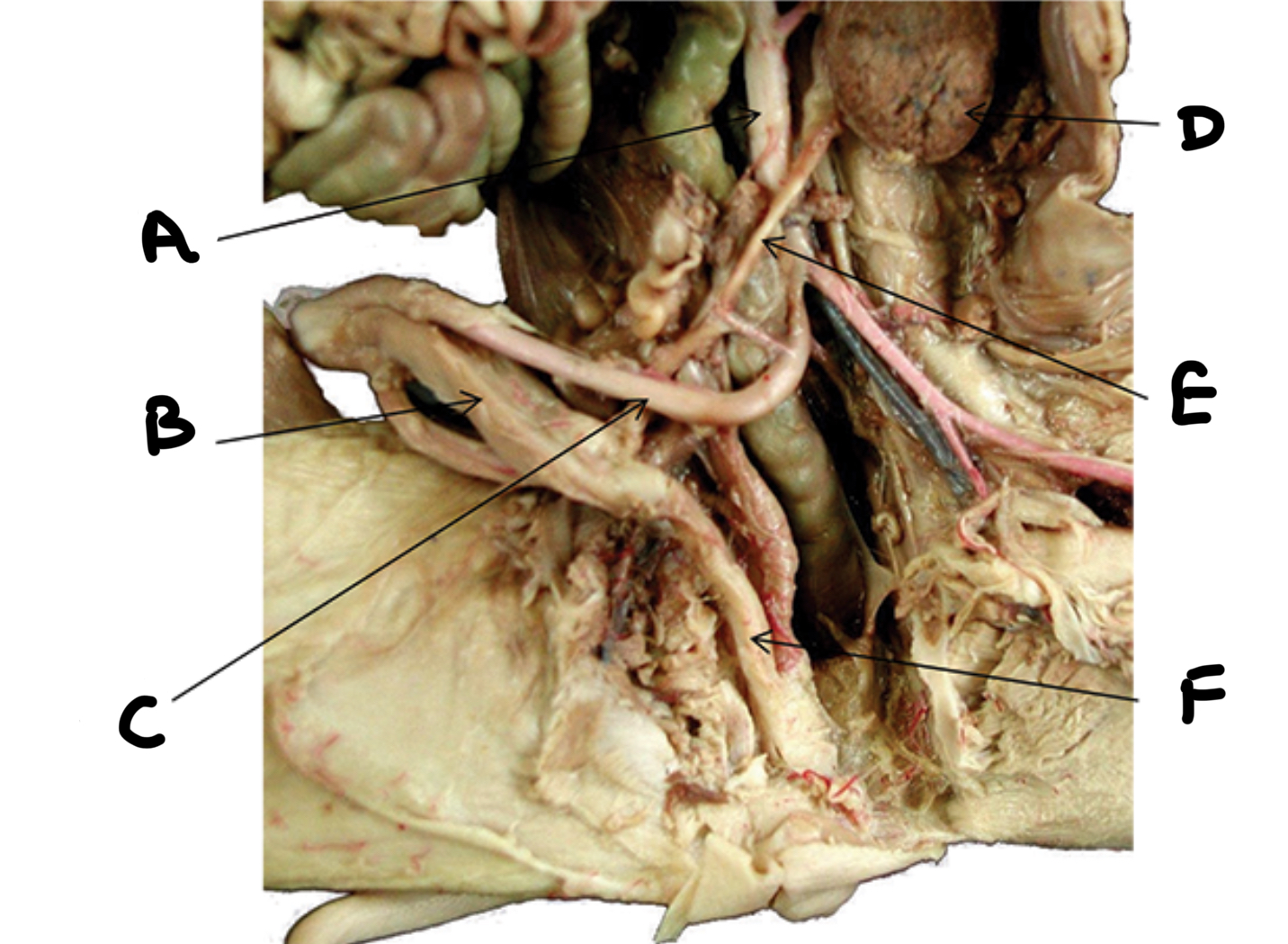
Urinary bladder
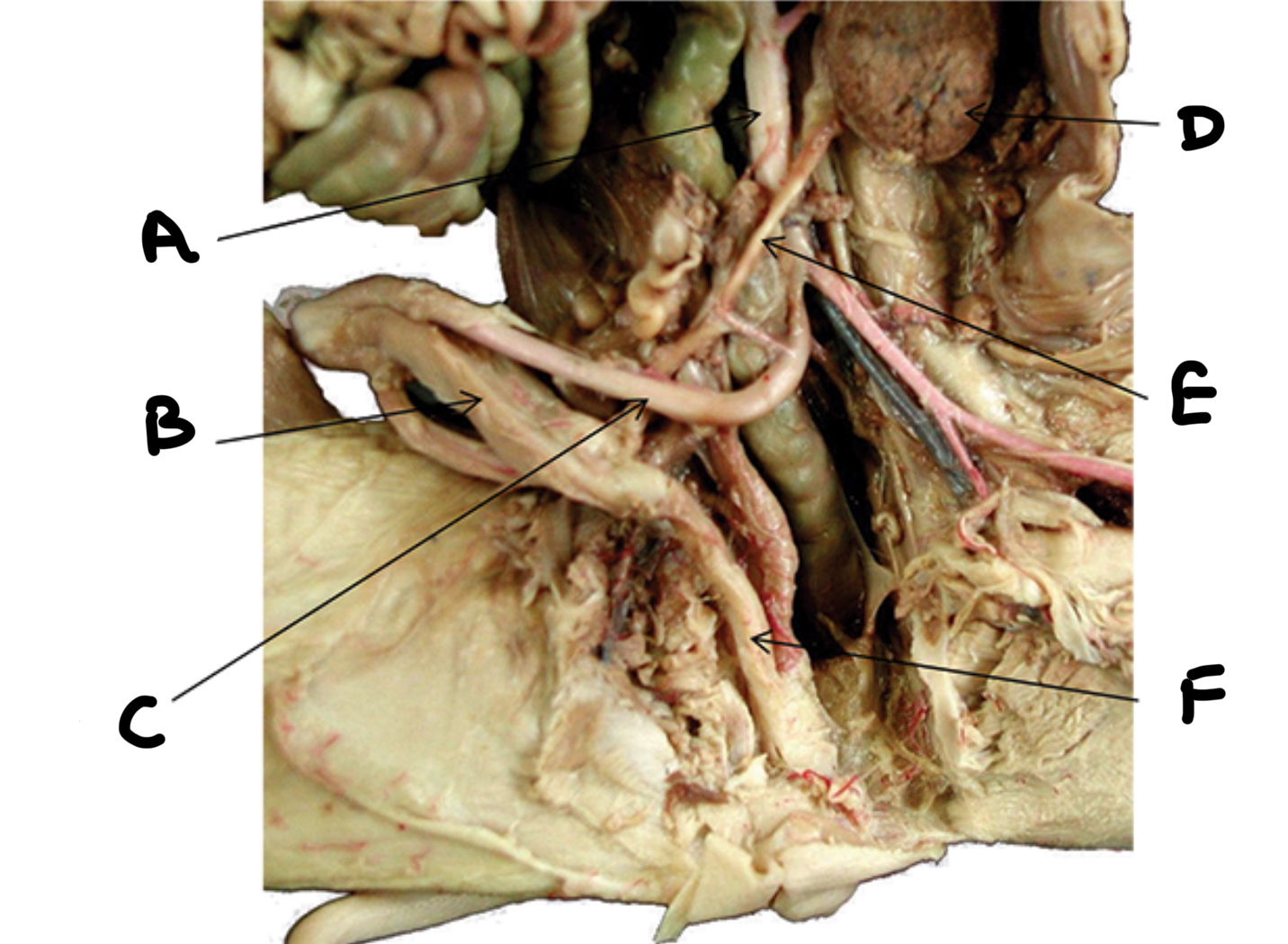
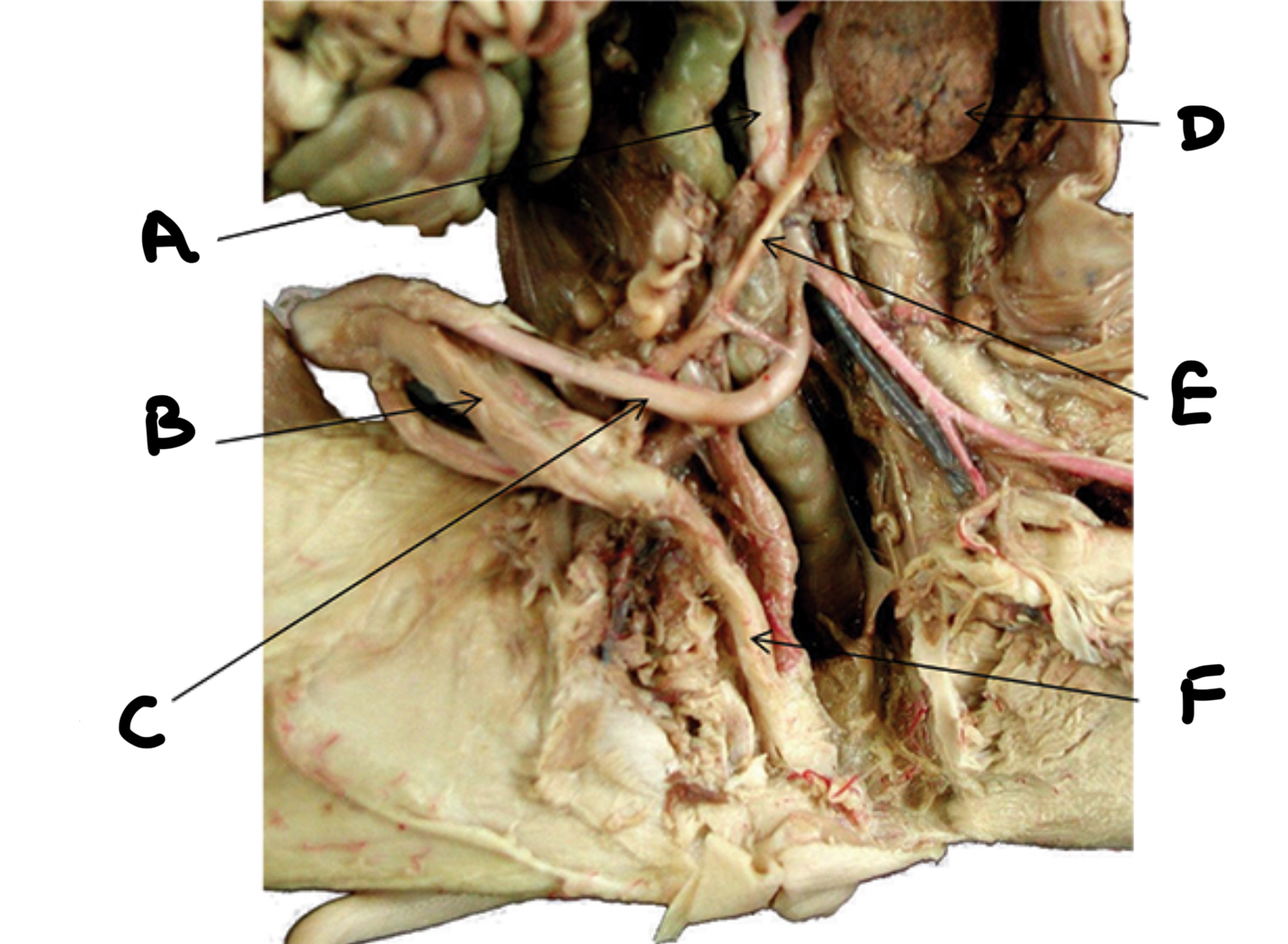
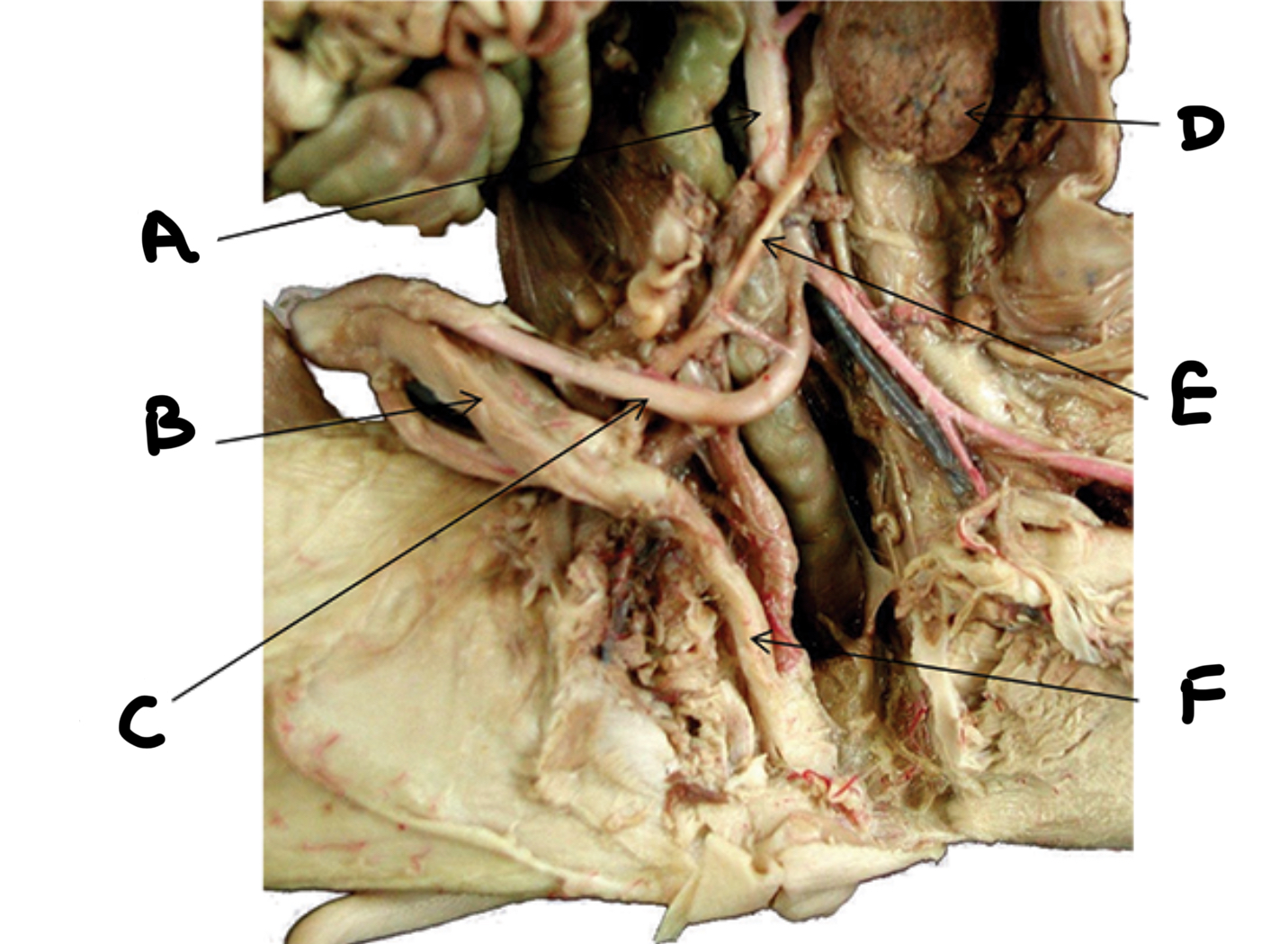
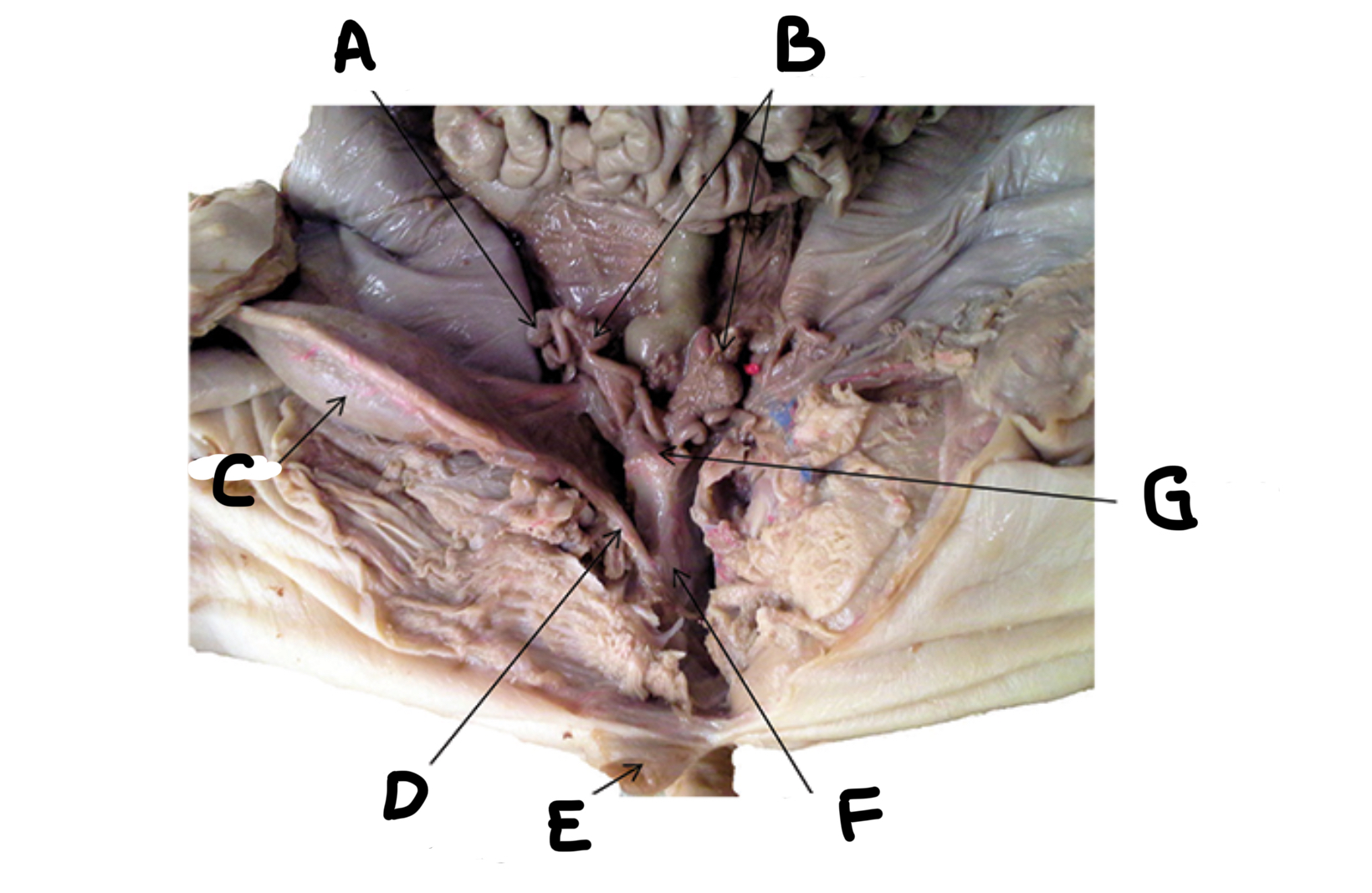
What is A
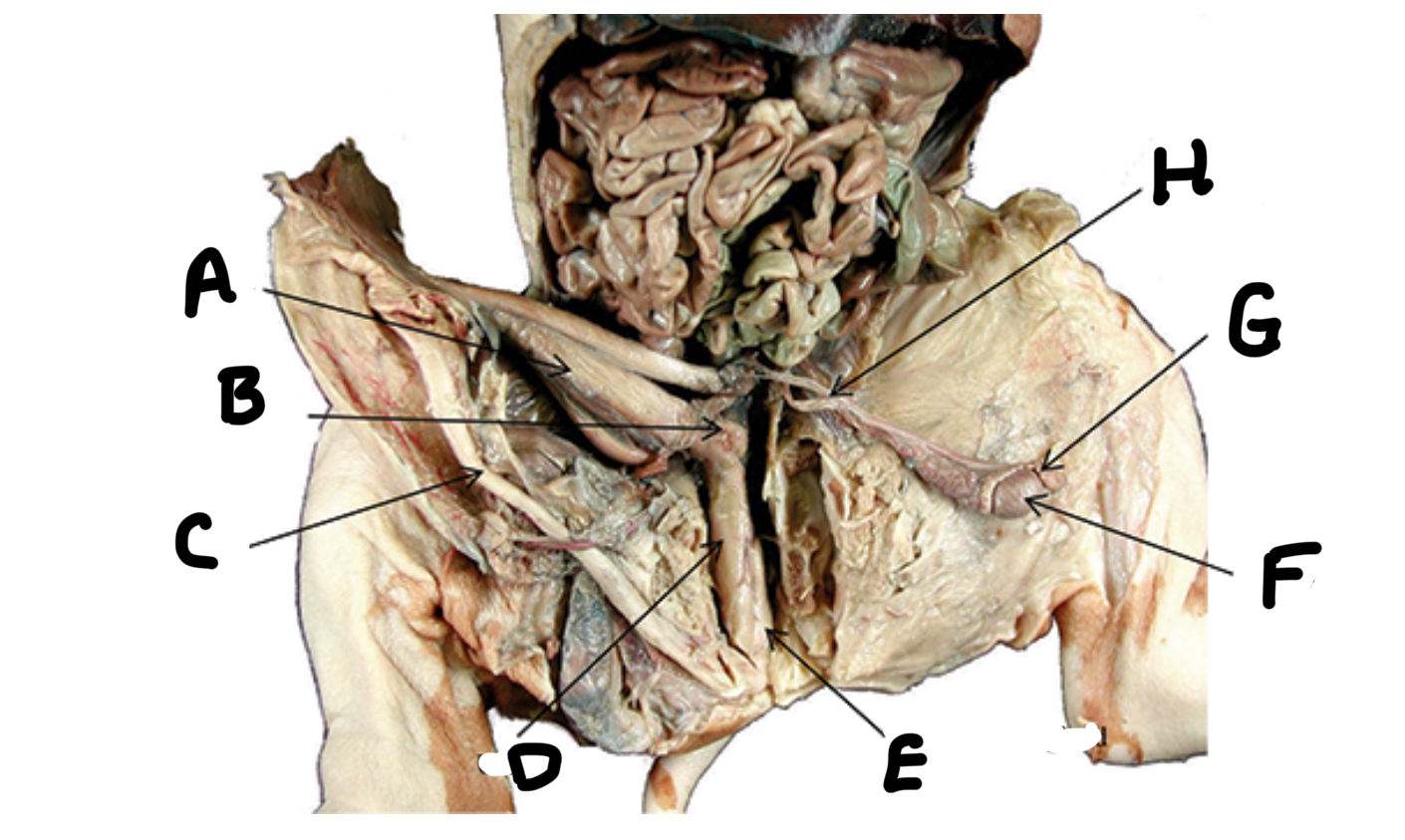
Seminal vesicles
What is B
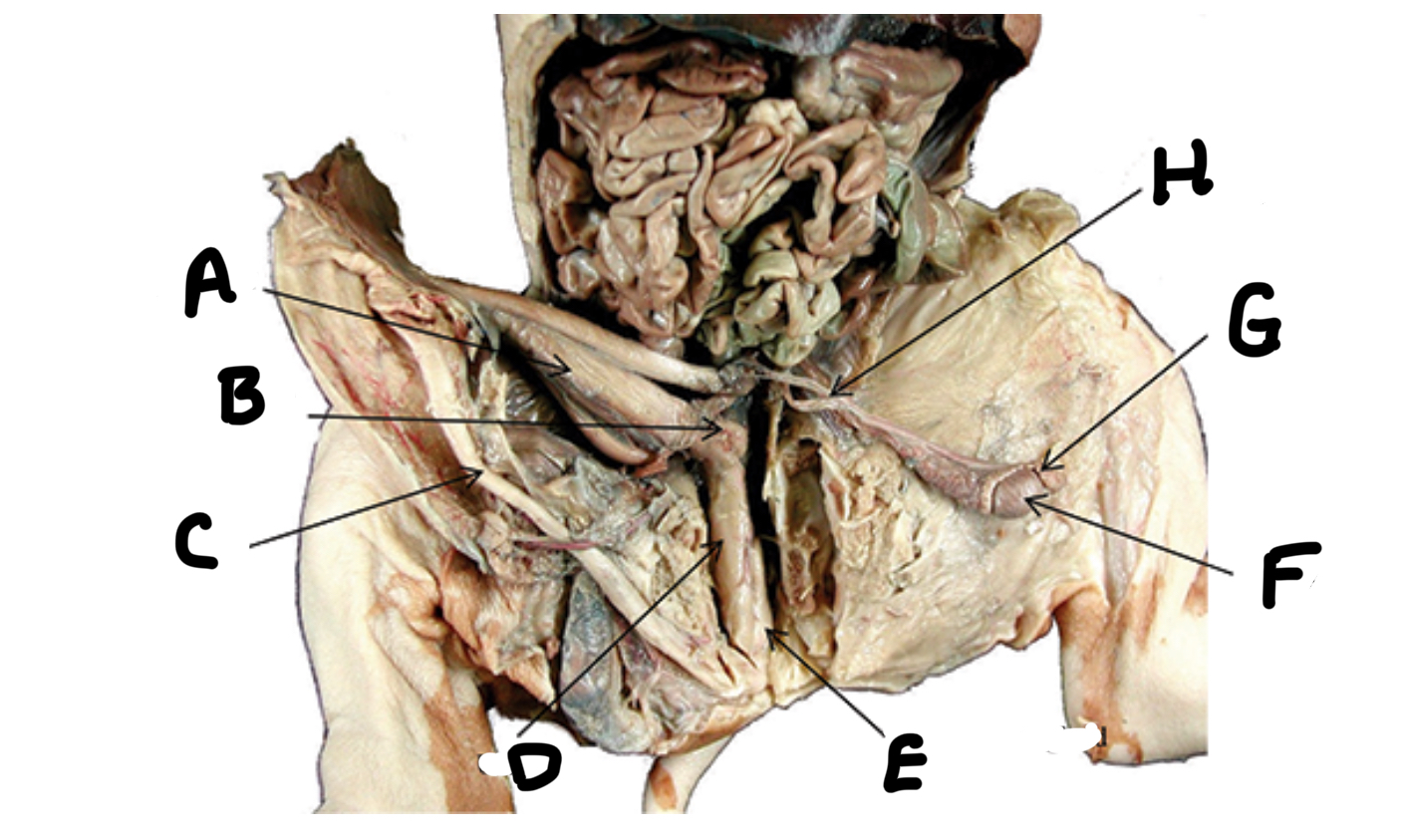
Penis
What is C
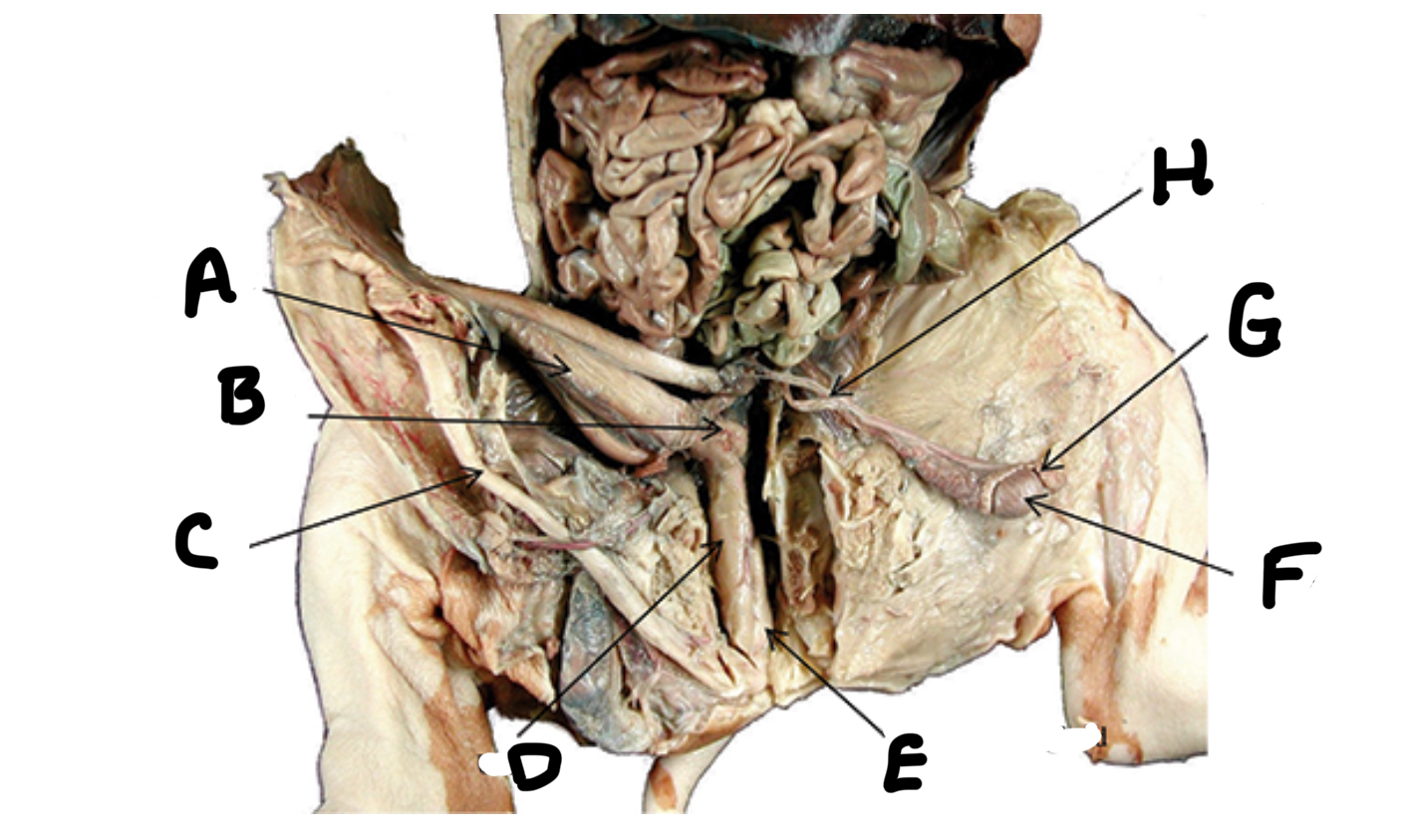
Urethra
What is D
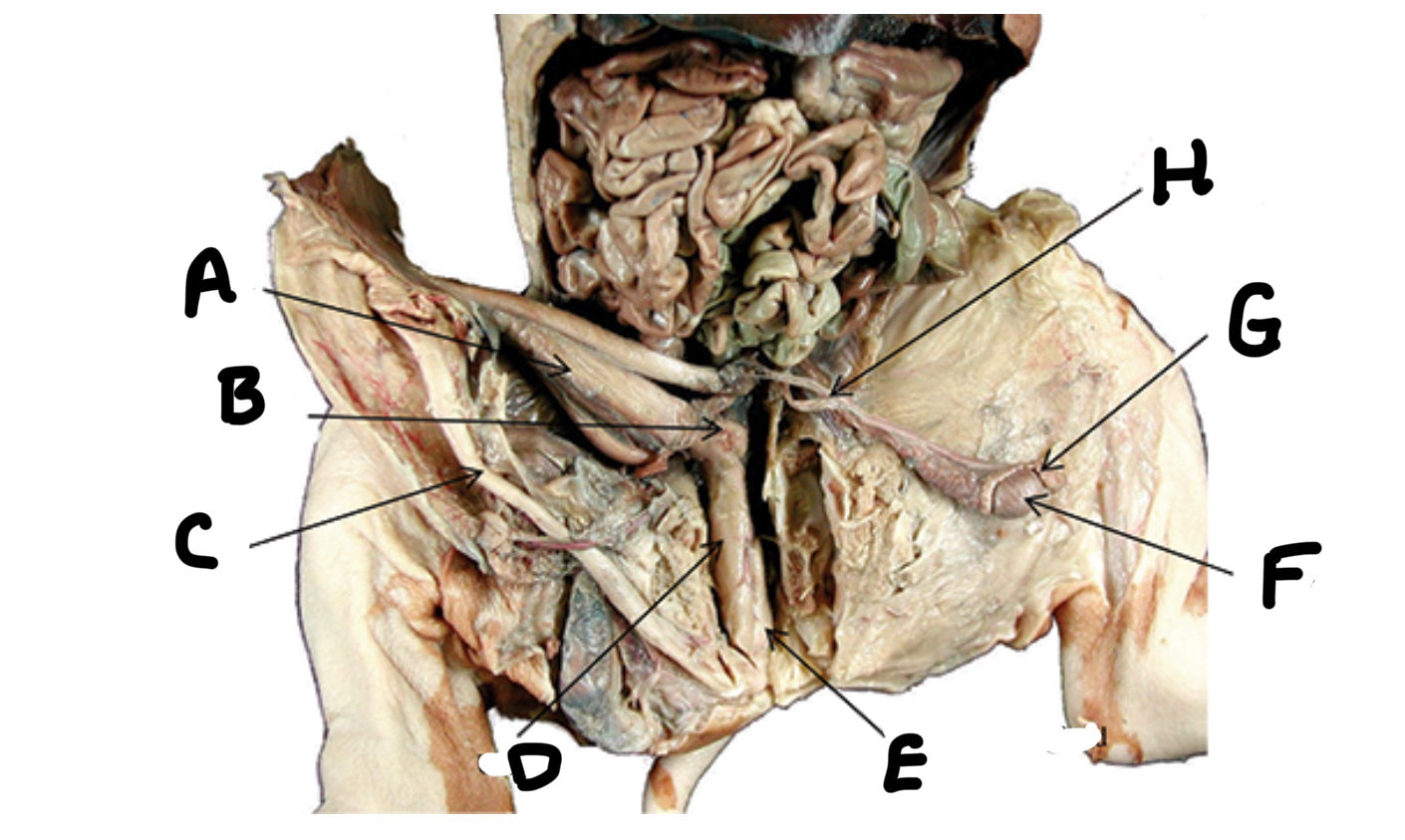
Bulbourethral gland
What is E
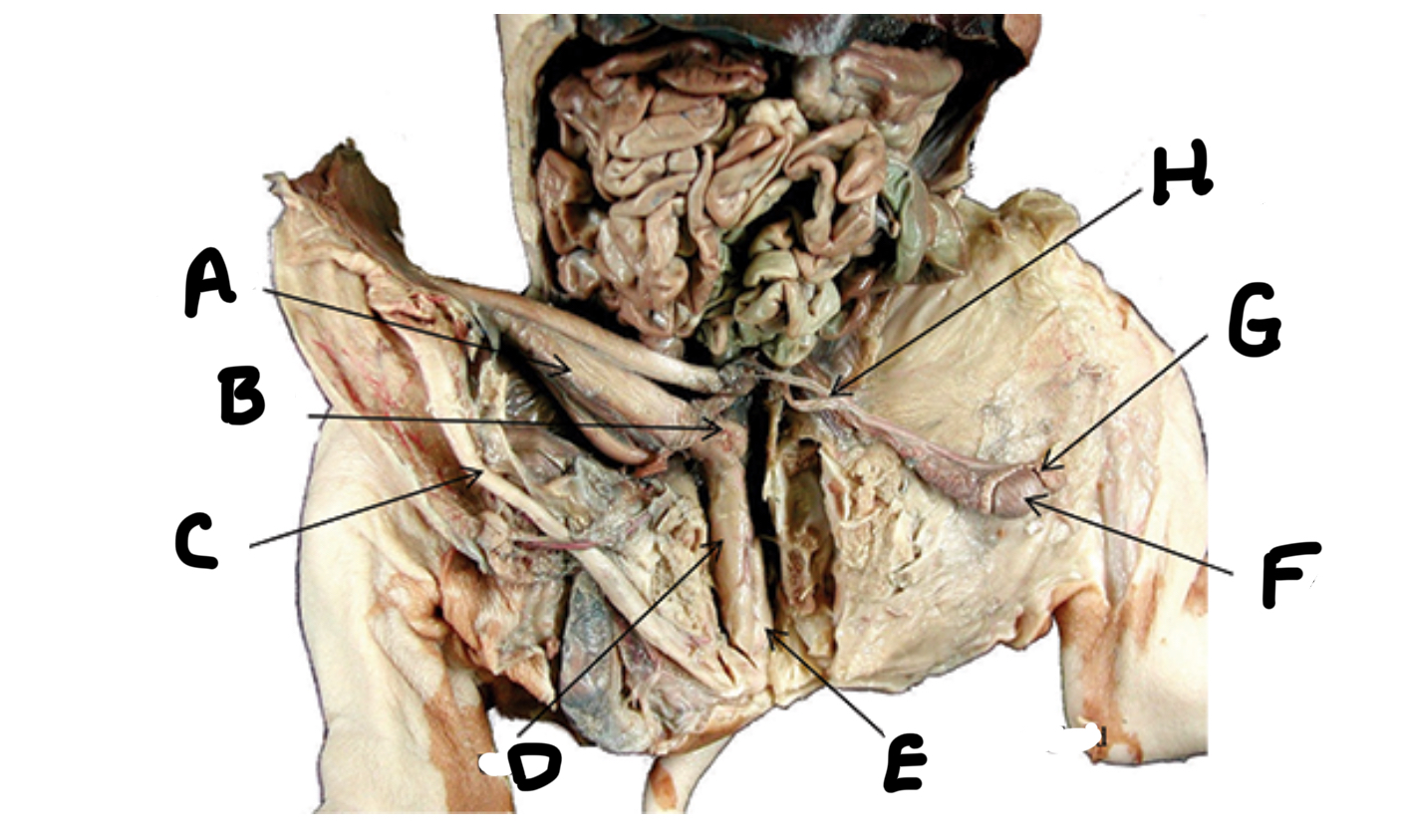
Testes
What is F
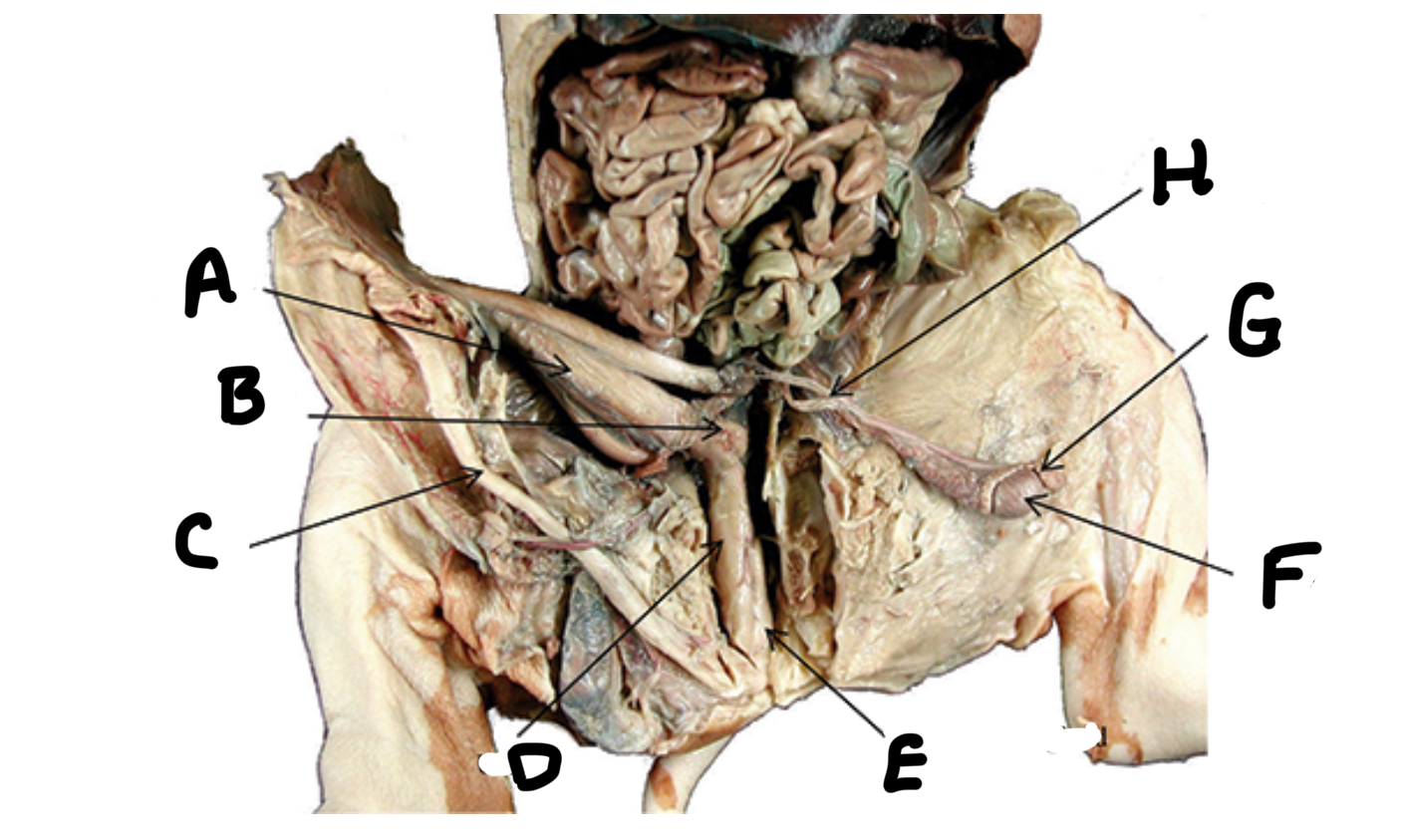
Epididymis
What is G
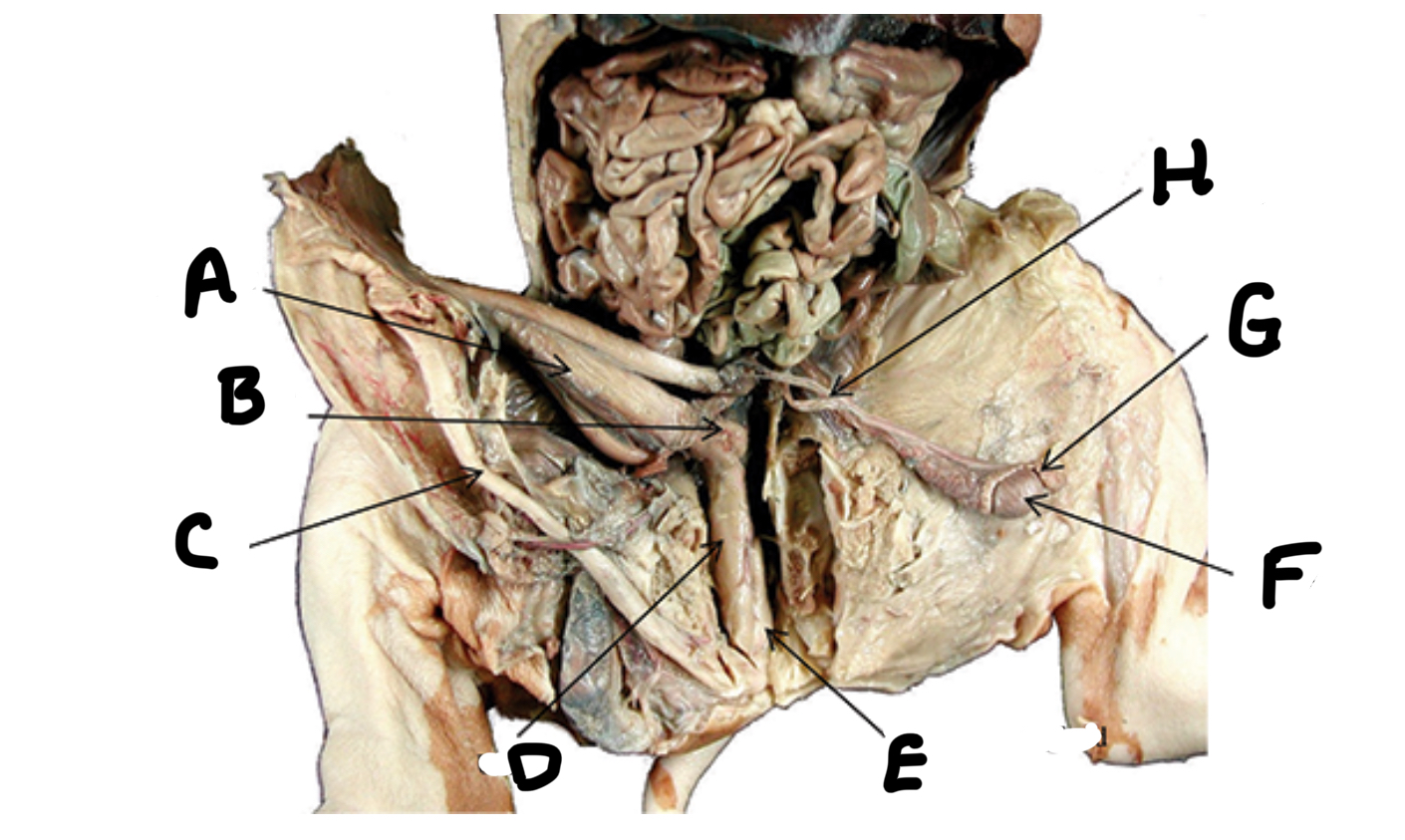
Ductus deferens
What is H
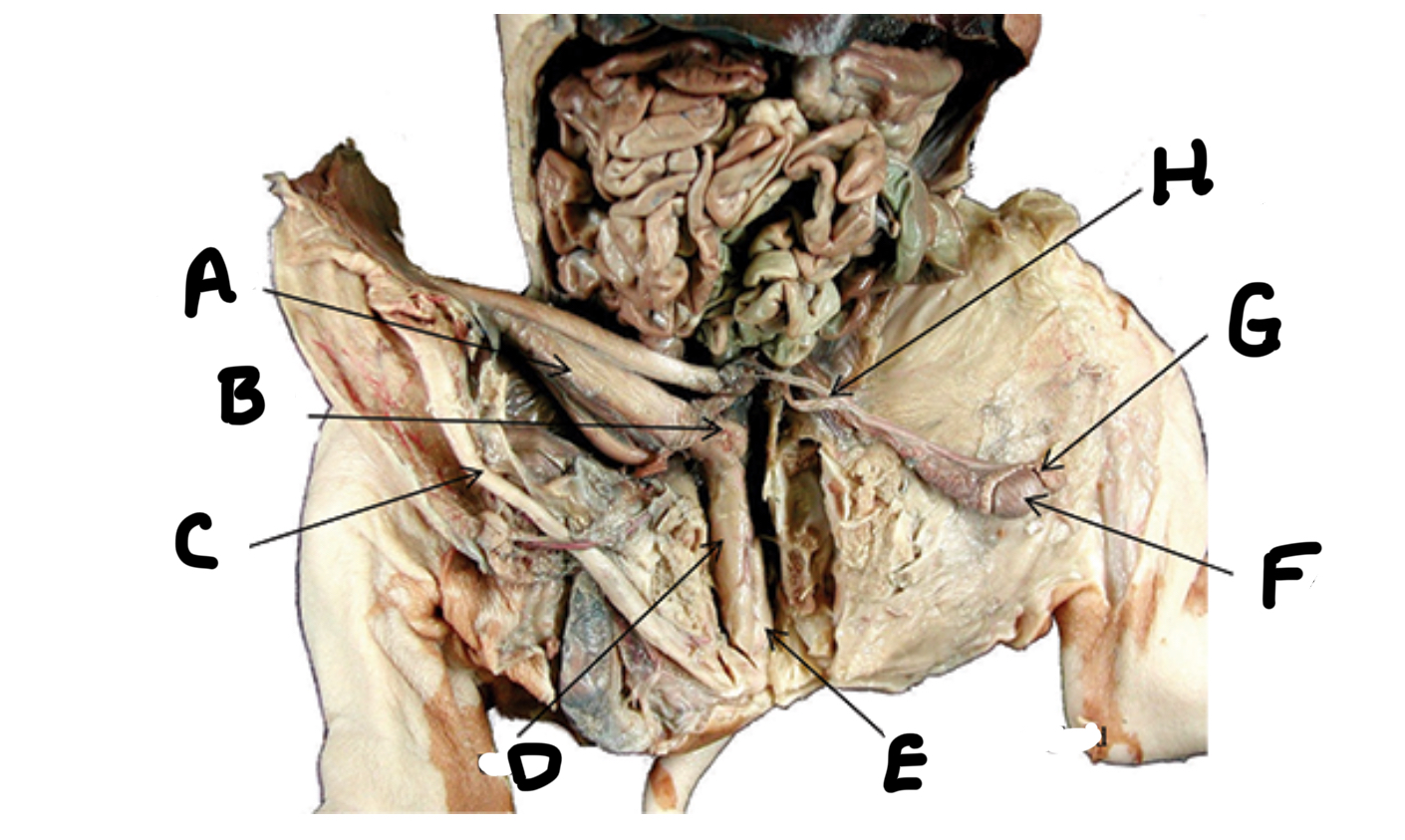
Ovaries
What is A
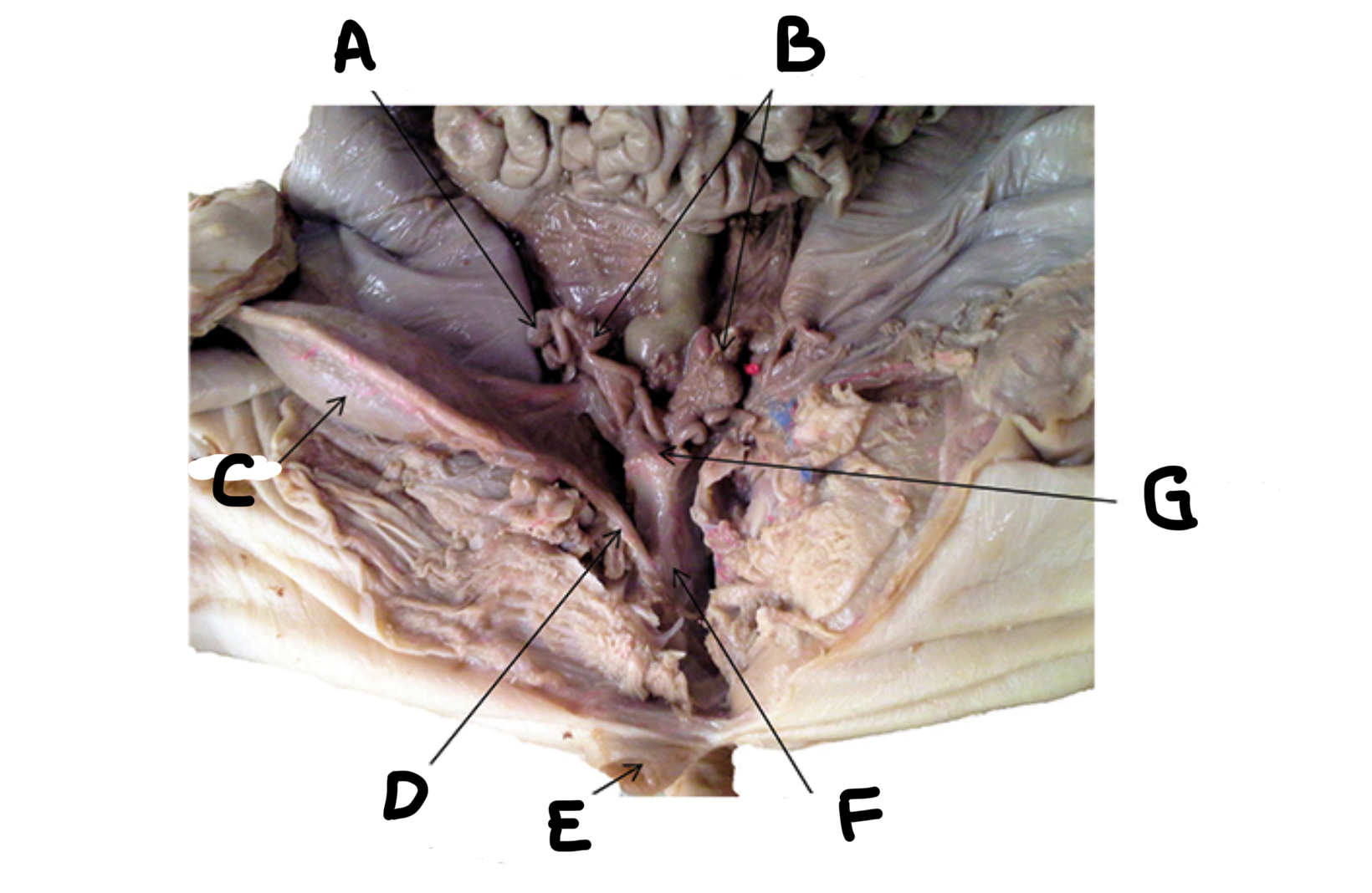
Uterine horns
What is B
Bladder
What is C
Urethra
What is D
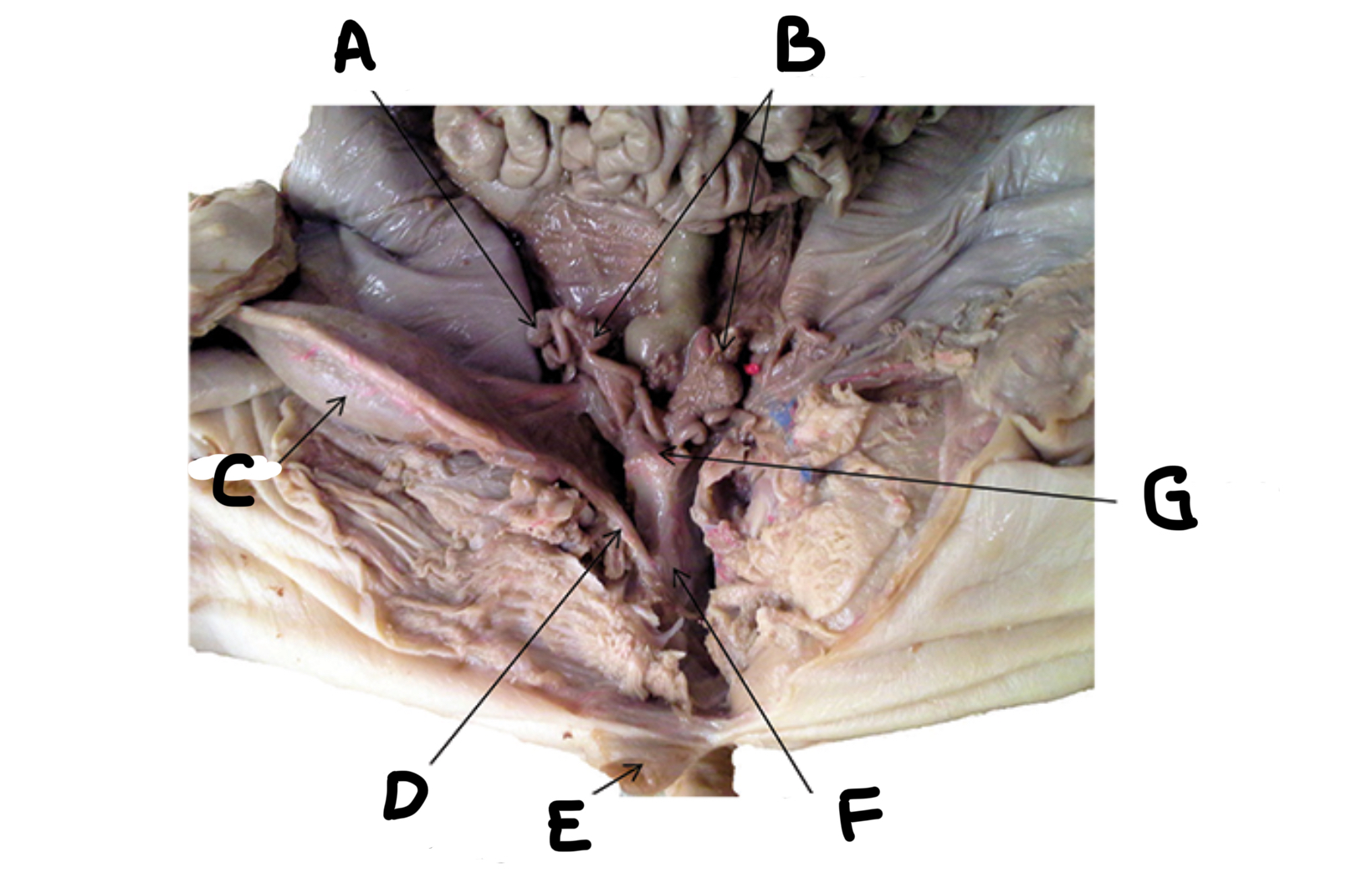
Genital papilla
What is E
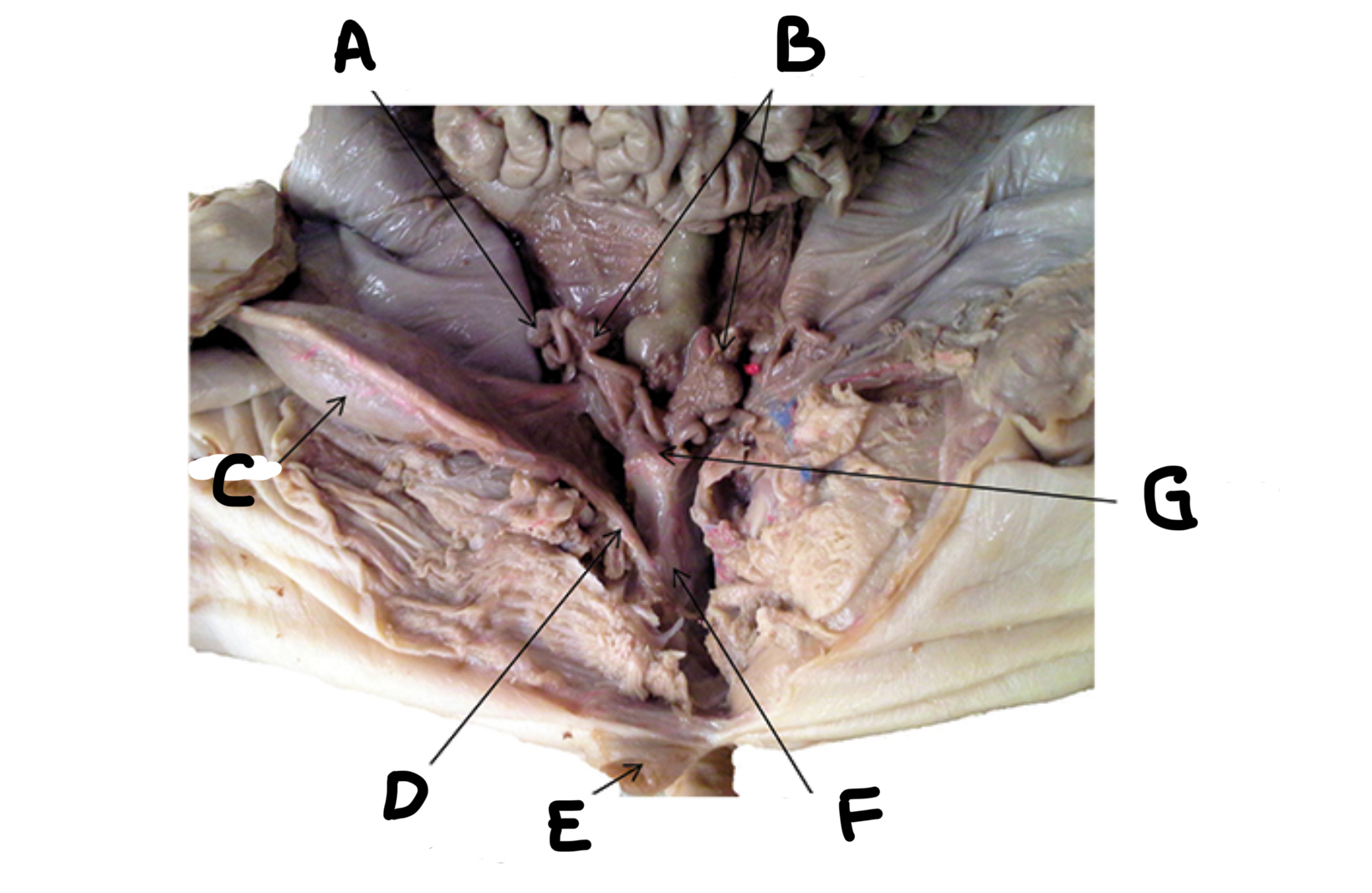
Vagina
What is F
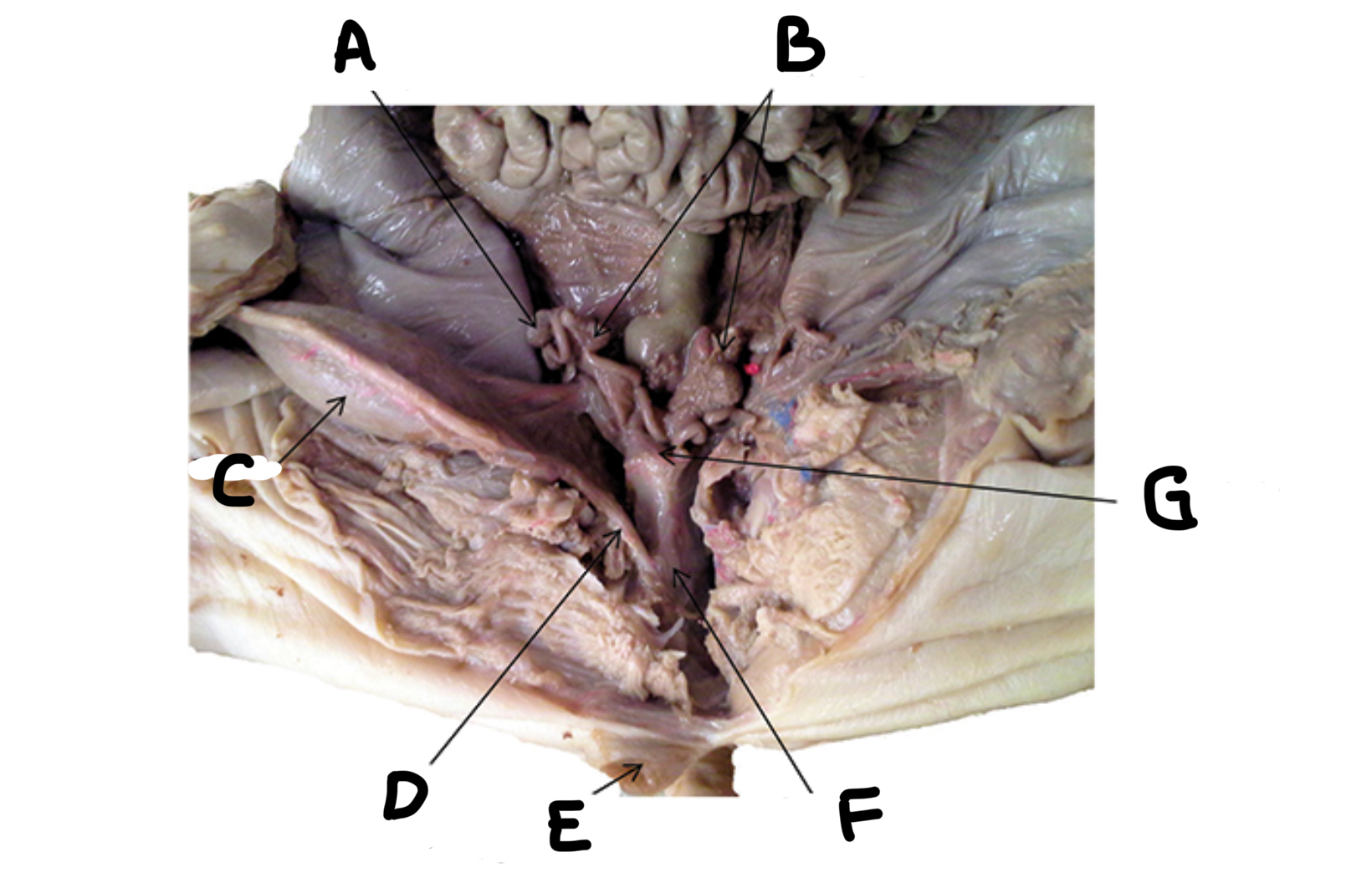
Uterine body
What is G