Exam 6 Human Anatomy
1/370
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
371 Terms
What is the main function of the digestive system?
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients.
What are three other names for the digestive system?
Digestive tract
Gastrointestinal (GI) tract
Alimentary canal
How does the digestive system exist in the body?
It exists as a continuous tube extending from the oral cavity to the anus.
What is the peritoneum?
A large, highly folded, serous membrane located in the abdomen.
What is the function of the falciform ligament?
It extends from the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and contains the round ligament of the liver (obliterated umbilical vein).
What does the greater omentum connect, and what is its appearance?
It extends from the greater curvature of the stomach to the transverse colon, forming a fatty apron over the small intestine.
What is the function of the mesentery?
It supports and suspends the jejunum and ileum.
What structures are contained within the oral cavity?
The tongue
Teeth
Openings of the salivary glands
What are the functions of the tongue?
The tongue functions in the sense of taste, mastication (chewing), and the movement of food.
How many teeth does an adult have, and what are the four types?
An adult has 32 teeth, including:
Incisors
Canines
Premolars
Molars
What are the three pairs of salivary glands?
The parotid
Submandibular
Sublingual glands
Why are salivary glands considered exocrine glands?
They have ducts that drain their secretions (saliva) into the oral cavity.
What is the pharynx composed of, and what is its function?
The pharynx is composed of skeletal muscle and functions in swallowing.
What are the three parts of the pharynx and their locations?
Nasopharynx – posterior to the nasal cavity
Oropharynx – posterior to the oral cavity
Laryngopharynx – posterior to the larynx
What is another clinical name for the laryngopharynx?
The hypopharynx
What structure is the pharynx continuous with?
The esophagus
What is the esophagus, and how long is it?
The esophagus is a muscular tube extending 30 cm from the lower end of the pharynx to the cardiac opening of the stomach.
What are the three regions of the esophagus?
Cervical (in the neck, posterior to the trachea)
Thoracic (posterior to the trachea in the upper half and posterior to the heart in the lower half)
Abdominal (after piercing the diaphragm, it enters the abdomen and joins the stomach at the gastroesophageal junction).
Where does the esophagus terminate?
It terminates by joining the stomach at the gastroesophageal junction.
What is the main function of the stomach?
The stomach is responsible for the storage of food and digestion.
What are the three main parts of the stomach?
Fundus – The part of the stomach above the entrance of the esophagus.
Body – The main mass of the stomach, between the fundus and the pyloric part.
Pyloric part – The lower part that extends toward the right and ends at the pyloric opening.
What is the pyloric opening?
It is the opening between the stomach and the first part of the duodenum.
What surrounds the pyloric opening, and what is its function?
The pyloric sphincter, a circular smooth muscle that controls the passage of food into the duodenum.
What are the two curvatures of the stomach?
Greater curvature – A convex margin that courses over the fundus and runs along the left side of the stomach to the pyloris.
Lesser curvature – A concave margin located on the right side of the stomach.
What are the two openings of the stomach?
Cardiac opening – The opening between the esophagus and the stomach.
Pyloric opening – The opening between the stomach and the first part of the duodenum.
Why is the cardiac opening called ‘cardiac’?
Because of its close relationship with the part of the diaphragm upon which the heart rests.
What surrounds the pyloric opening, and what is its function?
The pyloric sphincter, a circular smooth muscle that controls the passage of food into the duodenum.
What are the folds on the internal surface of the stomach called, and what is their function?
Rugae – They allow the stomach to expand when filled with food.
Where is the small intestine located in relation to the digestive tract?
It is the part of the intestine between the pyloric sphincter (stomach) and the ileocecal junction (large intestine).
How long is the small intestine?
Approximately 7 meters long
How does the diameter of the small intestine change along its length?
It gradually diminishes as it progresses.
What are the three subdivisions of the small intestine?
Duodenum – The first part, extends from the pyloric sphincter to the jejunum.
Jejunum – The proximal 2/5ths of the remaining small intestine.
Ileum – The distal 3/5ths of the remaining small intestine.
What is the shape of the duodenum, and what structures drain into it?
It is C-shaped, with its concave medial border receiving ducts from the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
What is the ileocecal junction?
The junction between the ileum of the small intestine and the cecum of the large intestine.
Where does the large intestine extend from and to?
It extends from the ileocecal junction to the anus.
What are the subdivisions of the large intestine?
Cecum
Appendix
Ascending colon
Transverse colon
Descending colon
Sigmoid colon
What is the cecum?
The part of the colon located at and below the level of entrance of the ileum.
What is the appendix and where is it located?
A lymphatic organ attached to the posteromedial surface of the cecum.
Where does the ascending colon extend, and what structure prevents it from continuing upward?
It extends superiorly from the right side of the posterior abdominal wall to the liver.
The liver prevents it from continuing upward, so it bends to form the right colic (hepatic) flexure.
What is the transverse colon, and where does it extend?
The portion of the colon that extends from the right colic flexure (on the right side) to the spleen (on the left side).
What happens when the transverse colon reaches the spleen?
It bends inferiorly to form the left colic (splenic) flexure.
Where does the descending colon extend?
It extends from the left colic flexure inferiorly along the left side of the posterior abdominal wall.
What is the sigmoid colon, and what does it connect to?
The sigmoid colon extends from the descending colon to the pelvis, where it continues as the rectum.
What is unique about the shape and position of the sigmoid colon?
It forms a loop, and its shape and position depend on how full it is.
What is the rectum, and what does it connect to?
The rectum is the portion of the digestive tract between the sigmoid colon and the anus.
What happens to the rectum as it moves inferiorly?
The rectum narrows inferiorly, forming the anal canal.
What is the anus, and what is its function?
The anus is the termination of the anal canal, where a sphincteric muscle is located. It functions in the retention of feces.
What is the liver, and what substance does it produce?
The liver is an exocrine gland that produces bile, which is conveyed to the duodenum via hepatic ducts.
What are the four lobes of the liver?
The right lobe
The left
The quadrate lobe
The caudate lobes
What structures enter and exit the liver at the porta hepatis?
The right and left hepatic arteries
The portal vein
The right and left hepatic ducts
Where do hepatic veins exit the liver?
They do not exist.
Where is the gallbladder located, and what is its function?
The gallbladder is located on the visceral surface of the liver, between the right lobe and the quadrate lobe. It stores and concentrates bile.
What are the two main functions of the pancreas?
As an exocrine gland, it produces digestive enzymes that pass via a duct to the duodenum.
As an endocrine gland, it produces insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin.
What are the three anatomical parts of the pancreas?
Head – Located in the concavity of the duodenum.
Body – Courses from the head toward the left across the vertebrae.
Tail – The left end of the gland, which approximates the spleen.
What is the duct system that drains bile and pancreatic juices?
The right hepatic duct drains the right half of the liver, and the left hepatic duct drains the left half of the liver. These two ducts join to form the common hepatic duct.
The gallbladder is drained by the cystic duct, which joins the common hepatic duct to form the bile duct (also called the common bile duct).
The bile duct joins the main pancreatic duct at the hepato-pancreatic ampulla, draining into the major duodenal papilla in the duodenum.
Is the spleen part of the digestive system?
No, but it is located close to it.
What is the function of the spleen?
The spleen functions like a lymph node and filters blood.
The falciform ligament extends from:
a. The liver to the obliterated umbilical vein
b. The liver to the round ligament
c. The greater curvature of the stomach to the transverse colon
d. The lesser curvature of the stomach to the transverse colon
e. None of the above
e. None of the above
All of the following are functions of the tongue EXCEPT:
a. Movement of food
b. Chemical breakdown of food
c. Mastication
d. Taste
b. Chemical breakdown of food
This structure is continuous with the esophagus:
a. Larynx
b. Nasal cavity
c. Laryngopharynx
d. Nasopharynx
e. Oropharynx
c. Laryngopharynx
This structure can be found posterior to the heart:
a. Thoracic esophagus
b. Larynx
c. Pharynx
d. Thyroid cartilage
e. Abdominal esophagus
a. Thoracic esophagus
The greater curvature can be found on which organ?
a. the structure that extends from the liver to the anterior abdominal wall
b. the structure where protein digestion begins
c. the structure where bile is stored
d. the structure that contains the openings of the salivary glands
e. the structure that produces glucagon
b. the structure where protein digestion begins
All of the following describe the duodenum EXCEPT: (Choose all that apply.)
a. C-shaped organ
b. Proximal two-fifths of small intestines
c. Receives fluid from liver and pancreas
d. Is adjacent to the appendix
b. Proximal two-fifths of small intestines
d. Is adjacent to the appendix
The sigmoid colon: (Choose all that apply.)
a. Extends from the left colic flexure inferiorly along abdominal wall
b. Is continuous with the rectum
c. Forms a loop
d. Narrows inferiorly to form the anal canal
e. Can be found adjacent to the cecum
b. Is continuous with the rectum
c. Forms a loop
The porta hepatis contains all of the following EXCEPT:
a. Right hepatic duct
b. Left hepatic duct
c. Hepatic artery
d. Hepatic vein
e. Portal vein
d. Hepatic vein
The common hepatic duct, which drains the ________, and the cystic duct, which drains the _______, connect to become the __________.
a. Spleen, cysts, bile duct
b. Spleen, cytosol, mixed hepatic duct
c. Liver, gall bladder, bile duct
d. Kidneys, pancreas, pancreatic duct
c. Liver, gall bladder, bile duct
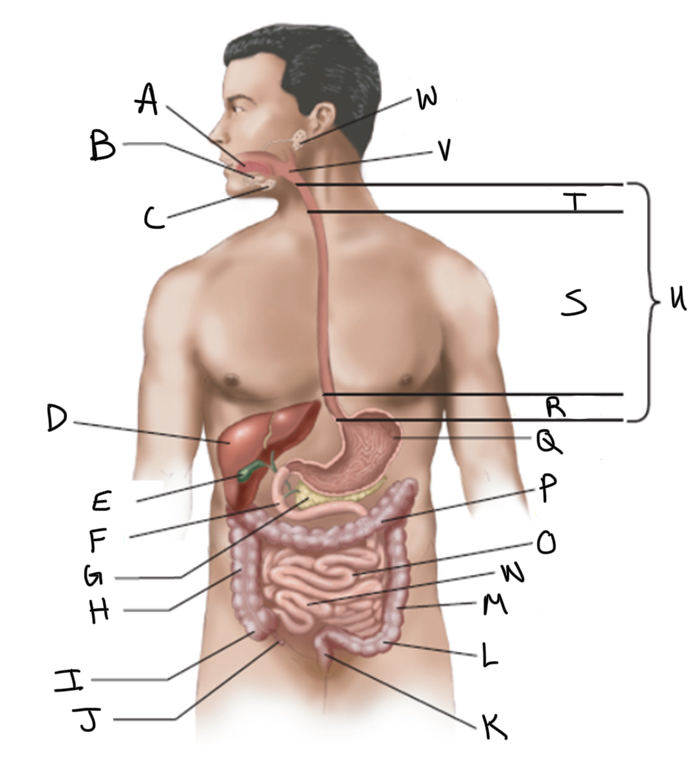
What is A?
Tongue
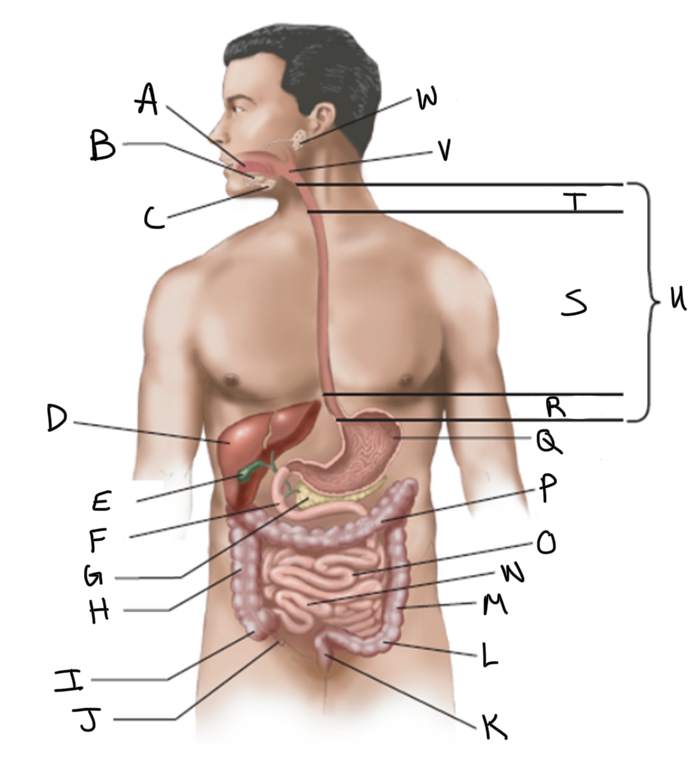
What is B?
Sublingual salivary gland
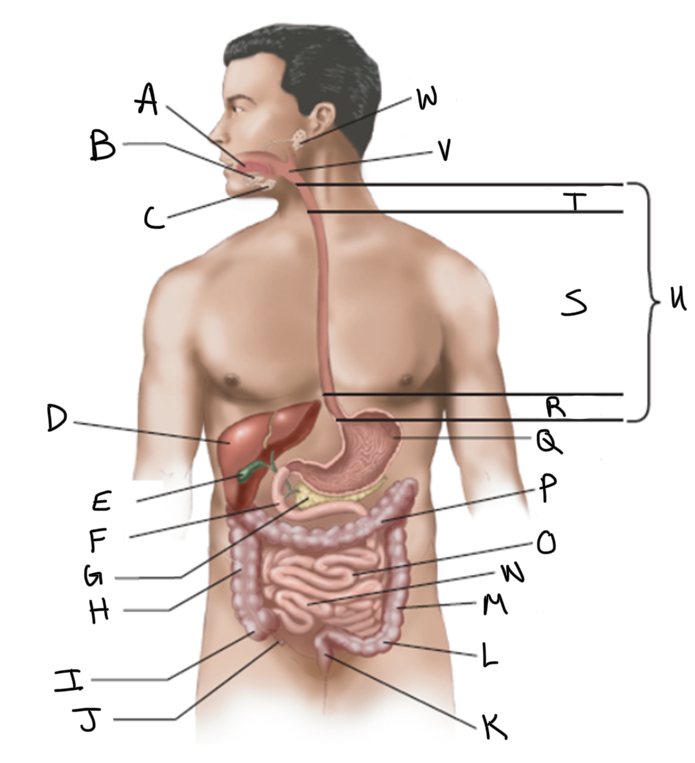
What is C?
Submandibular salivary gland
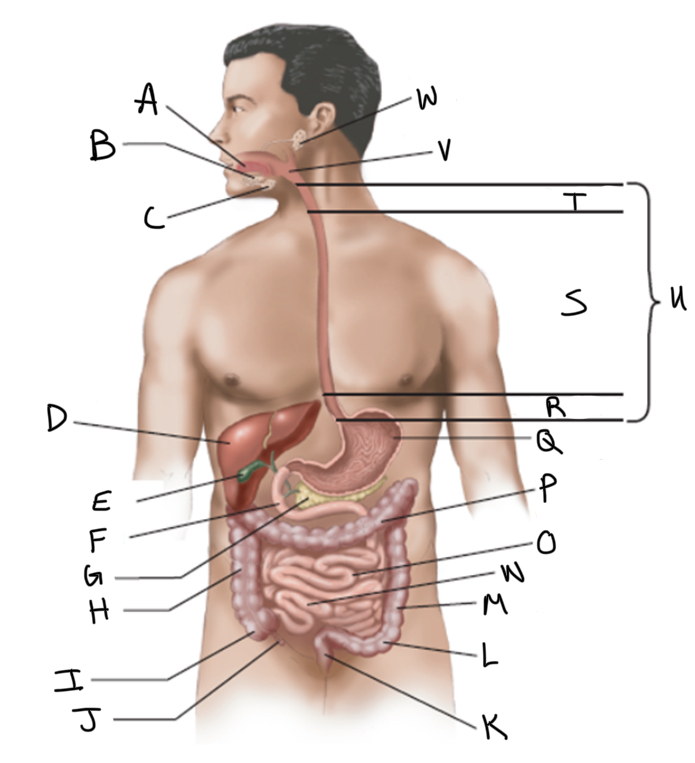
What is D?
Liver
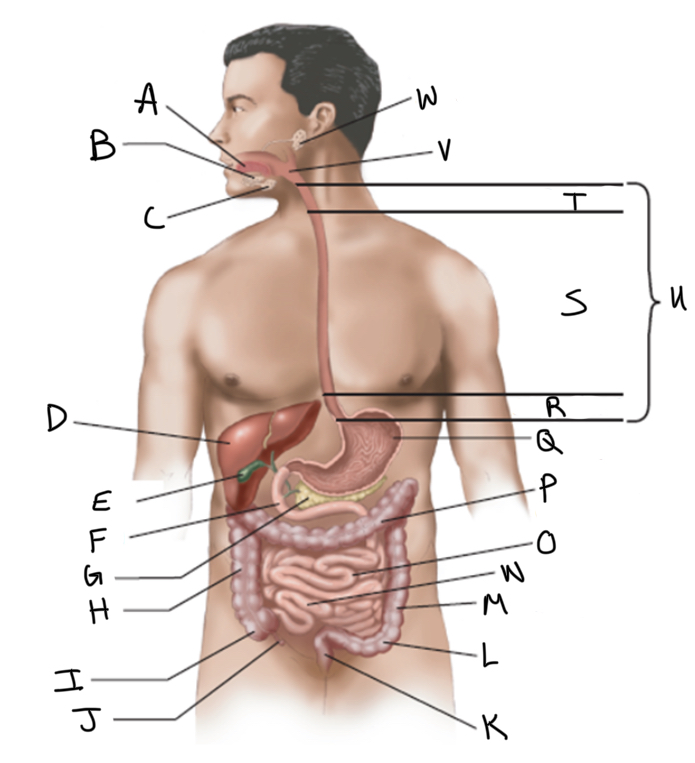
What is E?
Gallbladder
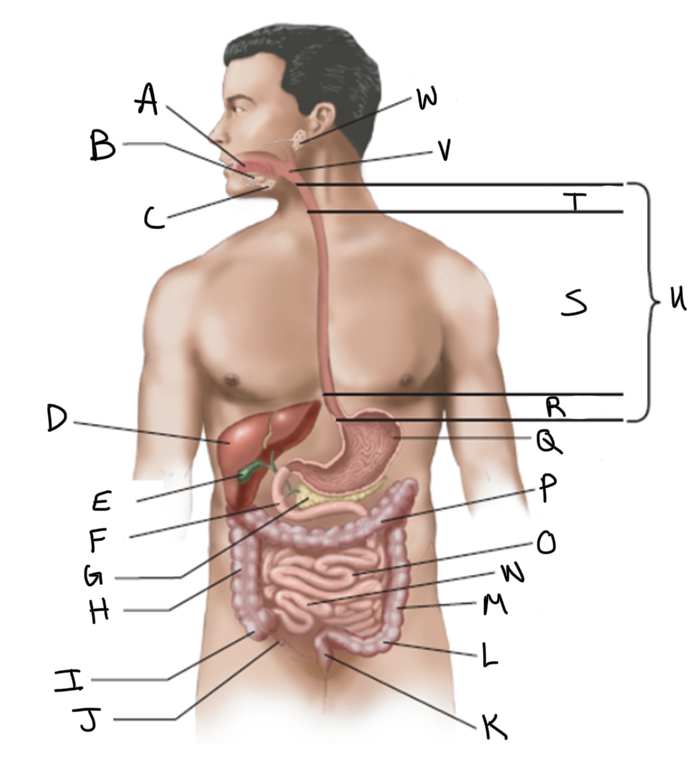
What is F?
Duodenum
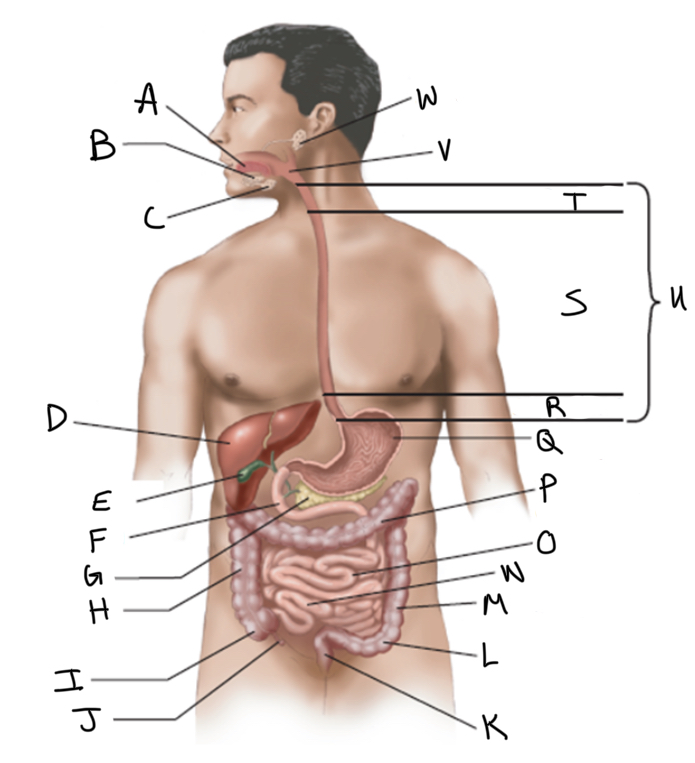
What is G?
Pancreas
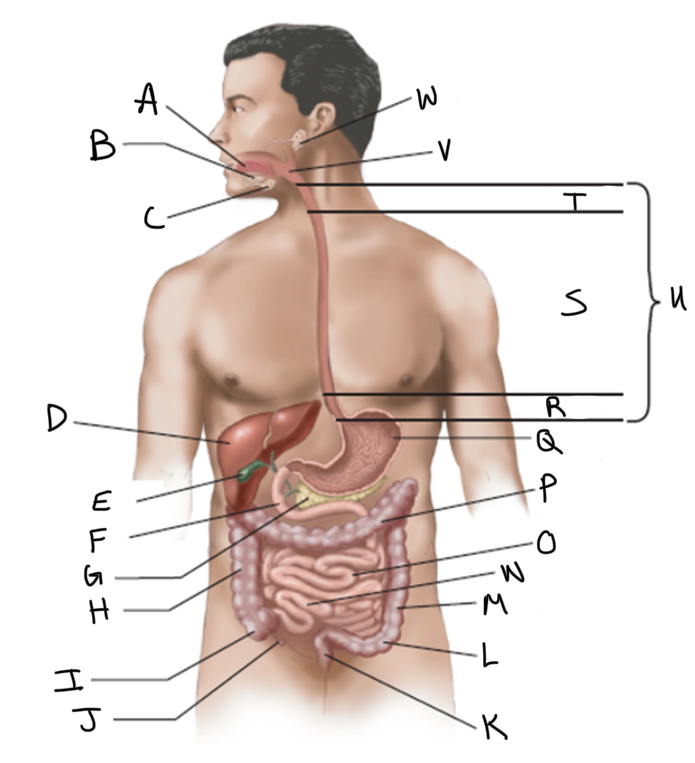
What is H?
Ascending colon
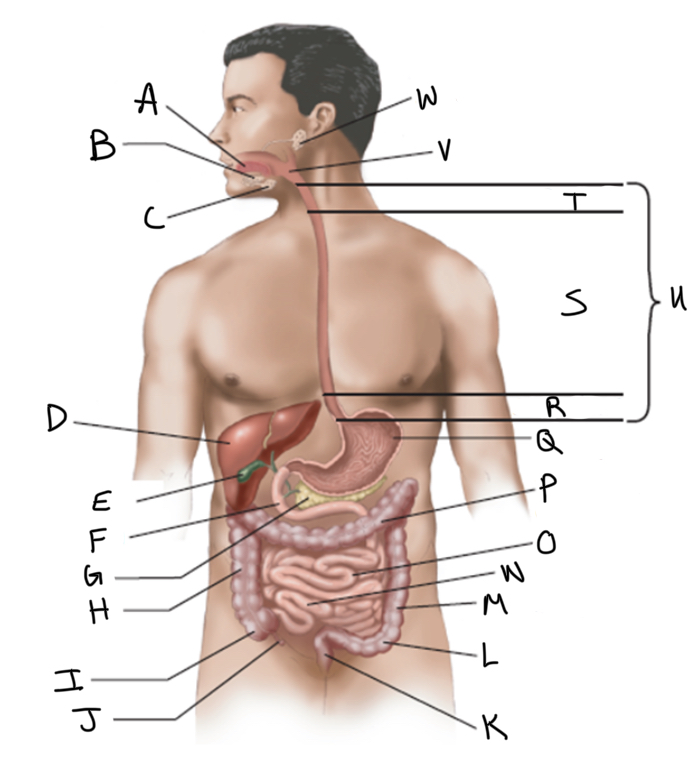
What is I?
Cecum
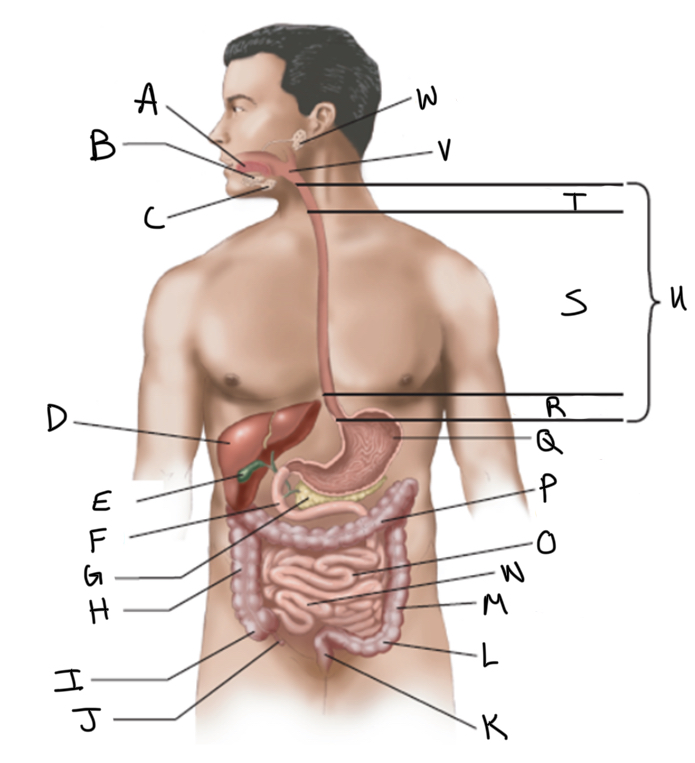
What is J?
Appendix
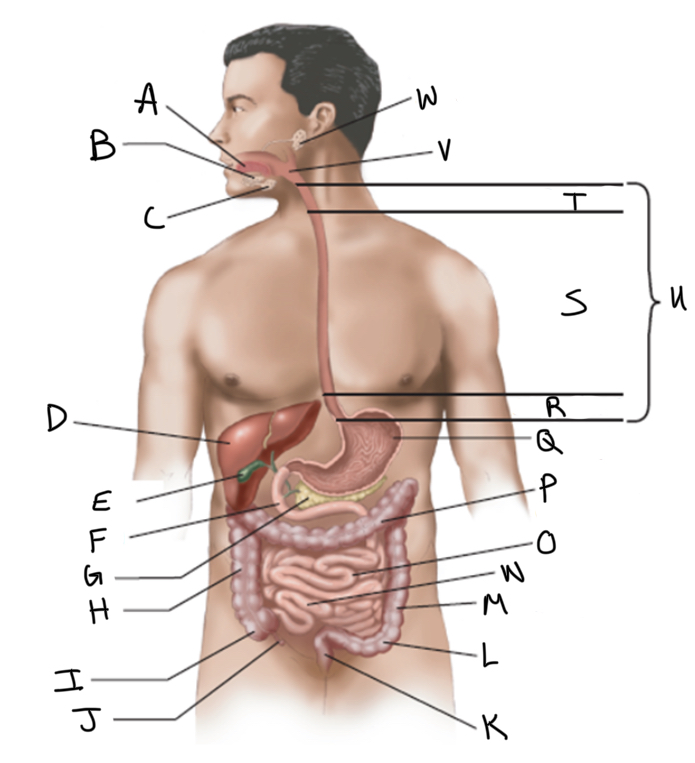
What is K?
Rectum
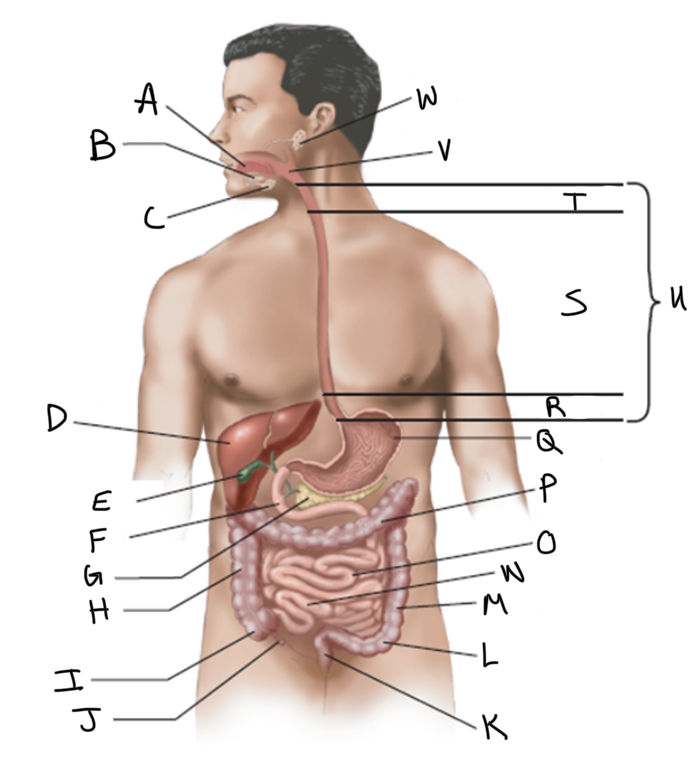
What is L?
Sigmoid colon
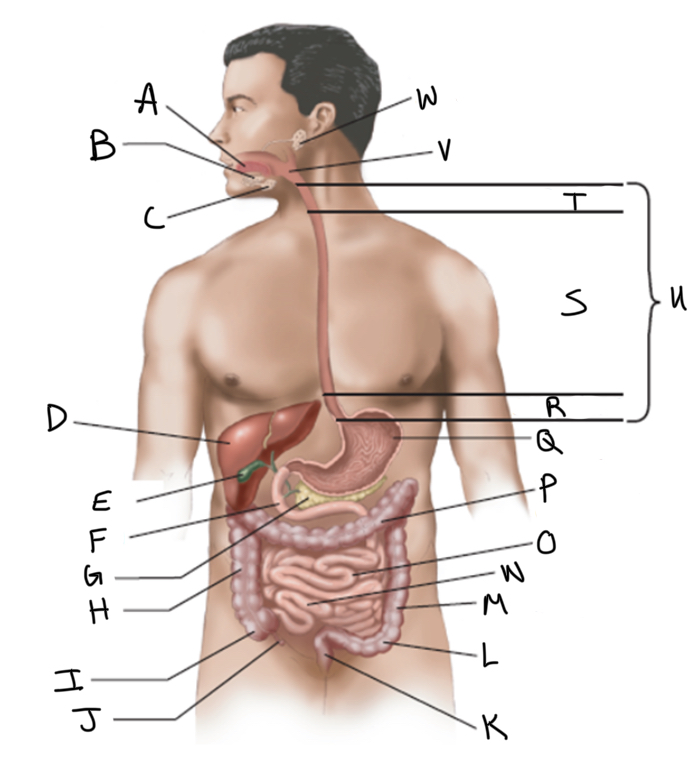
What is M?
Descending colon
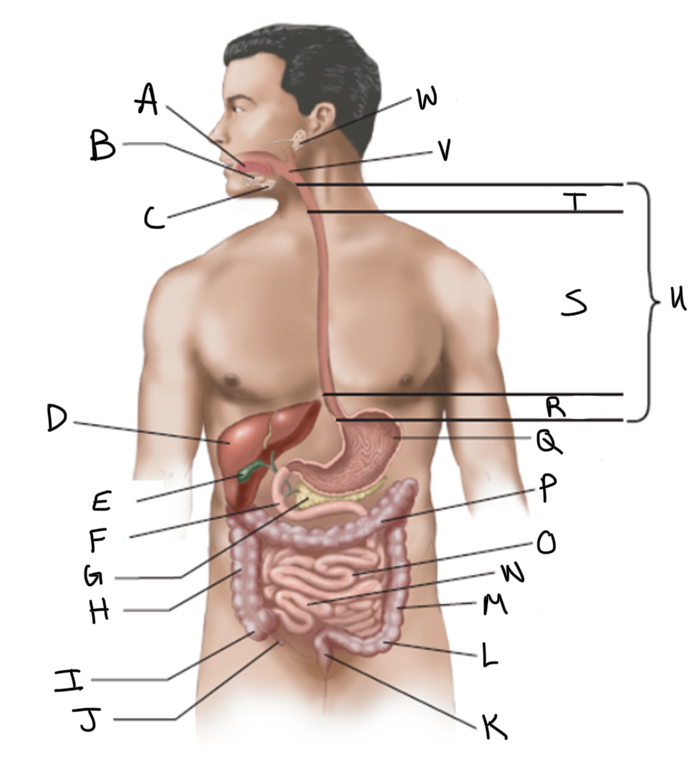
What is N?
Ileum
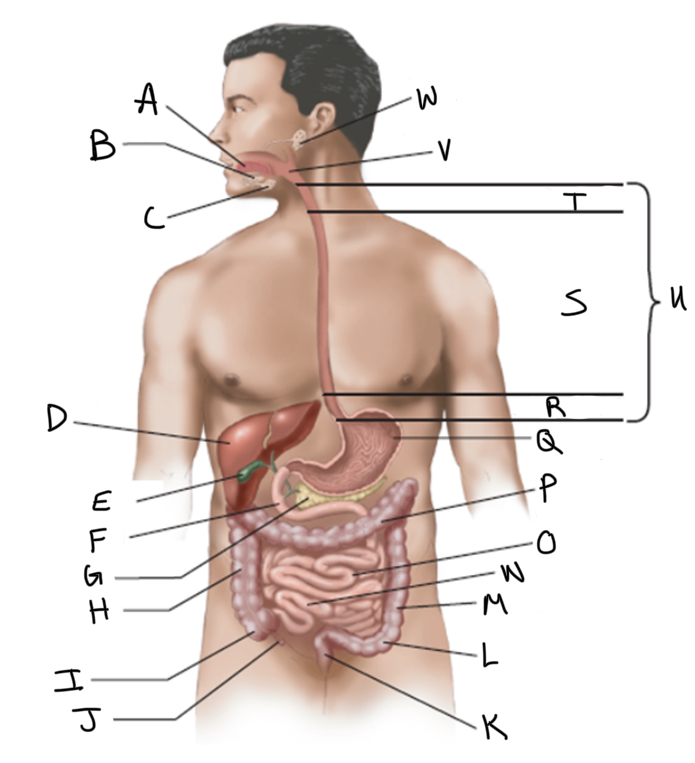
What is O?
Jejunum
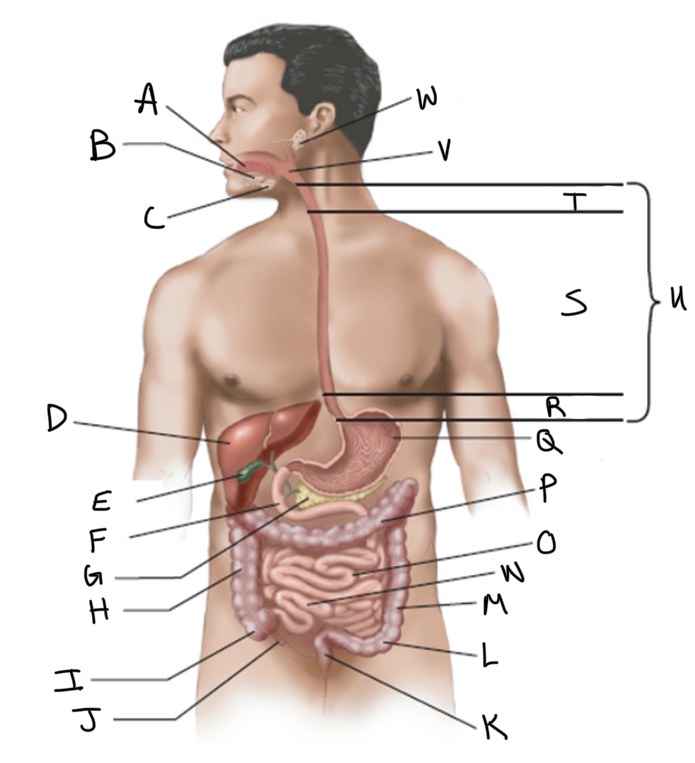
What is P?
Transverse colon
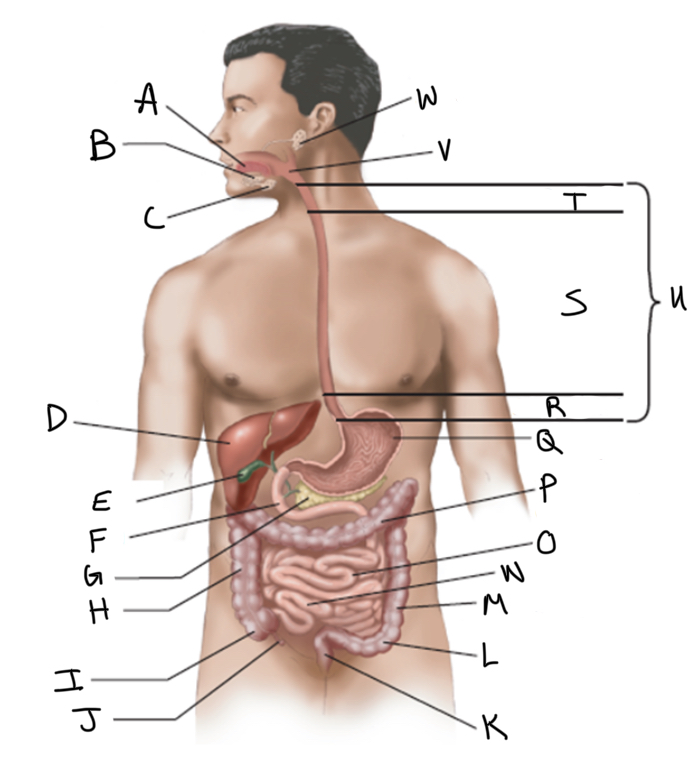
What is Q?
Stomach (interior)
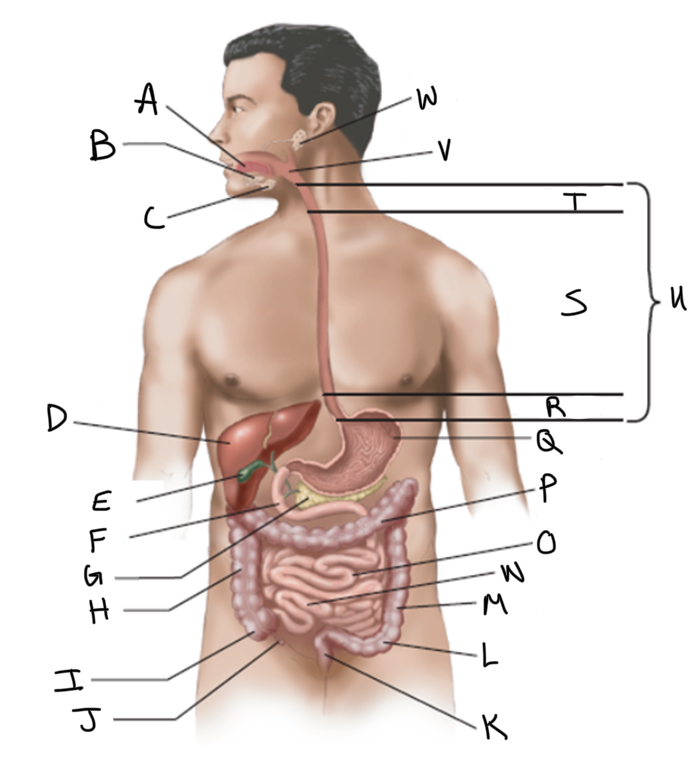
What is R?
Abdominal
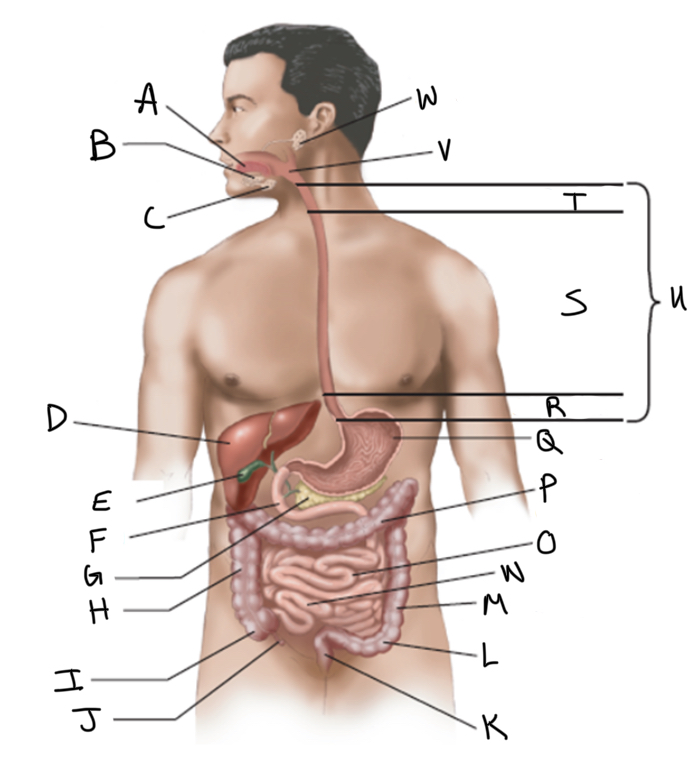
What is S?
Thoracic
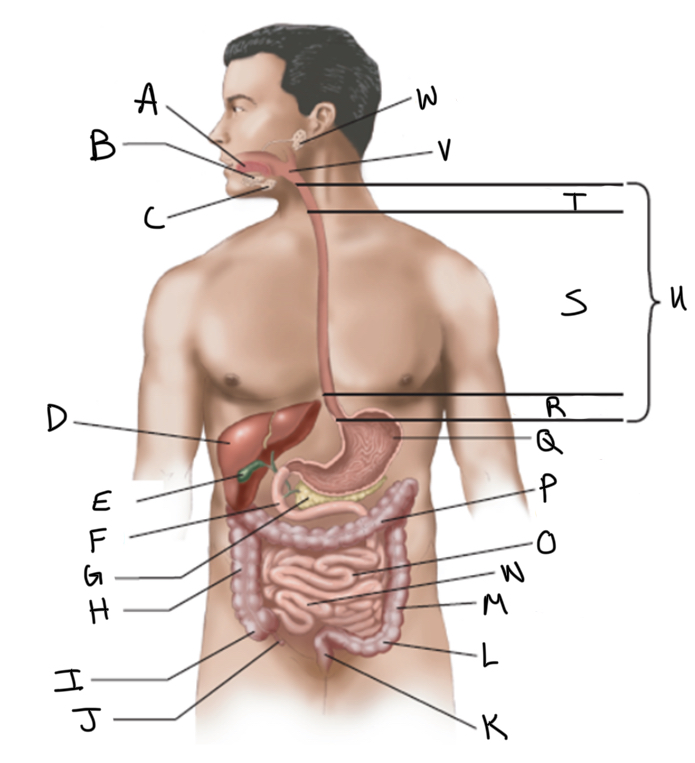
What is T?
Cervical
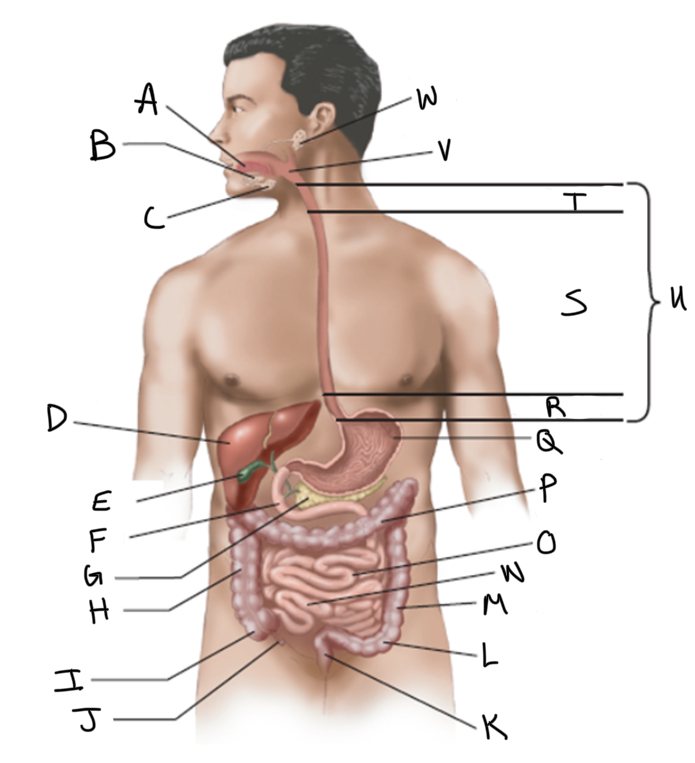
What is U?
Esophagus
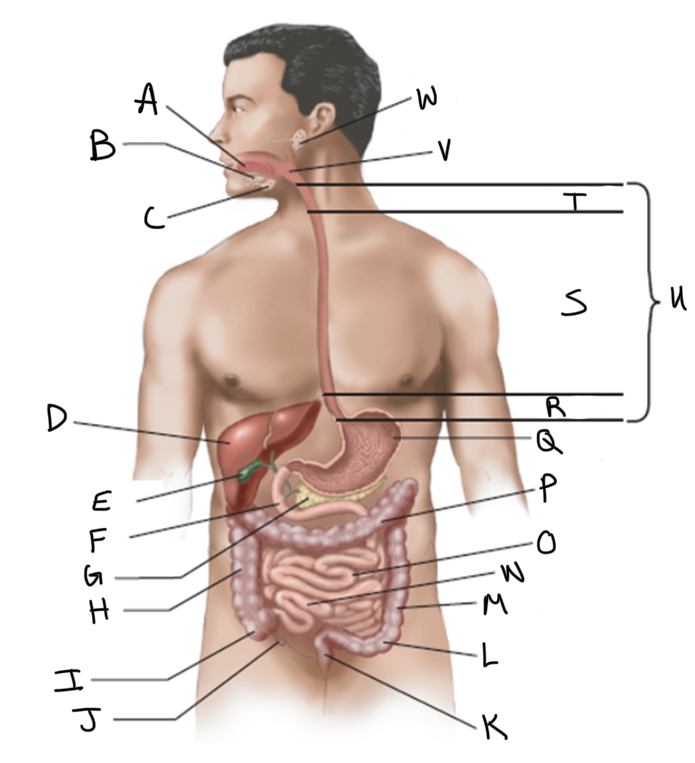
What is V?
Pharynx
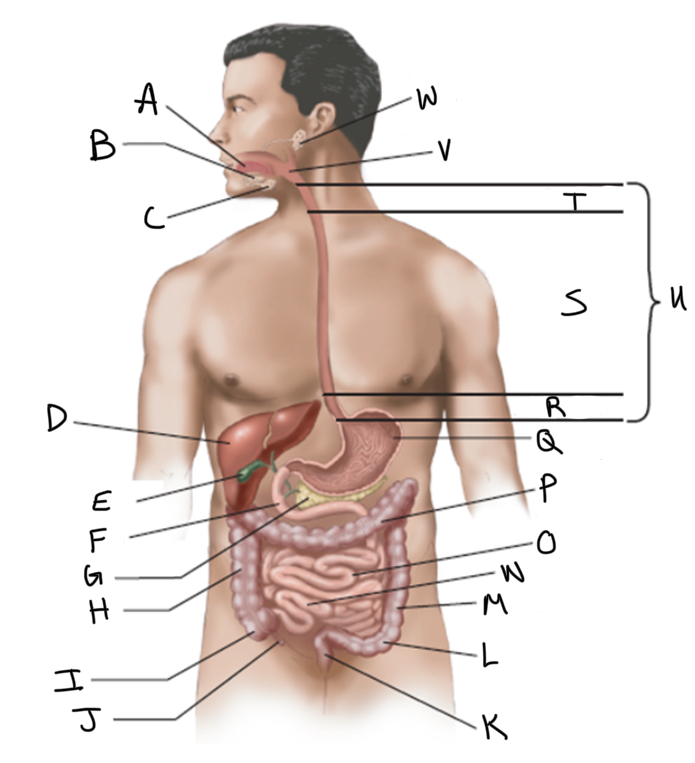
What is W?
Parotid salivary gland
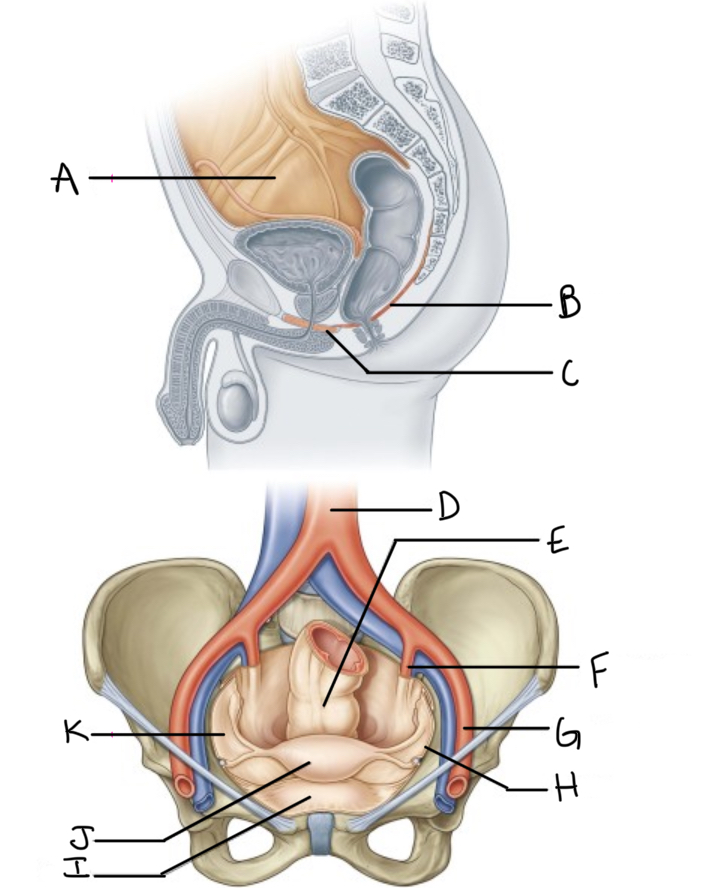
What is A?
Pelvic cavity lined by peritoneum
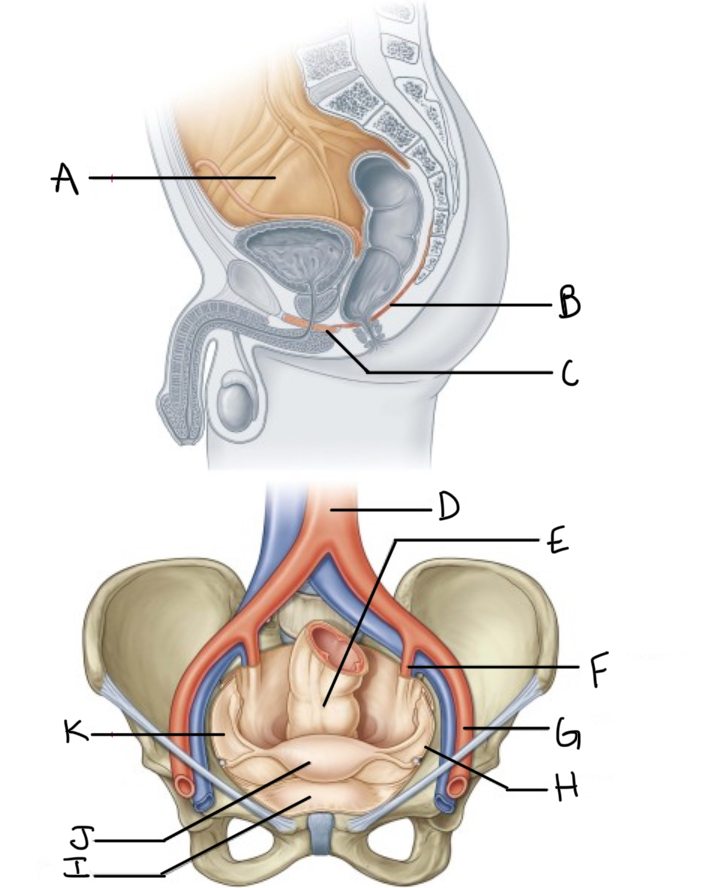
What is B?
Levator ani
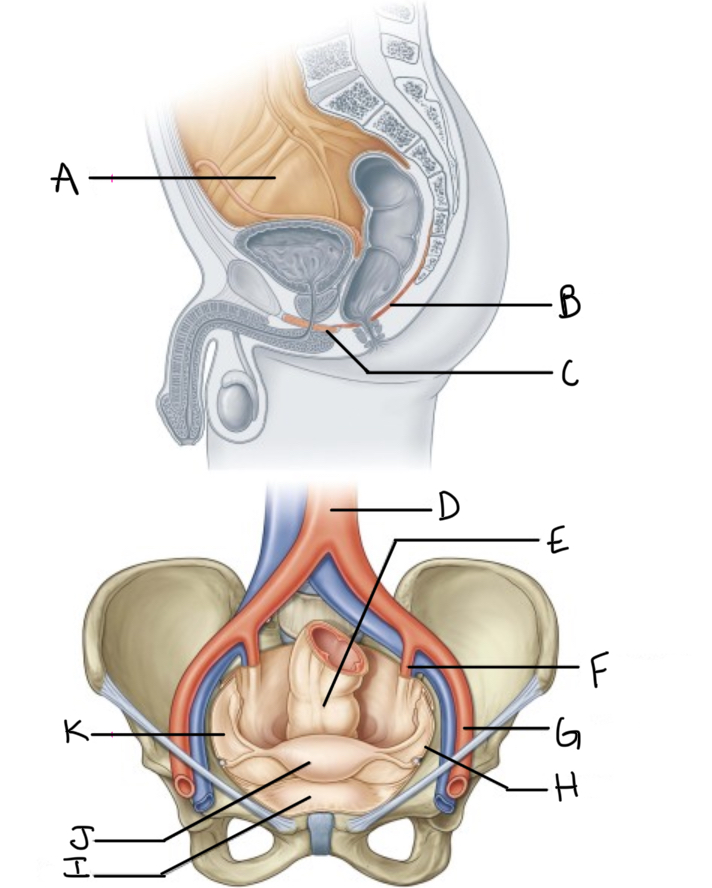
What is C?
Perineal membrane and deep perineal pouch
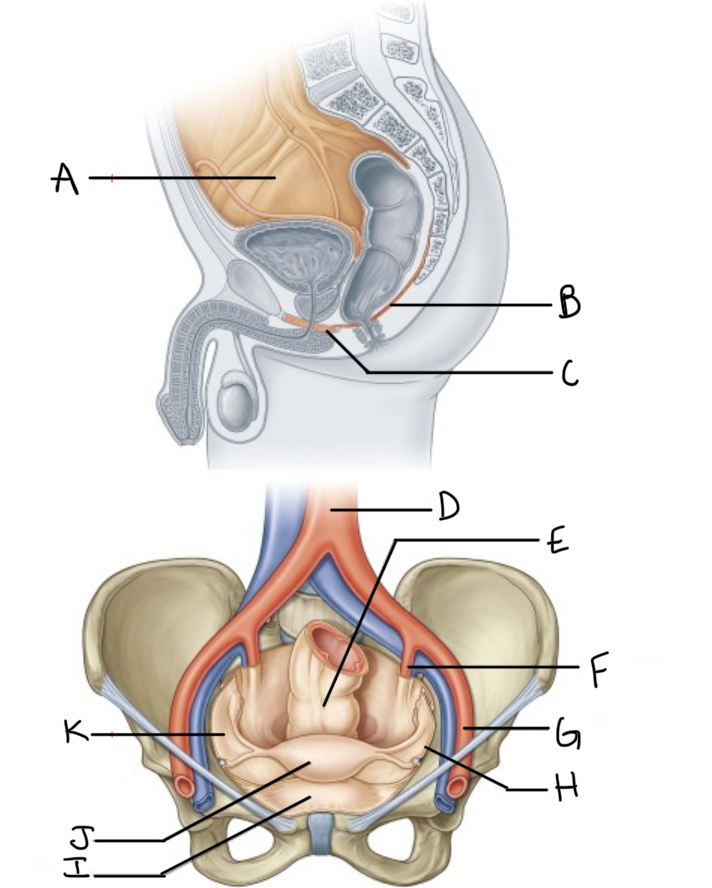
What is D?
Aorta
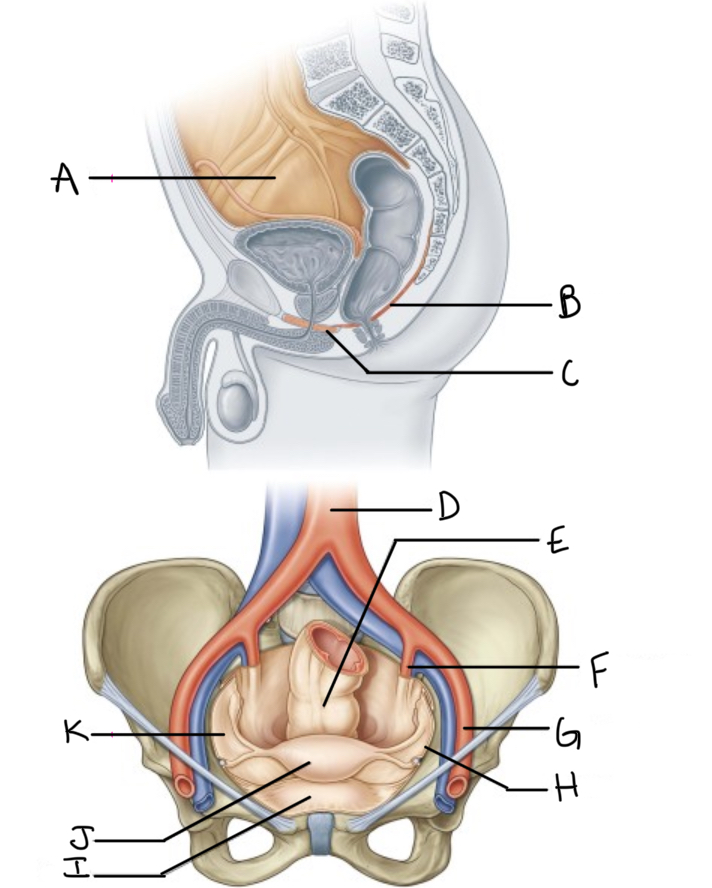
What is E?
Rectum
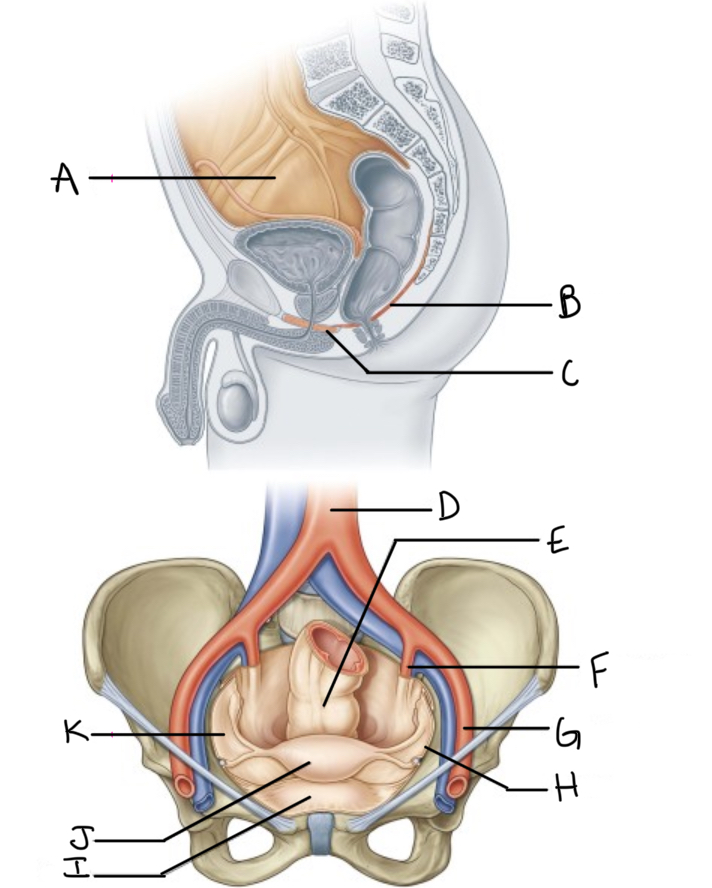
What is F?
Internal iliac artery (artery of pelvis)
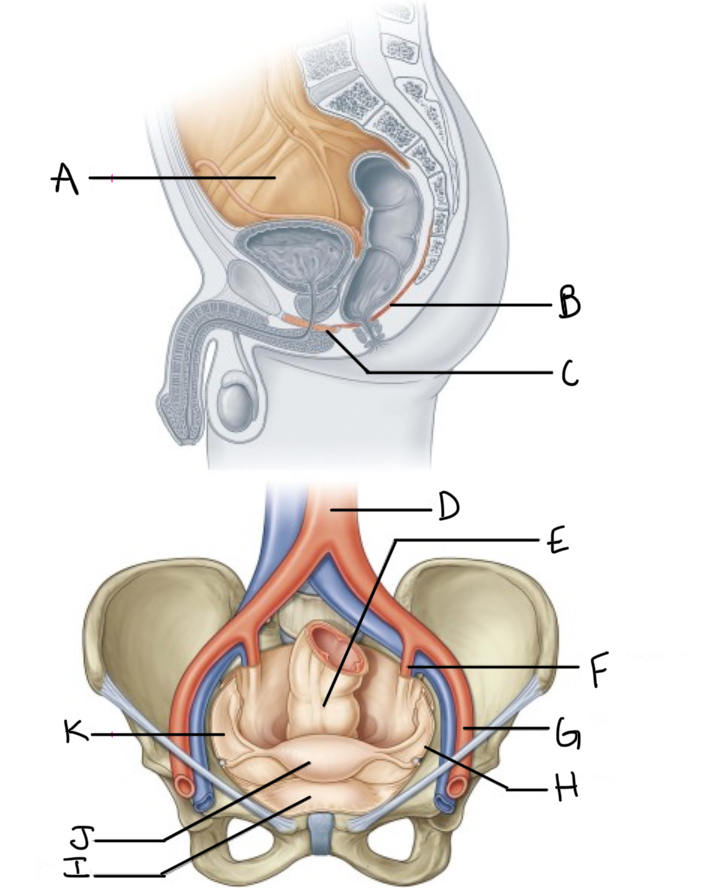
What is G?
External iliac artery
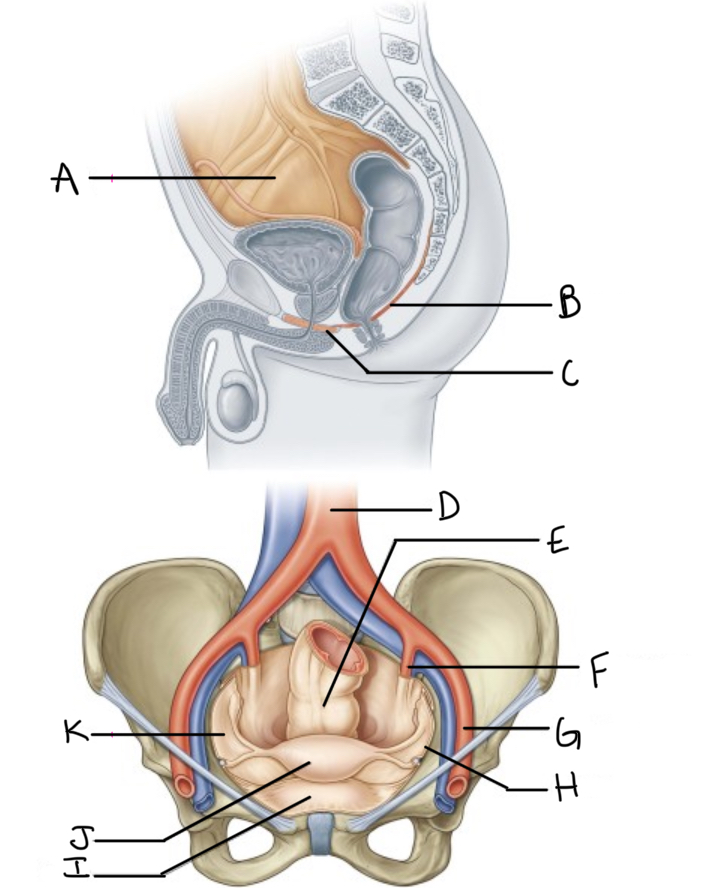
What is H?
Pelvic inlet
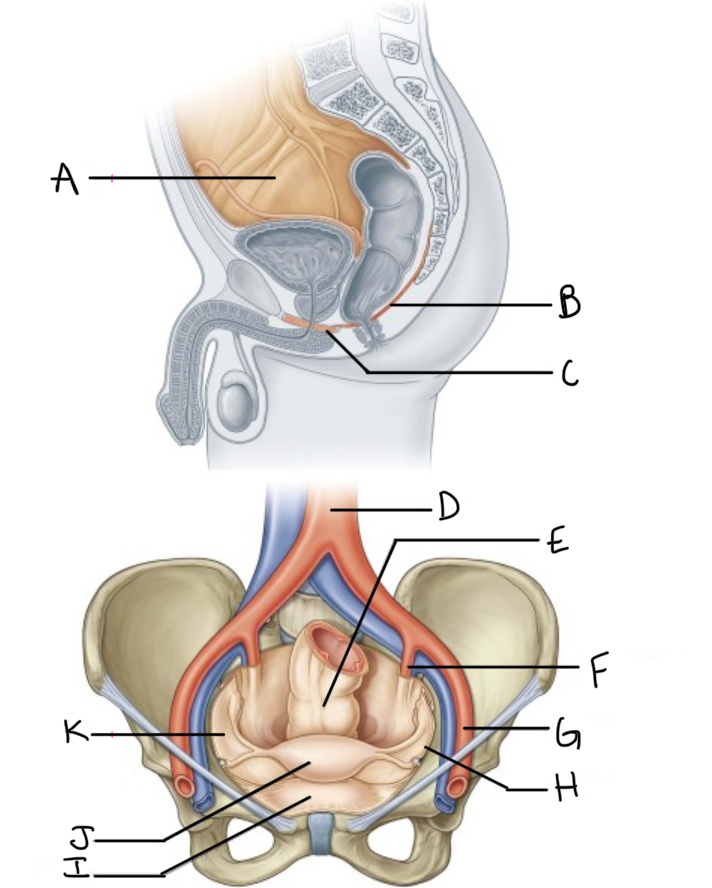
What is I?
Bladder
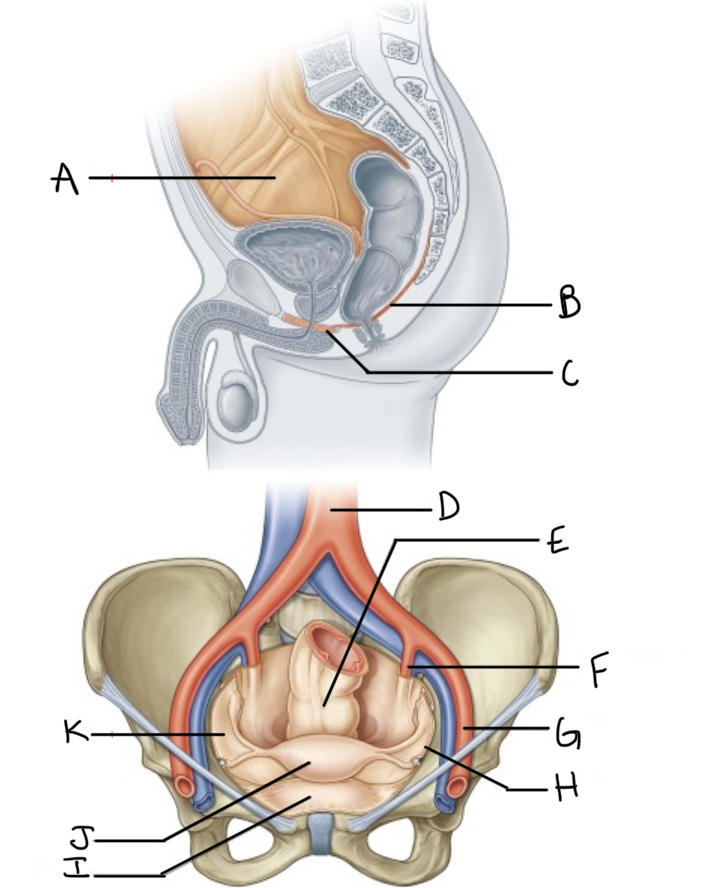
What is J?
Uterus
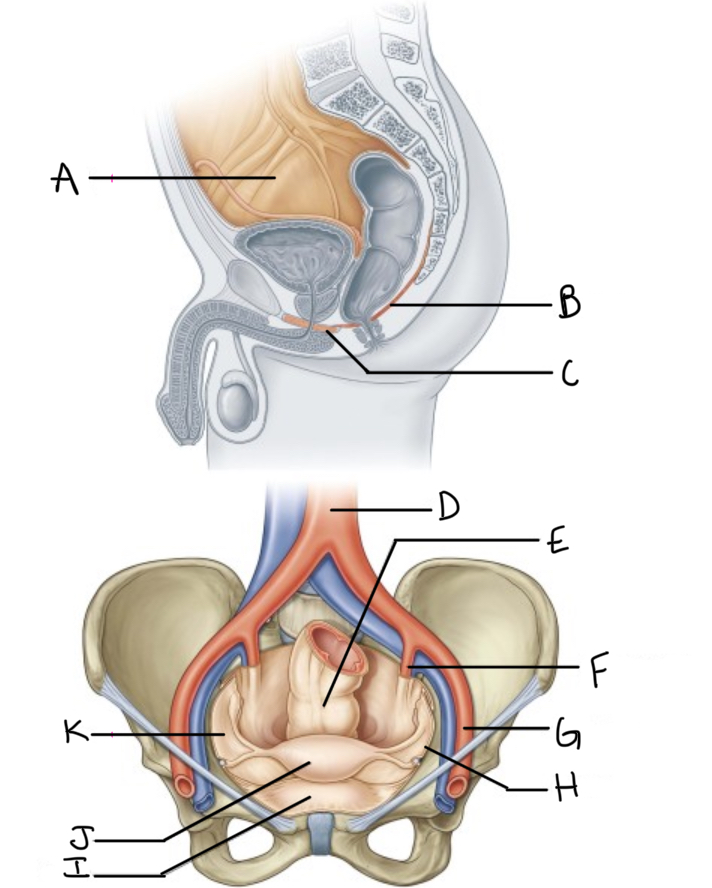
What is K?
Peritoneum