Unit 11 - Immunology
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
Pathogens
all around us (more pathogens in body then normal cells); most do no harm (symbiotic); need to contain them
Primary Defenses against Pathogens
physical barrier; inhospitable environment; attachment prevention; very efficient
Physical Barrier
skin and epithelia; body provides this for pathogens (make it harder for them to enter)
Inhospitable Environment
low pH in stomach (very acidic)
Types on Pathogens
viruses and microbes
Viruses
supply own genome (DNA/RNA); may supply polymerase; hijack cellular machinery for protein translation and packaging; not consider alive bc need host to carry out basic functions; may insert and lie dormant in genomic DNA; small # of diff. types of proteins
Corona Virus SARS-CoV 2
RNA-based viruses; large spike protein; SARS-CoV 2 (virus) causes Covid-19 (disease)
Large Spike Protein
determines which cells/aminals virus can attach to, allows endocytosis of virus, gives virus its characteristic ‘crown’ appearance, and present in many copies; critical to determining which cells it will attached to
Influenza Virus Life Cycle
viral HA protein present in multiple copies; sequence of HA protein used to subdivide viruses; RNA genome; escape endosome
RNA Genome
template for mRNA encoding viral proteins and multiple viral “chorosomes”
Escape Endosome
lower pH causes conformational change of HA and fusion of viral and endosomal membrane
Microbes
mostly bacterial prokaryotes; unilateral eukaryotes; usually live inside host, but outside of host cells (establish themselves in part of your body); some enter cells by phagocytosis and live inside host cells; where a microbe lives determines how the immune system interacts w/ it (outside of cells, immune system has easier access to it then inside cells); many benign and even beneficialAn
Antibiotics
can be efficiently targeted by antibiotics
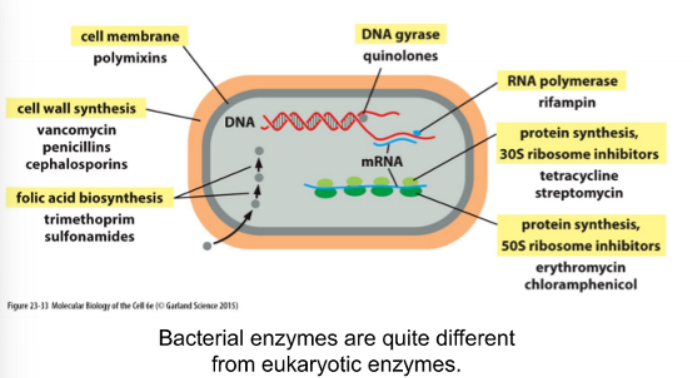
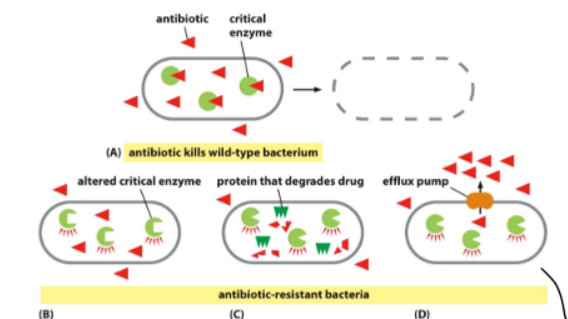
Antibiotic Resistance
3 ways diff. ways bacteria can become resistant to antibiotic (altered critical enzyme, protein that degrades drug, and efflux pump)
Efflux Pump
scariest for humains bc cell pumps everything it doesn’t recognize right back out
Pathogen Summary

Timeline of Immune Response
day 0 - infection
days 0-7 - innate immune response
days 4-7 - adaptive immume response
days 7+ - clearing of infection
Lines of Defenses
first and second line of defense
First Line of Defense
barrier function of skin and epithelial surfaces
Second/last Line of Defense (Immune System)
Innate immune system and adaptive immune system
Innate Immune System
removes tagged pathogens; containment; powerful co-activator of adaptive immunity; most of the work of getting ride of pathogens is done by the innate immune system; immediate recognition (hrs) of pathogen using conserved, invariant epitopes
Adaptive Immune System
identify/tagging specific pathogens; slower response time (days); memory function; recognition using unique, pathogen-specific epitopes
Antigen
molecule recognized by immune system (SARS-Cov2)
Epitope
specific part of an antigen that is recognized
Cross-talk
lots of it; need both innate and adaptive immune systems; adaptive regukates innat and innate regulates adaptive
Immune System Picture
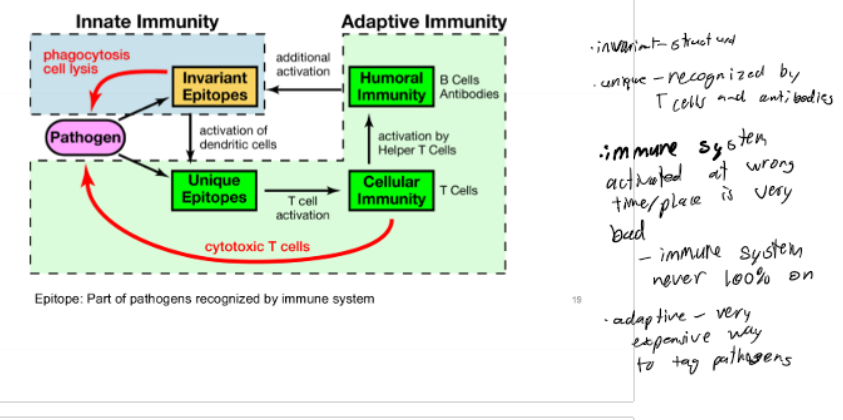
Innate Immunity
complement system, toll-like receptors, and cellar effectors
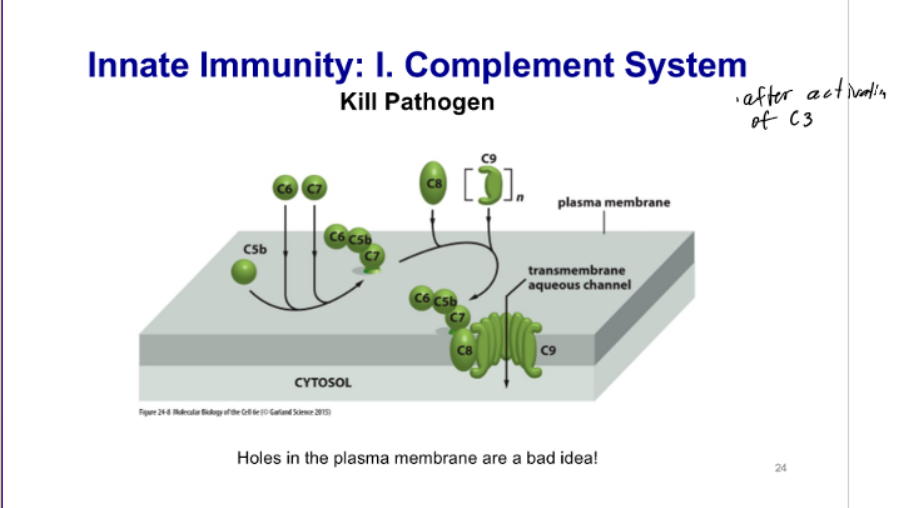
Complement System
set of proteins made in liver and secreted into bloodstream (extracellular); circulate throughout the body; exist as inactive, uncleaved precursors; activated by binding to pathogen surface and other activated complment proteins; A portion and B portion
A Portion
smaller; diffuses away; signaling molecule; short half-life; immune system sees cleaved A, it knows to send things to problem area (“there’s an infection”)
B Portion
larger and more stable; binds pathogen surface for stabilization; forms multimeric complexes; catalitic function; + activation feedback loop (can lead to more proteolysis); “here is the infection”
Proteolysis
breaks protein apart
Complement System again
3 ways to activate; key regulate step; key complement functions
3 Ways to Activate Complement Proteins
classical pathway (recognize bound antibody)
lectin pathway (recognize bacterial sugars)
alternative pathway (recognize pathogen surfaces)
Key Regulatory Step: Cleavage of C3
occurs by any of the 3 pathways - C3 activates a + feedback loop, C3a stimulates innate and adapative response, and C3b functions (tags pathogen and activation and killing pathogens → coat proteins and make pores to kill pathogens)
Key Complement Functions
tag pathogen; activate immune system (adaptive and innate); kill pathogen
Toll-like Receptors
family of transmembrane protein receptors; TLRs expressed on specific immune cells (microphages and dendritic cells → auto-stimulate themselves and induce phagocytosis and other cell behaviors); TLRs expressed on other cells (TLR activation causes release of signals to activate immune response); recognize invariant pathogen epitopes
TLR
Toll-like receptors; signaling proteins; when something binds to the extracellular part, signaling is activated; activate immunological signaling pathways; often release cytokines
TLRs Expression
not every cell makes this; some expressed on plasmamembrane to survey the environment and some on endosomes for intracellular environment
Cytokines
small peptides w/ signaling function (ligands); act over a short distance; most are members of IL; shape immunological response
Cytokines Shape Immunological Response
mark site of infection; influence differentiation of B and T cells; control longevity of activated B and T cells
Macrophages
distributed throughout body; reside under epithelial barriers and in tissues so they can patrol these surfaces; sentinels and killers; digest/dispose of apoptosed cells and microbes; have stages of activation
Dendritic Cells
distributed throughout body and under epithelial surfaces; move to thymus when activated; match antigens to T cells; link innate and adaptive; key role in activating adaptive response; sentinel (doesn’t kill); analyzes what kind of pathogen is and make sure immune system is activated correctly
Lymphatic System
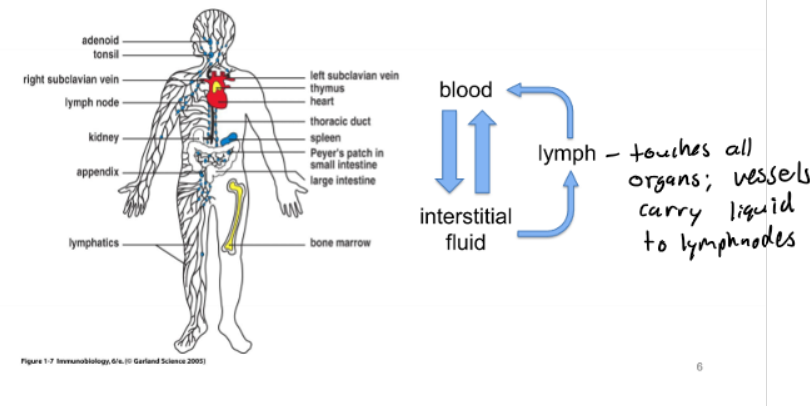
Immune Cells
derived from a hematopoietic precursor
Erytrhrocyte
red blood cell
Leukocyte
white blood cell (B/T cells)
Lymphoid Cell
leukocyte in lymphatic system
Myeloid Cell
leukocyte outside in the lymphatic system (in blood and tissues)
Lymphoid Effector Cells
B and T cells
B Cells
arise/mature in bone marrow and lymph; make antibodies/BCR; co-activate innate; act on extracellular epitopes; react w/ protein and non-protein epitopes; epitope must be on outside of pathogen; make one type pf antibody per cell; immunological memory; pretty much all RER - secretes massive amounts of antibodies and make 1 type

Clonality
make one type of antibody per B cell
T Cells
mature in thymus; make TCR; help activate B cells/kills cells; act on extra/intracellular epitopes; react w/ protein epitopes only; epitope can be outside or inside pathogen
Structure of an Antibody
2 identical heavy chains and 2 light chains (linked by disulfide bridges); y shaped; 2 major requirements - highly variable and conserved
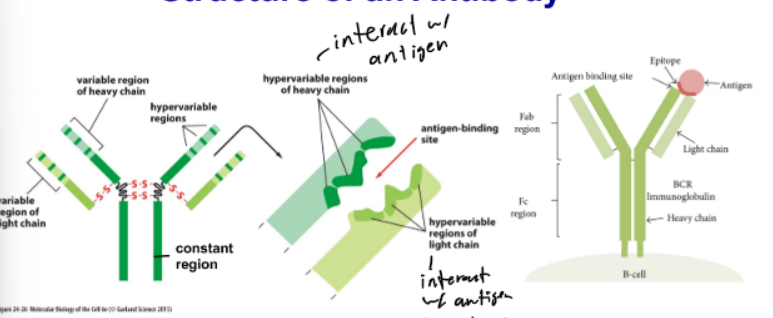
Antibody Light Chains
interact w/ antigen; want as much variation as possible so can detect as many different types of pathogens
Highly Variable - Antibody
antigen binding site; to detect as many epitopes as possible
Conserved - Antibody
constant region; body needs to know if it is an atibody; must be recognizable as an antibody
Problem w/ Encoding Antibody Diversity
want as many diff. antibodies as possible; need 2 genes to encode an antibody; requires 12 × 10^9 nt for antibodies alone (space issue)
How to Generate Antibody Diversity
somatic DNA recombination so assembly of a functional antibody locus and during an immune response
Assembly of a Functional Antibody Locus
2 types - V-region assembly and junctional diversity
V-Region Assembly
type of somatic DNA recombination (assembly of a functional antibody locus) - combinatorial use of DNA segments encoding variable region; take genomic DNA elements and mix them around to get what you want
Junctional Diversity
type of somatic DNA recombination (assembly of a functional antibody locus) - addition of random NT’s to joints between DNA segments; during recombination; DNA ends processed; key enzyme TdT
Junctional Diversity - DNA Ends Processed
removal of NTs → insertion of NTs → insertion and removal involve a random # of NTs and are non-templated
B Cell Antibody Diversity
heavy chain (1 locus)
light chain (2 loci - kappa and lambda) - antibodies use one of the other but not both; genomic DNA of individual B cells is NOT identical
During an Immune Response
class switching and somatic hypermutation
Class Switching
type of somatic DNA recombination during an immune response; use of different constant chains to generate diff. classes of antibody; switches out 1 constant region for another
Somatic Hypermutation
type of somatic DNA recombination during an immune response; mutate hypervariable region to obtain higher affinity antibodies; take antibody that recognizes a pathogen and mutate it to make it better
Genomic Antibody Locus
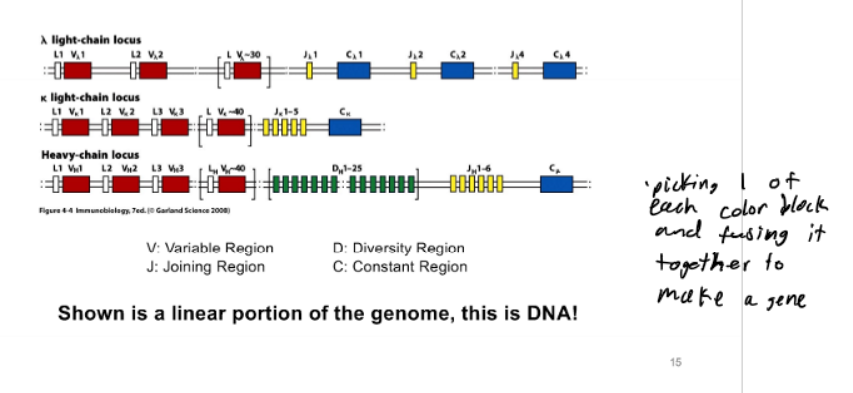
Antibody Locus Rearrangement
dedicated recombinases (Rag 1/2) carry out recombination rxn (similiar mechanism to Cre/LoxP); recombination creates dsDNA break (BAD/DANGEROUS/NOOO); permanetly alters genome; have 1 shot of this in 1 chromosome or cell dies
Pros and Cons
pros - a lot of variety of antibodies can potentially make; DNA encoded; molecular record; can be preserved and recalled later; B cell proliferation will amplify antibody
cons - most rearrangements are non-productive; not all light/heavy chains can pair; introduction of dsDNA breaks; some antibodies react w/ self-proteins
Reading Frame Picture

B Cell Rearrangements Occur in a Specific Sequence
alletic exclusion, clonality, and BCR
Alletic Exclusion
once 1 chain has rearranged successfully, shut down recombination at all loci for that chain; if first locus make good heavy chain, don’t start changing the second; then kappa first and then lambda; if have multiple heavy chains made by the same B cell = not good (if no good heavy chain locus, B cell dies)
Clonality
one antibody locus per B Cell
BCR (B Cell Receptor)
successful recombination turns antibody into receptor, initiates signal transduction
Testing for Productive Rearrangements
is a H-chain productivey rearranged? → is a L-chain locus productivity rearranged? -? are H and L chain compatible? → is there a lack of activation by self proteins?
if all these are true then antibody can bind a pathogenic antigen and allows B cell to enter into circulation
IgD/IgM produced by alternatve splicing and variable region identical, only constant region differs
Selecting a Functional Receptor
kill signal or growth signal; how to recognize between self/pathogen proteins
Kill Signal
if reactive w/ self-antigens, will delete B cell; if antibody binds to self-protein, co-stimulation not there
Growth Signal
if have a 2nd, + signal B cell proliferation or otherwise inactive/suppressed
Antibody Signaling: The BCR
antibody complexed w/ kinase proteins and engagement of BCR activates intracellular signal transduction; highly sensitivel; antigens often repetitive and in high abdundance; antibodies link w/ intracellular things for signaling to get B cell activation
Activation of B Cells Requires Co-Stimulation
T Cell Dependent and Independent Activation
T Cell Independent Activation
many active BCRs are clustered together; co-stimulatory signal present (antibody + complement protein binding); no T cell involvment; allows proliferation and antibody secretion; activation of BCR and binding of complement = pathogen
T Cell Dependent Activation
many active BCRs are clustered together; co-stimulatory signal from helper T cells also present; allows proliferation and antibody secretion; also activates class switching, somatic hypermutation, and differentiation to memory B Cell
Levels of B cell Activation
T cell independent (proliferation and antibody secretion) and dependent activation (proliferation, antibody secretion, class switching, and somatic hypermutation)
Class Switching
based on need of immune system, it will move to one of these types; uses multiple molecular processes (alternative splicing and somatic DNA recombination); co-stimulatory signal and co-activating cell direct B cell class switching via cytokines
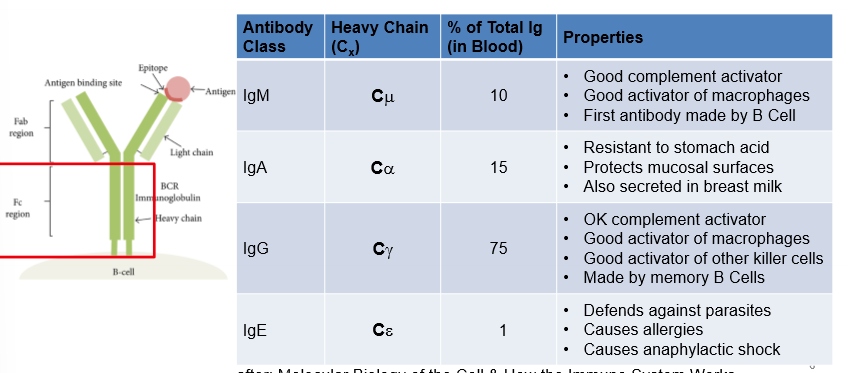
Alternative Splicing
can produce both secreted and membrane bound antibodies w/ the same constant region
Summary Picture
Antigens and Epitopes
immune system interacts w/ pathogenic proteins, sugars, and nucleic acids; molecules can be on the outside or inside; antibody can recognize any molecular shape but only sees the things on the outside of a pathogen (need T cells for inside)
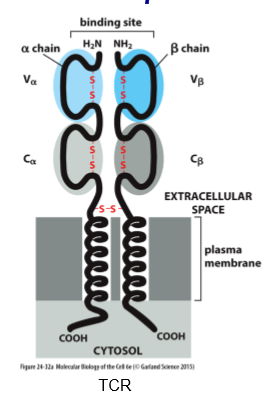
alpha-beta T Cell Receptor
2 chains instead of 4; constant and variable domain on each chain; most a-b heterodimers; associate w/ kinases to make receptor
T Cell receptor Rearrangement
diversity in TCR same way as antibodies; random blocks and put them together
Picture
2 Major Classes of T Cells
cytotoxic and helper
Cytotoxic T Cells
directly kill virus infected cells including host cells
Helper T Cells
activate B, T, and effector cells amd crucial for activating B cells
TCRs Recognize what?
peptides presented by MHC molecules
MHC Molecules w/ TCRs
present internal peptide fragments; MHC proteins very diverse; MHC class 1 and 2; HLA proteins are part of the MHC complex (why have transplant rejection)
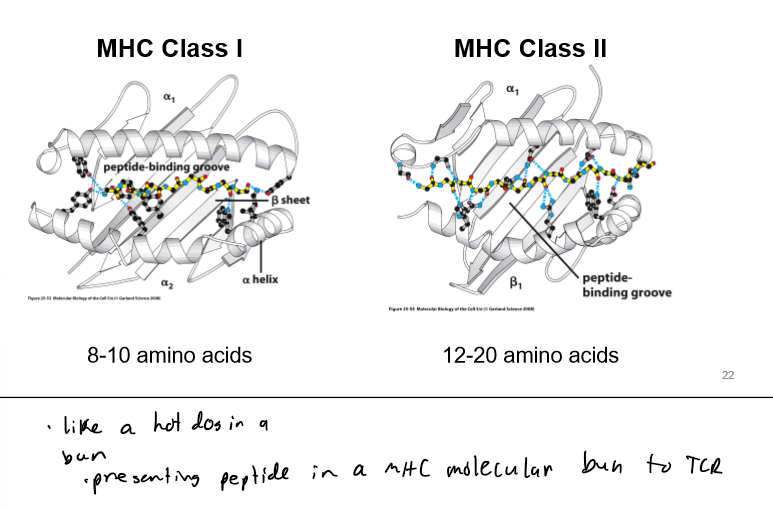
MHC Class 1
on all cells
MHC Class II
on antigen presenting cells (APCs)
MHC - TCR Interaction
TCR sits on top of MHC loaded w/ peptide; detects both MHC and peptide; hypervariable regions in direct contact w/ peptide
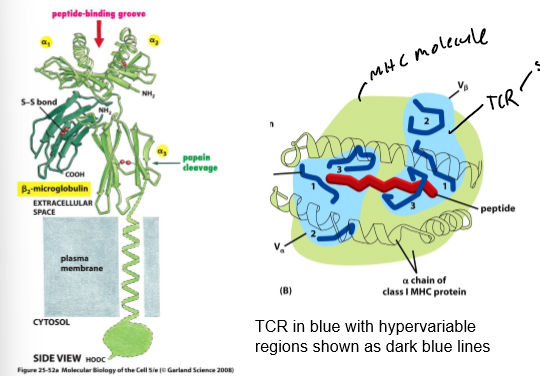
Loading MHC 1 Molecules
recognized by cytotoxic T cells; continous, low-level import peptides into the ER, loading and presentation on plasmamembrane; if viral, will express viral proteins on membrane (and in cases of need, this gets upregulated)
Loading MHC II Molecules
loaded in endosome; recognized by helper T cells; only expressed on subset of cells (APCs - macrophages, dendritic, and B cells); activation of TLRs and stimulates APCs