21. Nematodoses of the respiratory system of dogs & cats (Crenosoma, Angiostrongylus, Aeluostrongylus, Filaroides, Capillaria)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is the species of Angiostrongylus?
Angiostrongylus vasorum
What are the definitive hosts for Angiostrongylus vasorum?
Dog, canids
What is the species of Aelurostrongylus?
Aelurostrongylus abstrusus
What are the definitive hosts for Aelurostrongylus abstrusus?
Cat, felids
Where do adult Angiostrongylus vasorum worms live in the host?
Arteria pulmonalis and right heart
Where do adult Aelurostrongylus abstrusus worms live in the host?
Bronchioles and lung parenchyma
What are the intermediate hosts for Angiostrongylus vasorum and Aelurostrongylus abstrusus?
Snails, slugs
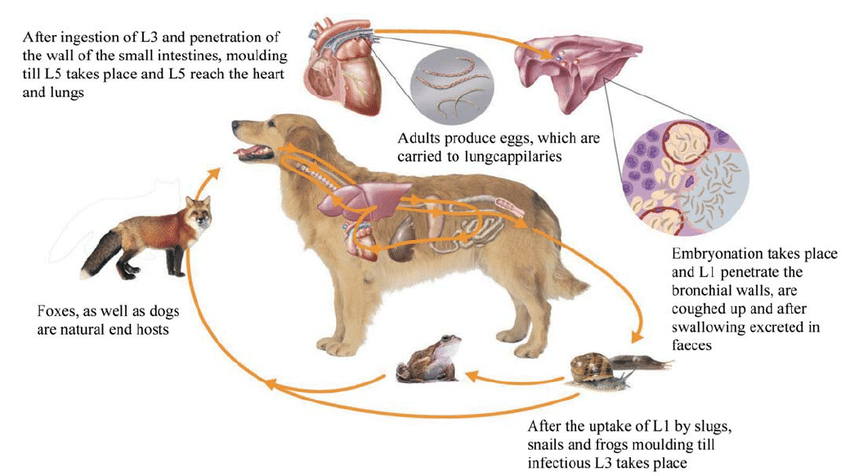
What are the paratenic hosts for Angiostrongylus vasorum and Aelurostrongylus abstrusus?
Frog, rodent, snake, ducklings, mice, sparrow
What is the pathogenesis of Angiostrongylidae infections?
Lungs: Accumulated egg surrounded by solid, yellowish granulomatous nodules (can become 1cm)
Heart: Signs of respiratory & circulatory disease. Granuloma formation, DIC.
Egg & larvae in pulmonary arterioles, capillaries → blockage → congestive heart failure.
What are the clinical signs of Angiostrongylidae infection?
Asymptomatic or symptomatic (respiratory and cardiovascular disorders, coagulopathy, central nervous disorders), exercise intolerance, coughing, sneezing, nasal discharge, respiratory acidosis, subcutaneous haematomas.
How is Angiostrongylus vasorum diagnosed?
Baermann technique (irregular excretion), serology (ELISA), x-ray (enlarged right heart), flotation (damaging to larva)
What is the treatment for Angiostrongylus vasorum?
Fenbendazole, ivermectin, milbemycin oxime, moxidectin + antibiotics.
What is the species of Filaroides?
Filaroides osleri
What are the definitive hosts for Filaroides osleri?
Dog
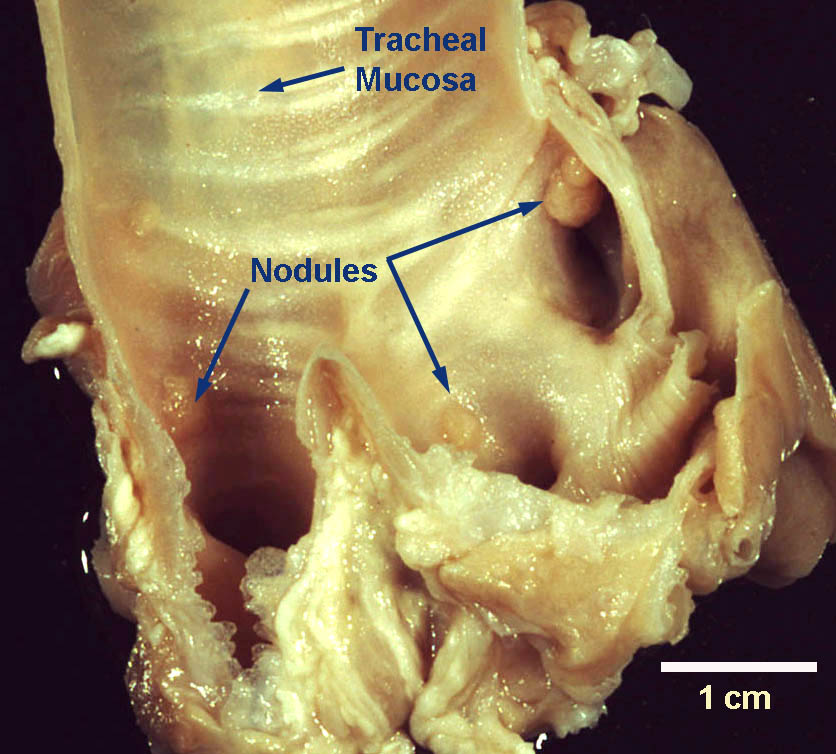
Where do adult Filaroides osleri worms live in the host?
Granulomatous nodules on the mucosal surface of the distal trachea, tracheal bifurcation, and bronchi.
Does Filaroides osleri have an intermediate host?
No, it has a direct life cycle.
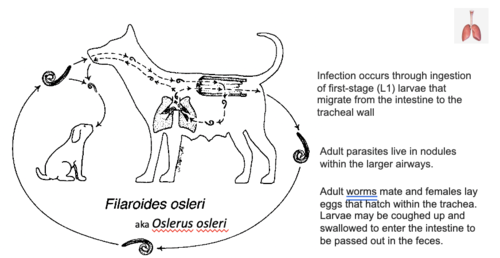
How is Filaroides osleri transmitted?
Faecal-oral, infected saliva from mother to puppy.
L1 is infective stage
What are the clinical signs of Filaroides osleri infection?
Usually asymptomatic, coughing, respiratory distress.
Immunosuppressed animals may develop hyper-infection with severe bronchopneumonia & may die
How is Filaroides osleri diagnosed?
Pharyngeal swab (sputum), Baermann bronchoscopy. (Eggs and larvae rarely seen in faeces)
What is the treatment for Filaroides osleri?
Fenbendazole, ivermectin, moxidectin, milbemycin.
What is the species of Capillaria in the respiratory system?
Capillaria aerophila
What are the species of Capillaria affecting other locations in the body?
Liver: Capillaria hepatica
Urinary bladder: Capillaria plica
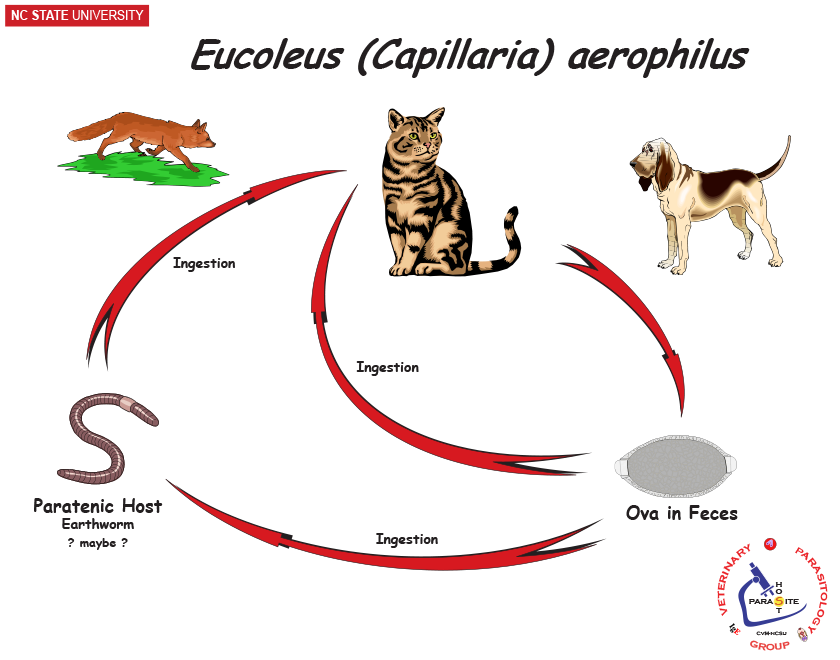
What are the definitive hosts for Capillaria aerophila?
Carnivores, humans Zoonotic
Where do adult Capillaria aerophila worms live in the host?
Frontal sinuses, trachea, bronchi, and rarely nasal cavities.
What are the paratenic hosts for Capillaria aerophila?
Earthworms
What are the clinical signs of Capillaria aerophila infection?
Dyspnea, bronchitis, tracheitis, cough, nasal discharge.
How is Capillaria aerophila diagnosed?
Flotation method.
What is the treatment for Capillaria aerophila?
Ivermectin, moxidectin, milbemycin.
What are the definitive hosts for Crenosoma vulpis?
Fox, dog, wolves, raccoon
What are the intermediate hosts for Crenosoma vulpis?
Snails
What are the paratenic hosts for Crenosoma vulpis?
Frog
What are the clinical signs of Crenosoma vulpis infection?
Persistent cough, pneumonia.
How is Crenosoma vulpis diagnosed?
Larvoscopy, x-ray.
What is the treatment for Crenosoma vulpis?
Ivermectin, fenbendazole, milbemycin, advocate, moxidectin + antibiotics.