NS&E L4 202(4-5) Finals Vocabulary (Combined w/o MYE Vocabulary)
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Proton
Positively charged part of an atom, gives the atom it's identity
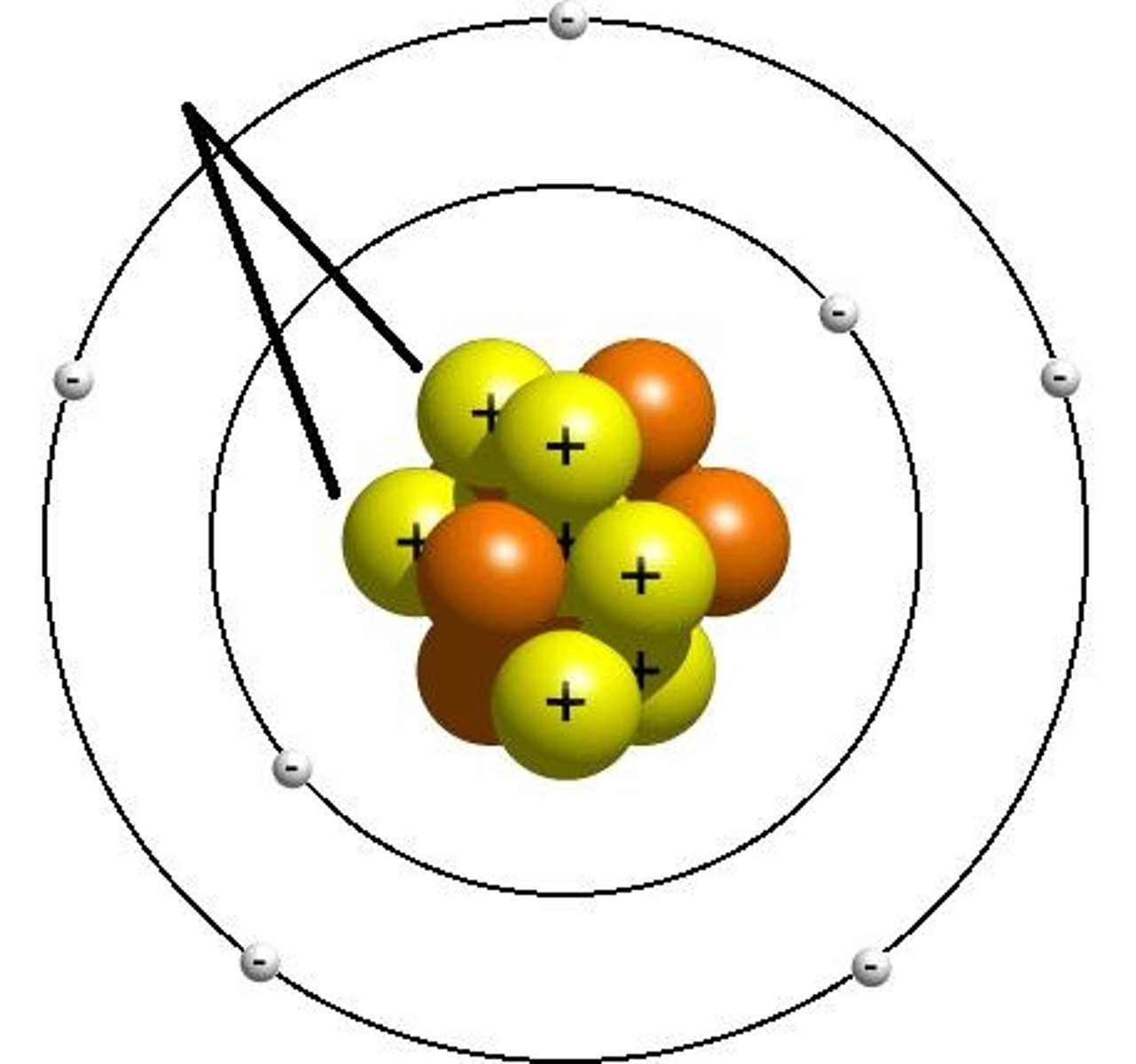
Electron
Negatively charged part of an atom, is responsible for bonding
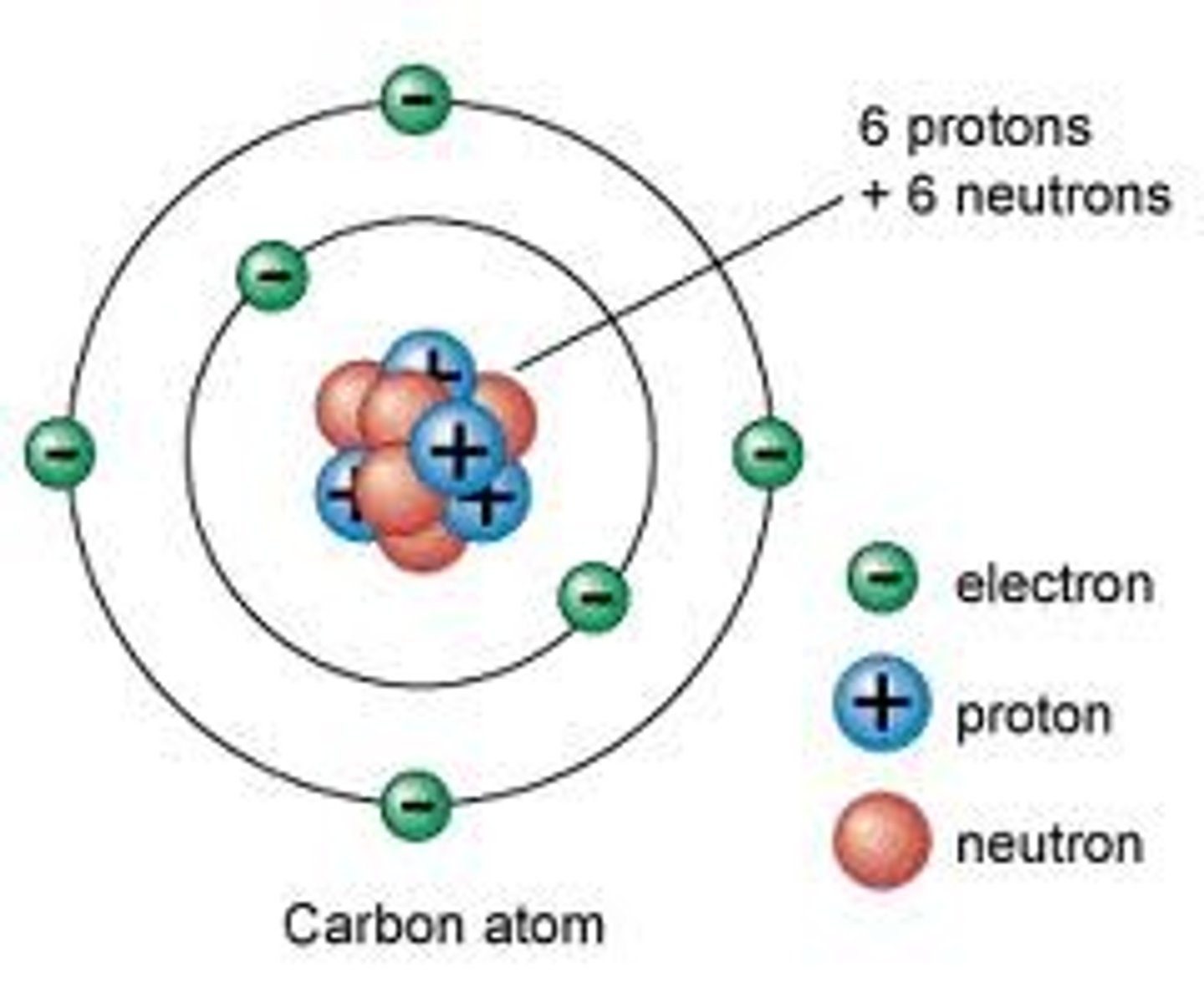
Neutron
Neutral part of an atom, holds the nucleus together since the protons would naturally want to repel each other

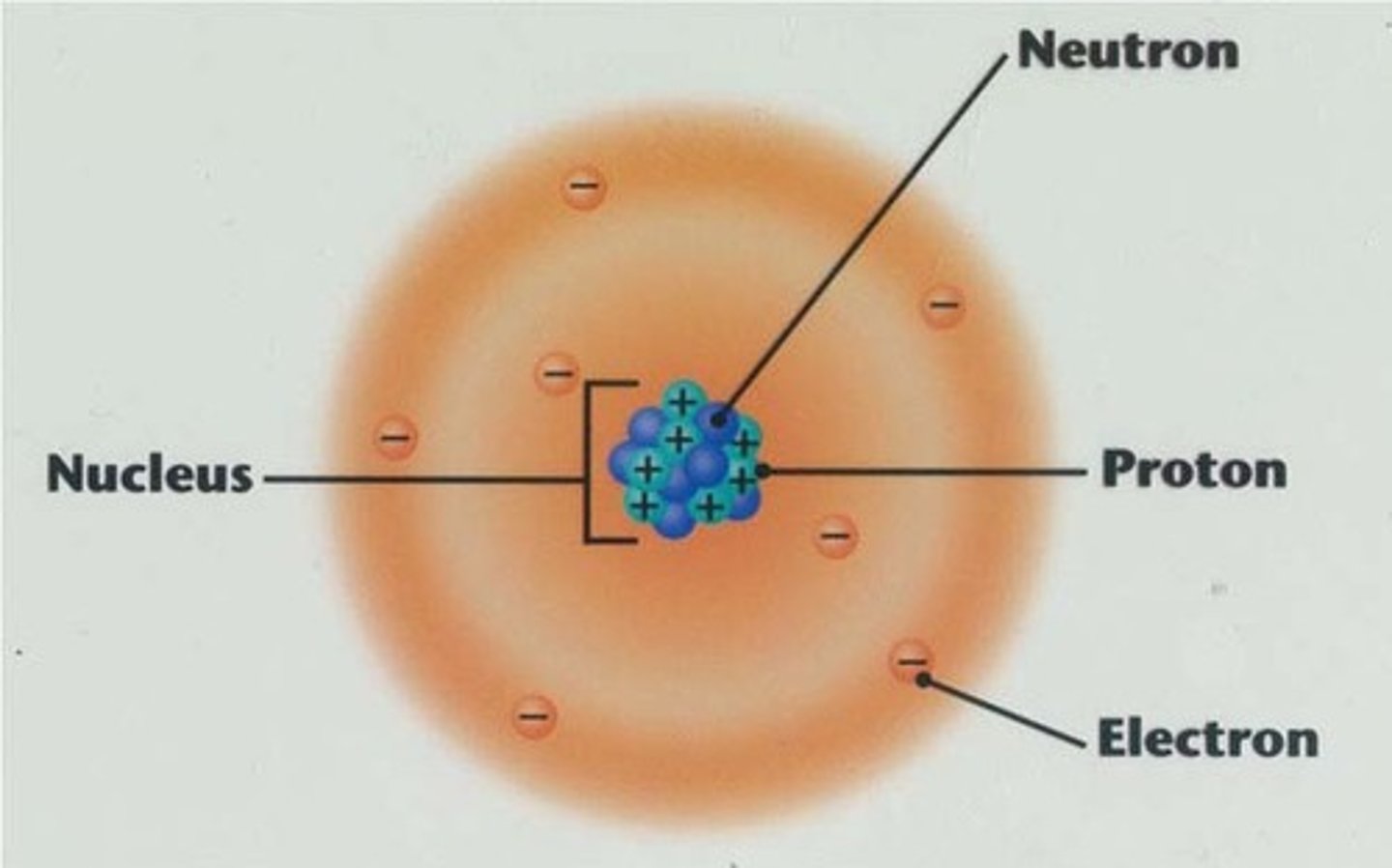
Nucleus
Center of an atom, that contains protons and neutrons
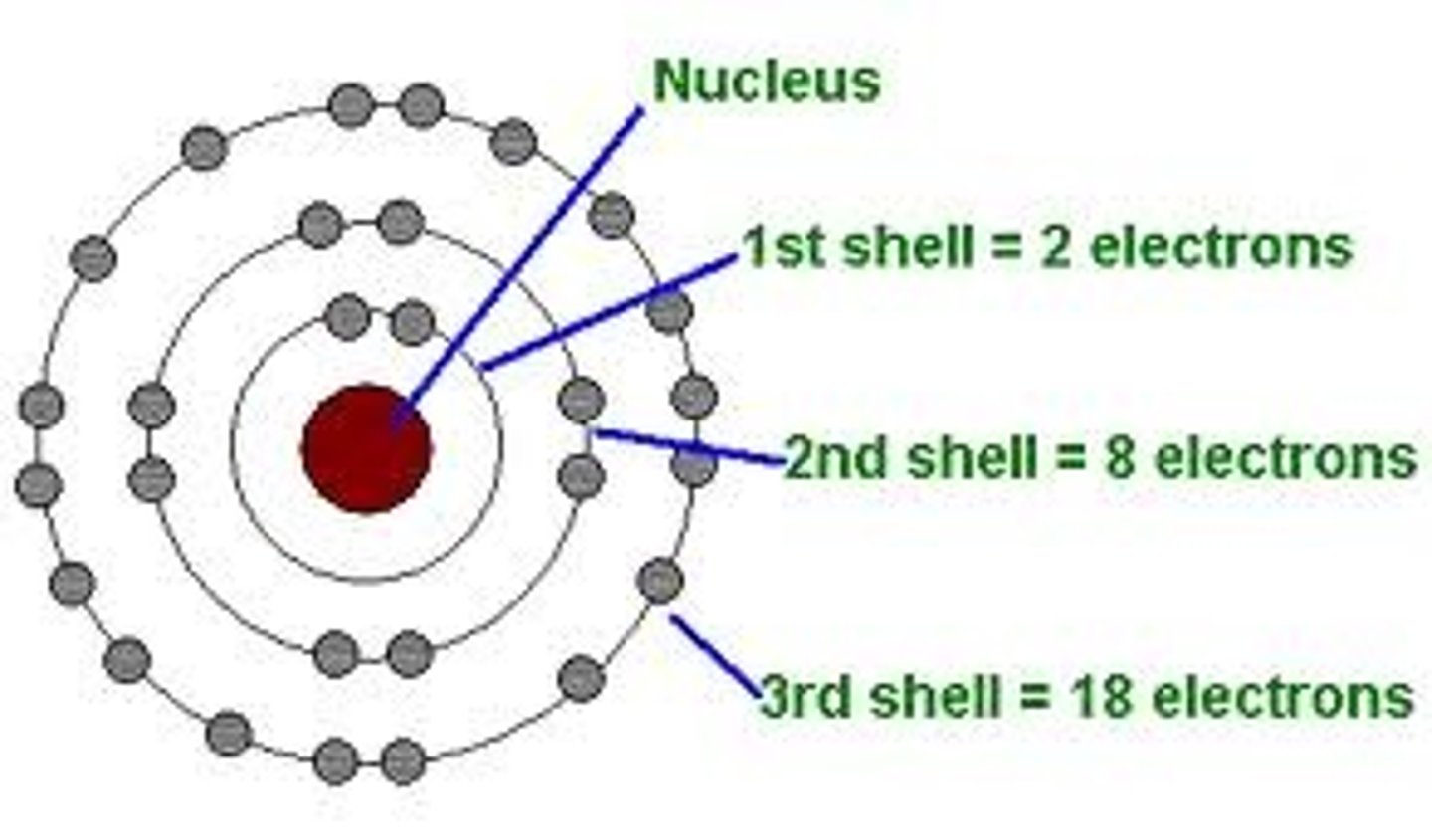
Energy Level
Path around the nucleus, where the electrons reside
Proton's charge
Positive

Electron's charge
Negative
Parts of the nucleus
Protons and neutrons
Neutron's charge
Neutral
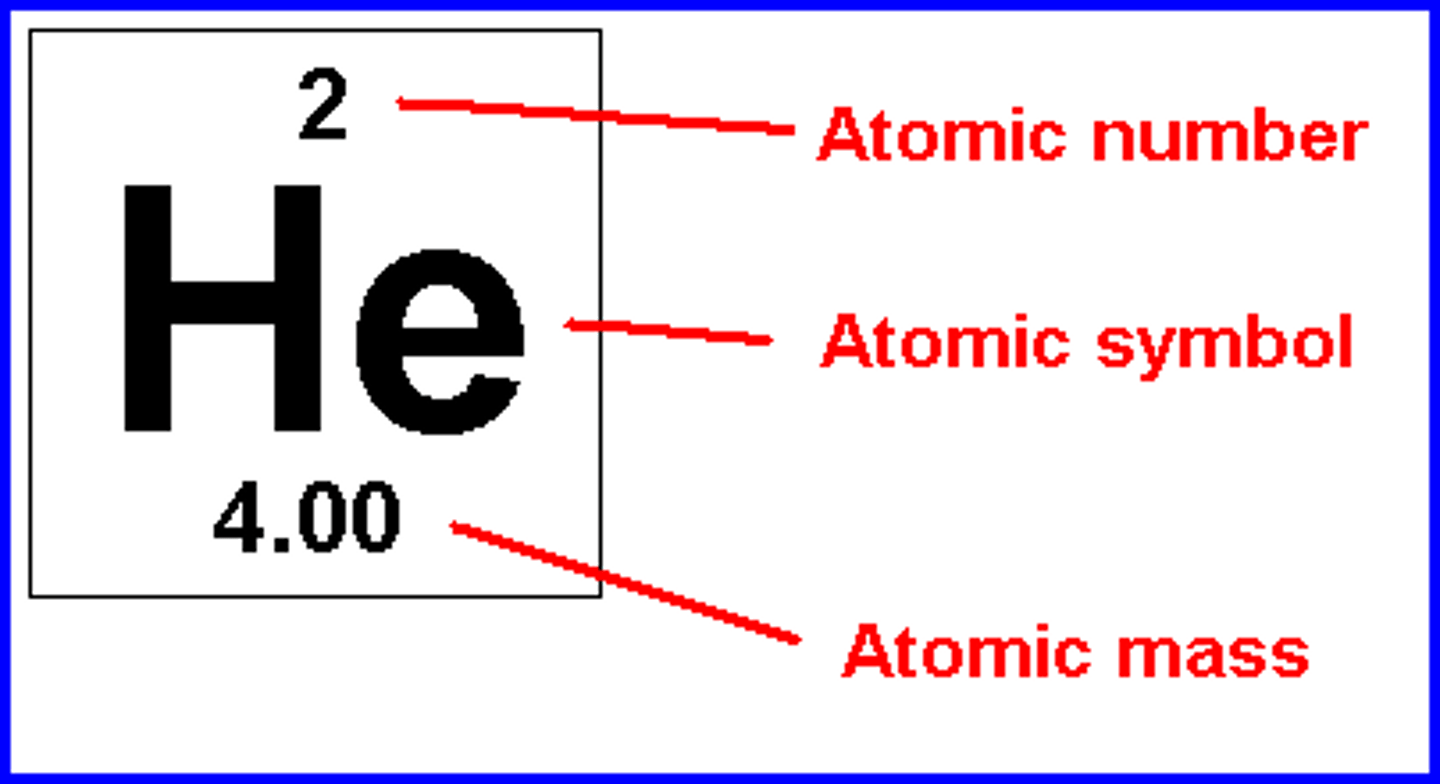
Atomic number
Number of protons in the nucleus of the atom, in an neutral atom it is also the number of electrons
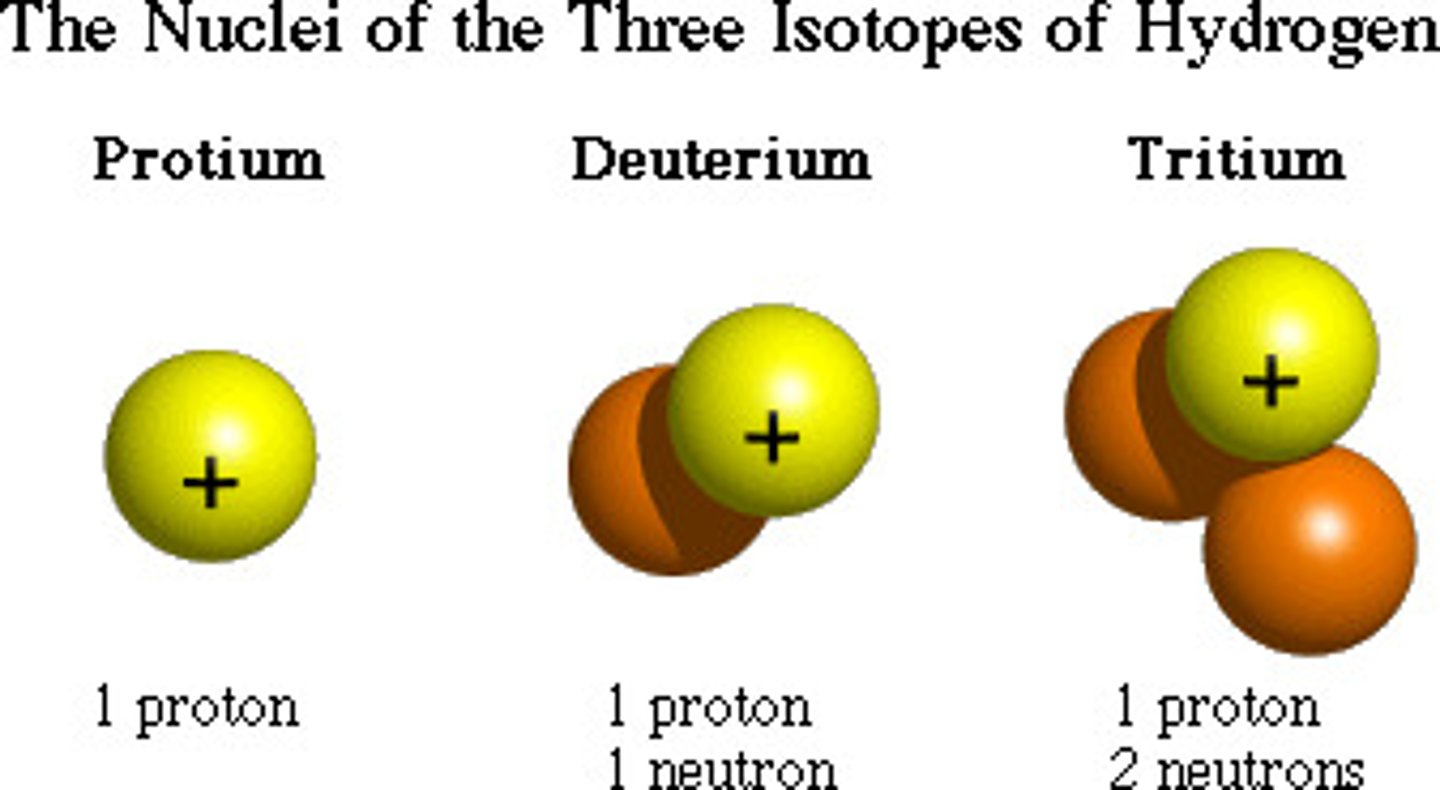
Isotope
An atom with a varying number of neutrons
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
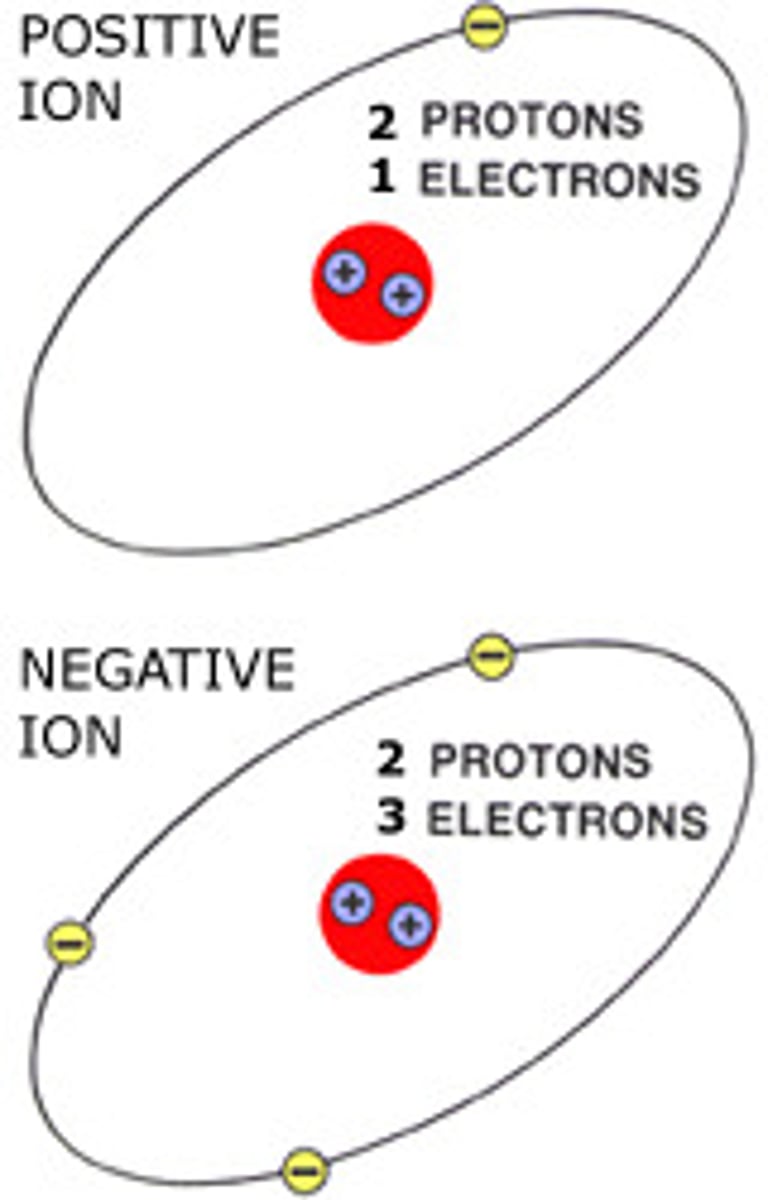
Ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge. Because of the number of electrons and protons are not the same.
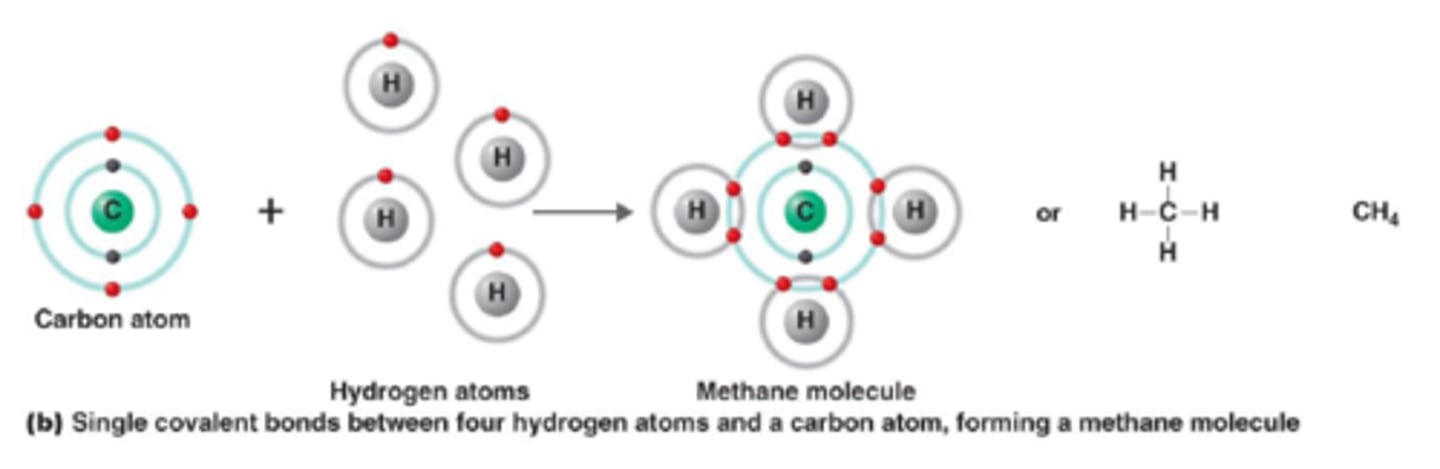
covalent bonding - definition
A type of atomic bonding where bonds formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons
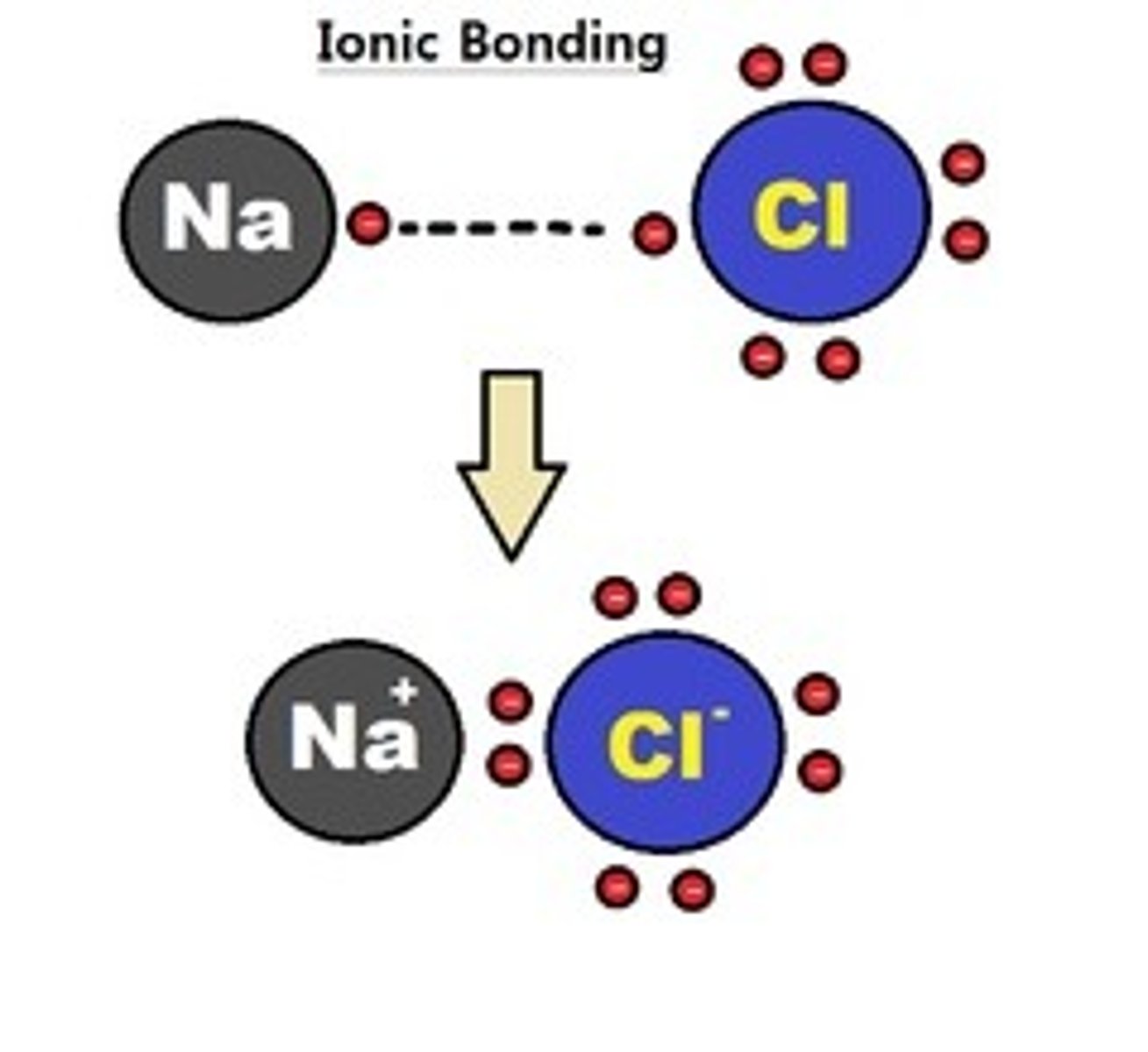
ionic bonding - definition
A type of atomic bonding where the bonds that forms as a result of the attraction between positively and negatively charged ions
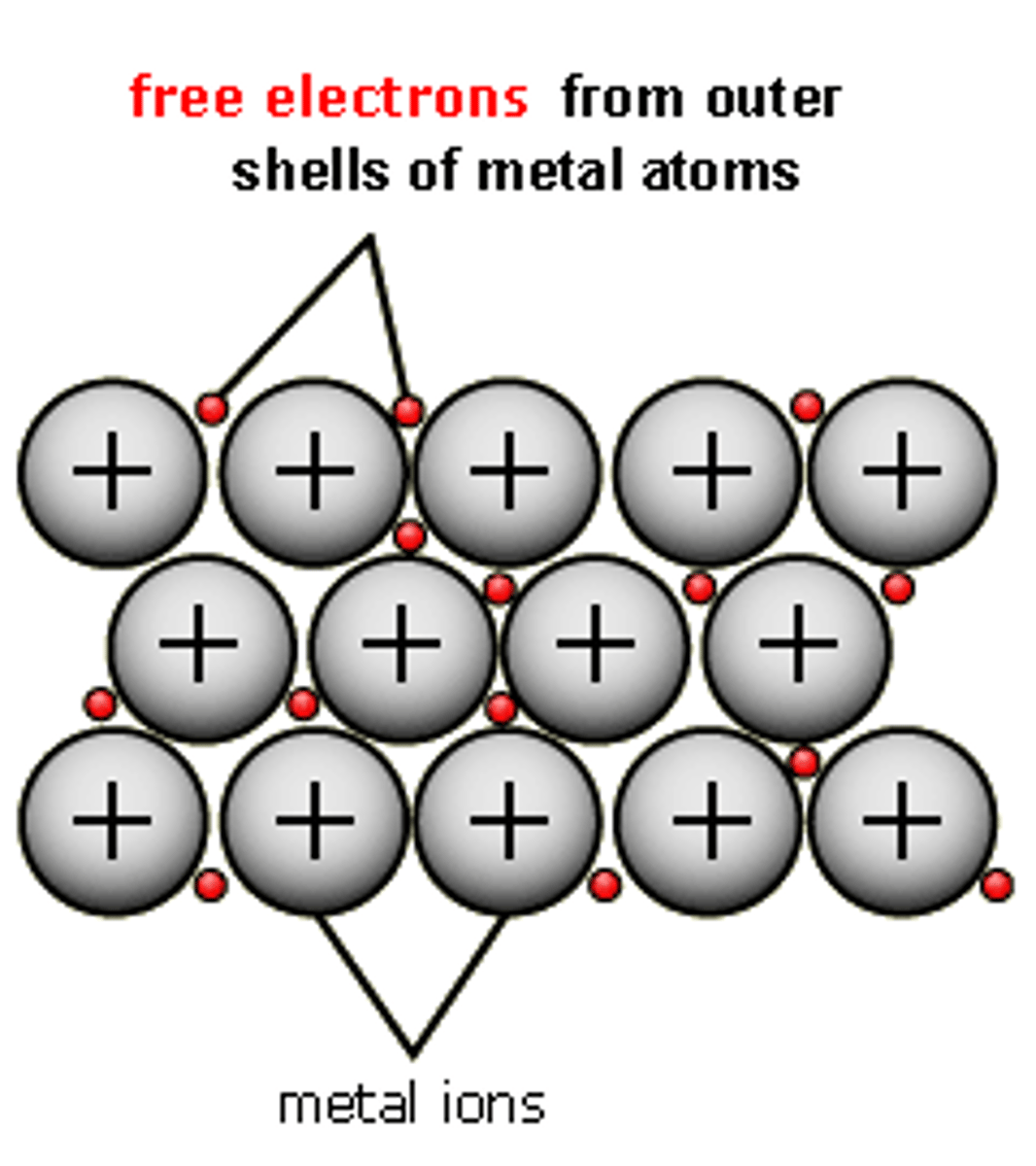
metallic bonding - definition
A type of atomic bonding where positively charged metallic ions, are surrounded by a sea of electrons
covalent bonding - image example
ionic bonding - image example
metallic bonding - image example
anion - definition
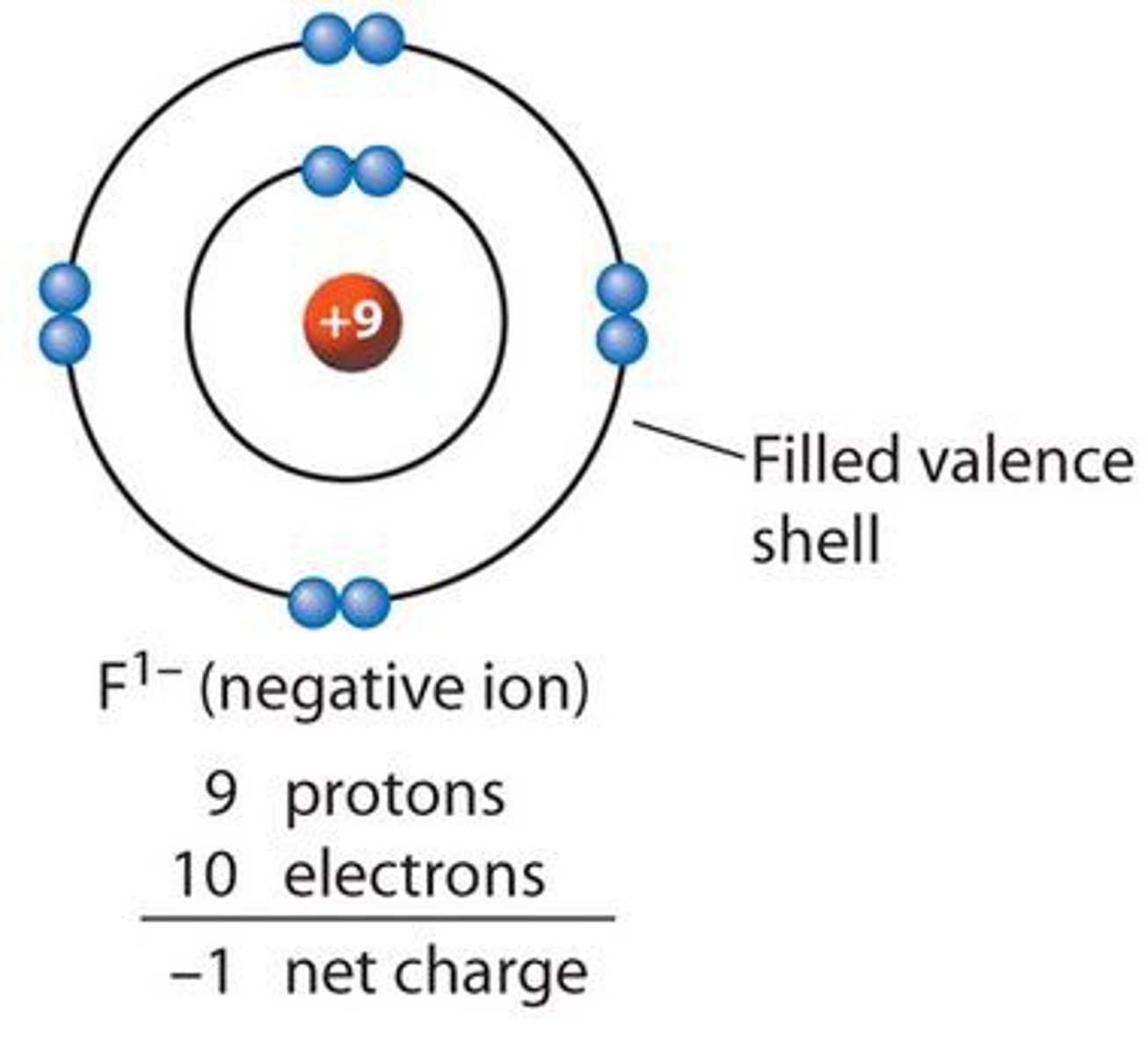
A negatively charged ion
cation - definition
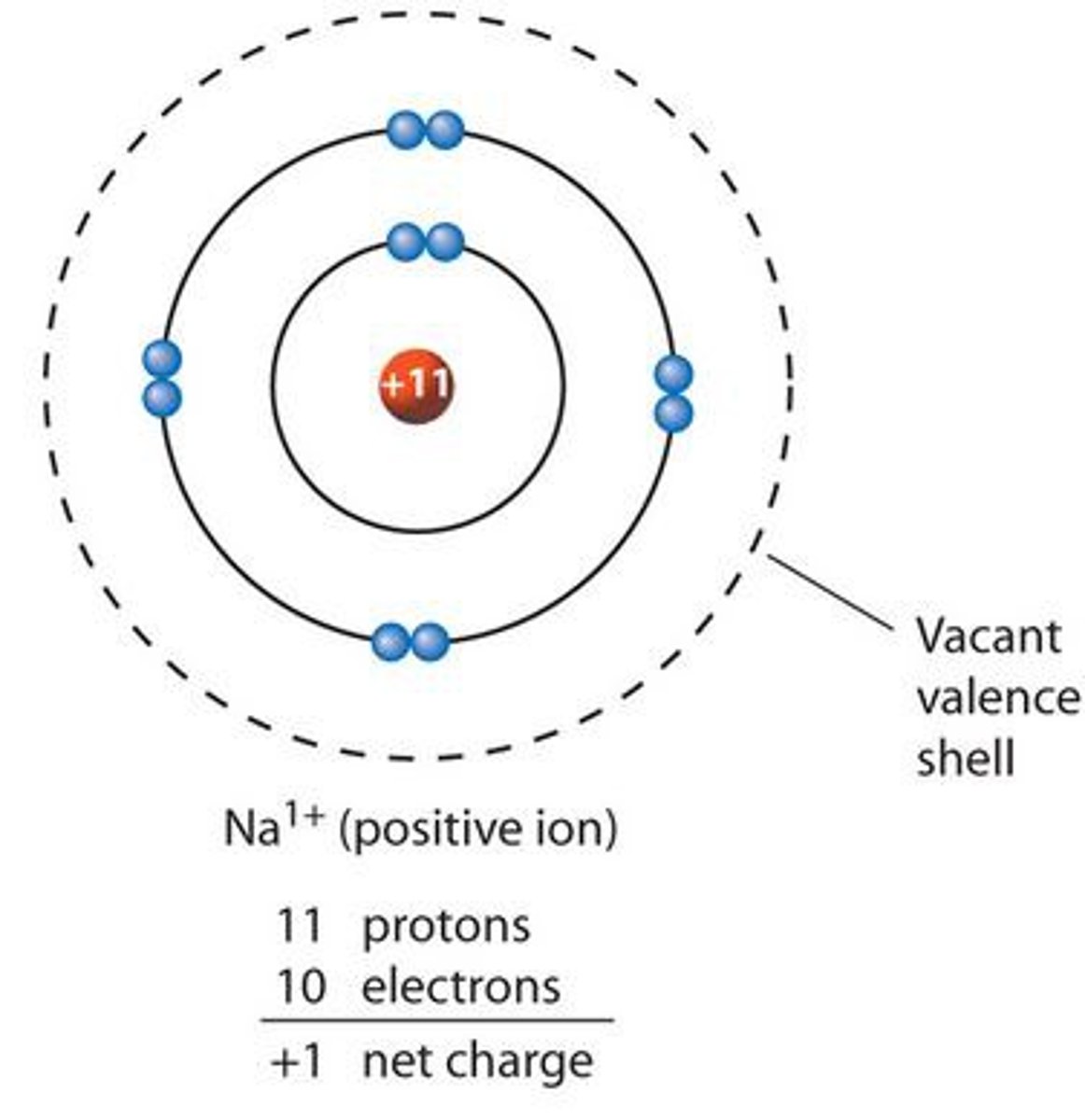
A positively charged ion
anion - image example
cation - image example
atom
Basic unit of matter that retains all the properties of the element
Atomic Bonding
Atomic bonding is chemical bonding. Chemical bonding is the physical process that is responsible for the interactions between atoms and molecules. Different types include: covalent, ionic, metallic, etc.
Relative Atomic Mass
The mass of an atom relative to that of carbon-12. This is approximately the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Where more than one isotope exists, the value given is the abundance weighted average.
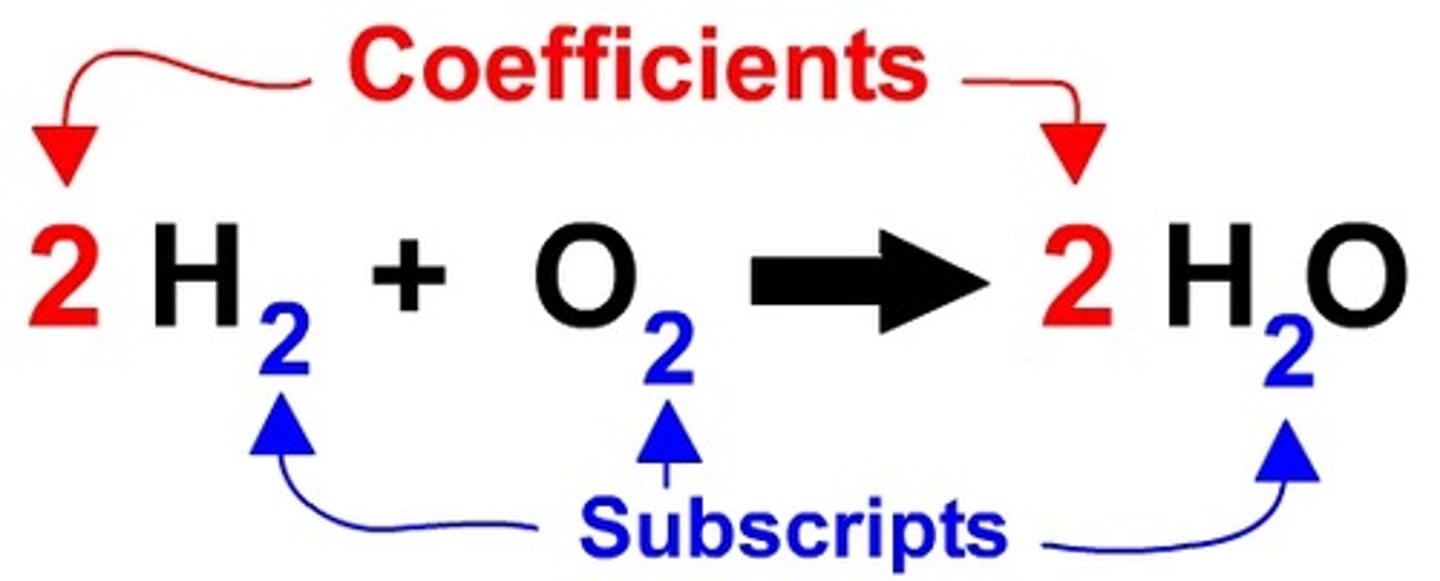
Coefficient
A number placed in front of a chemical formula to indicate how many particles there are. Ex: 2FeO means two particles of FeO and FeO. Used to balance equations to demonstrate the law of conservation of matter
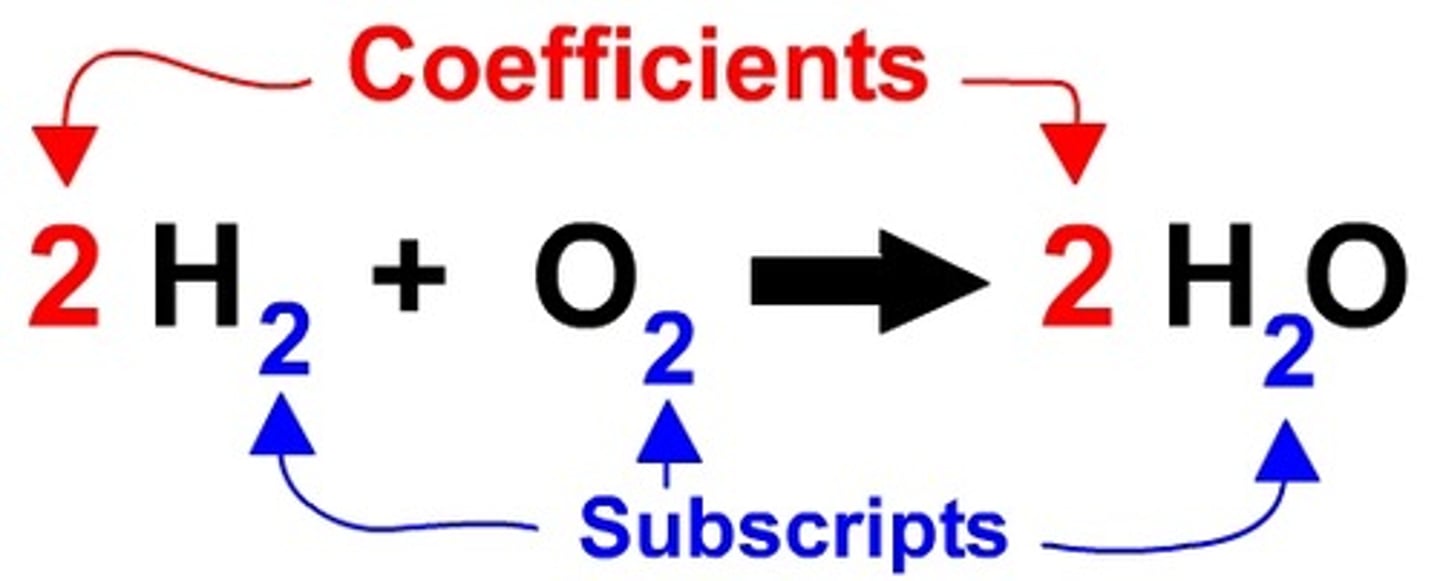
Subscript
The little number to the lower right of a symbol that indicates how many atoms of that symbol are included in that particle. Ex. H₂O the 2 means that there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom bonded together to form a single water molecule. Indicates BONDING
Molecule
A group of nonmetal atoms bonded together by covalent bonds to form a covalent particle. It is the smallest piece of a covalent substance that retains all the properties of that substance. (H₂ and CO₂ for example)
Formula Unit
A group of ions bonded together by ionic bonds to form an ionic compound. This is the smallest piece of an ionic compound that retains all the properties of that compound. They are composed of metal and nonmetal atoms.
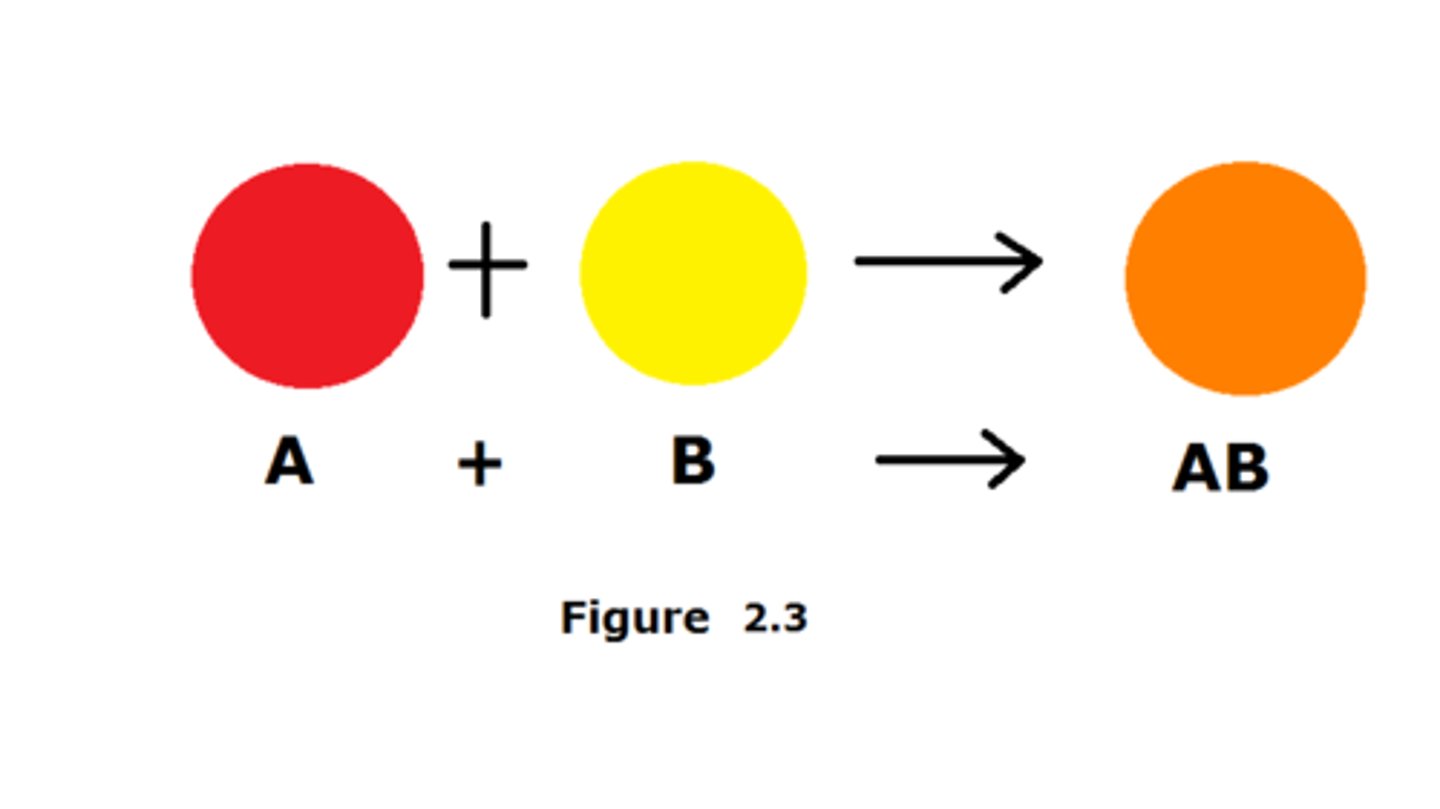
Synthesis Reaction
A chemical reaction where two or more reactants combine chemically to form one new product.
Ex. 2Cu + O₂ → 2CuO
Copper + Oxygen → Copper Oxide
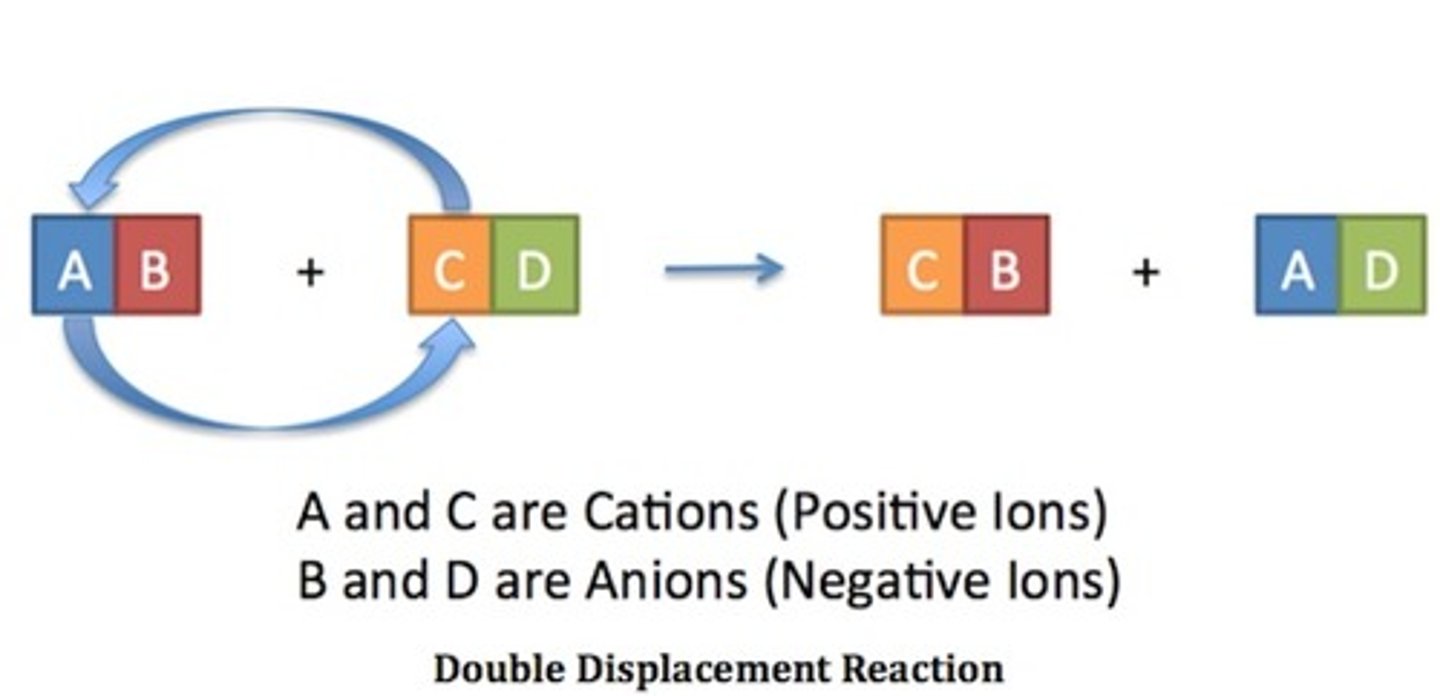
Double Replacement Reaction
A chemical reaction where two compound reactants break apart to recombine chemically and form two new compound products. Each reactant is formed from a metal bonded (ionically) with a nonmetal. To form the products the metals switch places. (*Note, in this special case, Hydrogen (H) is acting like a metallic element but still makes a covalent bond with chlorine!)
CuO(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CuCl₂(aq) + H₂O(l)
Copper Oxide + Hydrochloric Acid → Copper Chloride + Water
Combustion Reaction
A rapid reaction between oxygen and a hydrocarbon fuel that produces carbon dioxide, water, and thermal energy.
An example of the base of an unbalanced combustion reaction is:
CxHy + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
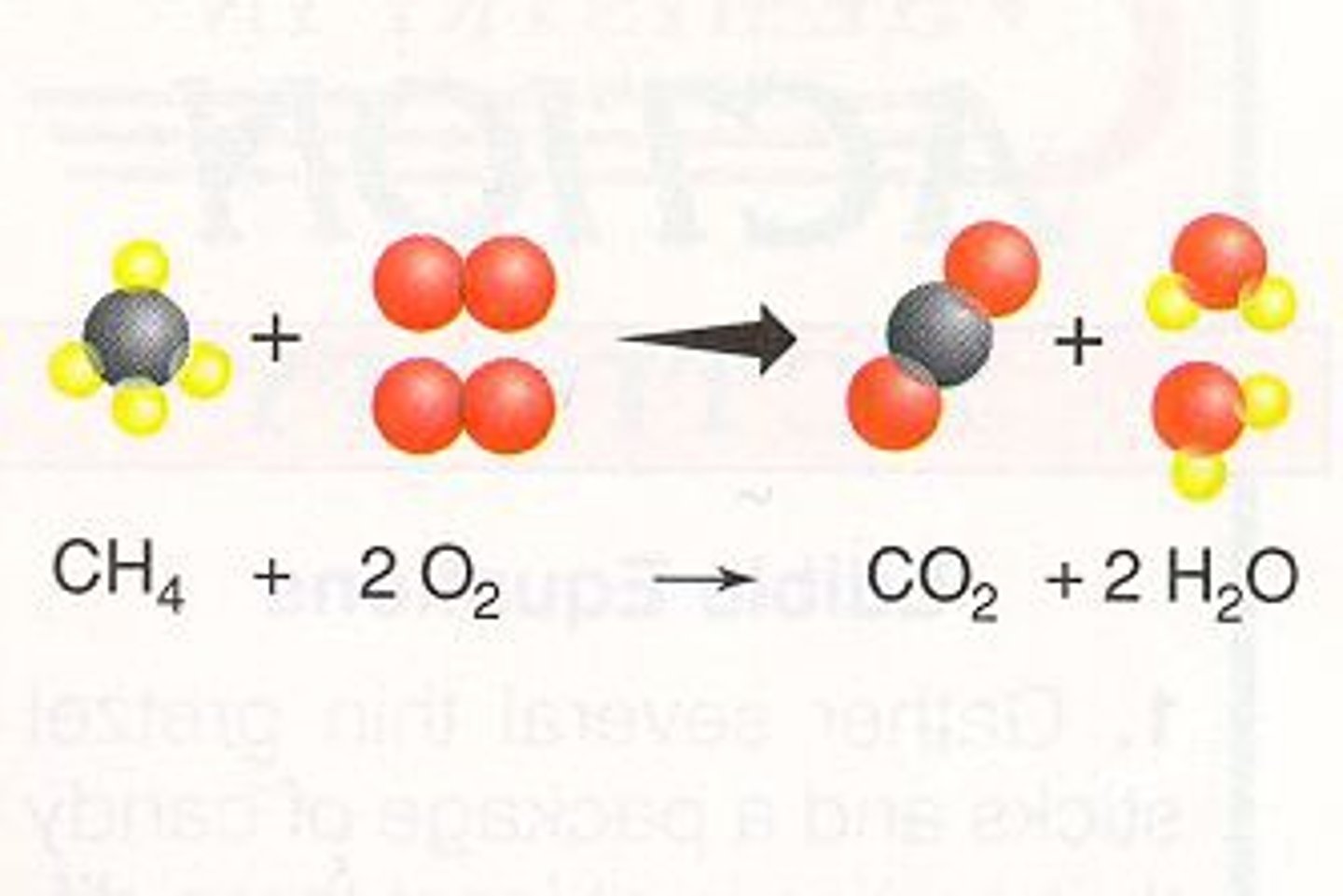
Ion
A particle with a positive or negative charge. It forms when an atom has an unequal number of protons and electrons. It may have a (cation) positive charge (loss of electrons to have more protons than electrons) or an (anion) negative charge (gain of electrons to have more electrons than protons).
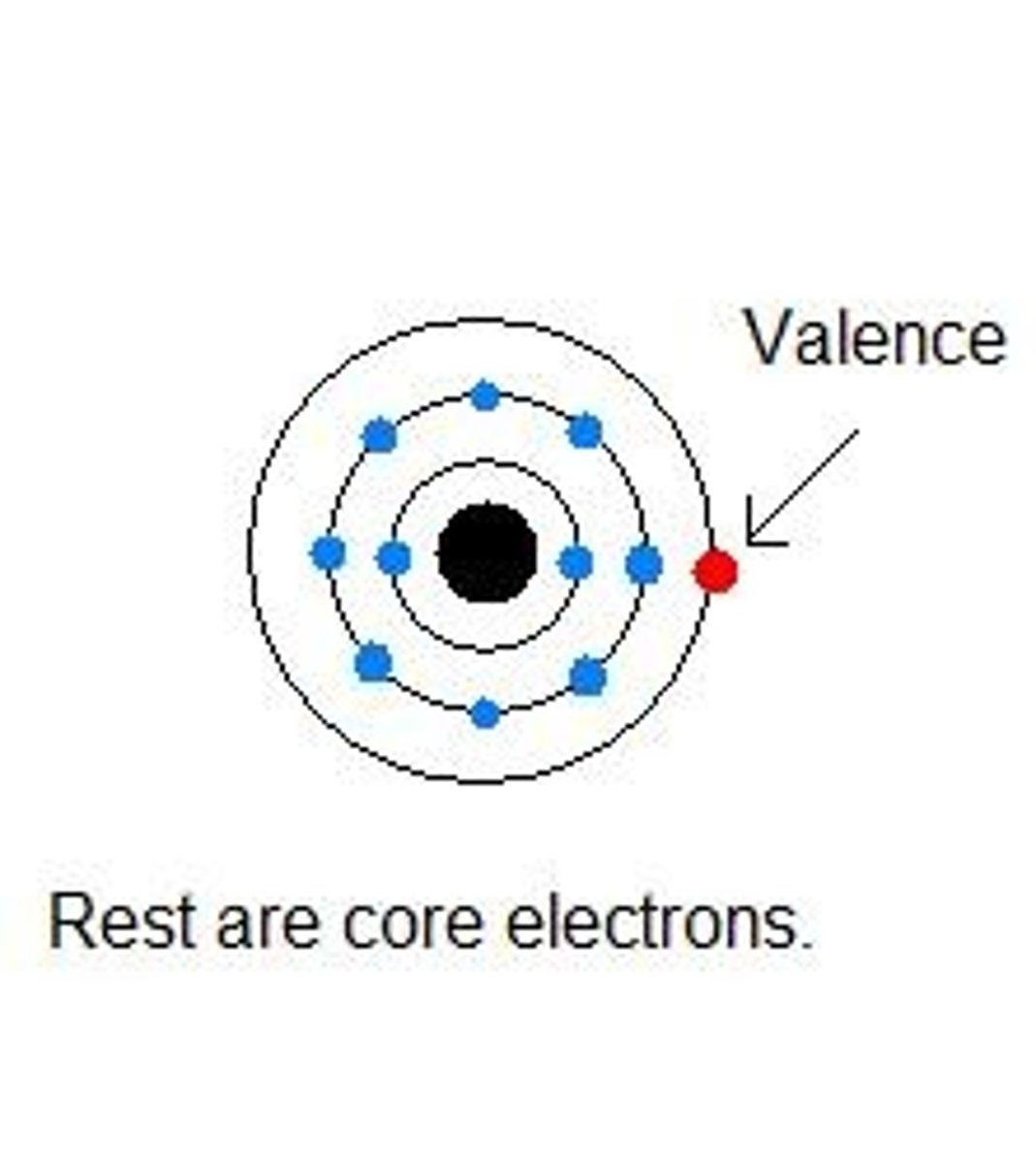
Valence Electrons
The electrons available to be lost, gained, or shared during bonding. Located in the outermost energy level of the atom.
Covalent bond
The bond between atoms that form when valence electrons are shared. A characteristic of nonmetals bonding with nonmetals (ex H₂O and O₂)
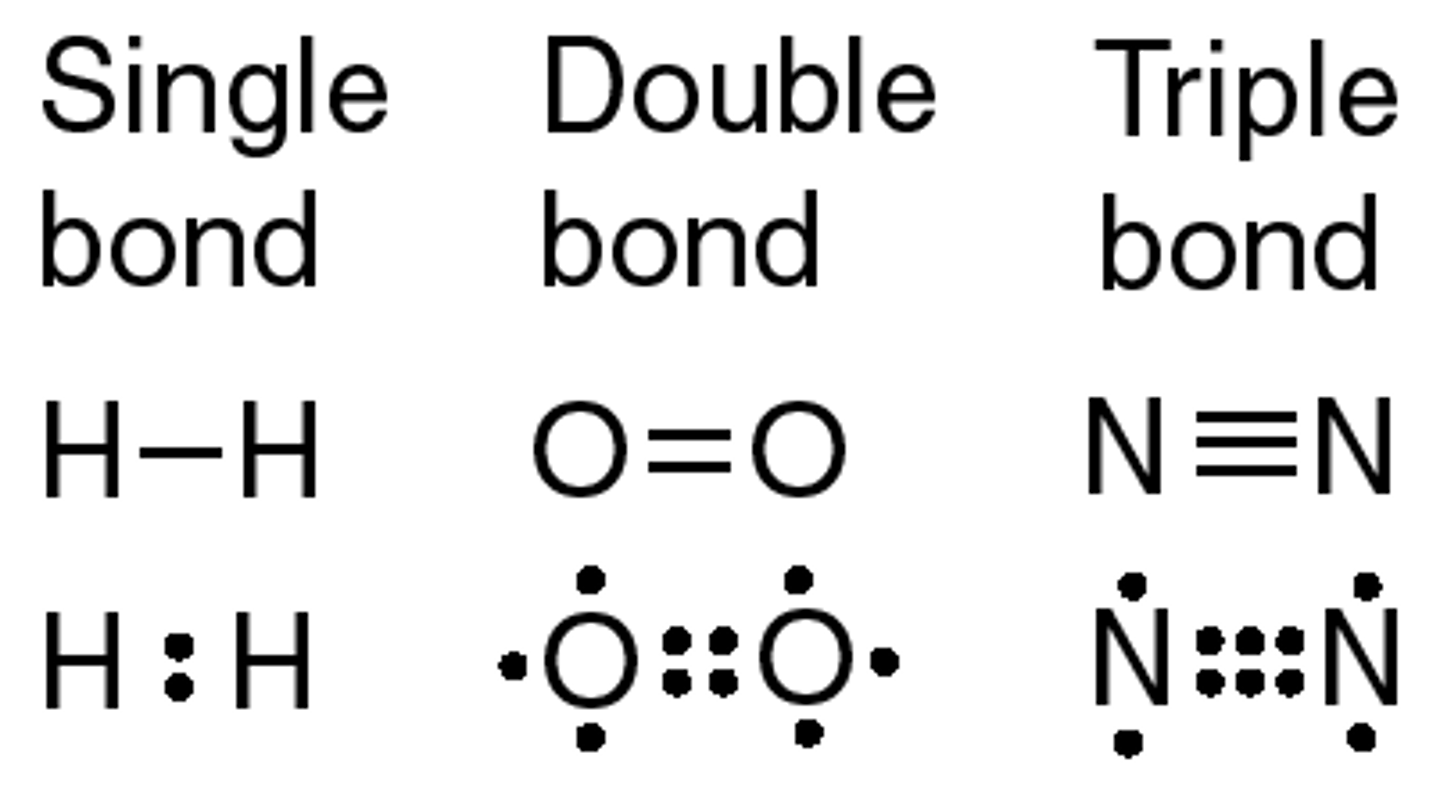
Ionic bond
Bond between atoms that forms from the transfer of electrons when valence electrons are lost from one atom and gained by another atom creating ions that are attracted to each other. A characteristic of metals bonding with nonmetals (ex NaCl).
Diatomic
Means being made from two atoms that are the same type bonded together by covalent bonds: H₂, O₂, N₂, Cl₂, F₂, Br₂ ,I₂.
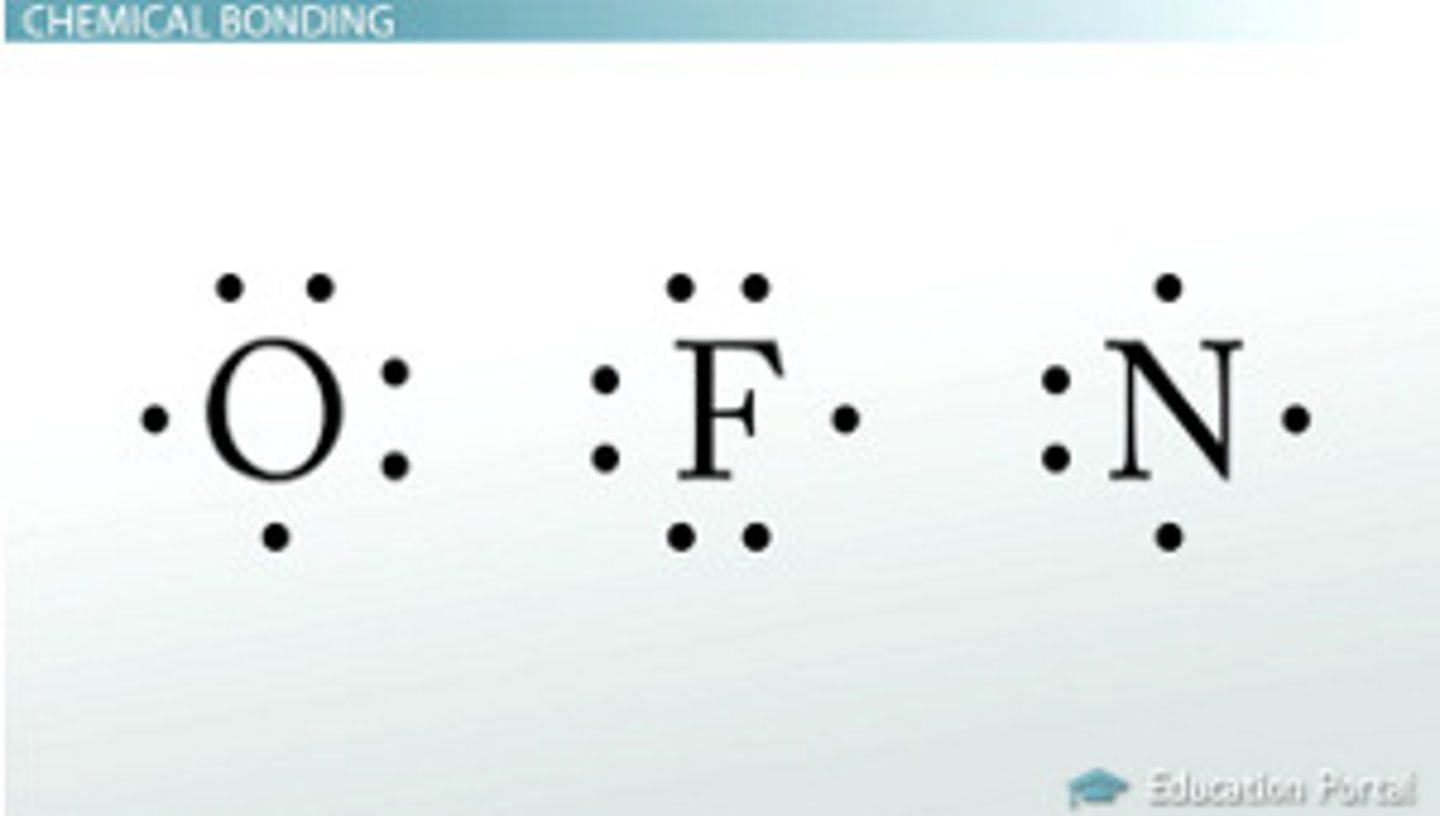
Lewis Dot Structure
diagram of a molecule using dots to represent valence electrons an atom has
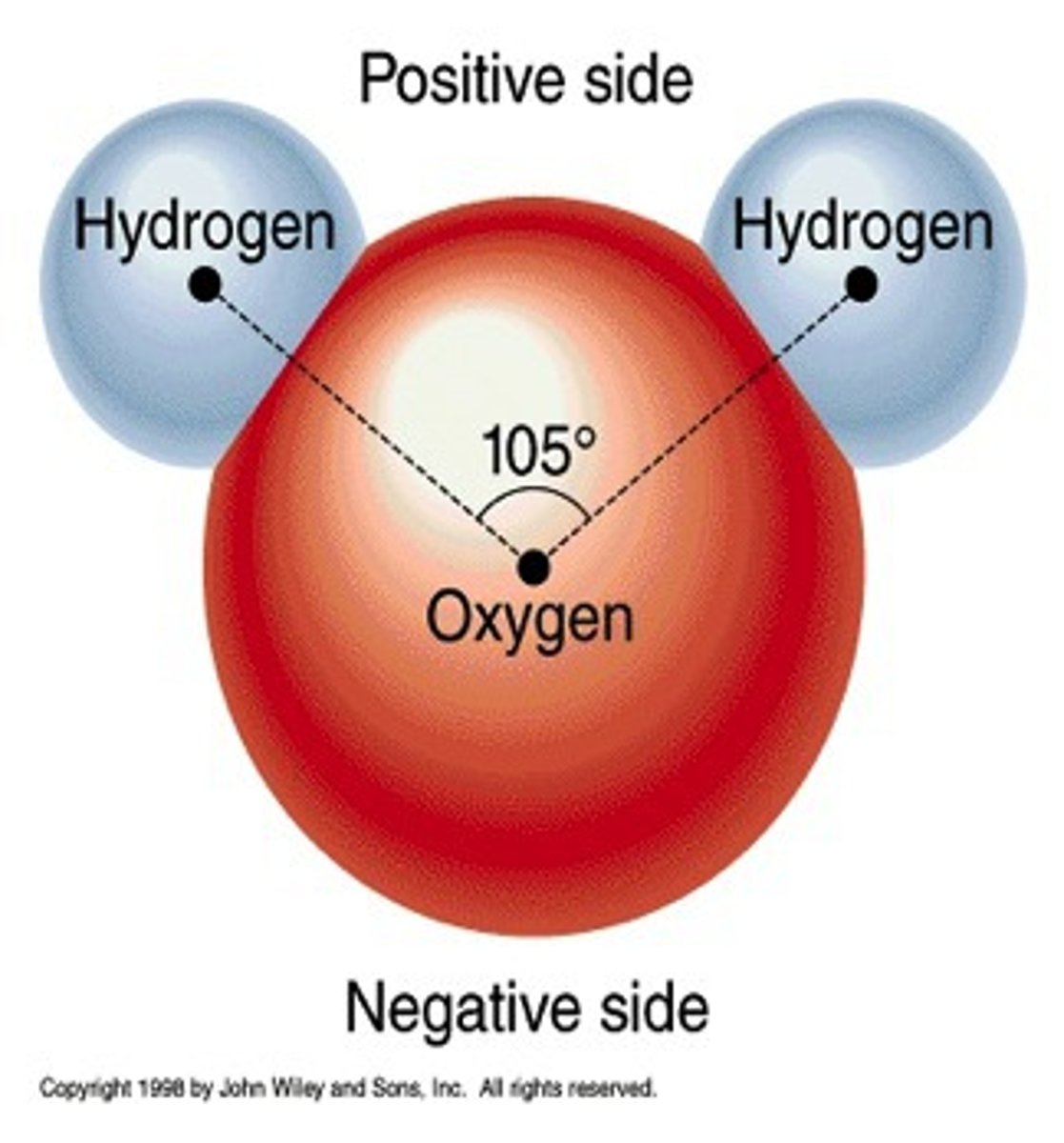
polar molecule
A molecule in which one side of the molecule is slightly negative and the opposite side is slightly positive, water is an example of a polar molecule
nonpolar molecule
A molecule that shares electrons equally and does not have oppositely charged ends

Compound
A substance comprises atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds.
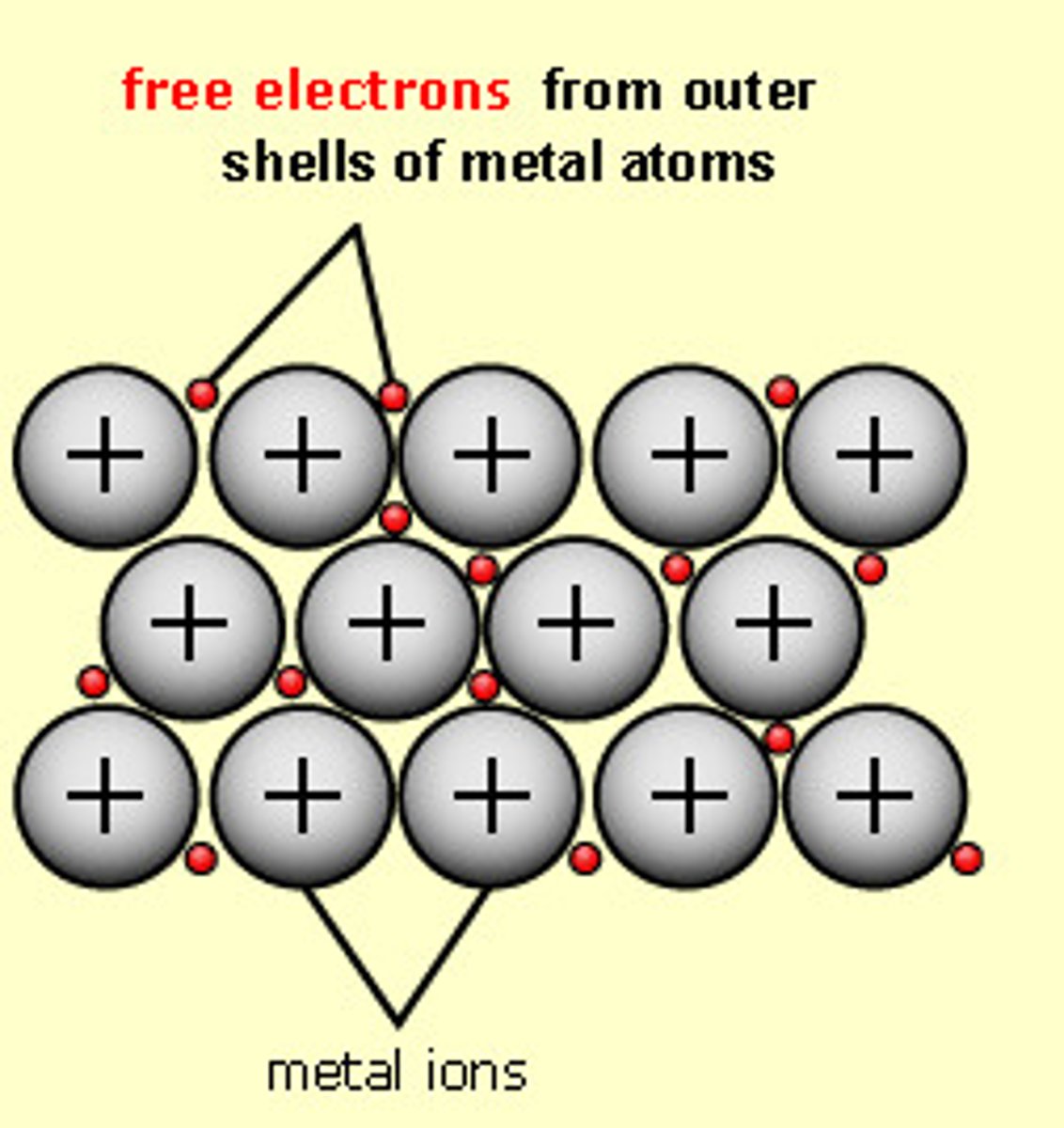
metallic bond
an attraction between a positive metal ion and the electrons surrounding it, electrons are a "sea" around the positive metal ions
Hydrogen bond
A type of weak molecular chemical bond is formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of one polar covalent molecule is attracted to the slightly negative atom of a polar covalent bond in another molecule.
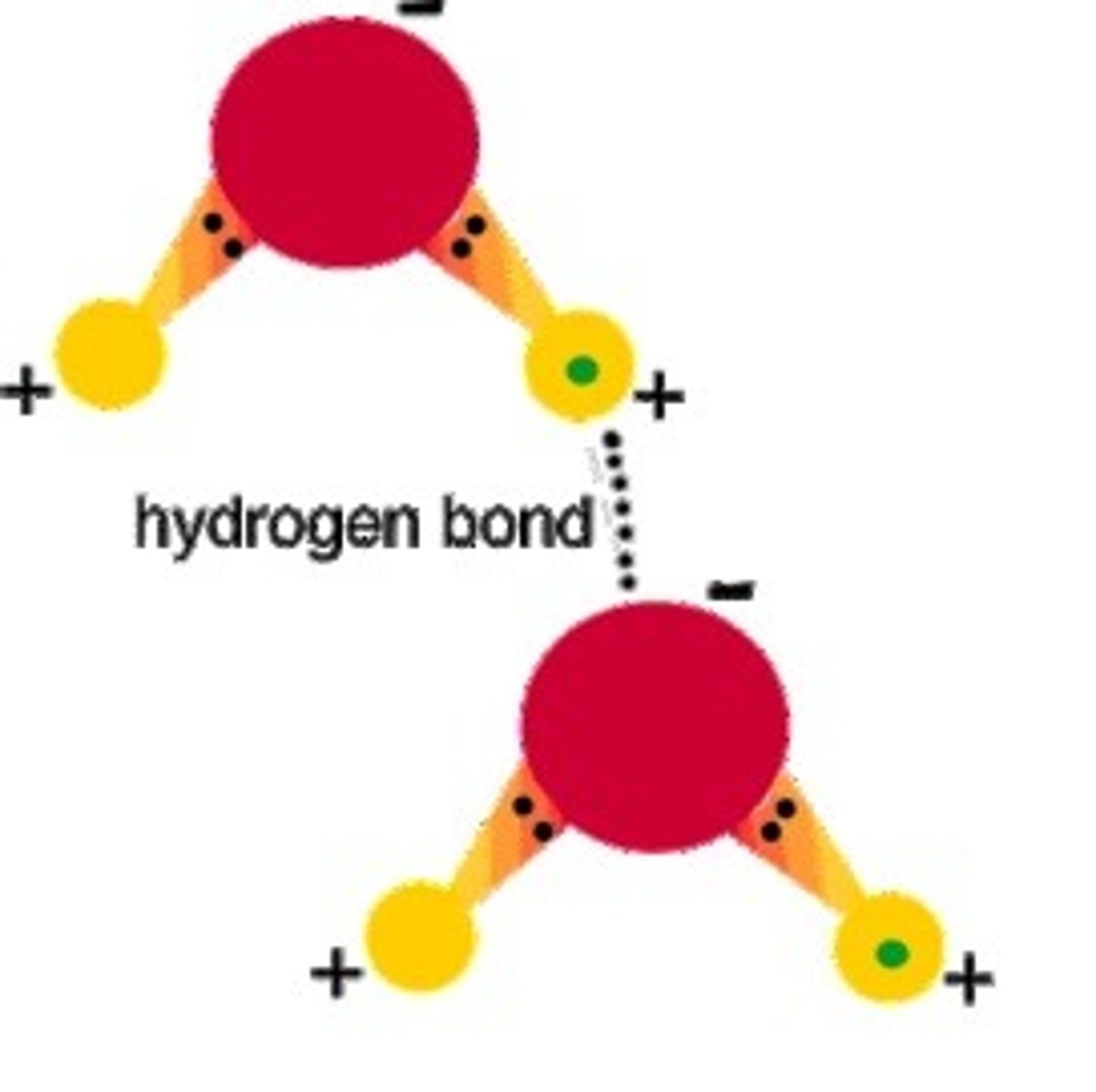
Anion
A negatively charged particle, where there are more electrons than protons present in the particle
Cation
A particle with a positive charge, where there are more protons than electrons present in the particle
Single replacement reaction
A chemical reaction where one compound reactant breaks apart to recombine chemically and form one new product.
Br₂ + 2KF --> 2KBr + F₂
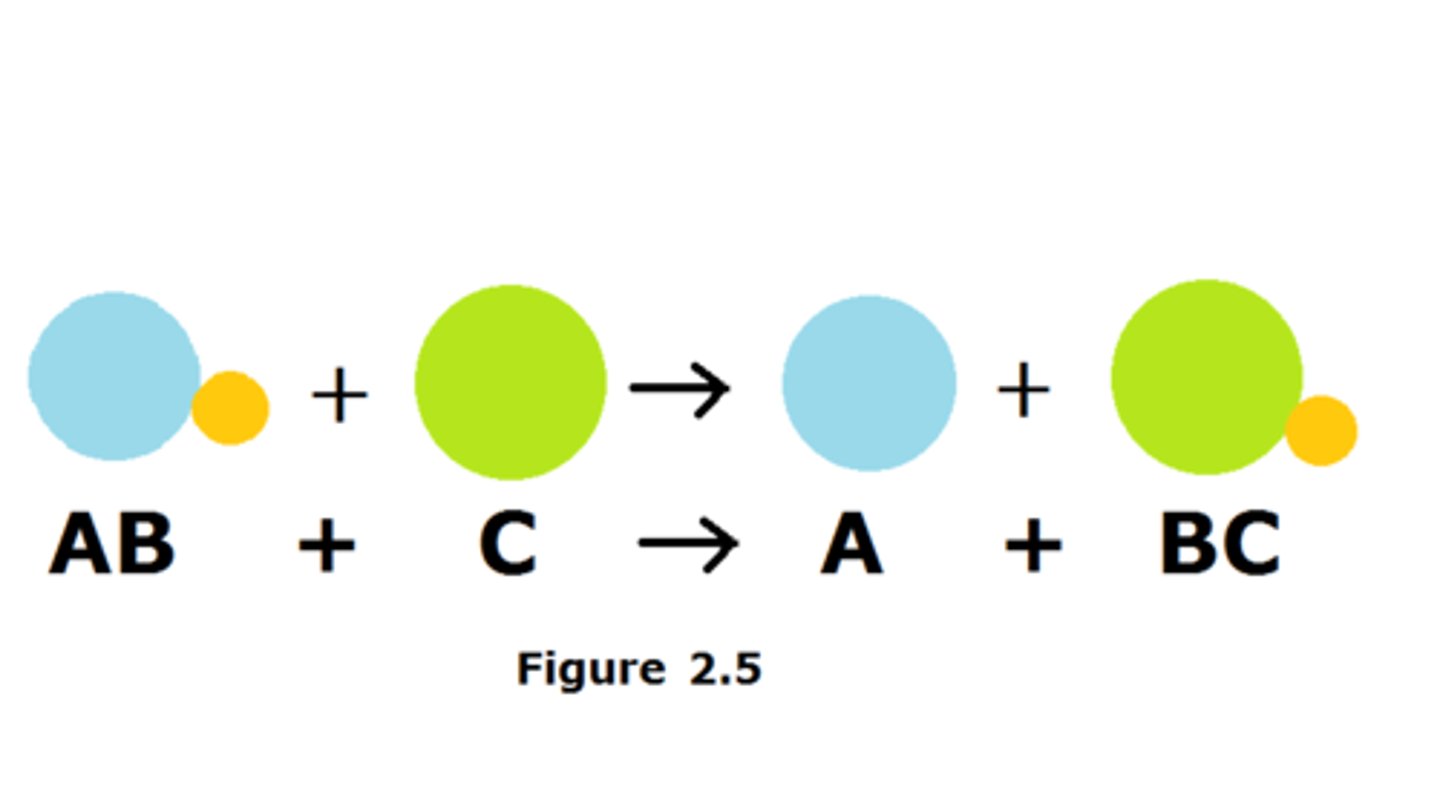
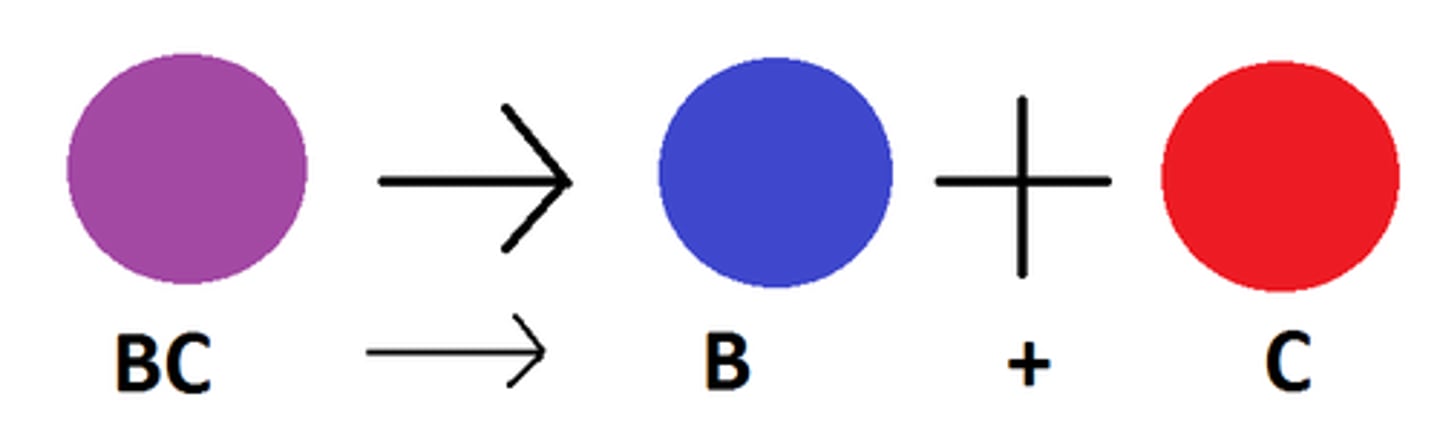
Decomposition Reaction
a reaction in which a single compound breaks down to form two or more simpler substances
2H₂O --> H₂ + O₂
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom, for example Carbon, there are unique 118 elements on the Periodic Table
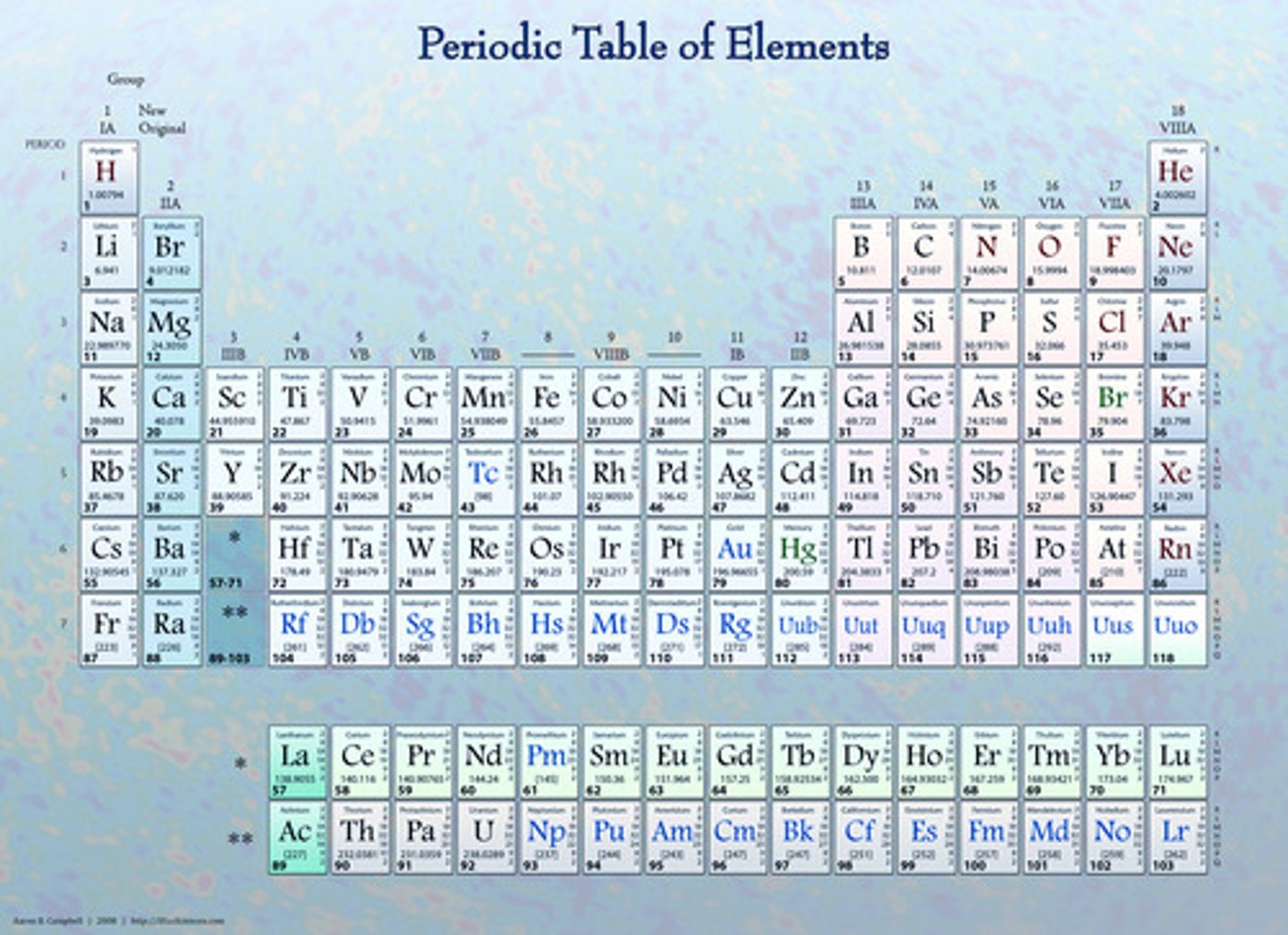
Periodic Table
A table that shows the elements, their atomic number, symbol, and average atomic mass; elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together.
force
A push or a pull
pressure (definition)
the amount of force exerted per unit area of a surface
viscosity
A liquid's resistance to flowing
newtonian fluid
constant viscosity, does not change with applied stress
nonnewtonian fluid
viscosity can change depending on the applied stress
density
mass/volume, kg/m³, g/cm³ = g/mL
velocity
the speed of an object in a particular direction
cylinder volume (equation)
V=πr²h, Volume = pi radius radius * height
weight (definition)
A measure of the force of gravity on an object
weight (equation)
weight = mass x gravity, w =mg
pressure (equation)
Pressure = Force/Area (P=F/A)
newton (definition)
SI unit of force, 1 N = (kilogram*meter)/second²
pascal (definition)
SI unit of pressure, 1 Pa = 1 Newton/1 meter²
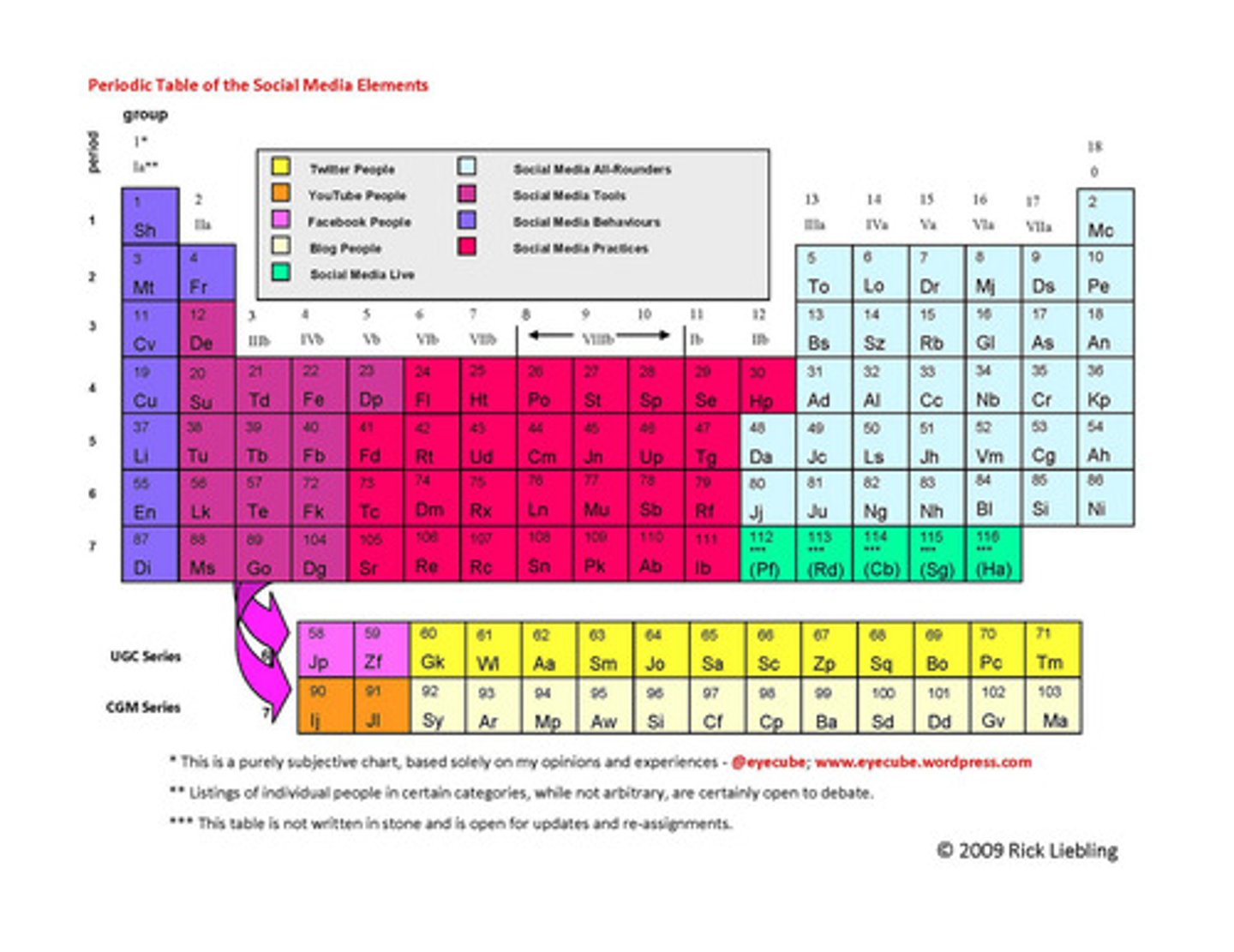
total pressure
sum of all the pressures felt by an object, at the bottom of the pool you would feel the pressure of the water AND the pressure of earth's atmosphere
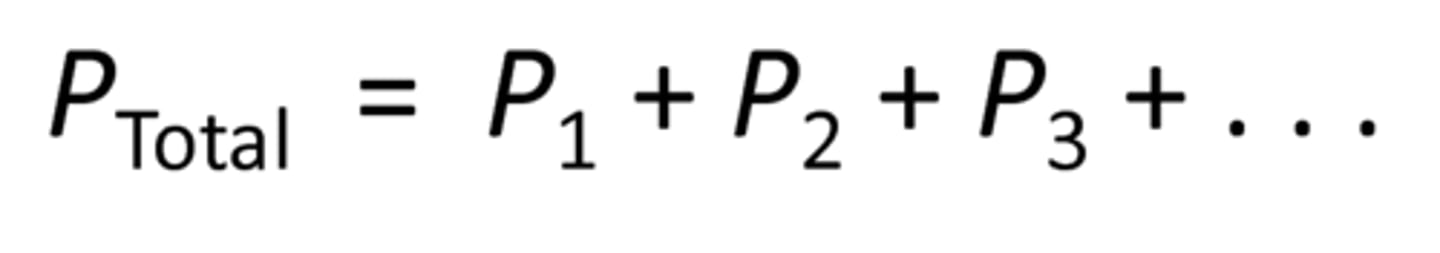
Liquid pressure (equation)
density gravity depth
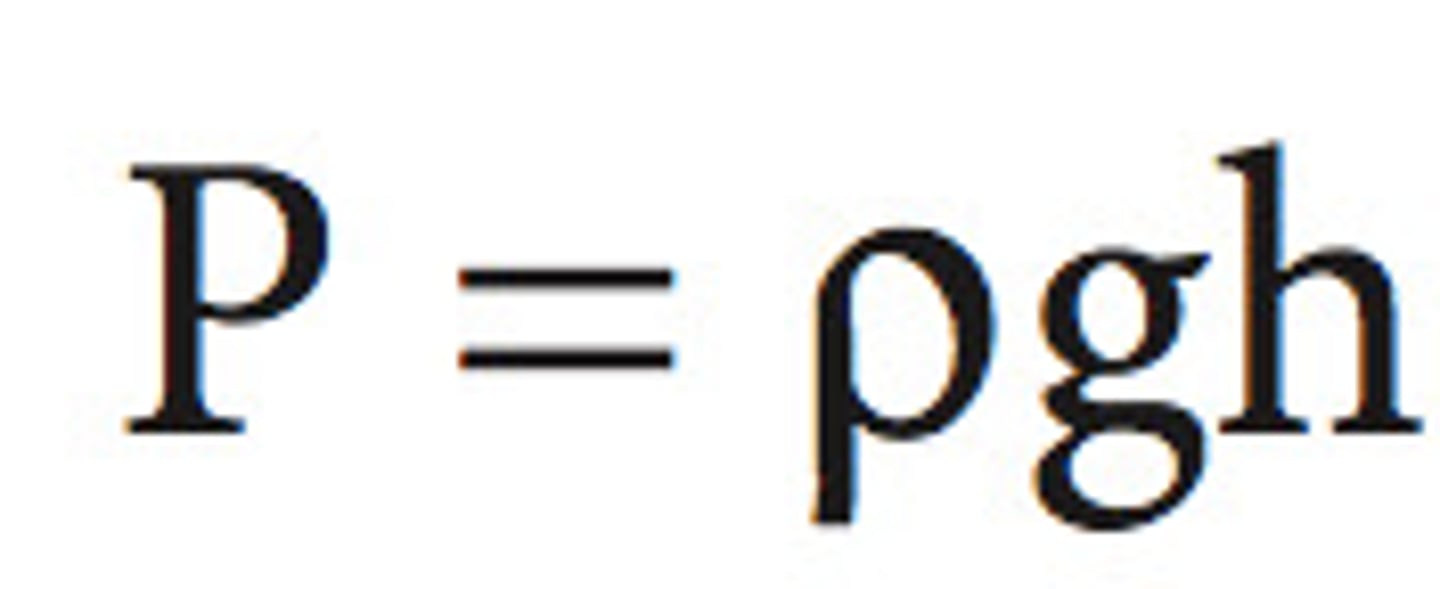
flux meter
Measures the volume of a fluid going through a cross-sectional area per unit of time
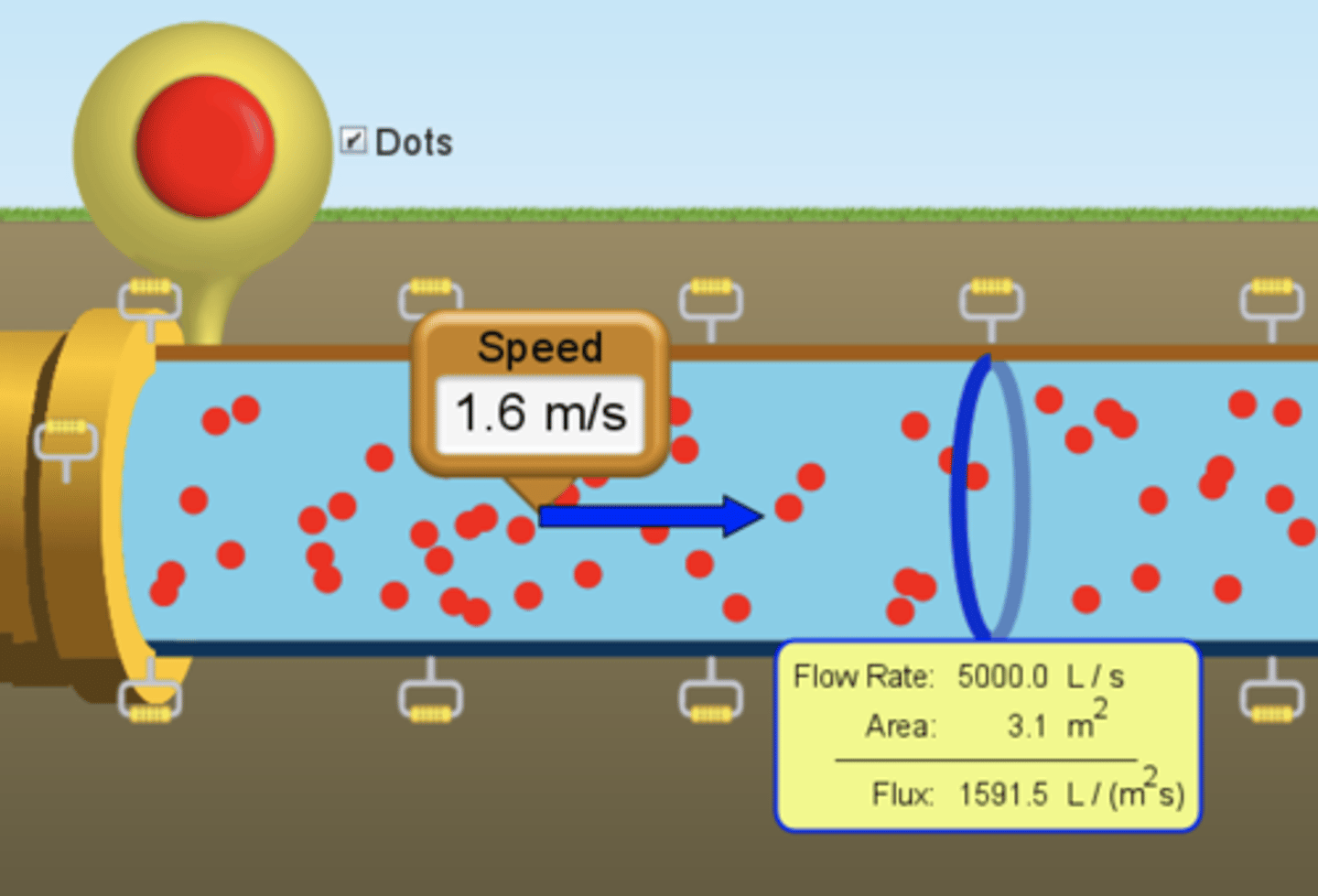
mass flow rate
the amount of mass flowing through a cross-section per unit time (kg/s)
volume flow rate
the volume of a fluid flowing through a cross-section per unit time (m³/s)
battery
A device that is used to convert chemical energy into electric energy. A group of voltaic cells connected together in a series or parallel (positive to negative)connection.
Ion
An atom with either a positive charge (+) because it has more protons than electrons, or a negative charge (-) because it has more electrons than protons
Current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits, this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. The unit is Ampere, 1 coulomb of energy/1 second of time
Electrolyte
A chemical medium that allows the flow of electrical charge between the cathode and anode. When a device is connected to a battery — a light bulb or an electric circuit — chemical reactions occur on the electrodes that create a flow of electrical energy to the device.
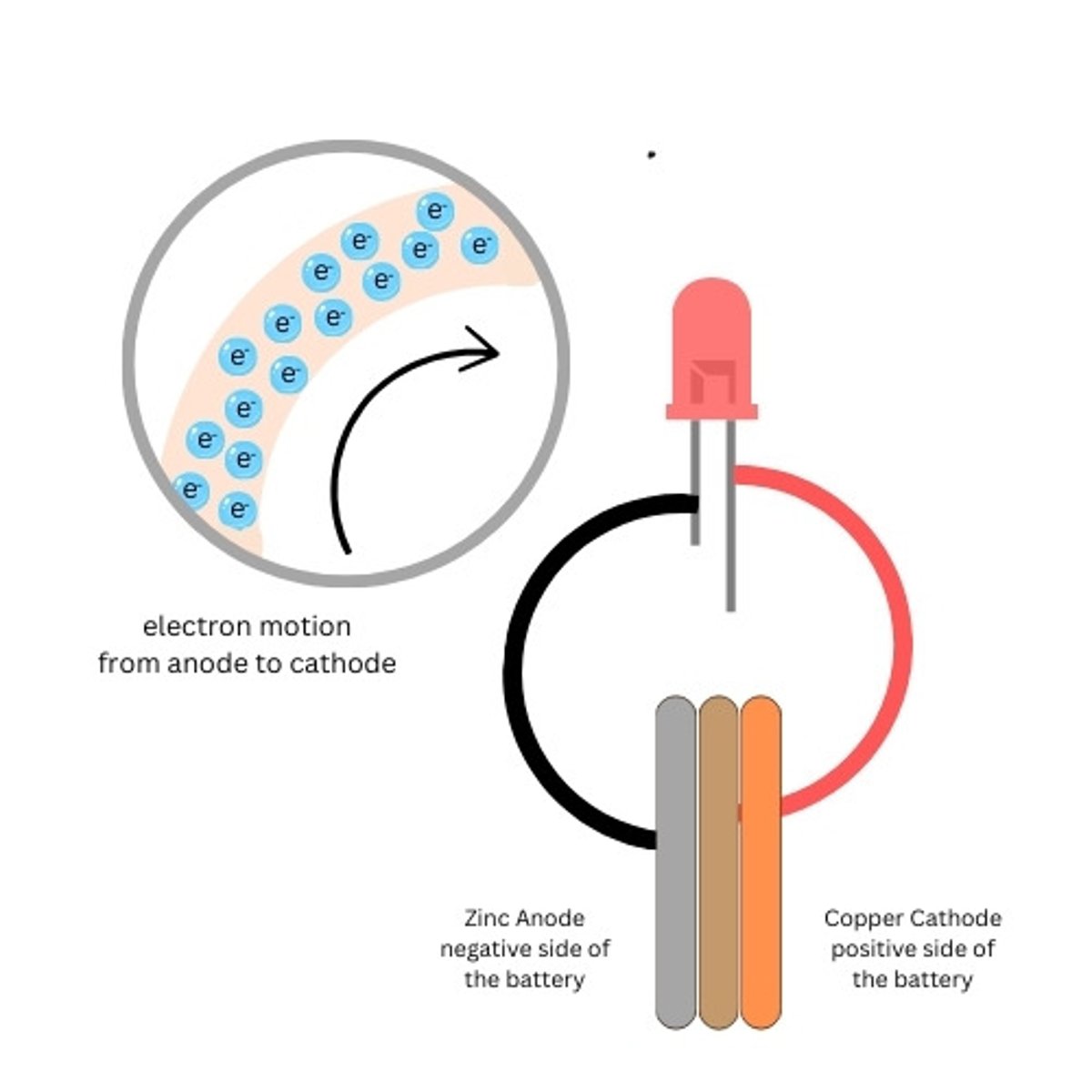
Copper Penny
The copper side of the battery is the positive side of our battery (cathode)
Zinc Washer
The zinc side of the battery is the negative side of our battery (anode)
Cardboard
Used to hold the electrolyte between the penny and the washer
Cation
A positively charged ion (#protons > #electrons in the atom)
Anion
A negatively charged ion (#electrons > #protons in the atom)
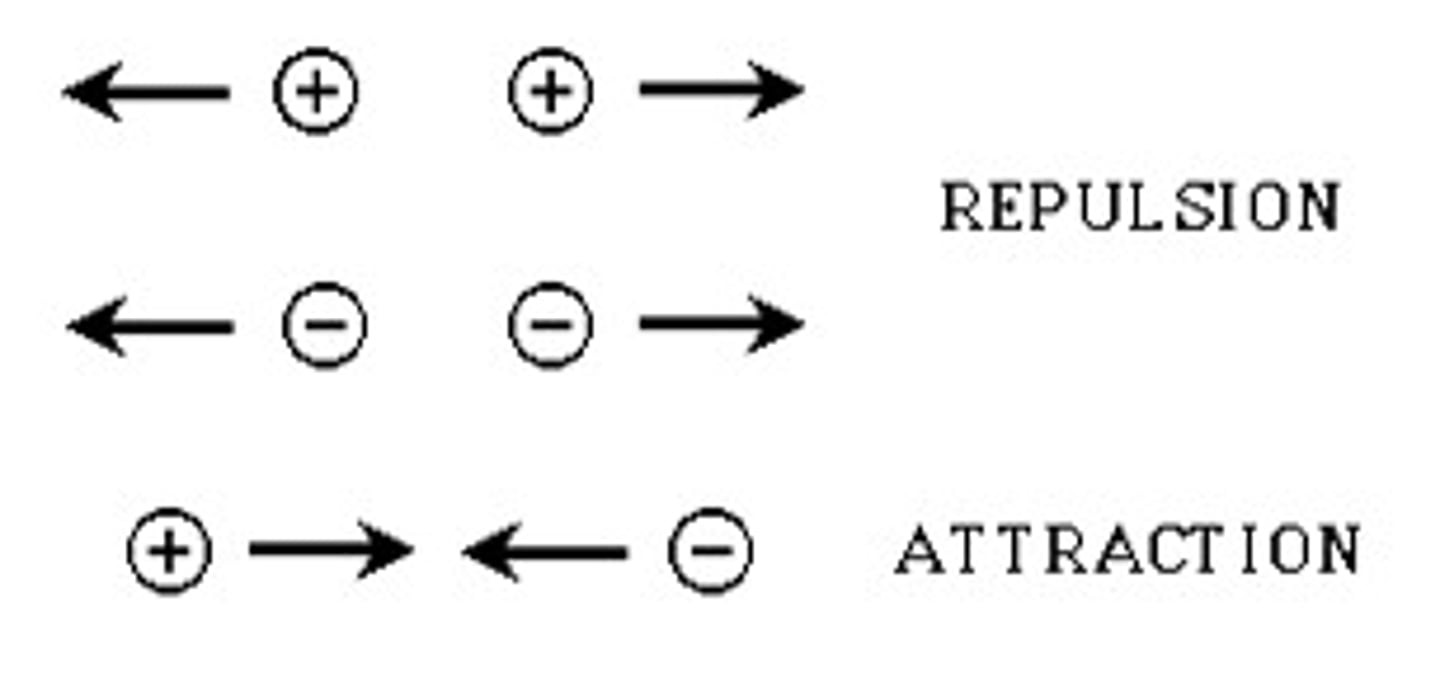
Repulsive Force
Like particles repel like particles. The electrons in our battery feel a mutual repulsion from other free electrons
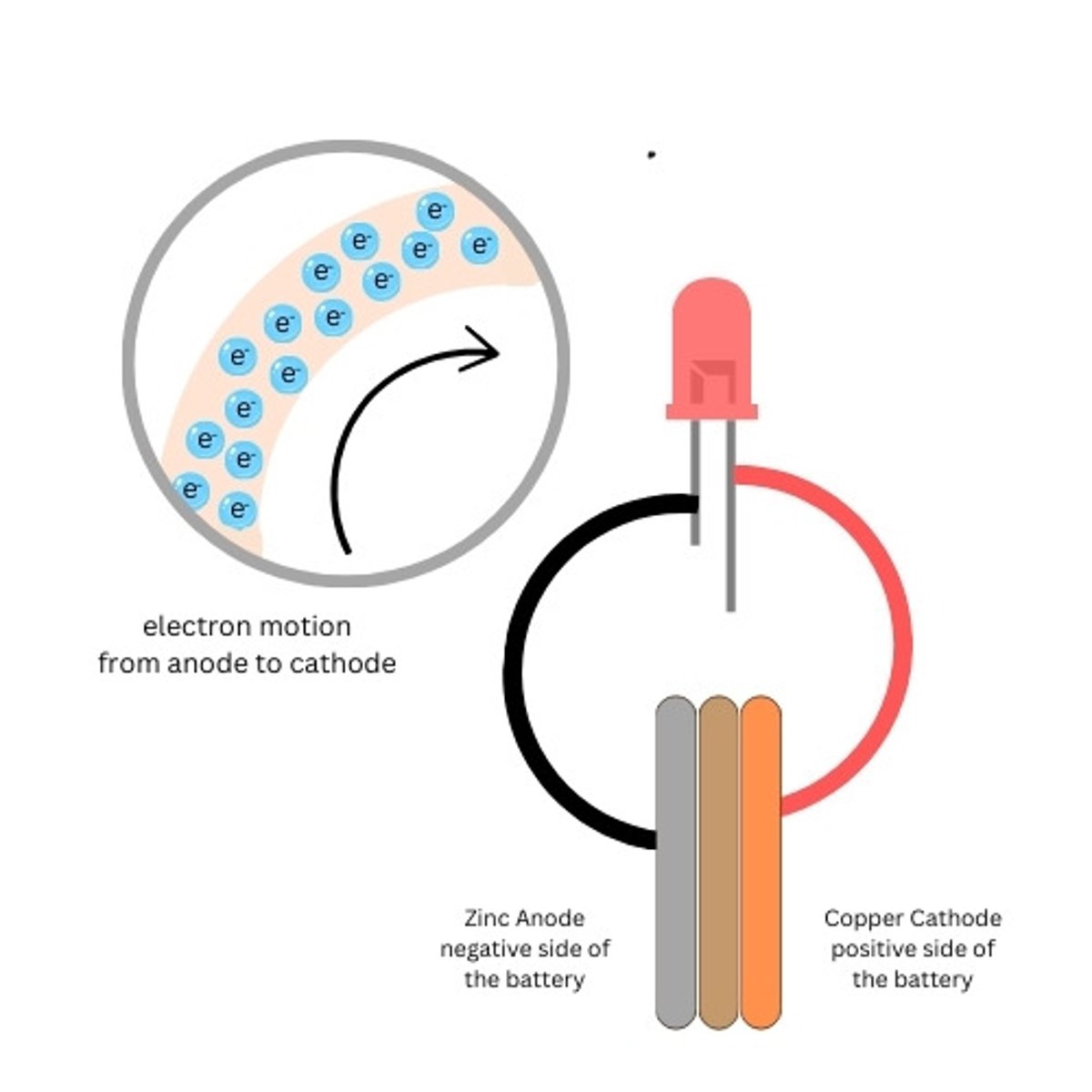
What creates the electricity in our battery
Persuading a couple of electrons to leave an atom (or join an atom) takes very little energy. For instance, when zinc reacts chemically with an acid, it can liberate electrons. (Nature of Electricity - Charles Platt)
Why do the electrons want to move in our battery?
As electrons accumulate on the zinc electrode. They feel a mutual force of repulsion because like charges repel each other. (Nature of Electricity - Charles Platt)
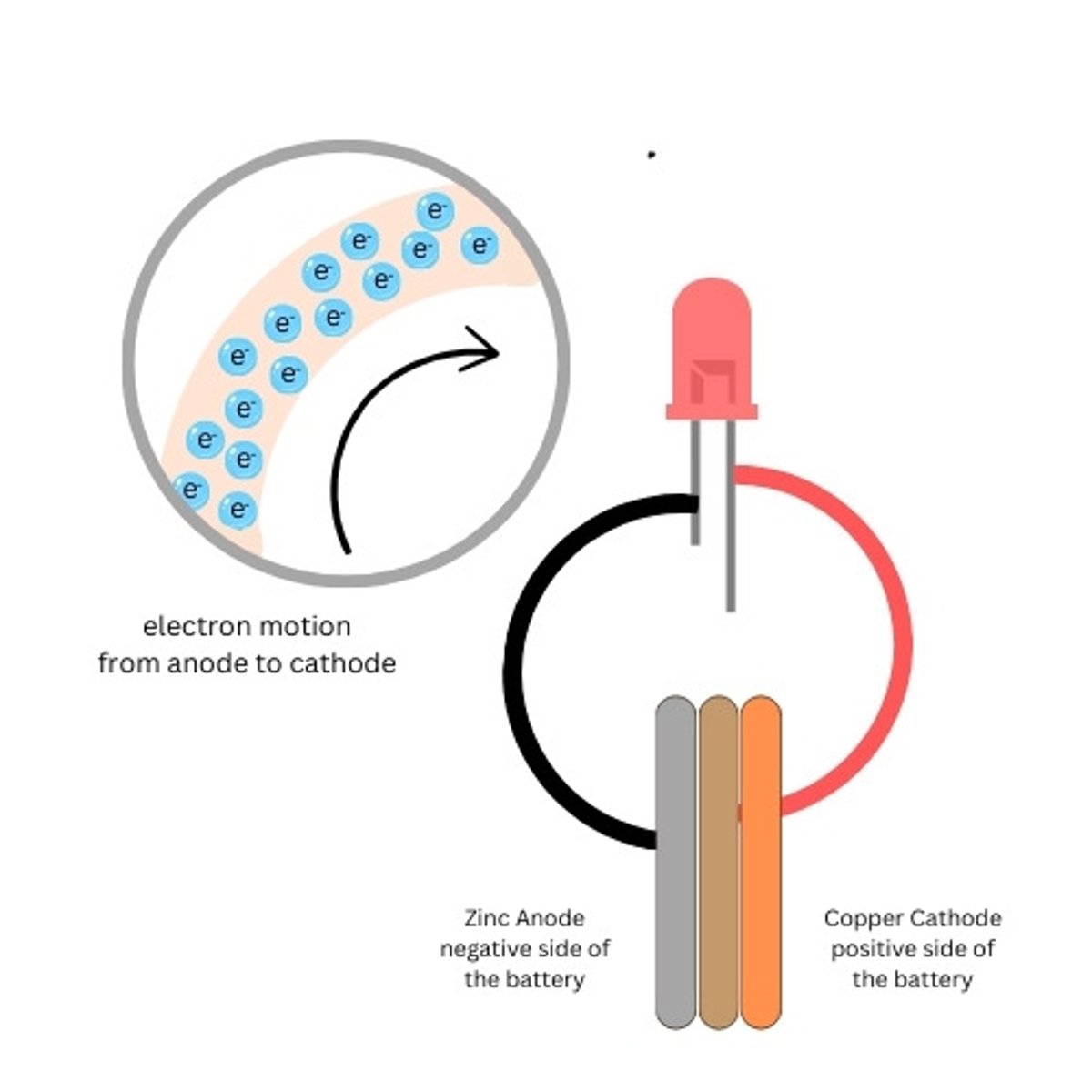
Where do the free electrons go in our battery
As soon as we open up a pathway from a zinc
electrode crowded with electrons to a copper electrode, which contains "holes" for the electrons, their mutual repulsion makes them try to escape from each other to their new home as quickly as possible. (Nature of Electricity - Charles Platt)
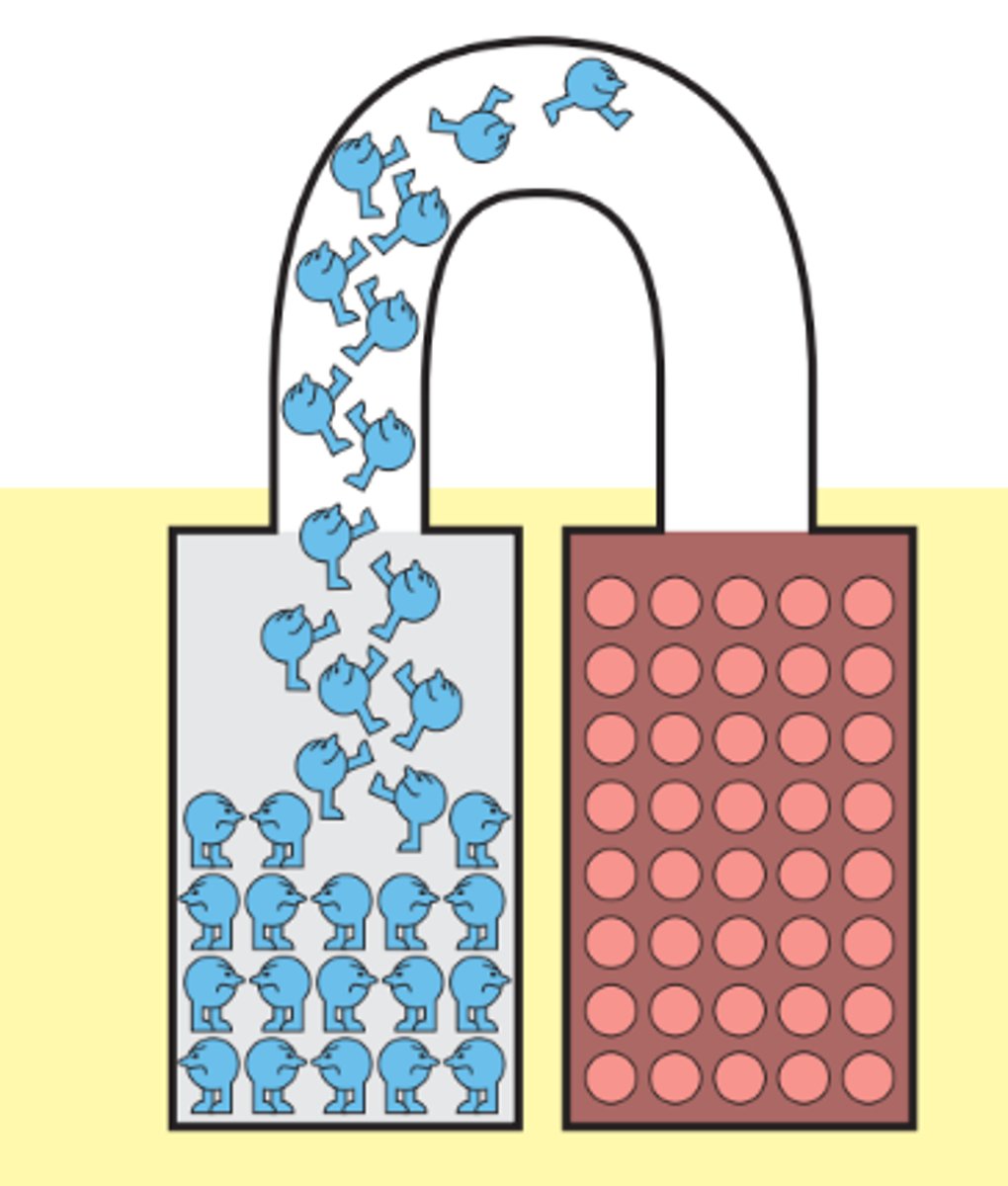
Why does the battery stop working after a while?
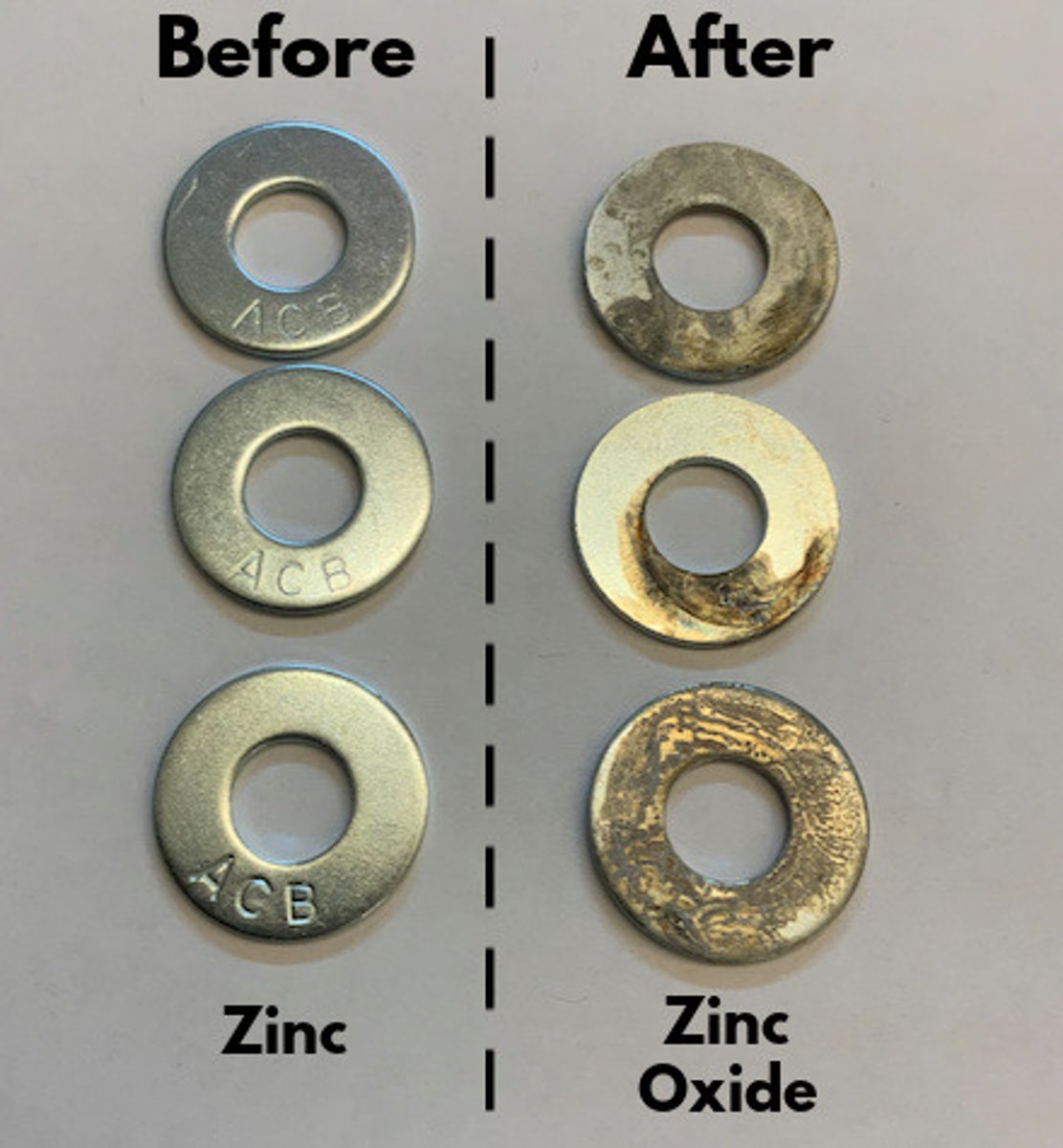
The process (of generating electric current) continues until the zinc-acid reaction grinds to a halt, usually because it creates a layer of a compound such as zinc oxide, which won't react with acid and prevents the
acid from reacting with the zinc underneath. This is why
your zinc electrode may have looked sooty when you pulled it out of the acidic electrolyte. (Nature of Electricity - Charles Platt)

cathode (galvanic cell)
considered positive electrode. Electrons move from negative (low potential) to positive (high potential). Anode considered negative electrode here.
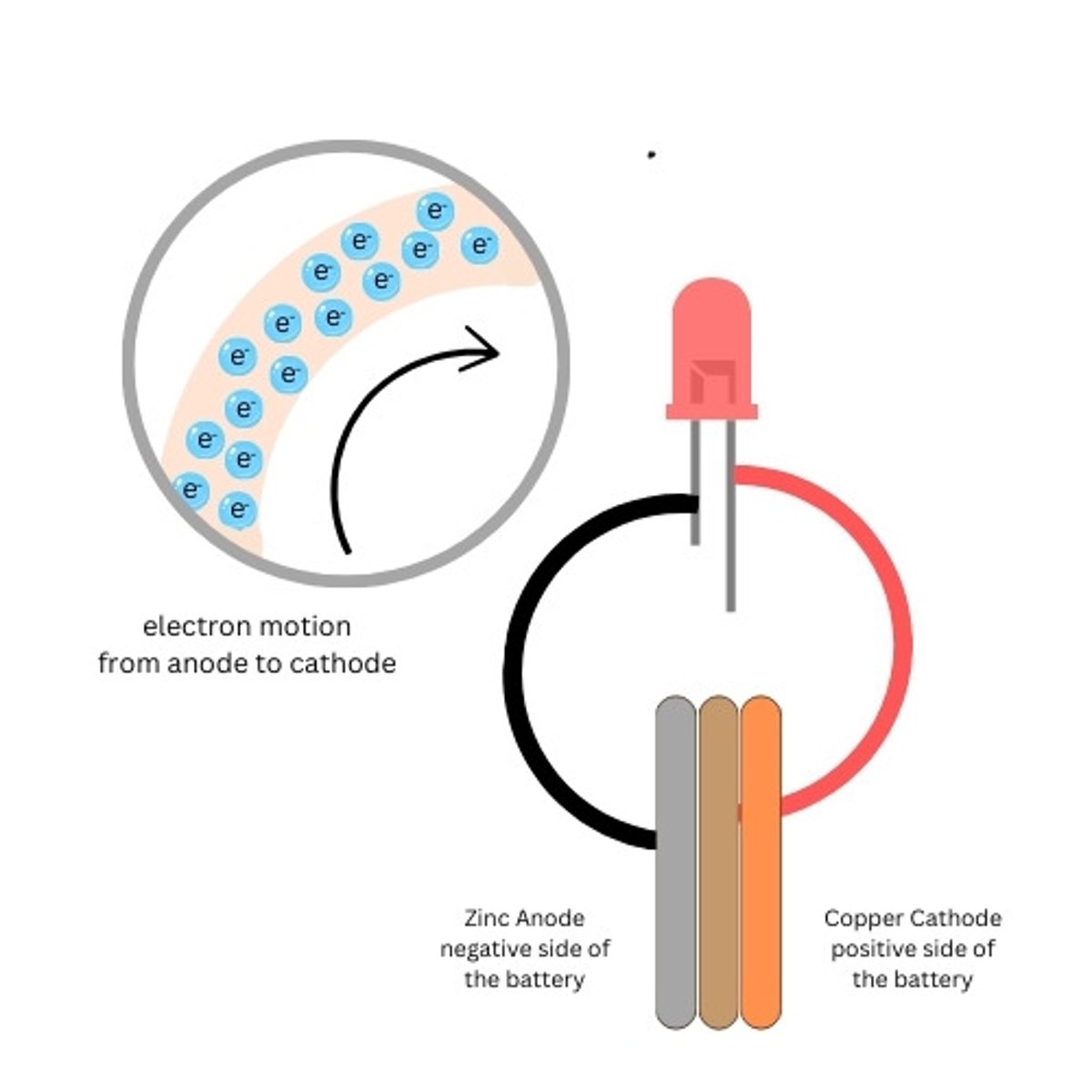
anode (galvanic cell)
is considered the negative electrode "The aNode of a galvaNic cell is always Negative"
Conduction
Form of heat transfer where heat energy is directly transferred between particles through particle collisions or direct contact.
Convection
The transfer of heat by the movement of a fluid
Fluid
any substance that can flow and take the shape of the container that holds it
q
The variable used for Thermal Energy
Δ (Delta)
The greek letter used to indicate change
Latent Heat of Fusion (Lf)
The amount of thermal energy absorbed per gram as solid melts (fuses) at its melting point. The same amount of heat per gram must be released to freeze the substance.
Latent Heat of Vaporization (Lv)
The amount of thermal energy absorbed per gram as a liquid boils (vaporize) at its boiling point. The same amount of heat per gram must be released to condense the substance.
c
Heat capacity is the number of joules of energy needed to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree. In physics, it is Cp; in chemistry it is c
Density
Mass per unit volume of a substance
Radiation
Energy that is radiated or transmitted in the form of rays or waves or particles.
Solid
A state of matter that has a definite shape and a definite volume
Liquid
A state of matter that has no definite shape but has a definite volume.
Gas
A state of matter with no definite shape or volume
Boiling Point
The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas
Melting Point
the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid
Phase change
a change from one state (solid or liquid or gas) to another without a change in chemical composition
Melt
change from a solid to a liquid