Exam 4 Combined
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
When Na+ voltage-gated channels open in an axon, Na+ follows a _______ gradient ________ the neuron.
A. Chemical; into
B. Electrical; into
C. Chemical; out of
D. Chemical and electrical; into
D. Chemical and electrical; into
When do voltage-gated channels open?
When the membrane potential reaches a specific voltage
When K+ voltage-gated channels open in an axon, K+ follow a ________ gradient ______ a neuron.
A. Chemical; into
B. Electrical; into
C. Chemical; out of
D. Chemical and electrical; out of
D. Chemical and electrical; out of
Enhanced release of a neurotransmitter will lead to _________ paralysis.
Spastic
Limited release of a neurotransmitter will lead to ________ paralysis.
Flaccid
What makes up the central nervous system?
Brain and spinal cord
What are afferent neurons?
Sensory neurons that send perception to the brain
What are efferent neurons?
Motor neurons that send a muscle response to the body
What does the acronym SAME refer to?
Neurons:
Sensory (afferent)
Motor (efferent)
What are some sympathetic nervous system responses?
Fight or Flight or Freeze:
Dilated pupils
Accelerated heartbeat
Adrenaline secretion
Inhibits digestion
What are some parasympathetic nervous system responses?
Rest and digest:
Constricted pupil
Salivary gland secretion
Heartbeat slows
Stimulated digestion
What are some functions of mechanoreceptors?
Mechanoreceptors regulate…
Blood pressure
Touch
Osmolarity
Sound
Balance
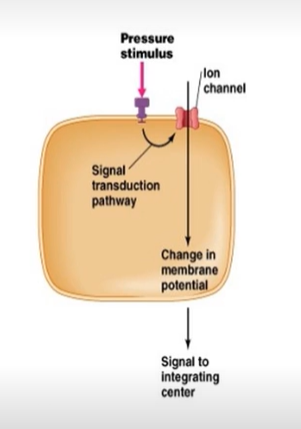
What type of receptor is this?
A. Thermoreceptor
B.Electromagnetic receptor
C. Chemoreceptor
D. Mechanoreceptor
D. Mechanoreceptor
Select all that apply:
Which senses involve chemoreceptors?
A. Taste
B. Touch
C. Sight
D. Hearing
E. Smell
A. Taste
E. Smell
Acetylcholine binds to a receptor on the surface of the muscle fiber. Once activated, the receptor acts as a _______ ion channel.
A. Sodium
B. Calcium
C. Potassium
A. Sodium
Sodium ions follow their gradient through the open receptor channel and move into the muscle fiber. This ion movement will __________ the membrane potential.
A. Decrease
B. Increase
C. not change
B. Increase
What is a sarcomere?
Area of muscle tissue made of actin and myosin that contracts the muscle.
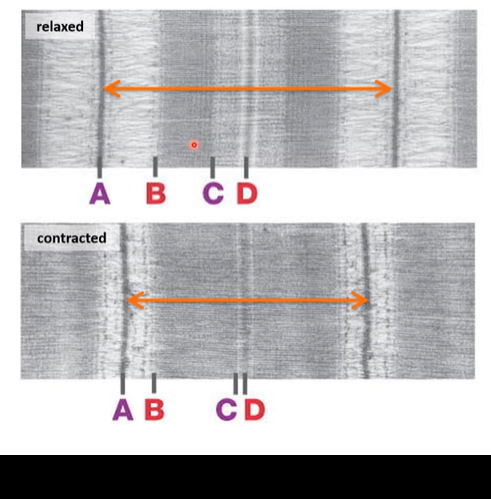
What area of the sarcomere decreases in length during contraction?
A-B
B-C
C-D
B-C
(the area with both actin and myosin, the darker band)
Which filament is bound to the Z line and pulled toward the M-line during muscle contraction?
A. Actin
B. Myosin
A. Actin
In the sliding filament model, ATP is needed to
A. Detach myosin heads from actin
B. Block myosin binding sites on actin
C. Expose myosin binding sites on actin.
A. Detach myosin heads from actin- ATP
B is incorrect; troponin blocks the binding sites
C is incorrect; calcium ions expose the myosin binding sites
What is the resting potential of a neuron?
-70 mV
What contributes to establishing the resting potential using ATP?
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Explain the sodium-potassium pump.
Pump uses ATP (active transport) to move 3 Na+ out of the cell, and move 2 K+ into the cell against their gradients.
Explain the potassium leakage channel.
Always open. Some K+ leak out, but this creates a negative charge inside the cell, preserving most of the K+ in the cell.
Movement of ions is an __________ gradient
electrochemical
Select all that apply. Which proteins move ions across the membrane to establish resting potential?
A. Sodium potassium pump
B. Potassium leak channel
C. Negatively charged intercellular proteins
A. Sodium potassium pump
B. Potassium leak channel
What happens if you add a sodium-potassium pump inhibitor to the cell?
A. More Na+ will accumulate outside the cell
B. Less K+ will accumulate inside the cell
C. Both Na+ and K+ gradients would disappear
B. Less K+ will accumulate inside the cell
What happens to cause an action potential?
Sodium ions flood into the neuron, creating a high positive charge in the cell.
At resting potential, the inside of the neuron is _______ compared to the outside.
A. Slightly negative
B. Positive
C. Neutral
A. Slightly negative
What prevents all the potassium from leaving through the potassium leak channels?
Negatively-charged proteins and ions in the axon
As sodium enters the neuron, the inside of the neuron becomes more ________ compared to the outside
Positive
Give the order of phases in an action potential
Resting potential → Rising phase → Depolarization → Repolarization → Hyperpolarization → Resting potential
This type of signaling involves a gland releasing a hormone into the bloodstream.
Endocrine
This type of signaling involves a gland releasing a hormone in a space where only nearby cells can access it.
Paracrine
This type of signaling involves a cell releasing a hormone that acts on itself.
Autocrine
A neuron secretes chemicals into the bloodstream. What type of signaling is it?
Neuroendocrine
A gland secretes chemicals via ducts onto epithelial tissue. What type of signaling is this?
Exocrine
(examples: sweat, digestive enzymes)
A gland secretes chemicals into the environment that communicate with other individuals. What type of signaling is this?
Ectocrine
(ex: pheromones)
Can water-soluble hormones enter their target cell? Why/why not?
They cannot, because they can’t pass through the lipid bilayer.
Can lipid-soluble hormones enter their target cell? Why/why not?
They can, because they can pass through the lipid bilayer.
Describe the release, transport, and reception of a water-soluble hormone (epinephrine)
Epinephrine is released from the secretory cell via vesicles (exocytosis) because water-soluble hormones can’t pass through the lipid bilayer.
Epinephrine dissolves in the blood by itself and travels through the bloodstream.
Epinephrine binds to a β receptor on OUTSIDE of target cell membrane. It can’t enter the target cell.
Describe the release, transport, and reception of a lipid-soluble hormone (estradiol)
Estradiol diffuses out of the secretory cell on its own, since it can pass through the lipid bilayer.
Estradiol is bound to a binding protein before it can dissolve in the blood.
Estradiol can bind to receptors on the outside of the target cell membrane, or cross the cell membrane to activate receptors inside the cell.
Select all that apply: Water-soluble hormones _________
A. have intracellular receptors
B. diffuse through the cell membrane
C. include peptide, protein, and monoamine hormones
D. Are soluble in blood
C. include peptide, protein, and monoamine hormones
D. Are soluble in blood
A majority of our hormones use _______ regulation.
negative
Secretin circulates through the blood to reach the pancreas. What type of signaling is this?
A. Paracrine
B. Endocrine
C. Ectocrine
D. Exocrine
B. Endocrine
What is the H-P-G axis?
Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Gonad
Controls testosterone/estradiol production
What is the difference between positive feedback and feedforward regulation?
Positive feedback involves a product stimulating its own production.
Feedforward regulation involves an intermediate stimulating the production of further products. (See the H-P-G axis; GnRH and LH are the intermediates, testosterone/estradiol is the product.)
What is oxytocin and where is it produced?
Peptide that stimulates contraction of uterus and mammary glands. Produced in posterior pituitary
What is ADH and where is it produced?
Peptide that promotes retention of water in the kidneys. Produced in posterior pituitary
Where is growth hormone produced?
Anterior pituitary
What is prolactin and where is it produced?
Protein that stimulates milk production and secretion. Produced in anterior pituitary
What is follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and where is it produced?
Glycoprotein that stimulates production of ova/sperm. Produced by anterior pituitary
What is luteinizing hormone (LH) and where is it produced?
Glycoprotein that stimulates ovaries/testes. Produced by anterior pituitary
What is thyroid-stimulating hormone and where is it produced?
Glycoprotein produced in anterior pituitary that stimulates thyroid cells
What is adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and where is it produced?
Peptide secreted by anterior pituitary that stimulates adrenal glands
What hormones are produced in the posterior pituitary?
Oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone
What hormones are released by the anterior pituitary?
Growth hormone, prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone
What is epinephrine/norepinephrine?
Amine secreted by adrenal medulla. Raises blood glucose, increases metabolism, constricts certain blood vessels
What are androgens and estrogens?
Steroids produced by the gonads. Support sperm/uterine growth and secondary sex characteristics.
What are tropic hormones? Give some examples.
Tropic hormones stimulate secretion of other hormones. Usually in the hypothalamus-pituitary-target (HPT) axis.
Ex: FSH, LH, TSH, ACTH
Name the hypothalamic-pituitary-target axes.
Hypothalamus-pituitary-gonad (HPG)
Hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid (HPT)
Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA)
A hormone not regulated by a hypothalamic-pituitary-target axis is…
A. GnRH
B. TSH
C. Insulin
D. LH
E. ACTH
C. Insulin
Which hormone is most likely to utilize second messengers such as cAMP?
A. Testosterone
B. Cortisol
C. Adrenaline
D. Estradiol
C. Adrenaline (it is the only one that is not lipid-soluble)
What would happen if a water-soluble hormone was injected into the cytoplasm of a target cell?
Absolutely nothing. There are no intracellular receptors for water-soluble hormones.
In a positive feedback loop, what ultimately ends the feedback loop?
The disappearance of the stimulus
What are mineralcorticoids and where are they produced?
Hormone that retains sodium ions and water by the kidneys, increasing blood volume and blood pressure. Released by adrenal cortex.
What are glucocorticoids and where are they produced?
Hormone that breaks down proteins and fats to increase blood glucose level. Suppresses immune system and digestion, redirecting energy to survival. Produced by adrenal cortex.
Predict the outcome of long-term stress.
A. Epinephrine secretion will increase
B. Corticosteroid secretion will increase
C. ACTH secretion will increase
D. A and C
E. B and C
E. B and C
What is parthenogenesis?
Asexual reproduction involving meiosis/a sex cell
(Ex: An unfertilized egg develops into a haploid adult)
What are the types of asexual reproduction?
Parthenogenesis
Budding
Fission
What is fission?
An adult organism divides in two using mitosis.
Select all that apply: In which environments would sexual reproduction be more successful than asexual reproduction?
A. Homogeneous environments (similar resources throughout)
B. Heterogenous environments (resource distribution differs)
C. Stable environment
D. Unstable environment
B. Heterogenous environment
D. Unstable environment
What is the role of the seminal vesicle and the prostate gland?
Create seminal fluid; introduce nutrients and alkalinity to sustain sperm life
What is the role of the testis?
Produce sperm
Which hormones are secreted by the anterior pituitary and stimulate spermatogenesis?
LH and FSH
Where does fertilization occur in humans?
A. Ovary
B. Oviduct
C. Uterus
D. Cervix
B. Oviduct
High levels of estradiol _______ the hypothalamus, while low levels of estradiol ______ the anterior pituitary.
A. Inhibit, stimulate
B. Stimulate, inhibit
Stimulate, inhibit
What produces progesterone during the luteal phase of the ovarian cycle?
A. Developing follicle
B. Corpus luteum
C. Uterine lining
D. Fallopian tuves
B. Corpus luteum
Which of the following modes of reproduction require meiois? Select all that apply.
A. Parthenogenesis
B. Budding
C. Fission
D. Mating between hermaphrodites
E. Mating between sperm and egg producers
A. Parthenogenesis
D. Mating between hermaphrodites
E. Mating between sperm and egg producers
Boulder star coral can produce both sperm and egg in the same polyp during the same season. They are…
A. Not hermaphrodites
B. Sequential hermaphrodites
C. Simultaneous hermaphrodites
C. Simultaneous hermaphrodites
Select all that apply: LH regulates human-assigned female reproductive funtion. LH in human females…
A. Stimulates follicle development
B. Stimulates ovulation
C. Maintains the lining of the endometrium
D. Stimulates the development of corpus luteum
E. Maintains corpus luteum after fertilization
A. Stimulates follicle development
B. Stimulates ovulation
D. Stimulates the development of corpus luteum
As the follicle develops, it produces estradiol in response to LH. At low levels, estradiol will exert ___________ feedback on LH production in the anterior pituitary.
Negative
In females that enter menopause, the ovary does not produce enough estrogen because of depletion of follicles. This will lead to
A. Low levels of LH and FSH
B. High levels of LH and FSH
C. No change in LH and FSH levels
B. High levels of LH and FSH
(no negative feedback to the hypothalamus stopping LH and FSH production)
A birth control pill containing progesterone and a low dose of estrogen will result in all of these, except:
A. Prevent follicle from developing
B. Prevent ovulation
C. Prevent the development of the uterine lining
C. Prevent the development of the uterine lining
The dark band contains ________-
Myosin and actinT
The light band contains _______
actin
Give the order of size of muscle parts
Muscle tissue > Muscle bundle > muscle fiber > myofibril > sarcomere
Which filament is bound to the Z line and pulled toward the M-line during muscle contraction?
Actin
What is the function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum>?
Store calcium ions