Quantatative Multiple Choice Questions (Final)
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
A process in which the volume of a reagent needed to react with an analyte is measured is called
A. titrant
B. indicator
C. primary standard
D. volumetric analysis
E. direct titration
D. volumetric analysis
The equivalence point of a titration reaction with1:1 stoichiometry is
A. The same as the end point of the titration
B. the point where the indicator changes color
C. the volume of the titrant at which pH = pKa
D. the volume of the titrant needed to titrate a blank sample
E. an inflection point on the titration curve.
E. an inflection point on the titration curve.
True or False: The end point of a titration is the same as the equivalence point of the titration
A. True
B. False
B. False
True or False: The difference between the endpoint and equivalence point can be estimated with a blank titration
A. True
B. False
A. True
Back titration is a procedure in which
A. titrant is added to the analyte solution until the reaction is complete
B. the weight of the titrant is measured instead of its volume
C. excess standard reagent is added to the analyte solution and the former is titrated with a second standard reagent
D. the reaction product is titrated with a second standard reagent
E. excess analyte is titrated with a second standard reagent.
C. excess standard reagent is added to the analyte solution and the former is titrated with a second standard reagent
The critical step in titration calculations is to relate
A. volume of titrant to volume of analyte
B. grams of titrant to grams of analyte
C. conductivity of titrant to conductivity of analyte
D. reduction of titrant to oxidation of analyte
E. moles of titrant to moles of analyte
E. moles of titrant to moles of analyte
A 25.00-mL solution of NaOH was used to titrate 0.7864 g potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP, FM 204.2) according to the following reaction. What is the concentration of the NaOH solution?
A. 0.1542 M
B. 0.003855 M
C. 6.423 M
D. 1.542 × 10−4 M
E. 1.542 × 10−2 M
A. 0.1542 M
A 25.00-mL HCl solution of unknown concentration is titrated with a 0.2480 M NaOH solution. It requires 36.78 mL of the NaOH solution to reach the endpoint. Calculate the concentration of the HCl solution.
A. 0.3649 M
B. 0.1686 M
C. 9.121 M
D. 0.003649 M
E. 0.091 21 M
A. 0.3649 M
When performing a precipitation titration on a mixture of ions, the observed endpoint is sometimes different from the expected value. This error is attributed to
A. turbidity
B. coprecipitation
C. the solubility of the precipitates
D. titration error
E. the indicator
B. coprecipitation
Which statement about gravimetric analysis is NOT true?
A. The analyte is converted to a low-solubility precipitate
B. It is an accurate and precise quantitative method
C. Calculations are based on the mass of the product obtained
D. It does not require calibration or standardization
E. It uses spectrometric methods to analyze the precipitate
E. It uses spectrometric methods to analyze the precipitate
Which of the following is NOT a desirable property of a gravimetric precipitate?
A. obtained in a pure form
B. insoluble in the media used for precipitation
C. consists of small particles
D. easily filterable
E. possesses a known composition
C. consists of small particles
True or False: Larger particles have less surface area to which impurities can become adsorbed
A. True
B. False
A. True
True or False: The nucleation phase of the crystallization process can occur on suspended impurity particles or scratches on a glass surface
A. True
B. False
A. True
Which technique is used to promote particle growth during crystallization? A. raising the temperature to increase solubility
B. decreasing the temperature to promote supersaturation
C. adding precipitant rapidly and mixing well
D. using a small volume of solution so that concentration of analyte and precipitant are high
E. All of the above
A. raising the temperature to increase solubility
In homogeneous precipitation
A. two homogeneous solutions are mixed
B. no precipitate is formed in the solution
C. the product is continuously removed from the mixture
D. the precipitating agent is generated in the analyte solution
E. the reaction takes place at elevated temperature to keep everything in solution
D. the precipitating agent is generated in the analyte solution
An excess of AgNO3 is added to a solution of KBr. What is the charge on the surface of the AgBr precipitate and what ions are responsible for the charge?
A. positive, K+
B. negative, NO3-
C. neutral
D. positive, Ag+
E. negative, Br−
D. positive, Ag+
True or False: Inclusions are pockets of impurities that are literally trapped inside the growing crystal.
A. True
B. False
B. False
Coprecipitation means
A. two insoluble compounds form a mixed precipitate
B. soluble impurities are included in the precipitate even though the solubility of the impurity has not been exceeded
C. residual solvent is entrapped within the precipitate
D. amorphous and crystalline forms of the product precipitate together
E. a coagulated colloid breaks up to smaller particles.
B. soluble impurities are included in the precipitate even though the solubility of the impurity has not been exceeded
After filtration, some precipitates are ignited. The purpose of this treatment is to
A. remove water and volatile solvents
B. remove the coprecipitated impurities
C. form a compound with known composition
D. study the degradation mechanism of the precipitated composition
E. determine the organic content of the sample.
C. form a compound with known composition
Which statement regarding thermogravimetric analysis is NOT true?
A. The sample is heated at high temperature, and the volume of the volatile products is measured
B. The mass of a heated sample is measured as a function of temperature
C. The composition of the product depends on the temperature and duration of heating
D. More than one decomposition product can be formed at different stages of heating
E. All decomposition products may be volatile.
A. The sample is heated at high temperature, and the volume of the volatile products is measured
True or False: A hygroscopic substance is one that picks up water from the air and is difficult to weigh accurately
A. True
B. False
A. True
Which statement regarding combustion analysis is TRUE?
A. It is used to determine C and H in organic compounds burned in an excess of oxygen
B. A catalyst is used to complete the combustion process of partially combusted products
C. For oxygen analysis, the sample is thermally decomposed in the absence of added oxygen
D. A result within ±0.3 wt% of theoretical is good evidence that the compound has the expected formula
E. All of the statements are true
E. All of the statements are true
A 25.00-mL aliquot of 0.1500 M HI was titrated with 0.100 0 M NaOH. Calculate the volume of NaOH needed to reach the equivalence point
A. 37.50 mL
B. 0.03750 mL
C. 16.67 mL
D. 25.00 mL
E. 0.016 67 mL
A. 37.50 mL
True or False: When both a strong acid and a weak acid are titrated with a strong base, the pH at the equivalence point is equal to 7.
A. True
B. False
B. False
The titration solution essentially only contains a weak acid
A. after the equivalence point of a strong-acid-strong-base titration
B. at the equivalence point of a weak-acid-strong-base titration
C. at the equivalence point of a weak-base-strong-acid titration
D. before the equivalence point of a weak-acid-strong-base titration
E. after the equivalence point of a weak-acid-strong-base titration.
C. at the equivalence point of a weak-base-strong-acid titration
Consider the titration of a monoprotic acid with a strong base. A buffer solution is formed
A. before the equivalence point of a strong-acid-strong-base titration
B. at the equivalence point of a weak-acid-strong-base titration
C. after the equivalence point of a strong-acid-strong-base titration
D. before the equivalence point of a weak-acid-strong-base titration
E. after the equivalence point of a weak-acid-strong-base titration
D. before the equivalence point of a weak-acid-strong-base titration
A 30.00-mL aliquot of a 0.150 0 M weak acid (HA) solution is titrated with 0.1000 M NaOH. Calculate the pH of the solution when 15.00 mL of 0.1000 M NaOH has been added. HA has a Ka = 4.75 × 10-6
A. 5.62
B. 0.30
C. 4.84
D. 5.02
E. 5.14
D. 5.02
True or False: The pH of the titration solution at the equivalence point of the titration is 9.45. This is consistent with a titration of a weak acid with a strong base
A. True
B. False
A. True
Which statement is NOT true about the titration of a weak base (B) with a strong acid?
A. At the equivalence point, the pH is calculated using the acid dissociation reaction of the conjugate acid, BH+
B. Past the equivalence point, the excess strong acid determines the pH
C. Before strong acid is added, the solution contains just the conjugate acid, BH+
D. Between the initial point and the equivalence point, the solution contains a mixture of B and BH+
E. The pH at the equivalence point is less than 7.
C. Before strong acid is added, the solution contains just the conjugate acid, BH+
True or False: In diprotic systems, the second equivalence point can be treated as a monoprotic weak acid
A. True
B. False
A. True
What must you consider when choosing an acid-base indicator for use in determining the end point of an acid-base titration?
A. The transition range of the indicator contains the pH at the equivalence point
B. The pH at which the indicator changes color is on the steepest portion of the titration curve
C. The protonated and deprotonated forms of the indicator have colors that are easily distinguishable
D. All of the above
E. None of the above.
D. All of the above
The pH at the equivalence point of a titration of a weak base with a strong acid is 6.24. The steepest part of the titration curve is from pH 7 to 5. Which of the following indicators would NOT be suitable for this titration?
A. methyl red, pH transition range 3.8-5.4
B. bromocresol purple, pH transition range 5.2-6.8
C. cresol purple, pH transition range 7.6-9.2
D. p-nitrophenol, pH transition range 5.6-7.6
E. Chlorophenol red, pH transition range 4.8-6.4
C. cresol purple, pH transition range 7.6-9.2
NaOH is NOT available as a primary standard because
A. it is hygroscopic
B. it reacts with glass
C. it forms carbonates with atmospheric CO2
D. evaporation from the bottle changes the concentration
E. it decomposes easily.
C. it forms carbonates with atmospheric CO2
In the Kjeldahl nitrogen analysis, nitrogen inorganic substances is analyzed by
A. combustion analysis
B. boiling the sample in concentrated NaOH
C. reducing the nitrogen with a metal
D. digesting the sample and converting the nitrogen into the ammonium ion
E. titrating the sample with acetic acid.
D. digesting the sample and converting the nitrogen into the ammonium ion
True or False: Due to the leveling effect, hydronium is the weakest acid in water
A. True
B. False
B. False
Which of the following is NOT a strong acid?
A. HBr
B. HClO4
C. H3PO4
D. HCl
E. HNO3
C. H3PO4
True or False: The pH of a 1.0 × 10−8 M solution of KOH is acidic
A. True
B. False
A. True
What is the concentration of OH− ions produced by water dissociation in a 1.0 × 10−4 M KOH solution?
A. 1.0 × 10−4 M
B. 1.0 × 10−10 M
C. 1.0 × 10−7 M
D. 1.0 × 1010 M
E. 1.0 × 104 M
B. 1.0 × 10−10 M
True or False: The larger the Ka value, the weaker the acid
A. True
B. False
B. False
Identify the chemical equation whose equilibrium constant is defined as the Ka for the trimethyl ammonium ion, (CH3)3NH+
A. (CH3)3N + H2O <-> (CH3)3NH+ + OH−
B. (CH3)3N + H2O <-> (CH3)3NOH − + H+
C. (CH3)3NH+ + H2O <-> (CH3)3N + H3O+
D. (CH3)3N + H3O+ <-> (CH3)3NH+ + H2O
E. (CH3)3NH+ + OH − <-> (CH3)3N + H2O
C. (CH3)3NH+ + H2O <-> (CH3)3N + H3O+
What is the pH of a 0.30 M p-hydroxybenzoic acid (Ka = 2.9 × 10−5) solution?
A. 0.0029
B. 2.53
C. 0.52
D. 5.06
E. 2.27
B. 2.53
Which of the following is NOT a property of a buffer solution?
A. A buffer is a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base
B. A buffer resists pH changes when acids or bases are added
C. The maximum capacity of the buffer is at pH = pKa
D. The pH of a buffer is dependent on the solution ionic strength and temperature
E. The pH of a buffer is independent of the concentrations of the species that form the buffer
E. The pH of a buffer is independent of the concentrations of the species that form the buffer
True or False: A buffer resists changes in pH because it consumes the added acid or base
A. True
B. False
A. True
True or False: In choosing a buffer, select one whose pKa is close to the desired pH of the buffer
A. True
B. False
A. True
Which pair of compounds will make a buffer in aqueous solution?
A. NaCN and NaOH
B. NaCN and KCN
C. HCl and NaOH
D. HCN and NaCN
E. HCN and HCl
D. HCN and NaCN
An Arrhenius acid is best defined as a
substance that dissociates in water to produce aqueous hydrogen ions
When dissolved in water, which of the following compounds in an Arrhenius acid?
HCN (produces H3O+)
An Arrhenius base is best defined as a
substance that dissociates in water to produce aqueous hydroxide ions
When dissolved in water, which of the following compounds is an Arrhenius base?
KOH (produces OH-)
Write a balanced equation for the dissociation of the Bronsted-Lowry acid HSO4- in water?
B. HSO4- (aq) + H2O (l) <-> SO4^2- + H3O (aq)
The equilibrium constant, K, for the reaction shown below, has a value 1.8x10^-5. In this reaction which is the strongest acid and which is the strongest base?
CH3CO2H (aq) + H2O (l) <-> H3O+ (aq) + CH3CO2- (aq)
H3O+ and CH3CO2-
An acidic solution at 25C has
[H3O+] > 1x10^-7 M > [OH-]
Calculate the hydroxide ion concentration in an aqueous solution that contains 3.50 × 10^−3 M in hydronium ion
2.86 x 10^-12 M
Human tears have a concentration of H3O+ that is 3.16 x 10^-8. The concentration of OH- in human tears is
greater than 3.16 x 10^-7 and tears are basic
The pH of 0.255 M HCN is 4.95. What is the value of Ka for hydrocyanic acid?
4.9 x 10^-10
The pH of 0.150 M CH3CO2H, acetic acid, is 2.78. What is the value of Ka for acetic acid?
1.9 x 10^-5
Which one of the following is least able to behave as a Lewis base?
(CH3)3NH+
The compound BF3 can be described as a(n) ______________
Lewis Acid
True or False: Metal ions are Lewis acids that accept electron pairs from ligands, which are Lewis bases
A. True
B. False
A. True
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a tetradentate ligand. This means that ATP
A. Binds to four metal ions
B. binds to metal ions with a charge of +4
C. occupies six coordination positions around a metal ion
D. binds to divalent metal ions
E. uses four atoms to bind to a metal ion.
E. uses four atoms to bind to a metal ion.
EDTA is a ___________ ligand that forms 1:1complexes with metal ions
A. monodentate
B. bidentate
C. tridentate
D. tetradentate
E. hexadentate
E. hexadentate
Identify the expression for the conditional formation constant for the reaction between Ca2+ and EDTA.
A. Kf' = [CaY^2-] / [Ca2+] [EDTA]
EDTA titrations of metal ions are pH-sensitive. Which statement is NOT true?
A. At low pH, the amount of EDTA in the form Y4− decreases
B. As the pH is lowered, the end point becomes less distinct
C. Metals with higher formation constants can be titrated at lower pH
D. All metal ions require alkaline titration conditions
E. At higher pH values, the metal hydroxide might precipitate.
D. All metal ions require alkaline titration conditions
Which statement about an auxiliary complexing agent is TRUE?
A. It increases the conditional formation constant
B. It forms a complex with the metal ion
C. It protects some components in the mixture from reacting with EDTA
D. It forms a complex with the indicator
E. It displaces the metal ion from the metal-EDTA complex.
B. It forms a complex with the metal ion
True or False: A metal-indicator complex that is more than 100 times weaker than the metal-EDTA complex will result in a diffuse end point
A. True
B. False
B. False
Which method can be used to detect the end point of an EDTA titration?
A. metal ion indicators
B. glass (pH) electrode
C. mercury electrode
D. ion-selective electrode
E. all the above
E. all the above
Mn2+ is titrated EDTA, and methylthymol blue (MT) is used as the indicator. In what pH range should the solution be buffered? A. 5−8
B. 3−5
C. 5.5−6.5
D. 8−11
E. 12−14
C. 5.5−6.5
In a direct titration, how many milliliters of 0.030 M EDTA are required to react with 25.0 mL of 0.050 M Co2+?
A. 75.0 mL
B. 25.0 mL
C. 30.0 mL
D. 41.6 mL
E. 15.0 mL
D. 41.6 mL
True or False: In an indirect titration, an anion is precipitated with a metal ion, and the excess metal ion is titrated with EDTA
A. True
B. False
A. True
What is the purpose of a masking agent in an EDTA titration?
A. It displaces a metal ion from the metal-EDTA complex
B. It complexes with one species in a mixture to prevent interference with the analysis of the other species
C. It binds to the metal ion to prevent it from precipitating as the metal hydroxide in alkaline conditions
D. It displaces the indicator from the metal ion at the end point
E. It forms a precipitate with all interfering species in solution.
B. It complexes with one species in a mixture to prevent interference with the analysis of the other species
Which of the following terms can be used to describe an electrochemical cell in which a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current?
I. an electrolytic cell
II. a galvanic cell
III. a voltaic cell
A) only I
B) only II
C) only III
D) II and III
D) II and III
Which cell involves a nonspontaneous redox reaction?
A) concentration cell
B) electrolytic cell
C) fuel cell
D) galvanic cell
B) electrolytic cell
During an electrochemical reaction, electrons move through the external circuit toward the________ and positive ions in the cell move toward the ________.
A) anode, anode
B) anode, cathode
C) cathode, anode
D) cathode, cathode
D) cathode, cathode
For a galvanic cell, the cathode has a ________ sign and is the site of ________.
A) negative, oxidation
B) negative, reduction
C) positive, oxidation
D) positive, reduction
D) positive, reduction
A salt bridge is used to
A) provide reactants in a fuel cell
B) determine the direction of the cell reaction
C) control whether the cell is electrolytic or galvanic
D) allow the ion flow necessary for cell neutrality
D) allow the ion flow necessary for cell neutrality
In a galvanic cell, the half-reaction MnO4-(aq) + 8 H+(aq) + 5 e- → Mn2+(aq) + 4 H2O(l) is
A) an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the anode
B) an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the cathode
C) a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the anode
D) a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the cathode
D) a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the cathode
In a galvanic cell, the half-reaction H2(g) + 2 OH-(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + 2 e- is
A) an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the anode
B) an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the cathode
C) a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the anode
D) a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the cathode
A) an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the anode
What species is oxidized in the reaction:
CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)?
A) CuSO4 (aq)
B) Fe (s)
C) FeSO4 (aq)
D) Cu (s)
B) Fe (s)
Given that Cl2(g) + 2 e- → 2 Cl-(aq) is the reduction half-reaction for the overall reaction
2Ag(s) + Cl2(g) -> 2AgCl(s)
what is the oxidation half reaction?
A) Ag(s) → Ag+(aq) + e-
B) Ag(s) + Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s) + e-
C) Ag(s) + Cl2(g) + e- → AgCl(s) + Cl-(aq)
D) 2 Cl-(aq) → Cl2(g) + 2 e-
B) Ag(s) + Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s) + e-
What is the reduction half-reaction for the following overall cell reaction?
Ni2+(aq) + 2 Ag(s) → Ni(s) + 2 Ag+(aq)
A) Ag(s) + e- → Ag+(aq)
B) Ag+(aq) + e- → Ag(s)
C) Ni2+(aq) + 2 e- → Ni(s)
D) Ni2+(aq) + e- → Ni(s)
C) Ni2+(aq) + 2 e- → Ni(s)
The iron content of foods can be determined by dissolving them in acid (forming Fe3+), reducing the iron(III) to iron(II), and titrating with cerium(IV):
Fe2+(aq) + Ce4+(aq) -> Fe3+ (aq) + Ce3+ (aq)
Identify the two half-reactions in the above reaction.
Oxidation half-reaction:
Fe2+ (aq) -> Fe3+ (aq) + e-
Reduction half-reaction:
Ce4+(aq) + e- -> Ce3+(aq)
What is the shorthand notation that represents the following galvanic cell reaction?
Fe(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) →
Fe(NO3)2(aq) + Cu(s)
A) Fe(s) ∣ Fe2+(aq) ∣∣ Cu2+(aq) ∣ Cu(s)
What is the shorthand notation that represents the following galvanic cell reaction?
2Fe2+(aq) + Cl2(g) → 2 Fe3+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
D) Pt(s) ∣ Fe2+(aq), Fe3+(aq) ∣∣ Cl2(g) ∣ Cl-(aq) ∣ C(s)
For the galvanic cell reaction, expressed below using shorthand notation, what half-reaction occurs at the cathode?
Zn(s) ∣ Zn2+(aq) ∣∣ Ni2+(aq) ∣ Ni(s)
D) Ni2+(aq) + 2 e- → Ni(s)
For the galvanic cell reaction, expressed below using shorthand notation, what half-reaction occurs at the anode?
Mg(s) ∣ Mg2+(aq) ∣∣Cd2+(aq) ∣Cd(s)
A) Mg(s) → Mg2+(aq) + 2 e-
What is the balanced chemical equation for the galvanic cell reaction expressed using shorthand notation below?
Al(s) ∣ Al3+(aq) ∣∣ Ni2+(aq) ∣ Ni(s)
A)
2 Al(s) + 3 Ni2+(aq) → 2 Al3+(aq) + 3 Ni(s)
What is the relation between joules (J), volts (V), and coulombs (C)?
A) 1 J = 1 V × 1 C
B) 1 J = 1 V ÷ 1 C
C) 1 J = 1 C ÷ 1 V
D) 1 J = 1 V × 1 C2
A) 1 J = 1 V × 1 C
In the relationship △G = - nFE°, what is the value of n for the reaction shown below?
3 Cu2+(aq) + 2 Al(s) → 3 Cu(s) + 2 Al3+(aq)
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 6
D)6
What is the balanced equation for the galvanic cell reaction expressed using shorthand notation below?
Mg(s) ∣ Mg2+(aq) ∣∣ Cl2(g) ∣ Cl-(aq) ∣ C(s)
B) Mg(s) + Cl2(g) → Mg2+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
For the galvanic cell Pt(s) ∣ Sn2+(aq), Sn4+(aq) ∣∣ Pb2+(aq) ∣ Pb(s), what is the function of the Pt(s)?
A) Pt is the anode and is a reactant in the overall cell reaction
B) Pt is the anode and does not appear in the overall cell reaction
C) Pt is the cathode and is a product in the overall cell reaction
D) Pt is the cathode and does not appear in the overall cell reaction.
B) Pt is the anode and does not appear in the overall cell reaction
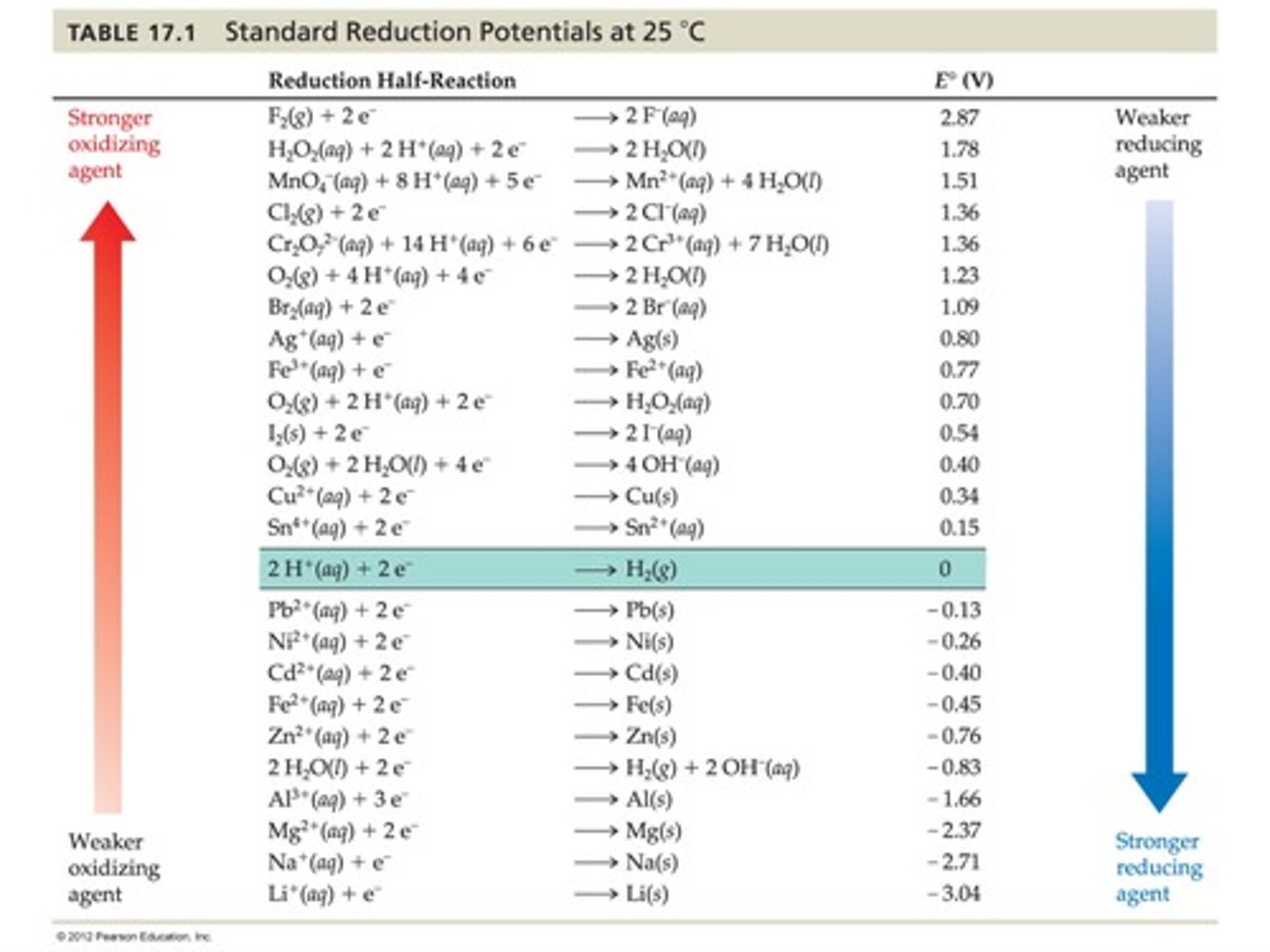
According to Table 17.1, which aqueous metal ion will reduce Ag+, but not Cu2+?
A) Fe2+
B) Fe3+
C) Mn2+
D) Sn2+
B) Fe3+
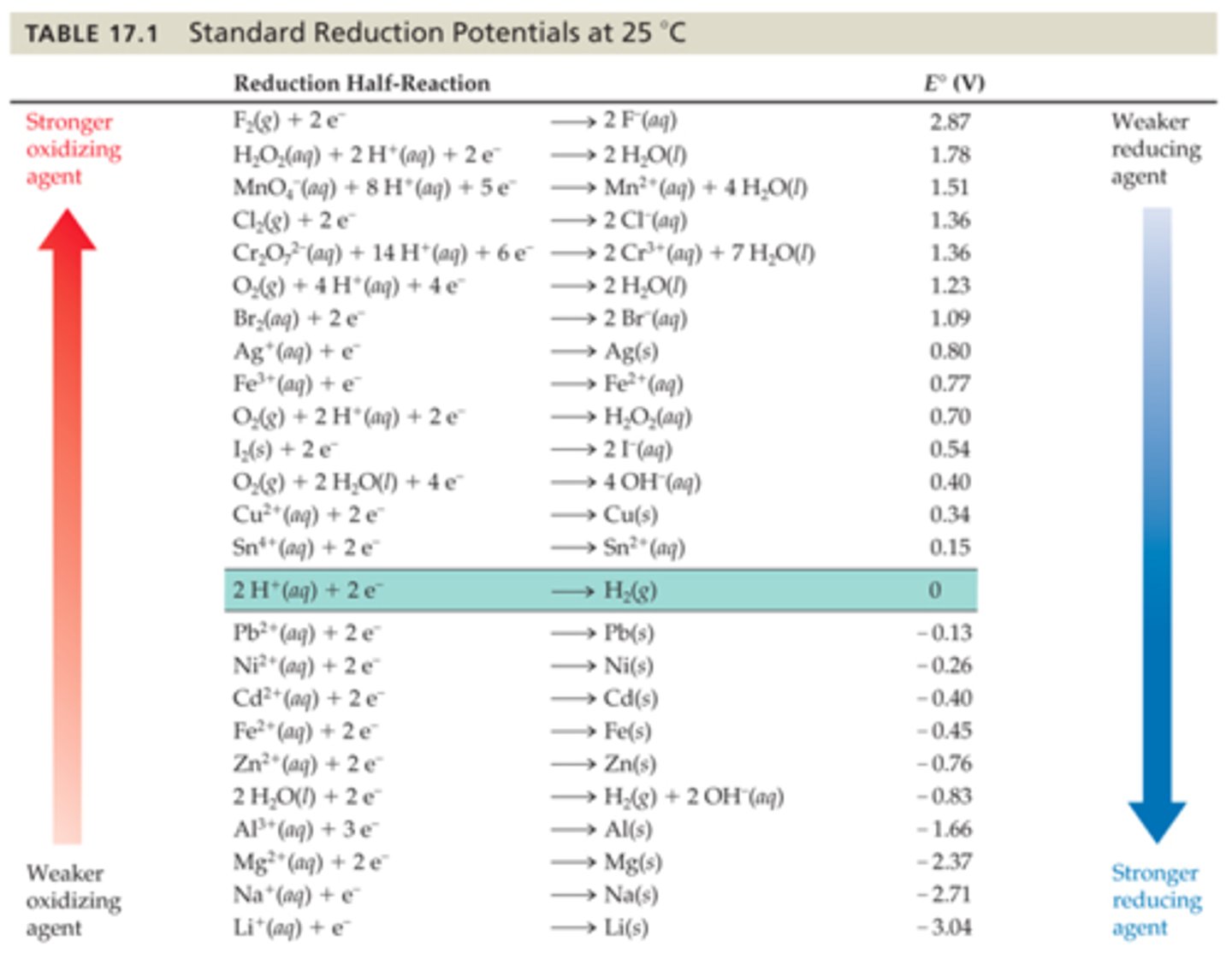
According to Table 17.1, which will reduce water but not Mg2+?
A) Al3+(aq)
B) Al(s)
C) Na+(aq)
D) Na(s)
B) Al(s)
Select the TRUE statement about the properties of light
A. The energy is proportional to the wavelength
B. The frequency is proportional to the wavelength
C. The longer the wavelength, the higher the energy
D. The shorter the wavelength, the higher frequency
E. The energy is inversely proportional to the frequency.
D. The shorter the wavelength, the higher frequency
What is the frequency of a photon with an energy of 1.56 × 10−36 J?
A. 2.35 ms−1
B. 705 Ms−1
C. 0.103 s−1
D. 2.50 × 102 s−1
E. 0.002 07 s−1
A. 2.35 ms−1
True or False: Visible radiation has a higher energy and frequency than infrared radiation.
A. True
B. False
A. True
What is the wavenumber of a photon with a wavelength of 2.0 nm?
A. 2.0 × 10^9 m^−1
B. 5.0 × 10^8 m^−1
C. 0.60 m^−1
D. 6.0 × 10^8 m^−1
E. 0.40 m^−1
B. 5.0 × 10^8 m−1
True or False: Transmittance is proportional to concentration
A. True
B. False
B. False
What is the transmittance of a solution if out of 100 photons, 25 photons pass through?
A. 25
B. 0.25
C. 4.0
D. 0.040
E. None of the above
B. 0.25
True or False: For most substances, Beer's law holds in dilute solutions (<0.01 M)
A. True
B. False
A. True
For visible and ultraviolet spectroscopy, the cuvette is made of
A. NaCl
B. KBr
C. diamond
D. fused-silica
E. glass.
D. fused-silica