Jungian and Humanistic approach
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
How did Jung’s views differ from Freud’s?
Jung rejected Freud’s emphasis on sexuality, focused on spirituality and religion, and believed psychology is future-oriented, unlike Freud’s past-focused approach.
What is Jung’s concept of the collective unconscious?
A universal level of the mind shared by all humans, containing archetypes—innate concepts like “the mother” that help us interpret the world → level below the sub concious
this came from a dream he had about a never ending floors in a house → representing there is more than just the conscious and un (sub) conscious
How did Jung interpret dreams compared to Freud?
Jung saw dreams as information and communication about personality balance; Freud saw them as expressions of forbidden desires.
What evidence supports the collective unconscious?
Archetypes appear across cultures in myths and legends (e.g., wise old man guiding the hero).
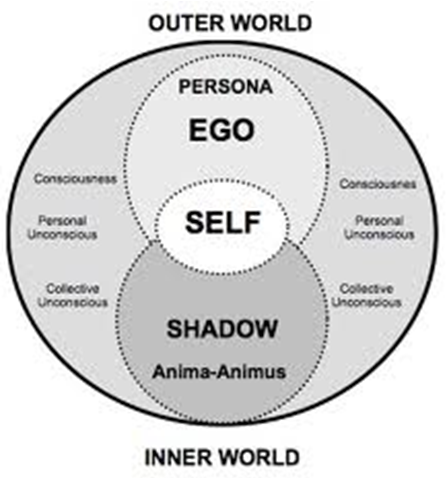
Name Jung’s personality components: Ego, personal unconscious, collective unconscious, persona, shadow, anima, animus
Ego: Consciousness
Personal unconscious
Collective unconscious
Persona: Social mask. what we are prepared to show to peopl
Shadow: Repressed material, the darker side of the persona
Anima: Feminine element in male psyche
Animus: Masculine element in female psyche
What is individuation?
Integration of all personality aspects (including shadow) for biological and spiritual fulfillment; psyche is self-regulating.
confront the darker shadow
the shadow compensates for persona
What are Jung’s two attitudes?
Introversion (inner world focus) and Extraversion (outer world focus).
What are Jung’s four functions of psychological types?
Thinking: Rational, truth-based → things are perceived in terms of truth and falsity
Feeling: Evaluative (good/bad)
Sensing: Objective facts → basic perceptual experience, not concerned with the wider context
Intuiting: Meaning and atmosphere
How does Jungian therapy differ from Freud’s psychoanalysis?
More collaborative, focuses on present/future, dreams indicate personality imbalance, not wish fulfillment.
How did Maslow critique psychoanalysis?
It focused on pathology; Maslow emphasized studying healthy, fulfilled individuals → why base your theory on the sick rather than those who live fulfilling lives
What are deficiency vs growth motives?
Deficiency motives: Reduce negative states (e.g., hunger).
Growth motives: Positive, enhance potential (e.g., curiosity)
Maslow tend to focus on growth motives as opposed to deficiency motives
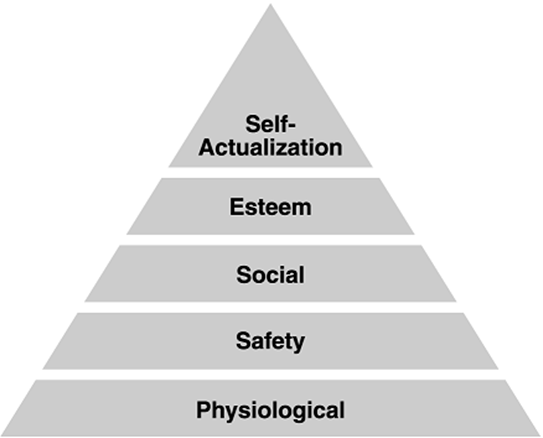
What are Maslow’s five levels of needs?
Physiological
Safety
Social
Esteem
Self-actualization
Characteristics of self-actualizers?
Accepting, honest perception, motivated by values, less concerned with trivialities, experience peak experiences.
not distorted by the defence mechanism
What is a peak experience?
A moment of intense focus and fulfillment, with clear goals and challenging but achievable tasks.
How does Rogers’ approach differ from the medical model?
Non-directive, client actively finds solutions; therapist provides empathy and non-judgmental support.
client centred therapy
Medical model = patient is passive and cured by the therapist
What is actualization in Rogers’ theory?
Expressing true nature; conflict arises between self and organism if misaligned.
What is the goal of Rogers’ therapy?
Reintegration of self and organism through understanding the client’s perspective.