SDL 4: diseases of posterior pituitary
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
central diabetes inspidus or idiopathic diabetes insipidus
hypothalamic diabetes insipidus is aka
gestational diabetes insipidus
type diabetes insipidus caused by accelerated metabolism of vasopressin
antibodies directed against magnocellular neurons
typical cause of idiopathic diabetes insipidus
idiopathic hypothalamic diabetes insipidus
-histology shows lymphocytic inflammation of the pituitary stalk and posterior pituritary
thickening or enlargement of pit. stalk or post pit
MRI findings of idiopathic diabetes insipidus
autosomal dominant mutation of AVP gene
inheritance of familial hypothalamic DI
craniopharyngiomas and primary germ cell tumors
-lymphomas, leukemias
tumors that are characteristically associated with DI
sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, langerhans cell histiocytosis
granulomatous diseases associated with DI
vasopressinase
this enzyme rises late in pregnancy and degrades ADH, causing gestational DI
-X linked recessive mutation in AVPR2 gene, which encodes V2 receptor
-less common: AD or AR mutation of AQP2 gene
inheritance of hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
lithium drugs
acquired nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by
polyuria and polydipsia
predominant symptoms oof diabetes insipidus
-severe hypernatremia with devastating effects on CNS---> hypertonic encephalopathy (brain shrinkage, obtundationo, coma, seizures)
complication of diabetes inssipidus
1) polyuric phase via inhibition of vassopressisn
2) antidiuretic phase due to release of stored hormones
3) permanent DI when stores of vasopressin are exhausted
triphasic clinical presentation of DI resulting from head trauma
the 24-hour urine osmolality is <200 mOsm/L. The average normal 24-hour urine osmolality is 500-800 mOsm/kg
urine osmolality in pt with DI
-dehydration phase: no oral intake fromo 10PM to 6AM; measure osmolarity/weight
-desmsopressin phase (administer and measure)
what are the three phases of the water deprivation test to determine cause of DI?
similar to that of normal pts
water deprivation test findings in pts with primary polydipsia
-psychogenic and dipsogenic
what are the two types of primary polydipsia?
Dispogenic polydipsia
includes patients with an increased sensation of thirst due to hypothalamic lesions (inflammation, infiltration, and infection) and subjects with habitual polydipsia, which is typically seen in life-style conscious men and women, which is the use of water to detox the body.
stress induced increases in dopamine levels stimulatless thirst centers
suggested pathogenesis of psychogenic polydipsia
manifest as nausea, vomiting, delirium, ataxia, seizures, and coma, and may even be fatal
presentation of water intoxication
Desmopressin
tx for central diabetes insipidus
renal absorption of excessive amounts of free water, hyponatremia and plasma hypo-osmolality.
-concentrated urine and reduced urine volume
effect of SIADH
SIADH
most frequent cause of hyponatremia in the hospital setting
-secretion of ectopic ADH by malignant neoplasm
-excessive ADH from posterior pituitary in meningitis, encephalitis, abscess stroke, neurosurugery
-drug induced
most frequent causes of SIADH
meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess, stroke, intracranial bleeding, and neurosurgery
diseases that can cause excessive ADH secretion
ANP
-increases urinary sodium excretion; reduces hypervolemia but aggravates hyponatremiia
compensatory increases in ______ hormone with SIADH
vasopressin esscape
-mechanism in SIADH whereby water excretion will increase over time with decrease in urine osmolality
-helps keep urine lesss concentrated
-most pts are asymptomatic
-weight gain
-edema clinically undetectable
-ccellular swelling and brain edema due to hyponatremia
presentation of SIADH
gastrointestinal manifestations such as anorexia, nausea, and vomiting; and (ii) neuropsychiatric manifestations such as headaches, blurred vision, lethargy, apathy, disorientation, agitation, irritability, and seizures.
symptoms of SIADH
hyponatremia (serum sodium under 135)
-high urine sodium
-BUN <10
defining feature of SIADH
complete recovery when agent withdrawn
prognosis of drug induced SIADH
permanent neurologic impairment from central pontine myelinolysis
complication of rapidly correcting sodium
Craniopharyngioma
rare extra-axial epithelial tumor the sellar region
adamantinomatous and papilllary
histological types of craniopharyngioma
CTNNB1 mutation resulting in accumulation of B-catenin
gene associated with adamantinoomatous craniopharyngnioma
B-catenin accumulation
-immunohistochemical sign of cranyiopharyngnioma
functions in cell adhesion and as a downstream transcriptional activator in the Wnt signaling pathway
function of B-catenin protein
activating BRAF V600E mutation; component in MAPK signaling pathway
mutation associated with papillary craniopharyngiomas
Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma
CPH tumor type that occurs mostly in children
lobulated spongy mass that usually contains cystic spaces
gross pathology of Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma
Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma
what type of CPH?
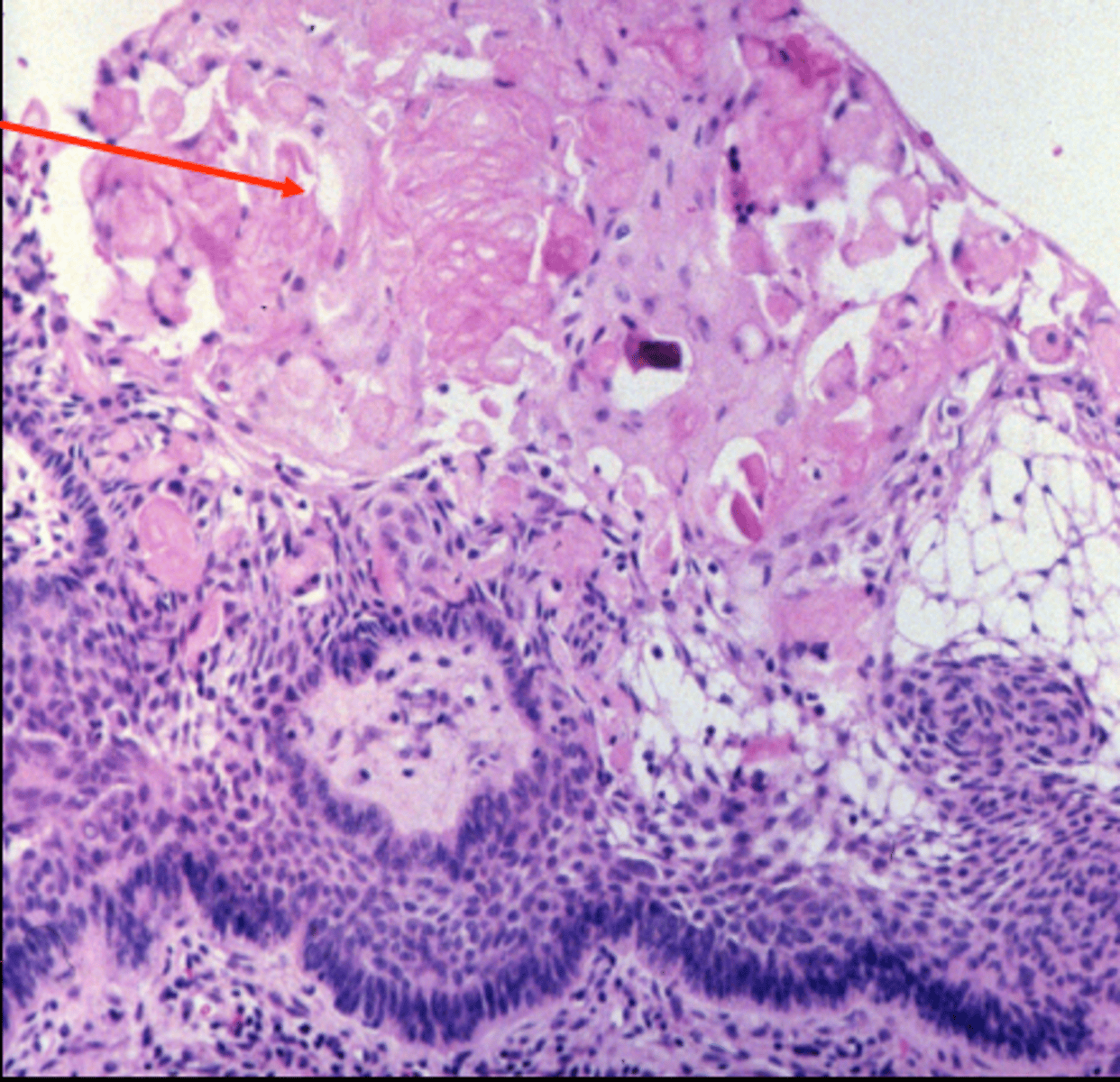
-nests of stratified squamouss epithelim
-top layer forms wet keratin which is heavily calcified
-basal layer
-inermediate layerr of reticulum
-top layer--> wet keratin
layers of the nests in Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma
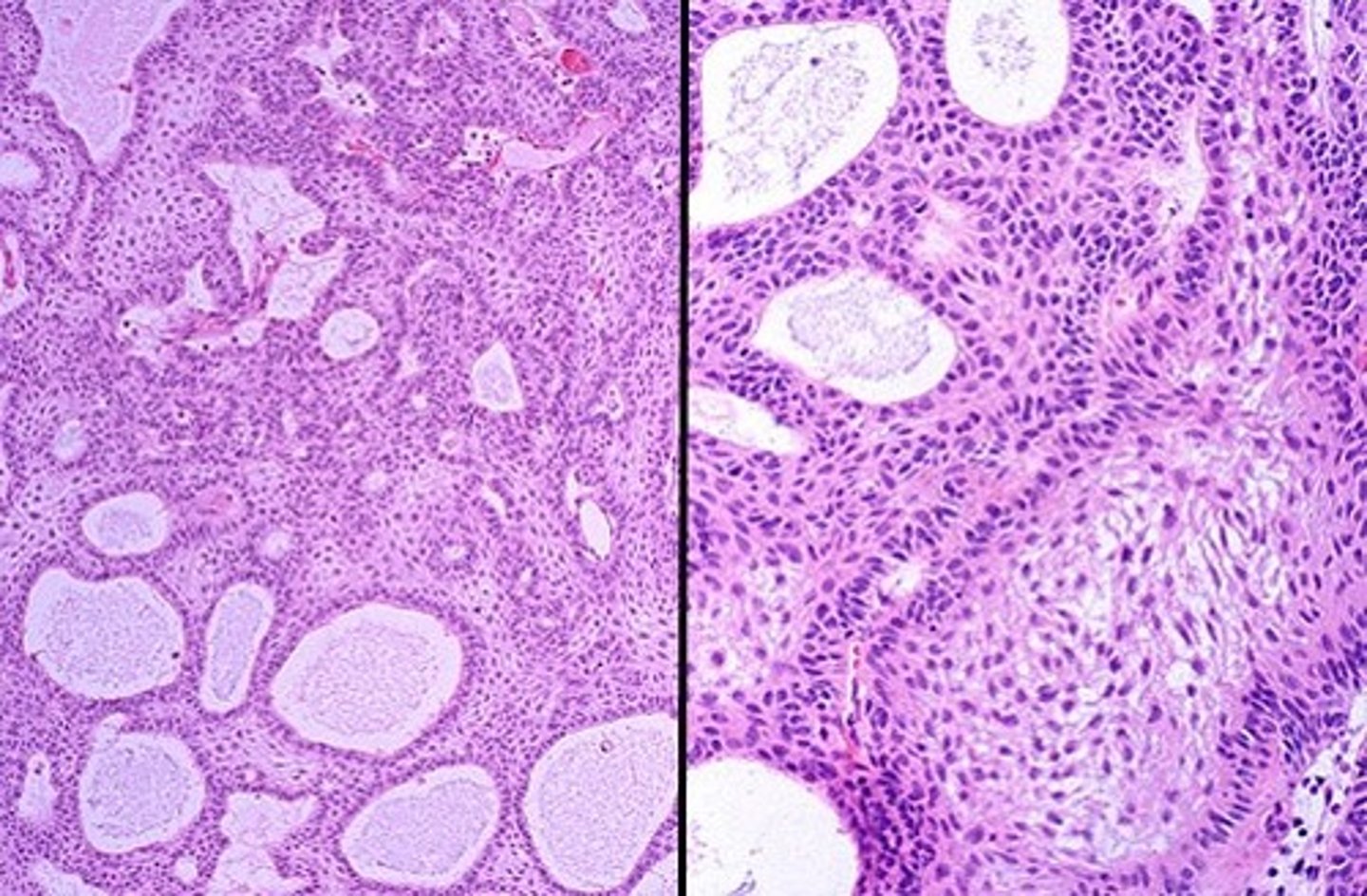
Papillary craniopharyngioma
CPH with fibrovasculuar core covered by mature squamous epithelium
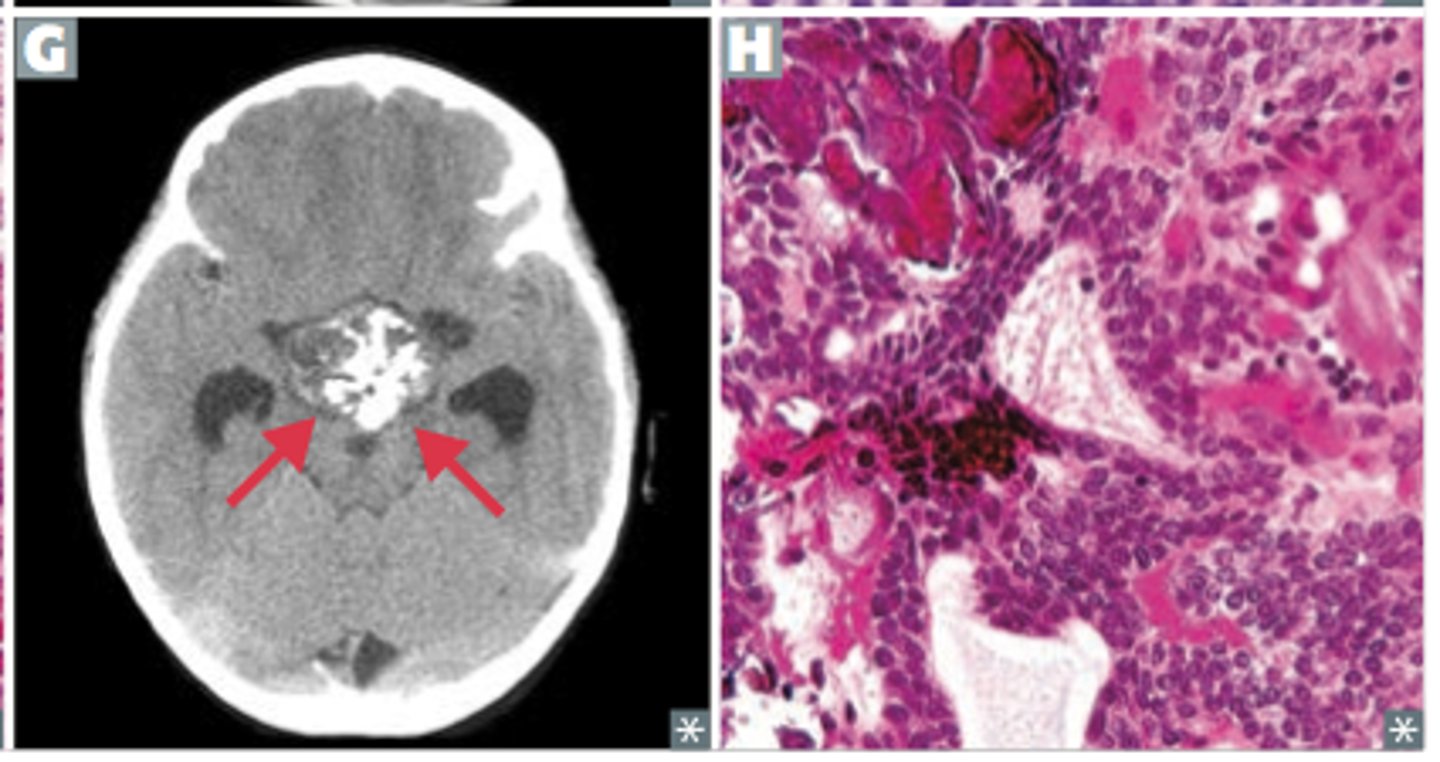
craniopharyngeal canal; remnant of rathke's pouch
where do CPH tumorss arise
increased IICP, compression of optic chiasm, symptoms of hypopituitarism
clinical presentation of CPH
Adamantinomatous CPHs typically have a lobulated contour as a result of usually being multiple cystic lesions. Papillary CPHs tend to be more spherical in outline
Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma vs papillarry on MRI
CT or MRI
imaging of choice for CPHs