Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MEE1018: Fluid Mechanics 1 - Lecture 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
3 branches of fluid mechanics
Fluid statics, fluid kinematics and fluid dynamics.
Fluid statics
Mechanics of fluid at rest.
Fluid kinematics
The motion of fluids without considering forces or energy.
Fluid dynamics
Involves the relation between the motion of fluids and the forces exerted by or on them.
Applications of fluid mechanics
Alaska oil pipeline, aircraft, cars (aerodynamics), ferries, wind turbines, dams.
Importance of fluid mechanics
A knowledge of fluid mechanics is required to properly design vehicles, wind turbines, fuel and water supply systems.
Fluid
A substance which deforms continuously (flows) under the action of shearing forces, no matter how small they may be. Liquid and gas.
Shearing force
A force which acts tangentially to the surface.
Forces of a fluid at rest
There are no shearing forces and therefore all forces in the fluid must be perpendicular to the planes on which they act.
Effects of shearing force on a solid
The solid deforms but does not continuously deform.
Provided the elastic limit is not exceeded the deformation is proportional to the applied shear stress and it will disappear when the force is removed.
stress ∝ strain
Effects of shearing stress on a fluid
In control, the fluid element continuous to deform as long as the shearing force is present, i.e. the force flows
stress ∝ rate of strain
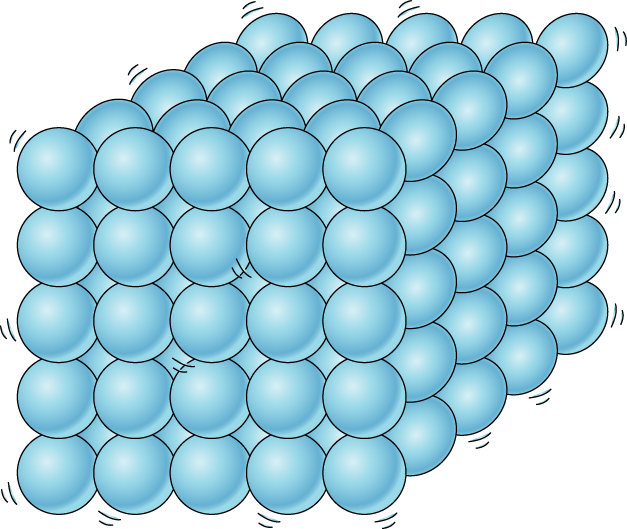
Molecular structure of a solid
Molecules densely and regularly packed
Movement restricted to small vibrations
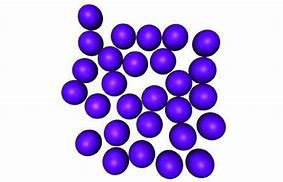
Molecular structure of a liquid
Molecules closely packed but have greater movement
Relative positions of molecules can change
Flows under action of applied forces
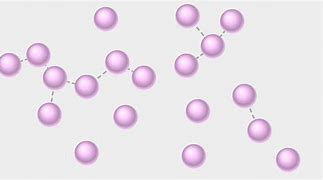
Molecular structureof a gas
Molecular spacing 10 ties greater than liquids
Molecules move freely
Intermolecular forces in a solid
Each molecule restrained by its neighbours; strong intermolecular forces
Intermolecular forces in a liquid
Relatively strong intermolecular forces
A given mass of liquid occupies a fixed volume
Intermolecular forces in a gas
Weak intermolecular forces
A given mass of gas has no fixed volume and expands continuously unless restrained by container
Continuum
When the fluid is treated as a continuous substance in which conditions to a point represents the average effects of many molecules.
Why continuum is used
In typical engineering structures the number of molecules is huge and the spacing between them is usually negligible compared with the distance involved in the problem.
Density
Mass of fluid per unit volume
Relative density or specific gravity of a liquid
Ratio of density of liquid to density of water. No units.
Specific volume
The volume occupied by unit mass, i.e. reciprocal of density
Usually applied to gases
Specific weight of fluid
The weight of fluid per unit volume
= mass of fluid per unit volume x g