Exam 3
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What is a graph?
A collection of distinct vertexes and distinct edges
V: set of elements
E: set of pairs of V’s, connections/relationships between them
What is a path in a graph?
A path between two vertices in a graph is a sequence of edges.
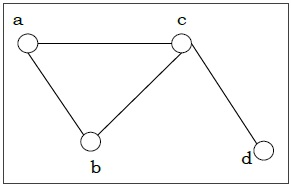
Which term describes the following graph?
connected
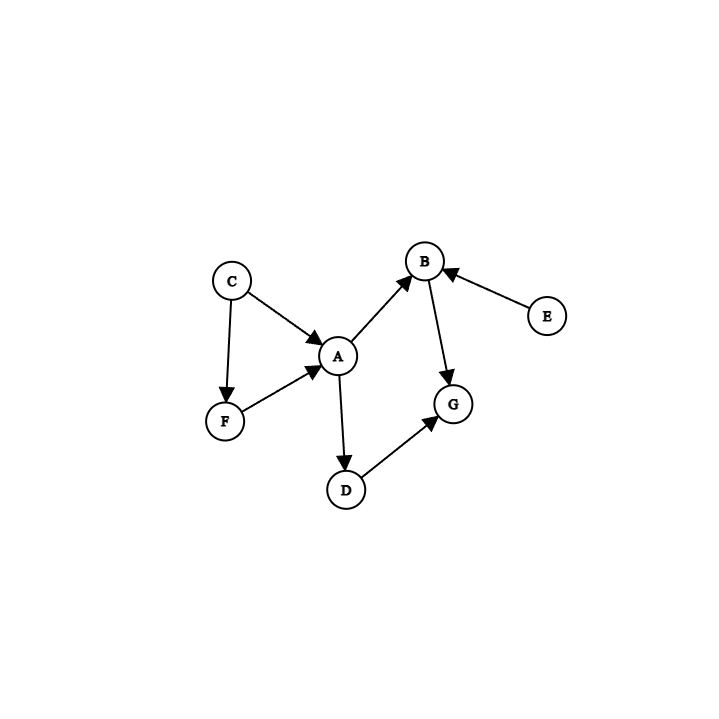
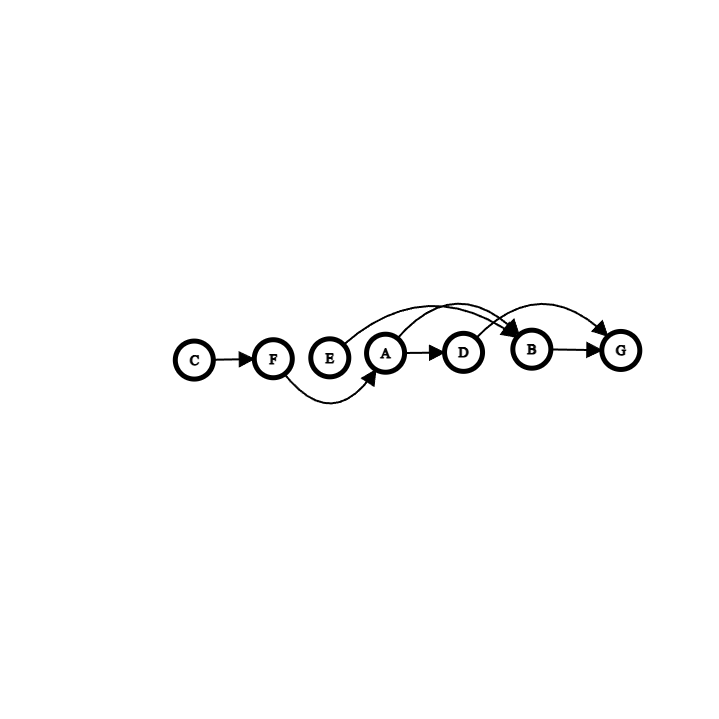
Give a topological sort for this graph?
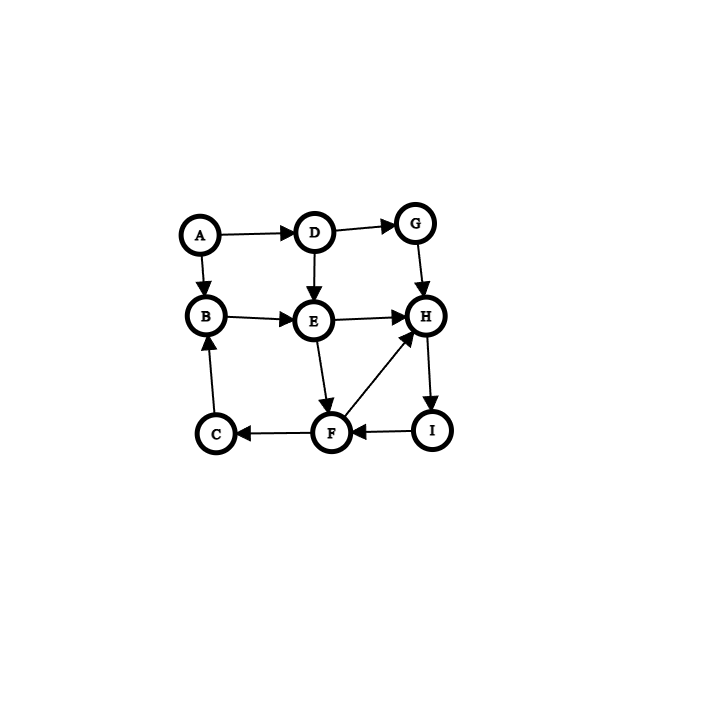
Give the breadth-first traversal of the graph beginning at vertex A
A B D E G F H C I
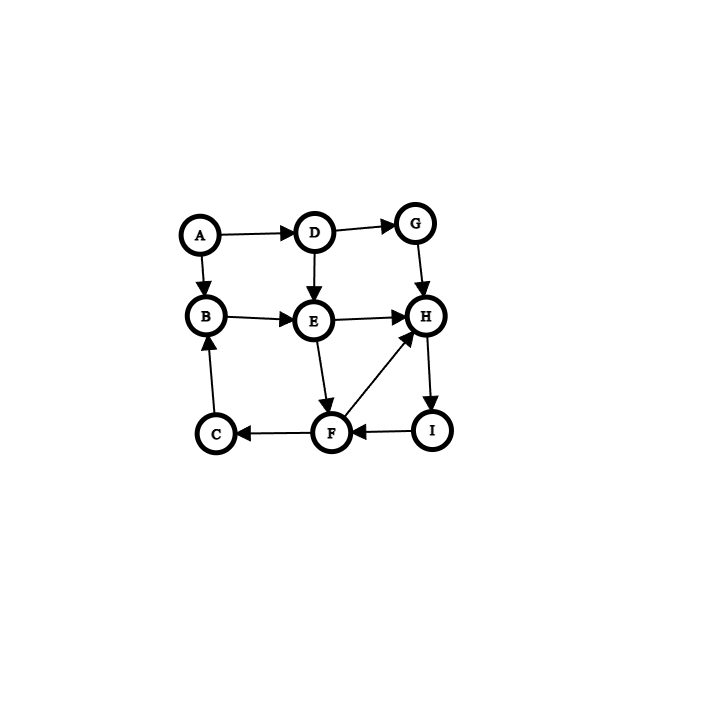
Give the depth-first traversal of the graph beginning at vertex A
A B E F C H I D G
A graph that has an edge between every pair of distinct vertices is called a
complete graph
What is a cyclic graph
a closed path where a vertex returns to its starting point without repeating any edges or other vertices, except for the start and end vertex
Which of the following is true about a directed acyclic graph
it has no cycles and all edges have direction
What is a acyclic graph
a graph that contains no cycles, meaning you cannot start at a node, follow a path of edges, and return to the same starting node.
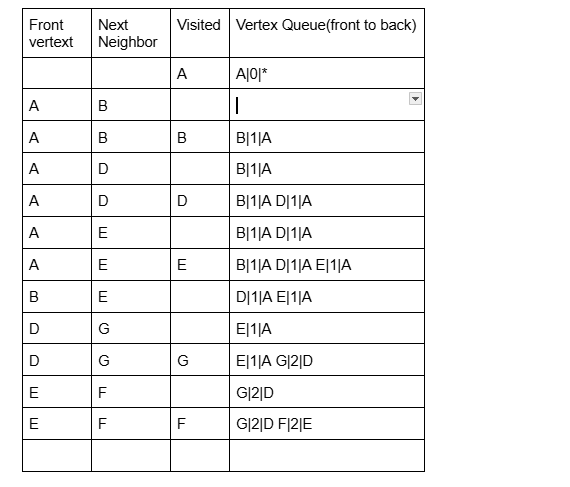
Find and show the shortest path stack and length in Directed graph from A to H show the final content of the queue
A
E
H
length 2

A common implementation of a graph that uses a list to represent the graphs edges is called a
adjacency list
If two paths from O to E have the same total cost, Dijkstra’s algorithm will
randomly choose either path
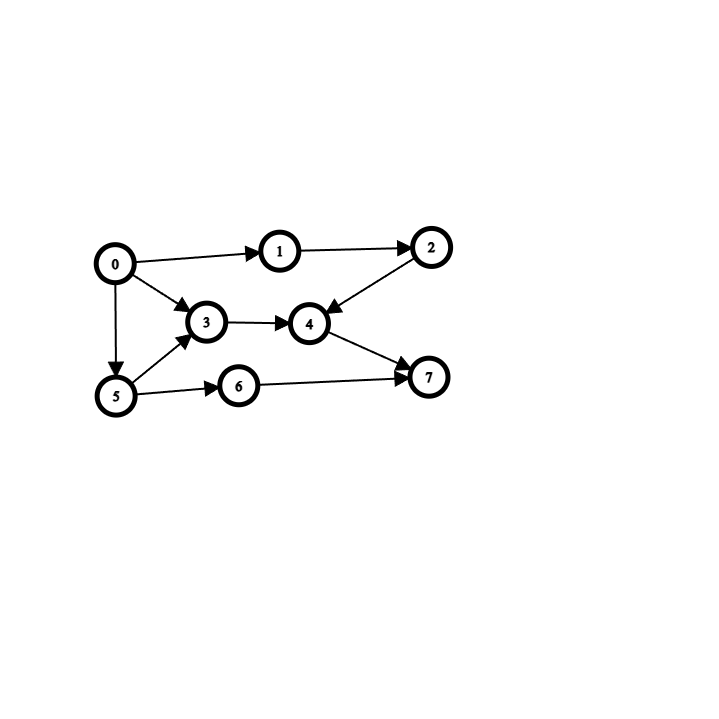
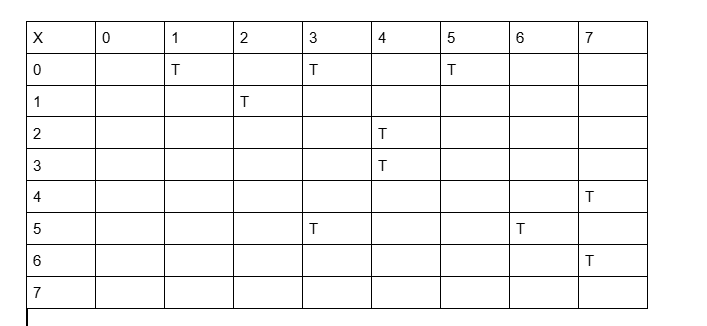
Fill in the adjacency matrix for the following graph
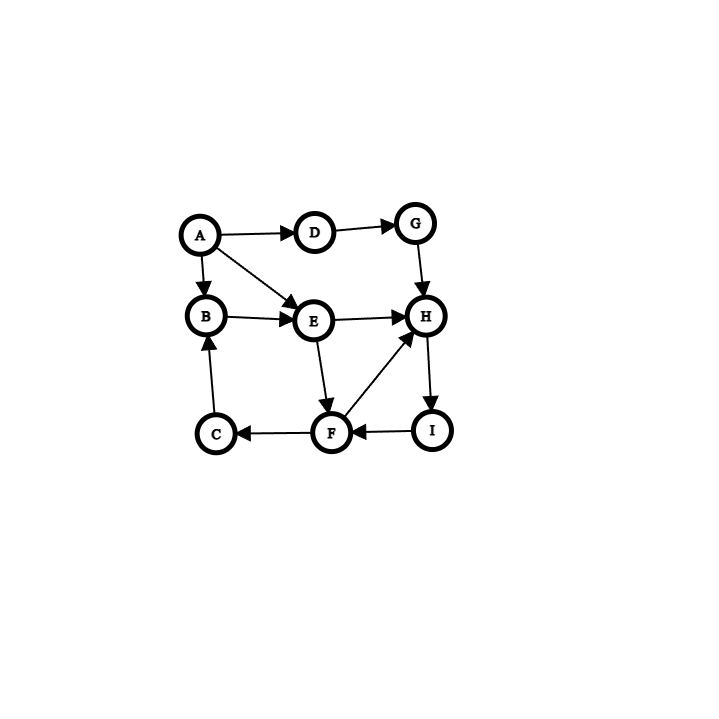
Find and show the shortest path stack and length in the directed graph from A to F
A
E
F
length 2
What are the two main types of graphs?
Directed and Undirected
After executing Dijkstra’s algorithm, how can you retrieve the actual cheapest path to a vertex?
By backtracking from the end vertex using a stack.
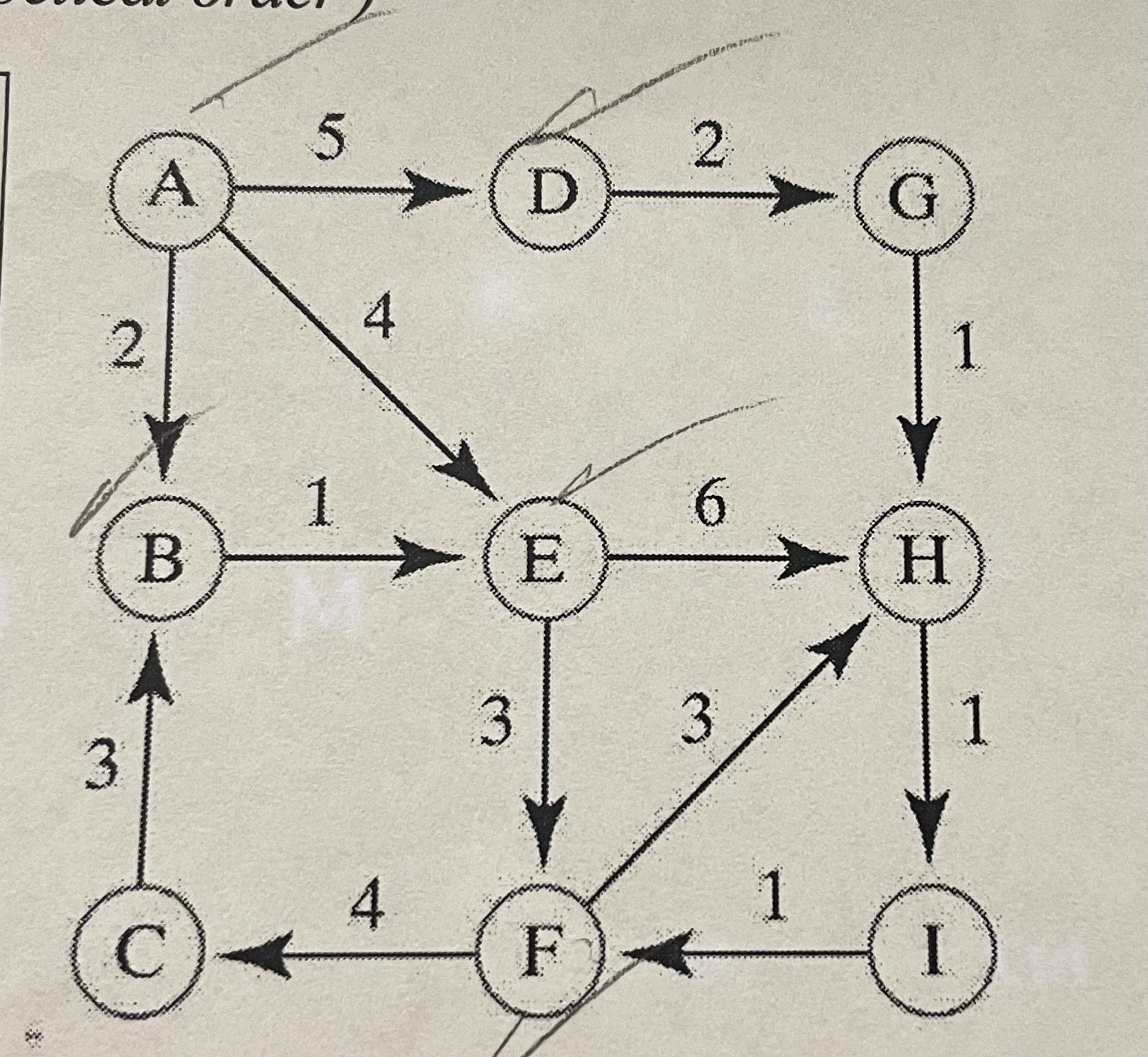
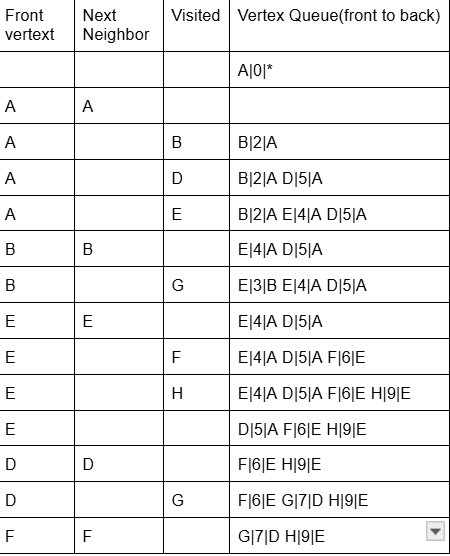
Find and show the cheapest path stack and length in the directed graph from A to F
Stack
A
B
E
F
Length 6
Advance file
raw binary format
FileOutputStream, FileInputStream
DataOutputStream, DataInputStream
DataOutputStream data = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(“file.txt”)
DataInputStream data = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(“file.txt”)
Unicode text format
To write a string to a file
String name = “Chloe”;
outputFil.writeUTF(name)
To read a String from a file
String name = inputFile.readUTF();
RandomAccessFile(String filename, String mode)
rndFile.seek(long position);
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile(“MyInfo.dat”,”r”);
file.seek(99);
byte b = file.readByte();
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputFile = new ObjectOutputtream(outStream)
objectOutputFile.writeObject(account);
BankAccount2 account;
account = (BankAccount2) objectInputFile.readObject();
Define the Dictionary ADT?
A dictionary is a collection of pairs (search key, corresponding value). It represents a set of key–value associations, and the number of pairs in the collection indicates the size of the dictionary.
Explain the two steps that typical hash functions perform?
a. Convert the search key into a hash code (an integer)
b. Compress the hash code into the range of indices for the hash table.
When you write a program for an algorithm and it is taking much longer than expected you should?
try to design a better algorithm
Which of the following is not a characteristic of the List ADT?
the elements can only be integers
The effect of doubling the input size on an algorithm with time complexity O(log n) is?
negligible
A binary tree in which every node has either 0 or 2 children is called a
Full binary tree
What is a complete binary tree?
All levels except possible the last are completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible
What is the primary purpose of a dictionary ADT?
To associate keys with values
What is not an example of a binary tree?
General Tree
What is the time complexity of searching for a key in a well-implemented hash-based dictionary ADT?
O(1)
In a hash-based dictionary, what issue does “collision” refer to?
multiple keys hashing to the same index
A hash table has 7 slots, and the hash function is defined as h(k) = k.hashcode % 7. Using linear probing determine the index where the key 16 will be inserted if slots 2,3 and 4 are already occupied?
5
Construct the expression tree for the following infix arithmetic expression: (a + b) * (c/e)
*
/ \
+ /
/ \ / \
a b c eReconstruct the binary tree described by the following traversals. Clearly indicate the left and right children of each node?
Inorder(LNR): D,B,E,A,F,C
Preorder(NLR):A,B,D,E,C,F
A
/ \
B C
/ \ /
D E F Build a binary search tree (BST) for the following input sequence: mango,apple,peach,banana,cherry,acai. Show the inorder traversal of the tree, and then show the BST after removing apple.
mango
/ \
apple peach
/ \
acai banana
\
cherry
acai, apple, banana, cherry, mango, peach
mango
/ \
banana peach
/ \
acai cherryConstruct a min heap using the following input values: 4,9,5,6,7,3,8. Show how the elements are stored in the array representation of the heap (root at index 1), and explain how to compute the parent, left child, and right child indices for a given node k.
[ -, 3, 6, 4, 9, 7, 5, 8, , , , ]
parent(k) = k / 2
left(k) = 2k
right(k) = 2k + 1
What is an abstract data type?
A specification of a data set and the operations on that data set.
The specification does not indicate how to store the data or how to implement the operations, and is independent of any programming language
The three main steps in designing an abstract dat type(ADT)?
Step 1; Design the ADT and provide the interface
Step 2: Test the interface with an application
Step 3: Implement the ADT using a specific data structure
When using abtraction as a design principle you should focus on?
what you want to do with the data
You should express the complexity of an algorithm in terms of its
problem size
A deque ADT behaves
like a queue and a stack
Convert the following infix expression to a postfix expression: (a + b) (c - d) / ((e - f) (g + h))
a b + c d - * e f - g h + * / Show the code to add the first entry to an empty bag.
firstNode = new Node(newEntry, firstNode);
numberOfEntries++; Show the push and pop methods for Valuestack as shown in the UML top index is initialized at -1
ValueStack
-stack[]:double
-topIndex:integer
+push(entry:double)
+pop():double
public void push(double value) {
if (topIndex + 1 == stack.length) {
throw new Exception("stack full"); // or resize
}
stack[++topIndex] = value;
}
public double pop() {
if (topIndex == -1) {
throw new Exception("stack empty");
}
return stack[topIndex--];
} Provide the java interface Queue ADT
public interface QueueInterface<T> {
public void enqueue(T newEntry);
public T dequeue();
public T getFront();
public boolean isEmpty();
public void clear();
} Provide the code for the implementation of the class LinkedQueue using a chain data structure. Show only the implementations for the data structure, enque, and showQ methods.
public class LinkedQueue<T> implements QueueInterface<T> { private Node front, back; @Override
public void enqueue(T newEntry) {
Node node = new Node(newEntry);
if (front == null) {
front = node;
} else {
back.next = node;
}
back = node;
} public void showQ() {
Node currentNode = first;
while (currentNode != null) {
System.out.println(currentNode + " ");
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
}
}What is a tree ADT?
Set of nodes connected by edges that indicate the relationships among the nodes
getHashIndex
private int getHashIndex(K key)
{
int hashIndex = key.hashCode() % hashTable.length;
if (hashIndex < 0)
hashIndex = hashIndex + hashTable.length;
return hashIndex;
} // end getHashIndexPseudo code adding an entry into a hasheddictionary
V add(K key, V value)
hashIndex = getHashIndex(key);
if hashTable[hashIndex] is empty
result = null
else
result = hashTable[hashIndex]
hashTable[hashIndex] = value
return result;Pseudocode infix to postfix
Algorithm convertToPostfix(infix)
// Converts an infix expression to an equivalent postfix expression.
operatorStack = a new empty stack
postfix = a new empty string
while (infix has characters left to parse)
{
nextCharacter = next nonblank character of infix
switch (nextCharacter)
{
case variable:
Append nextCharacter to postfix
break
case '^' :
operatorStack.push(nextCharacter)
break
case '+' : case '-' : case '*' : case '/' :
while (!operatorStack.isEmpty() and
precedence of nextCharacter <= precedence of operatorStack.peek())
{
Append operatorStack.peek() to postfix
operatorStack.pop()
}
operatorStack.push(nextCharacter)
case '( ' :
operatorStack.push(nextCharacter)
break
case ')' : // Stack is not empty if infix expression is valid
topOperator = operatorStack.pop()
while (topOperator != '(')
{
Append topOperator to postfix
topOperator = operatorStack.pop()
}
break
default:
break // Ignore unexpected characters
}
}
while (!operatorStack.isEmpty())
{
topOperator = operatorStack.pop()
Append topOperator to postfix
}
return postfix
Stack ADT
A collection of objects in reverse chronological order and having the same data type
Bag ADT
A finite collection of objects in no particular order
– Can contain duplicate items
List ADT
A collection of objects in a specific order and having the same data type
– The number of objects in the collection