orientation and safety, microscopes, and aseptic technique
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Ubiquitous
present, appearing or found everywhere
Biosafety
application of safety precaution that reduce a laboratorian’s risk of exposure to a potentially infectious microbe and limit contamination of the work environment and, ultimately, the community
The biosafety levels in this lab
BSL-1 and BSL2
BSL-1
microbes are nonpathogenic and pose minimal risk to laboratory personnel and the environment.
BSL-2
Microbes that pose moderate hazards and are typically indigenous.
BSL-3
microbes are either indigenous or exotic, and they can cause serious or potentially lethal disease.
BSL-4
microbes are dangerous and exotic, posing high risk or aerosol-transmitted infections.
Simple Microscope
type of microscope uses a single lens for magnification of a sample.
Compound Microscope
type of microscope has more than one lens and has two optical parts known as objective lens, this microscope is also the one used in lab
Electron Microscope
type of microscope uses a beam of accelerated electron as the source of illumination
Stereo Microscope
type of microscope that provides a 3-D dimensional view of a specimen
Head/Body Tube
Holds the eyepiece and connects it to the objective lenses
Arm
supports the microscope head and connects it to the base; used for carrying the microscope
Base/foot
the bottom part that supports the microscope and keeps it steady
Nosepiece
The rotating part that holds the objective lenses and allows you to change magnification
Stage
The flat platform where you place the slide
Stage Clips
Hold the slide in place on the stage
Mechanical Stage Knob
Moves the slide left/right and forward/backward on the stage for better viewing
Iris Diaphragm
Controls the amount of light that passes through the specimen
Condenser
Focuses light onto the specimen to make it clearer
Coarse Adjustment Knob
Moves the stage up and down quickly to focus the image
Fine Adjustment Knob
Moves the stage slightly to sharpen the focus
Illuminator
the light source at the base that shines light through the specimen
Eyepiece/Ocular Lens
The lens you look through at the top of the microscope; usually magnifies 10x
Objective Lenses
Lenses with different powers (e.g., 4x, 10x, 40x) that magnify the specimen further
Resolving Power
the ability to distinguish close adjacent objects as being separate objects
Working Distance
the distance separating a specimen and the objective lens
Microscopic Field of View
the area on the slide one can observe while looking through the oculars
Parfocal
ability of a microscope to need only minor focus adjustments after the specimen is found and focused using the lowest power
Immersion oil
used when using 100x
The media
A nutrient-rich substance used to grow microorganisms, cells, or plants
Nutrient Broth
a liquid media that allows microbes to grow but have a limit amount of nutrients available
Solid Media
this can be a plate, a slant, or a deep. For growth and isolation of individual microbial colonies
Basic nutritional requirements
water, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, trace elements
Agar
stabilizing thickening agent derived from seaweed
Turbidity
Cloudiness or haziness of a liquid caused by the growth of microorganisms or particles
Inoculum
small amount of bacteria sample
Inoculate
transfer the inoculum into a new growth medium
Aseptic Technique
fundamental to your safety and to the success of your lab experiment
Streak Plate Dilution Method
the bacterial cells to be wide spread and isolated from other growth seen on the plateCo
Colony morphology
the shape, size, margin, elevation, odor, and color of the organism
Mixed Culture
a culture that contains more than one species of microbes
Pure Culture
a culture containing only one species of microbes
Inoculating Loop
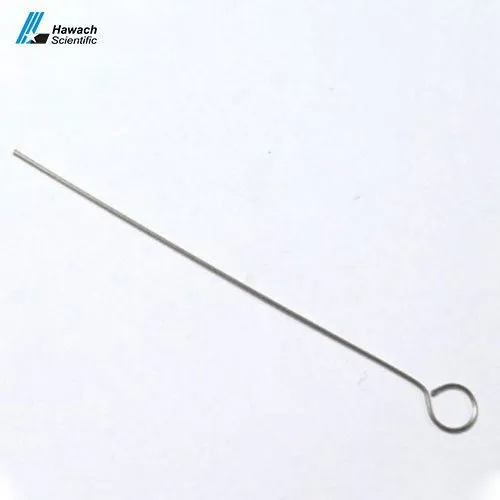

Inoculating Needle

Transferring Pipette

Bunsen Burner

Spread Plate
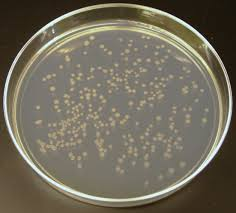
Streak Plate
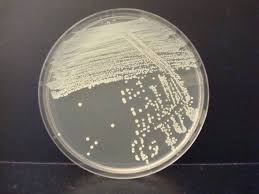
Colony Morphology
refers to the shape, size, margin, elevation, odor, and color of the microorganism