The development of the model of the atom
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Describe the nuclear model
-Most of an atom is simply empty space
-In the centre we have a positive nucleus which contains most of mass of atom
-Around edge with have electrons
What did Niels Bohr proposed
-That electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances
Why was Bohrs ideas accepted
As it agreed with the results of experiments by other scientists
What do we call the orbits now because of Niels Bohr
Energy levels or shells
What do scientists found out several years later
That the positive charge in the nucleus is due to tiny particles called protons
What happened around 20 years later after the nuclear model was first proposed
James Chadwick discovers that the nucleus also contains neutral particles which are called neutrons
What is the radius of an atom
0.1 nanometres or 1X10-10m
What is the radius of the nucleus
1X10-14m or 1/1000 less than radius of atom
Where is almost all the mass of a atom
In the nucleus
What is the relative mass of Proton,Neutrons and electrons
Proton-1
Neutron-1
Electron-Very mass
What is the mass number and atomic number for an element
Big number tells us the mass number
Small number is the atomic number
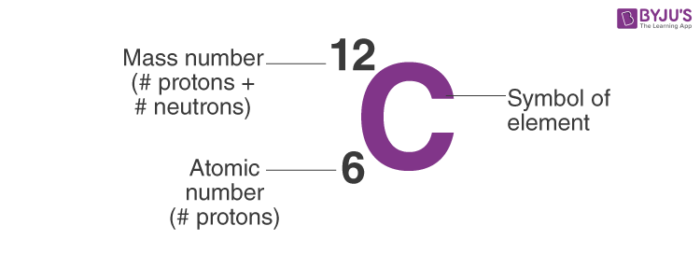
What does the Mass number and atomic number tells us
Mass number tells us number of protons and neutrons in an atom
Atomic number tells us number of protons
How can we get number of neutrons from an element
Mass number-Atomic number
What is a Ion
Ion are atoms which have an overall charge as they’ve gain or loss electrons
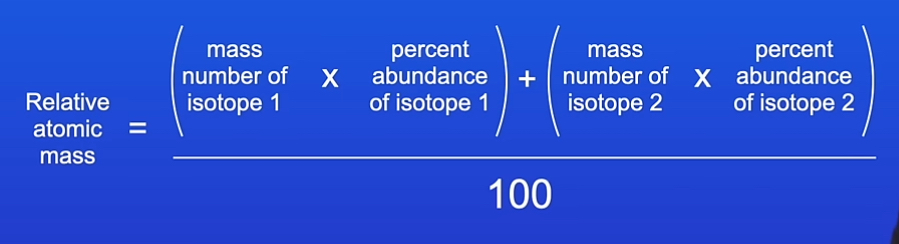
What is the relative atomic mass of an element
The relative atomic mass of an element is an average value that takes account of the abundance of the isotopes of the element.
How do we calculate relative atomic mass
What does the number of electrons in the outer energy level tell us
What group number the element is in
What are the groups in the periodic table
The vertical columns
What is group 0 called and why
Noble gases as they have a full outer energy level
Why is the table called a periodic table
As similar properties occur at regular intervals
Why do all elements in a group react in a similar way
As they have the same number of electrons in their outer energy level
How did they categorise elements in early 1800s
-Their physical and chemical properties
-Their atomic weight
What did the scientist John Newlands do
He arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic weight and he saw that every eighth element reacts in a similar way
What did Newlands call his theory
Law of octaves
What problems did Newlands system have and why wasn’t it taken seriously by other scientists
By sticking to the order of atomic weight,sometimes elements were grouped together when they had totally different properties
How did Dimitri Mendeleev make the first periodic table
-He arranged all elements in order of Increasing weight
-However,if he needed to he would switch the order of specific elements so they fitted the patterns of other elements in the same group
-Also he realised that some elements had not been discovered so he left gaps in his periodic table where he thought an element was missing
What did Mendeleev do as he was so confident that his table was correct
He predicted the properties of the undiscovered elements based on other elements in the same groups
What happened several years later
The missing elements were discovered and this matched Mendeleev predictions. So other scientists accepted Mendeleev table was correct
What is the elements in modern periodic table arranged in
Order of atomic number/Protons
Why did Mendeleev order his elements by atomic weights and what is the problem of doing that
As protons have not been discovered.
-Problem with this is that it can appear in the wrong order due to the presence of isotopes
How did Mendeleev address the problem of ordering by atomic weights
By switching order of elements when he needed to
Why does the Mendeleev period table not have group 0
As these elements have not been discovered when Mendeleev published his table
Describe alpha scattering experiment and results
-Rutherford shot positive alpha particles at a thin foil of gold
1)Most particles pass through so the atom is mainly empty space
2)Some particles slightly deflected so atom has a positively charged nucleus
3)Some particles completely deflected so the mass of the atom is concentrated in the middle