AP Biology Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Ribosomes
Organelles that are the site of protein synthesis
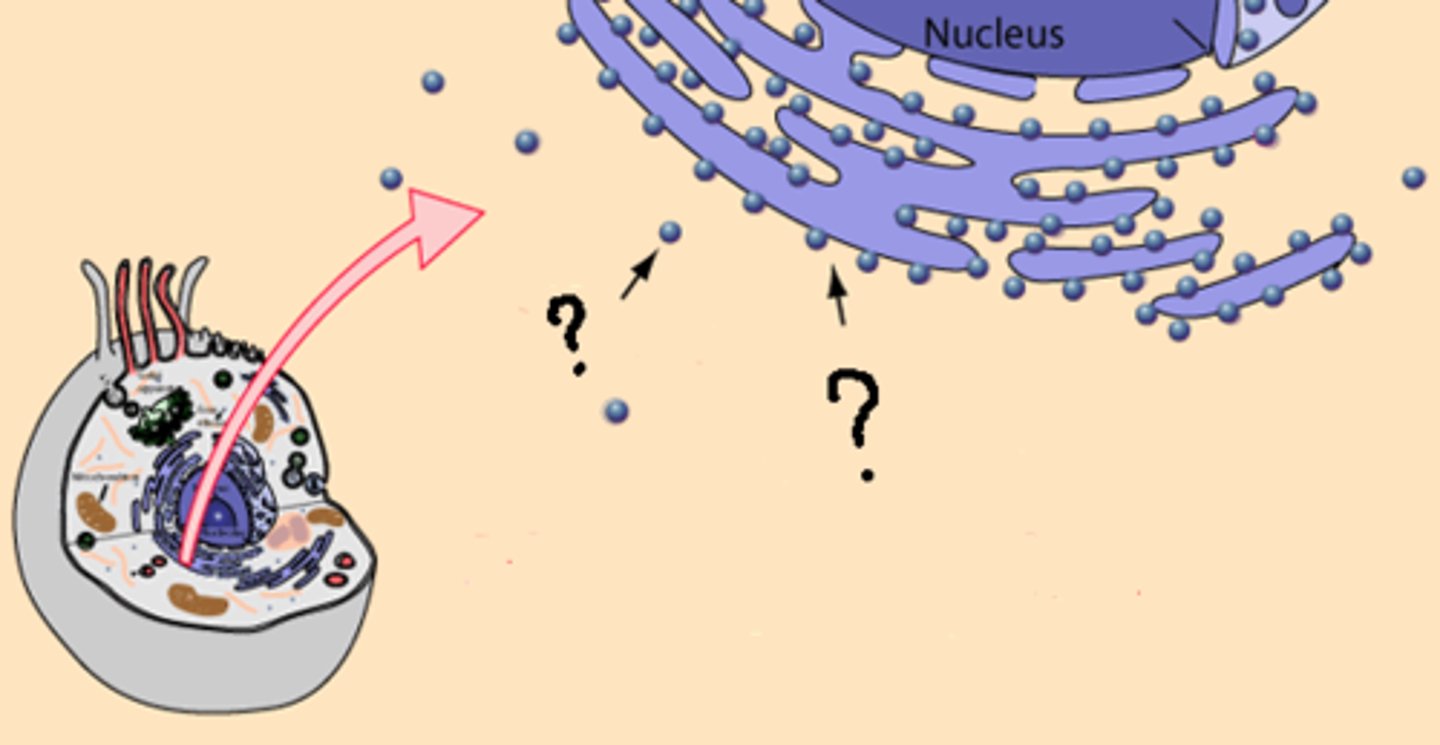
Endoplasmic reticulum
A system of membranes that is found in a cell's cytoplasm and that assists in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and in the production of lipids.
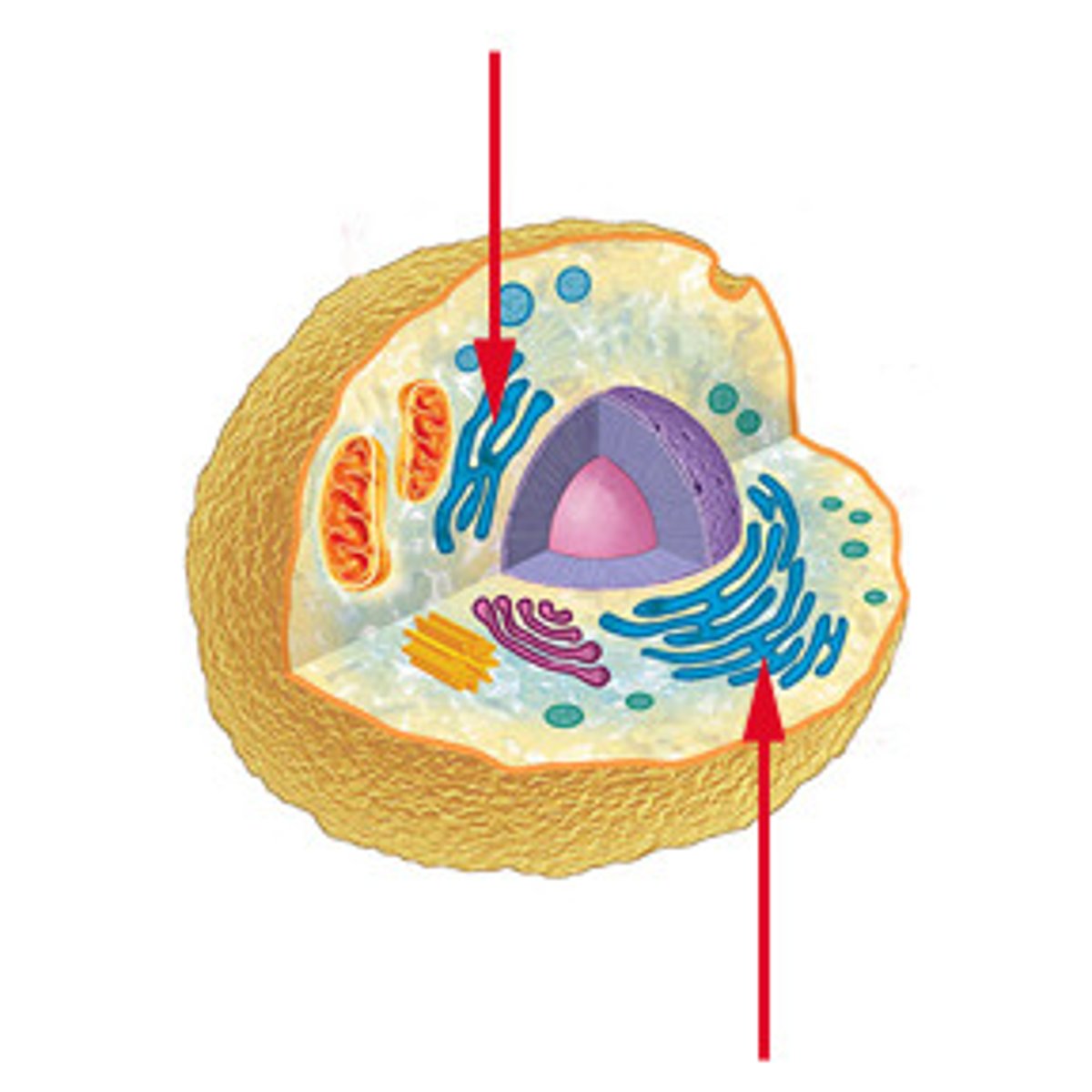
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell

Mitochondria
An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur.
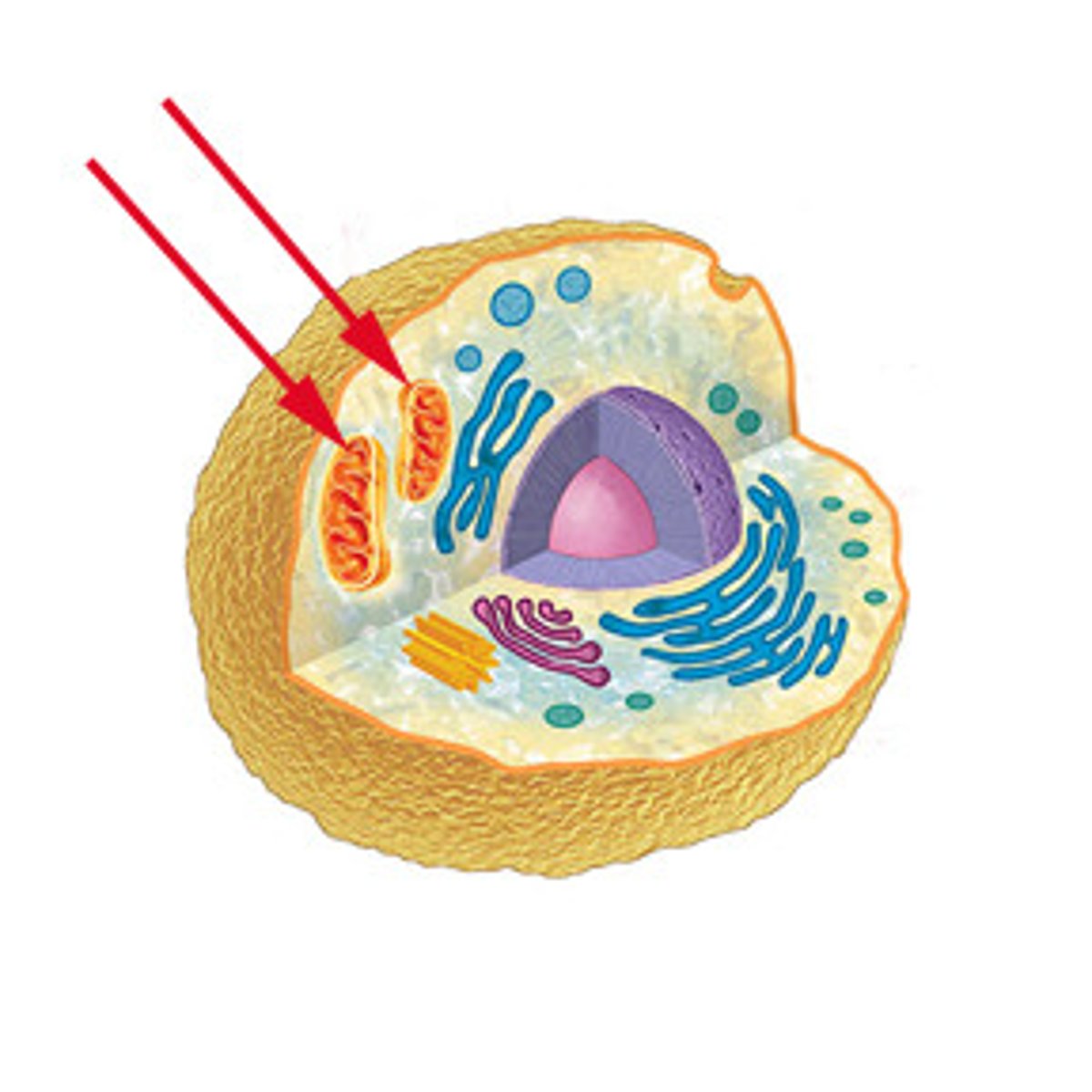
Lysosomes
Cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
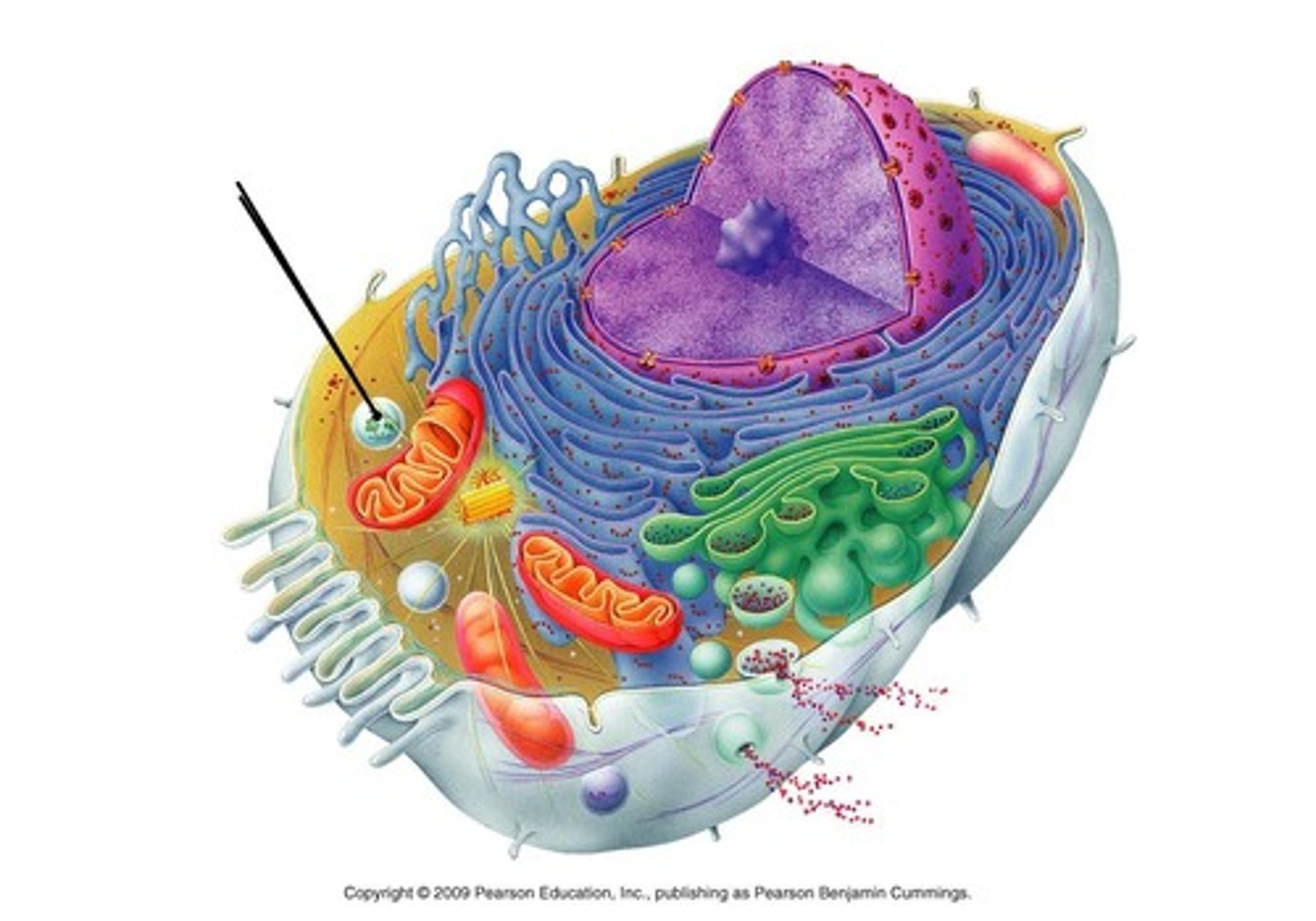
vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
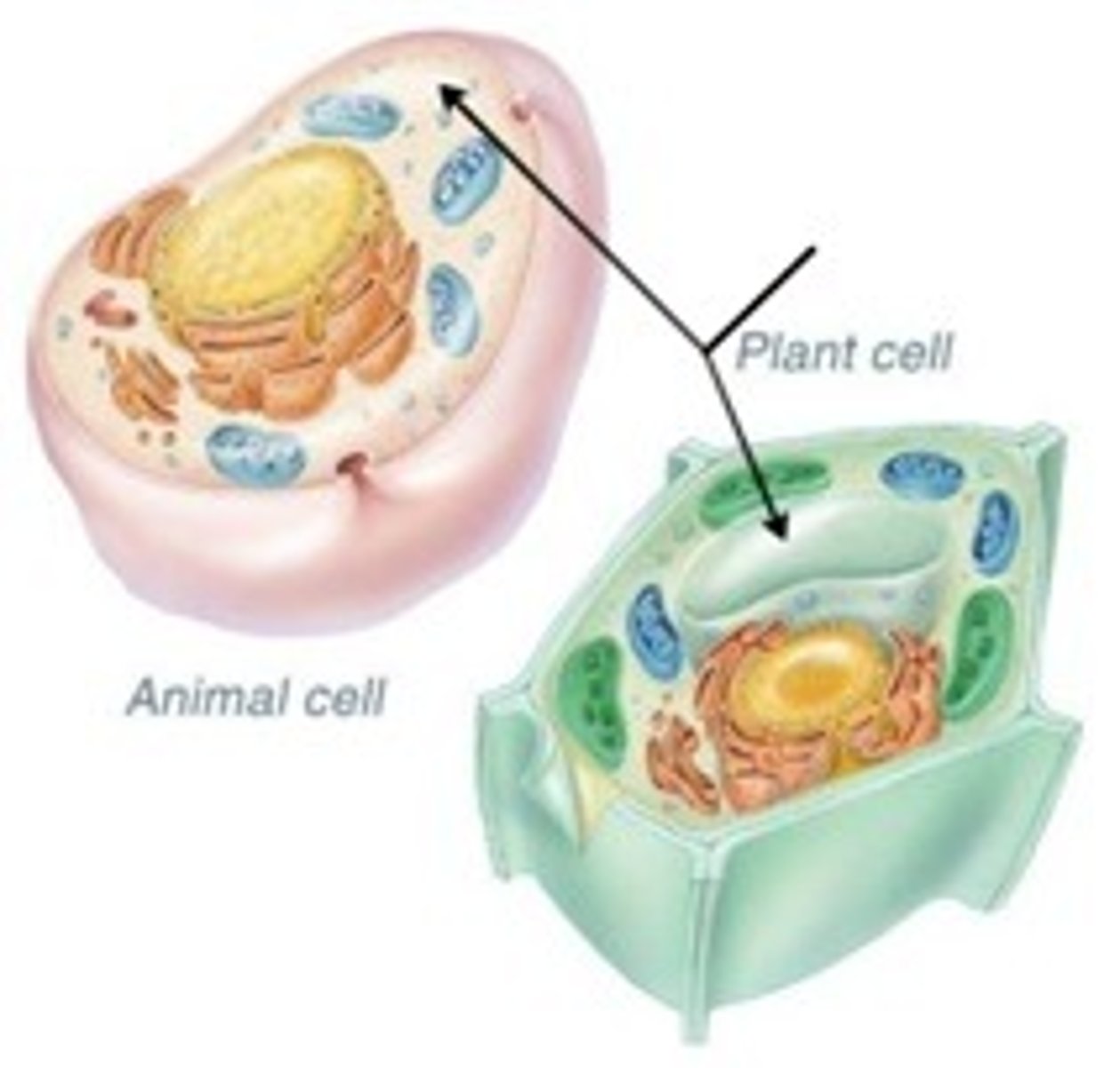
Chloroplasts
Organelles that capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in a process called photosynthesis
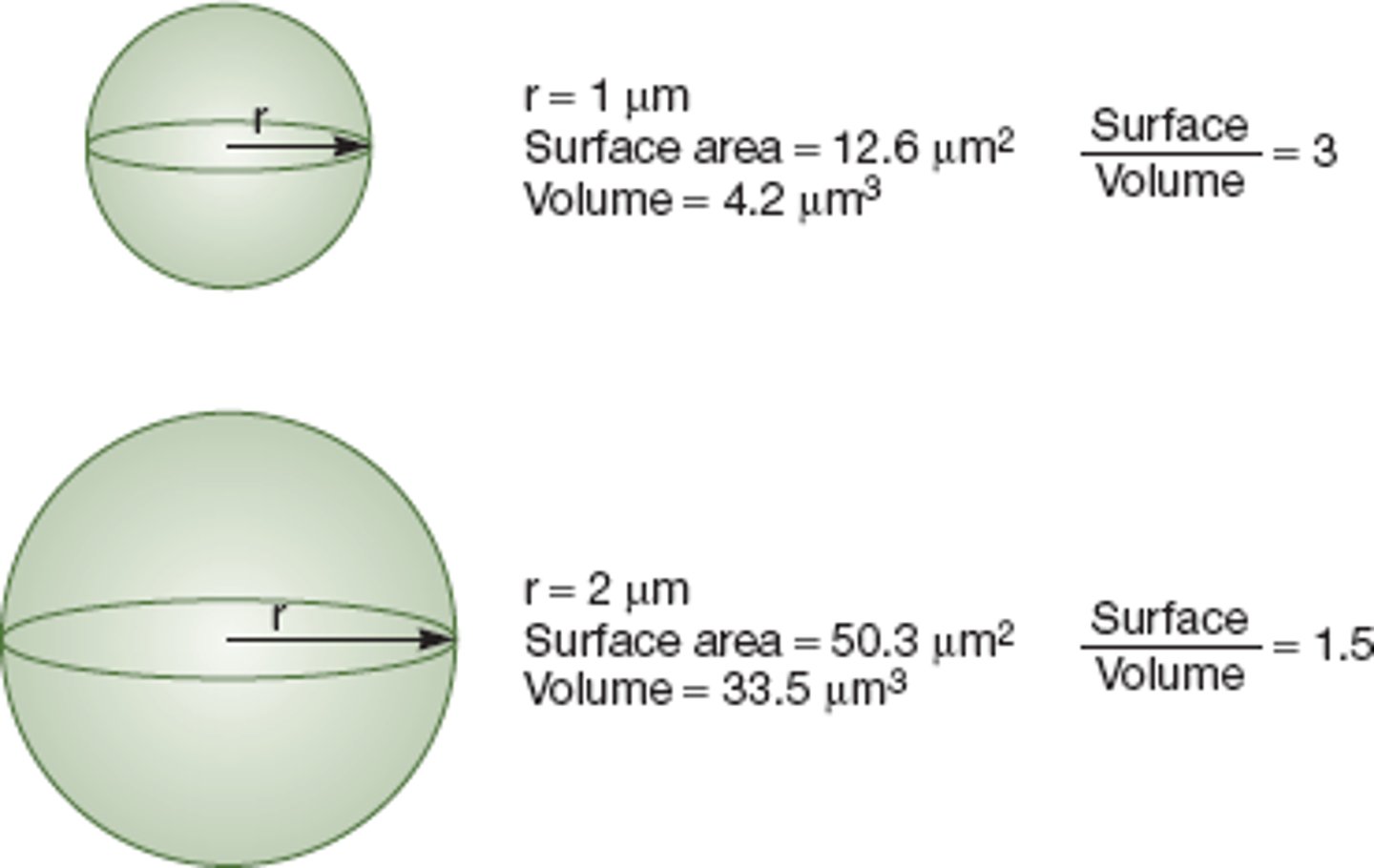
Surface area-to-volume ratio
A variable that decreases as cells grow, so that it sets a limit to the size of cells.
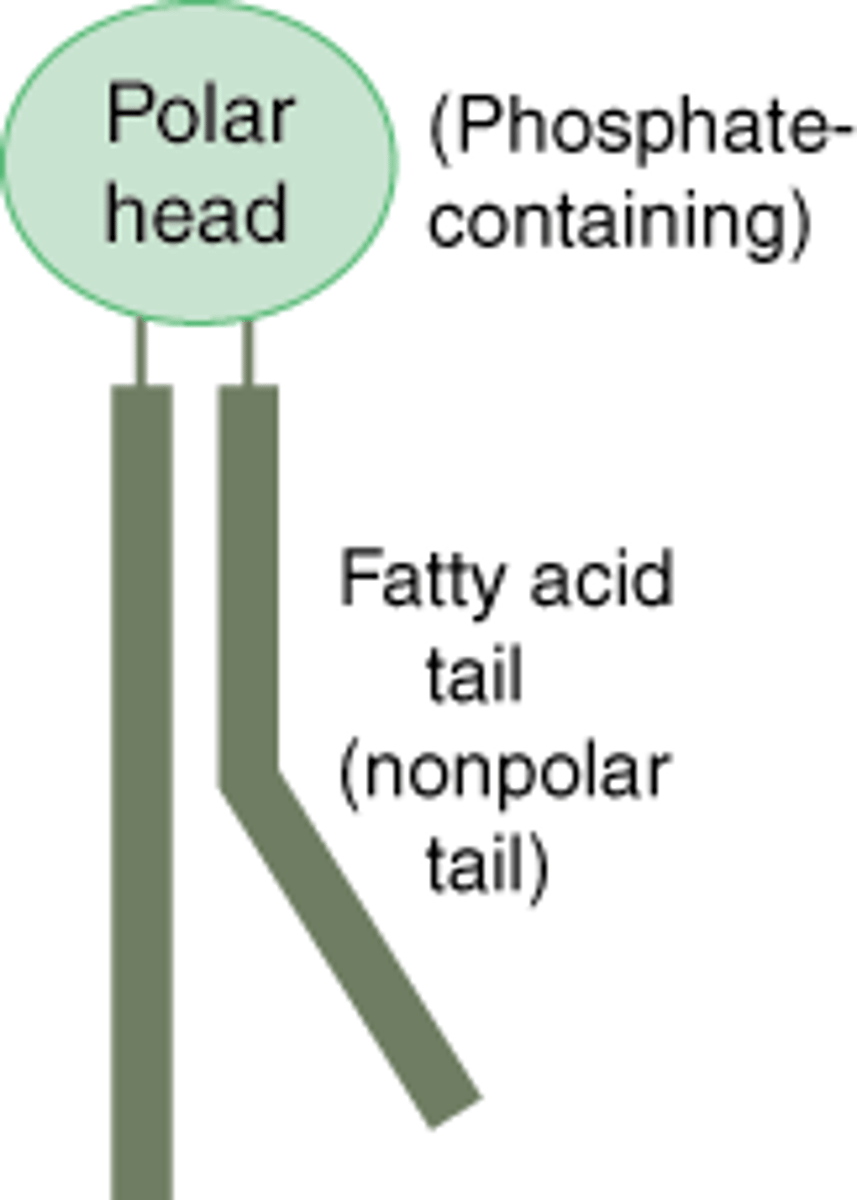
Phospholipids
A molecule that is a constituent of the inner bilayer of biological membranes, having a polar, hydrophilic head and a nonpolar, hydrophobic tail.
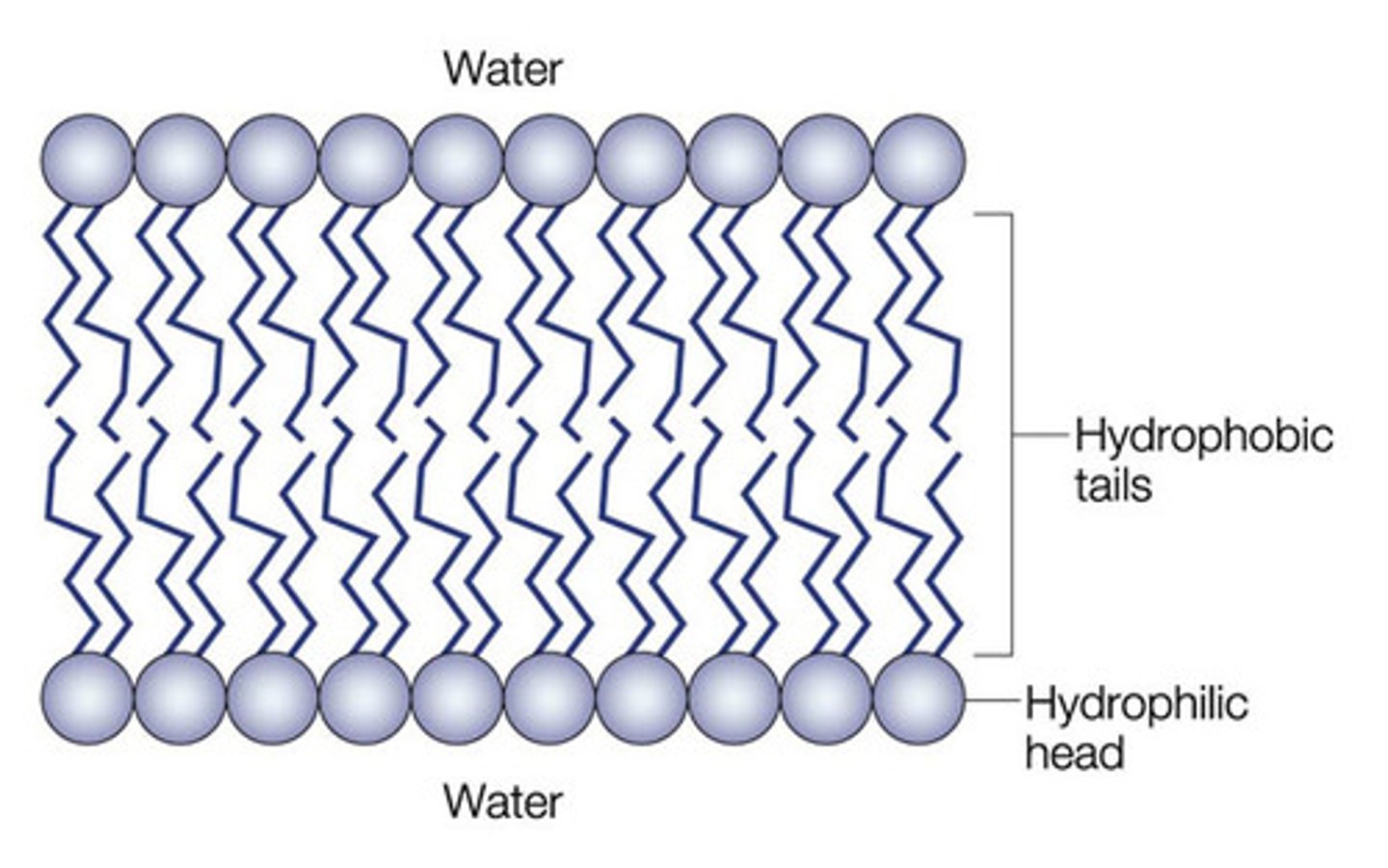
Cell membrane
The semipermeable membrane surrounding the cytoplasm of a cell.
phospholipid bilayer
Plasma membrane layers composed of phospholipid molecules arranged with polar heads facing the outside and nonpolar tails facing the inside.
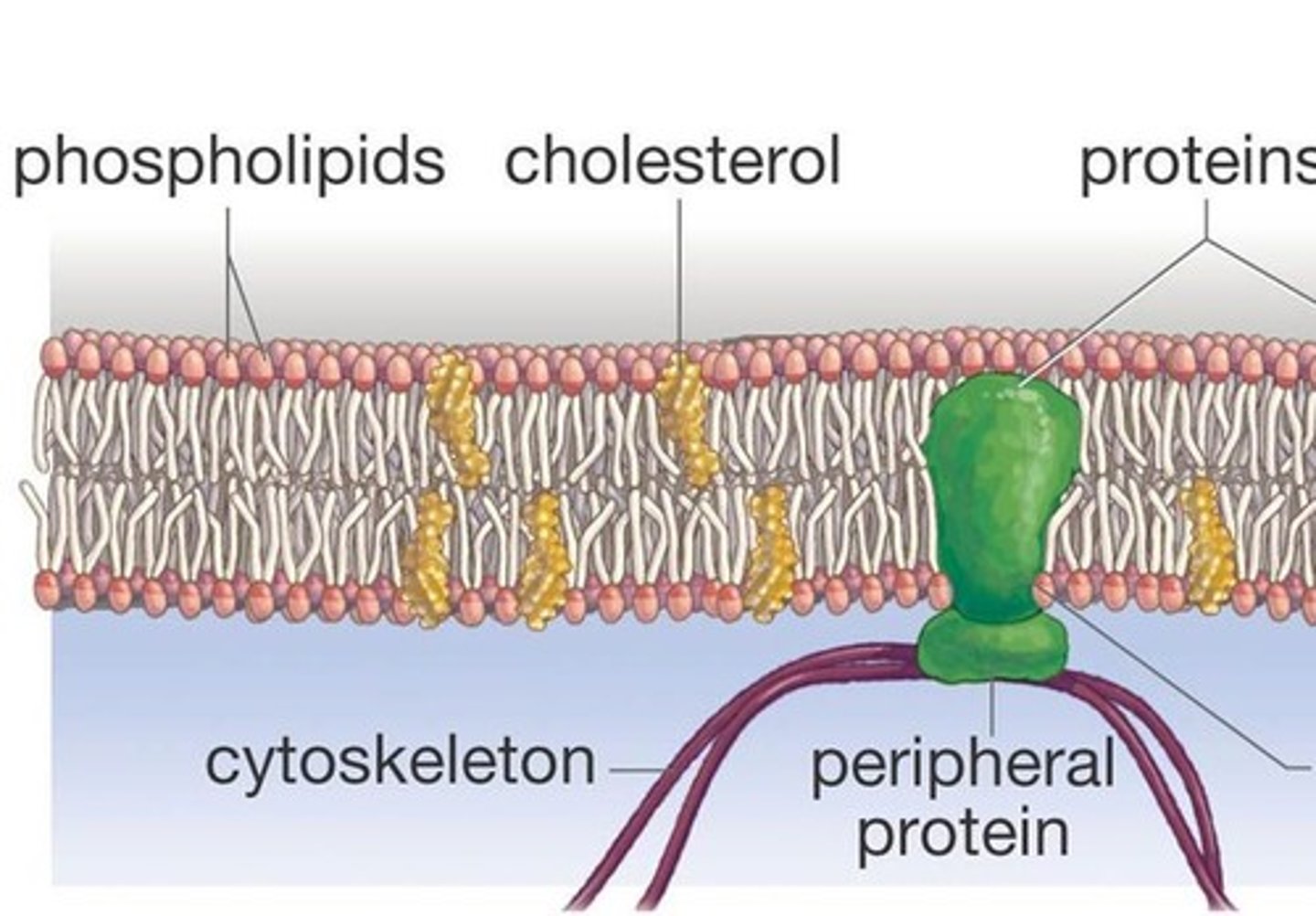
cholesterol
A lipid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes.
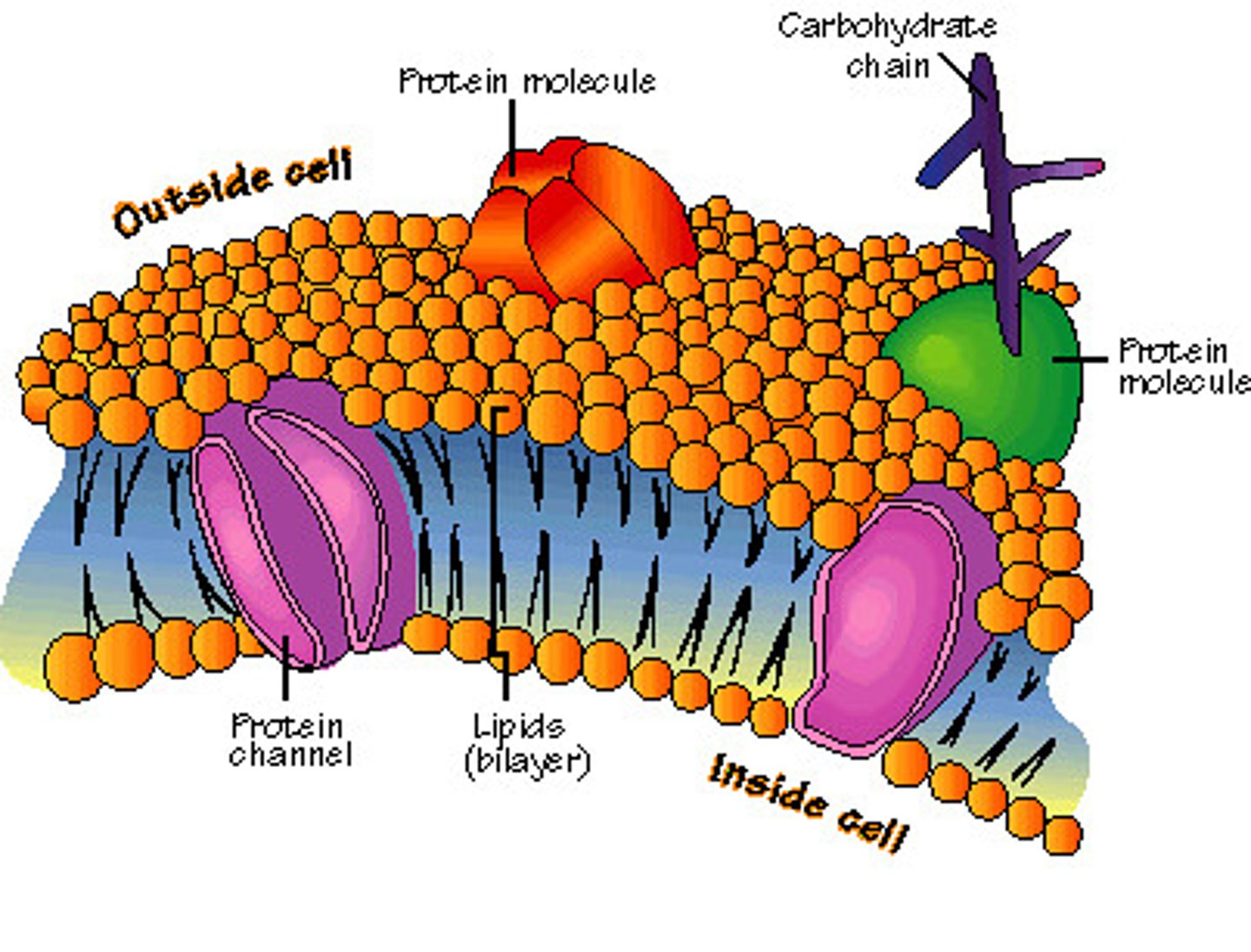
selective permeability
A property of a plasma membrane that allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
fluid mosaic model
The currently accepted model of cell membrane structure, which envisions the membrane as a mosaic of individually inserted protein molecules drifting laterally in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids.
Small nonpolar molecules
Substances that can freely pass through the cell membrane
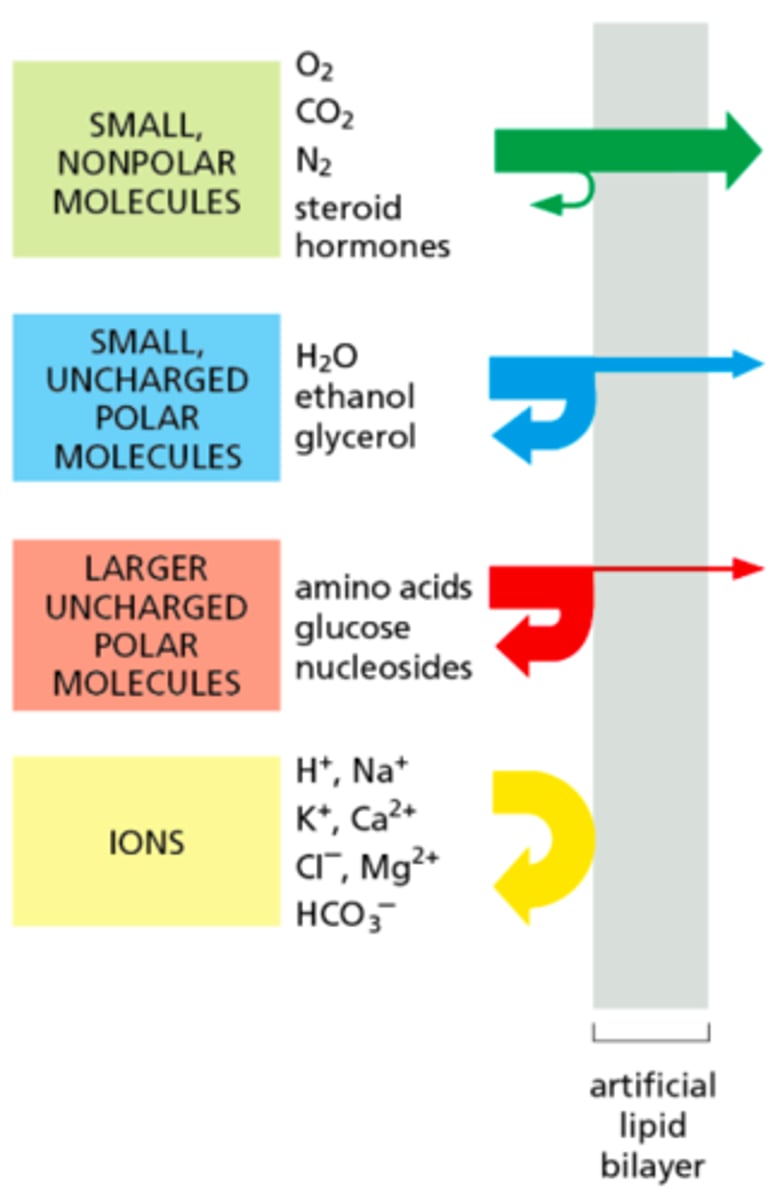
large polar molecules
Move slower or not all through membrane / possibly need a protein
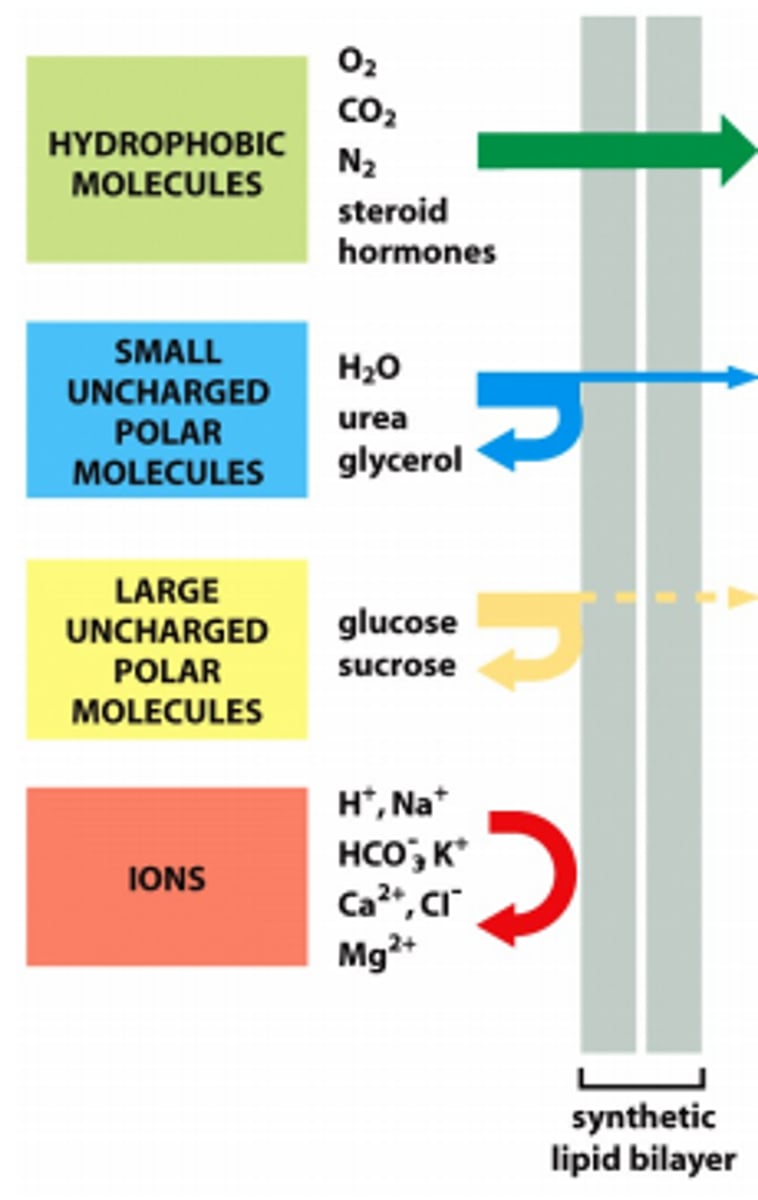
Polar uncharged molecules
pass through the membrane in small amounts
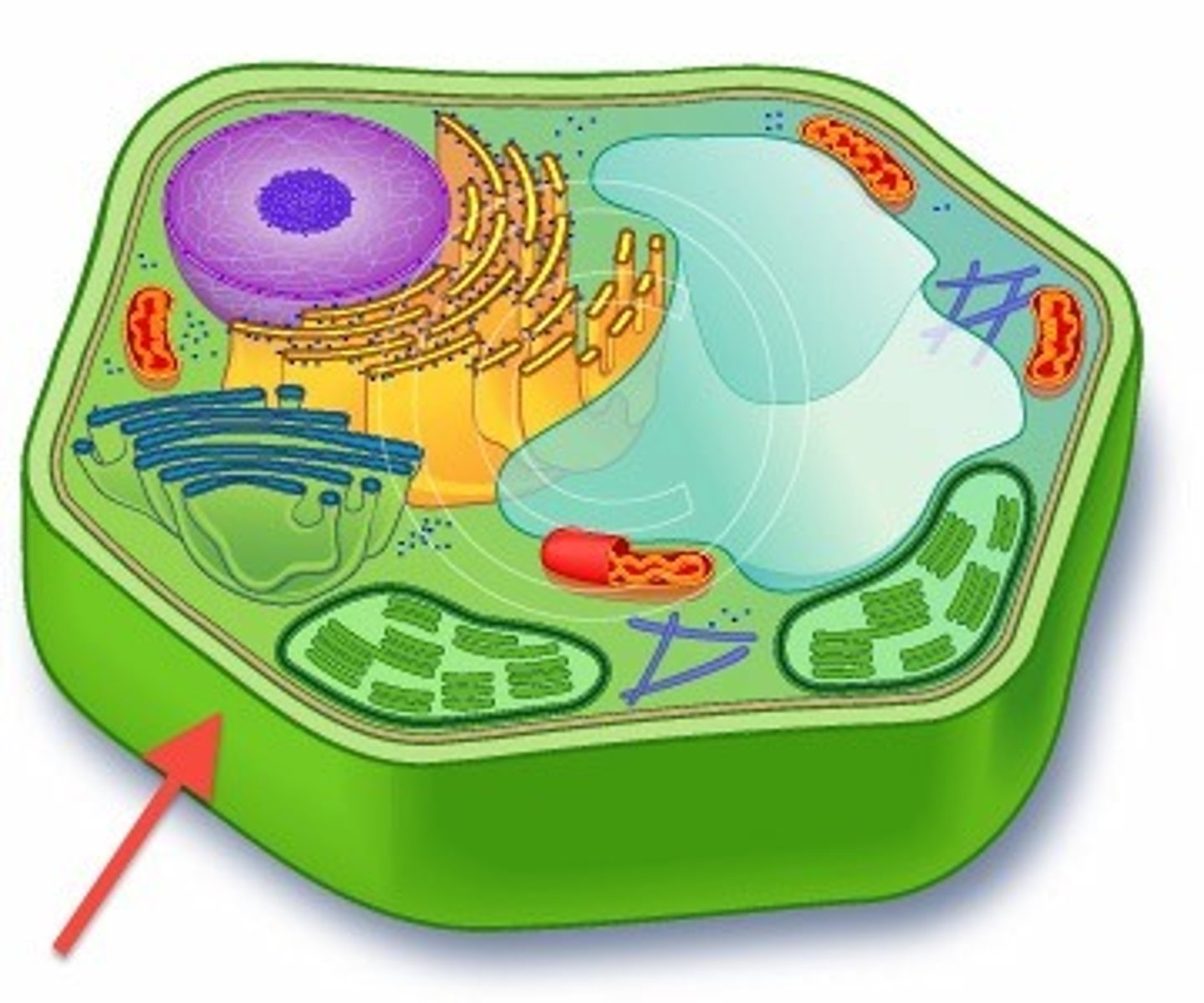
Cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
Passive transport
The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
Active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
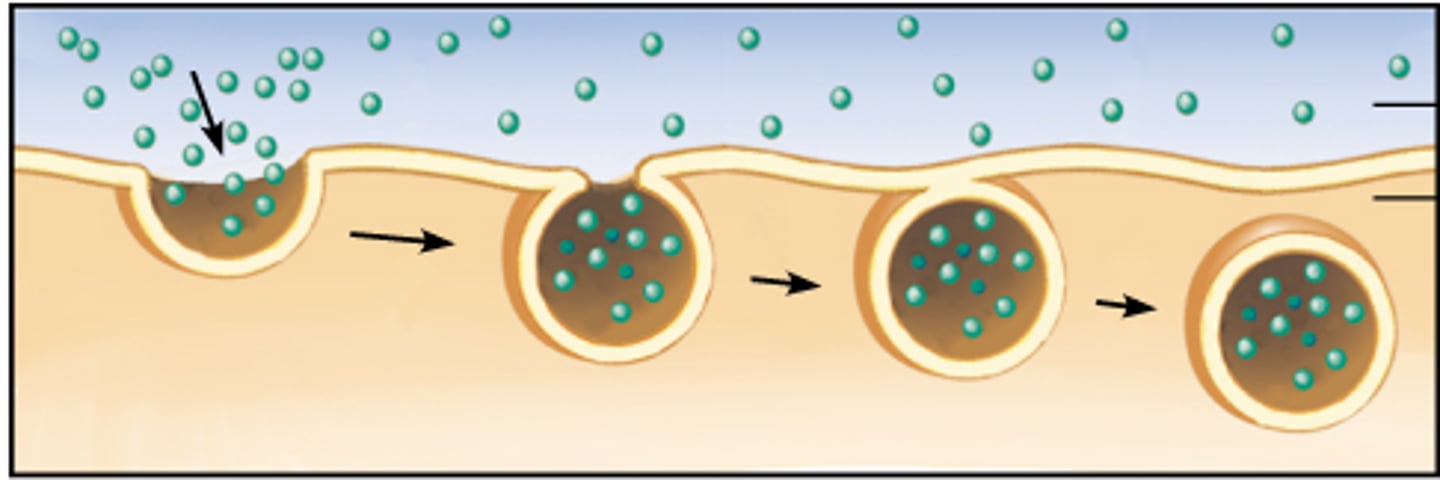
endocytosis
A process in which a cell engulfs extracellular material through an inward folding of its plasma membrane.
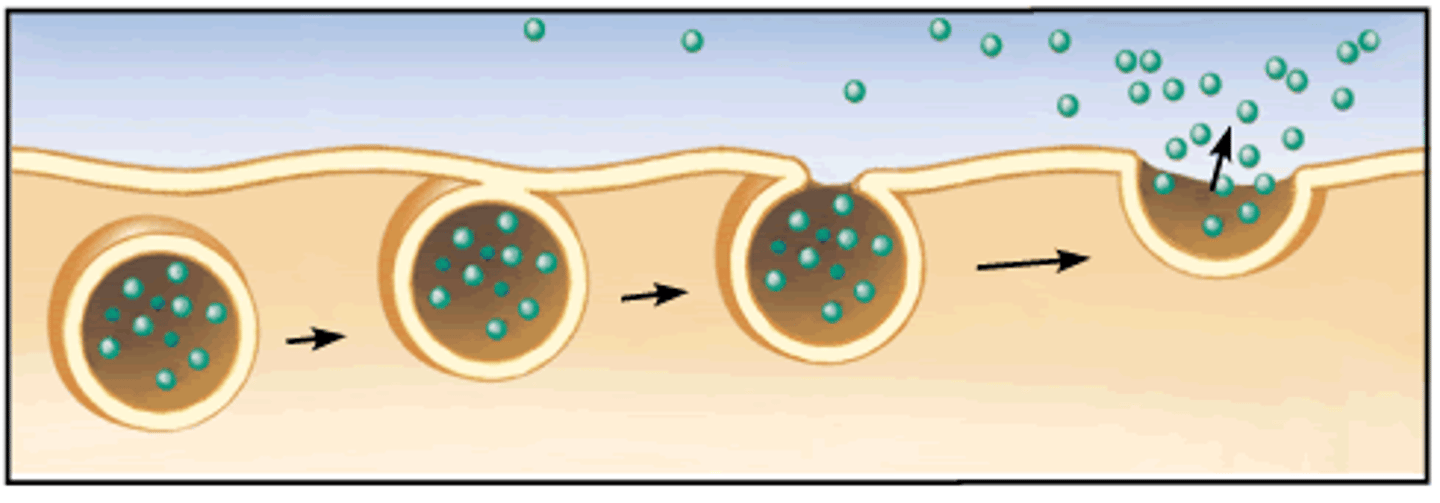
exocytosis
a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
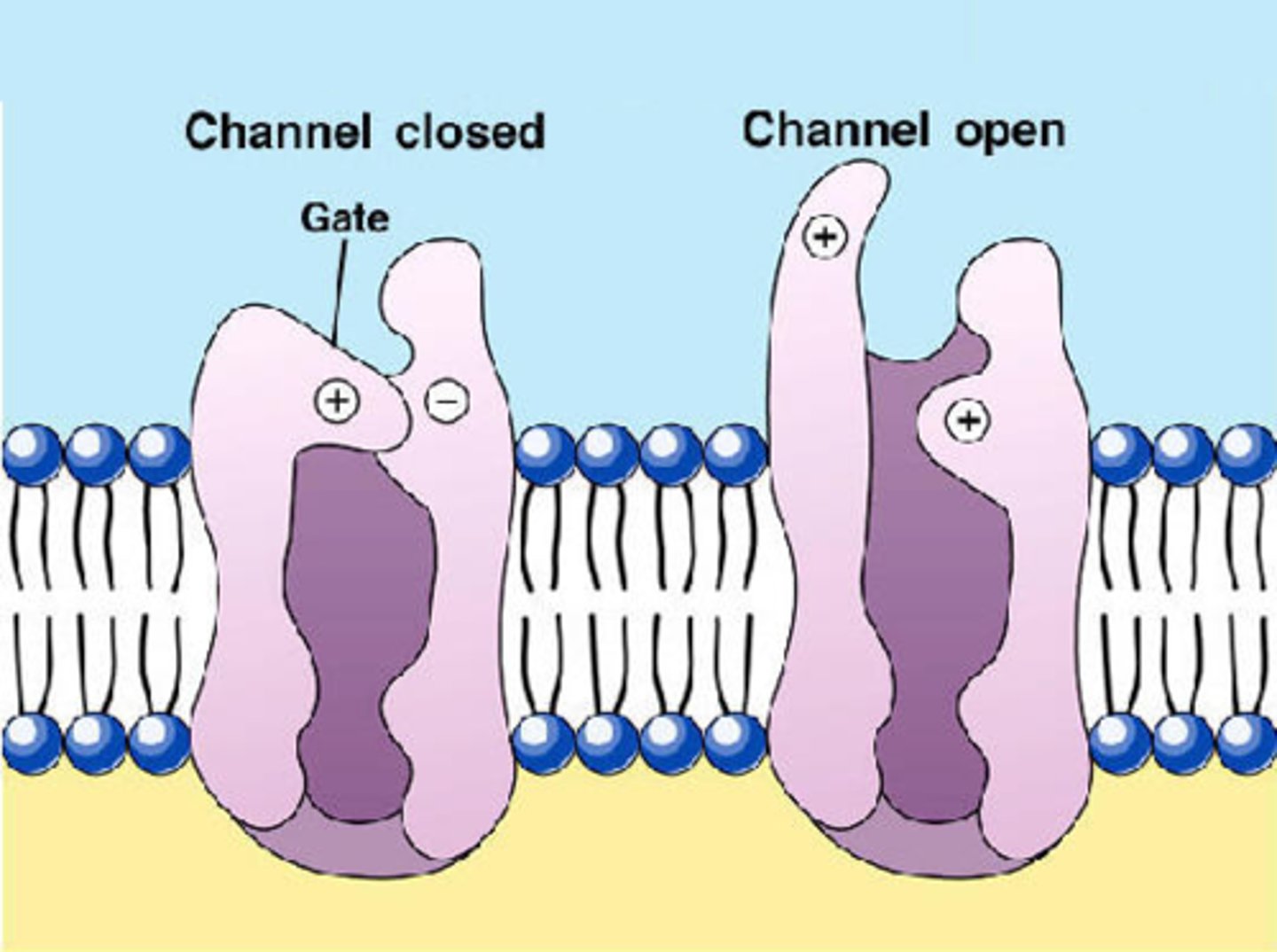
Ion Channels
A transmembrane protein channel that allows a specific ion to diffuse across the membrane down its concentration or electrochemical gradient.
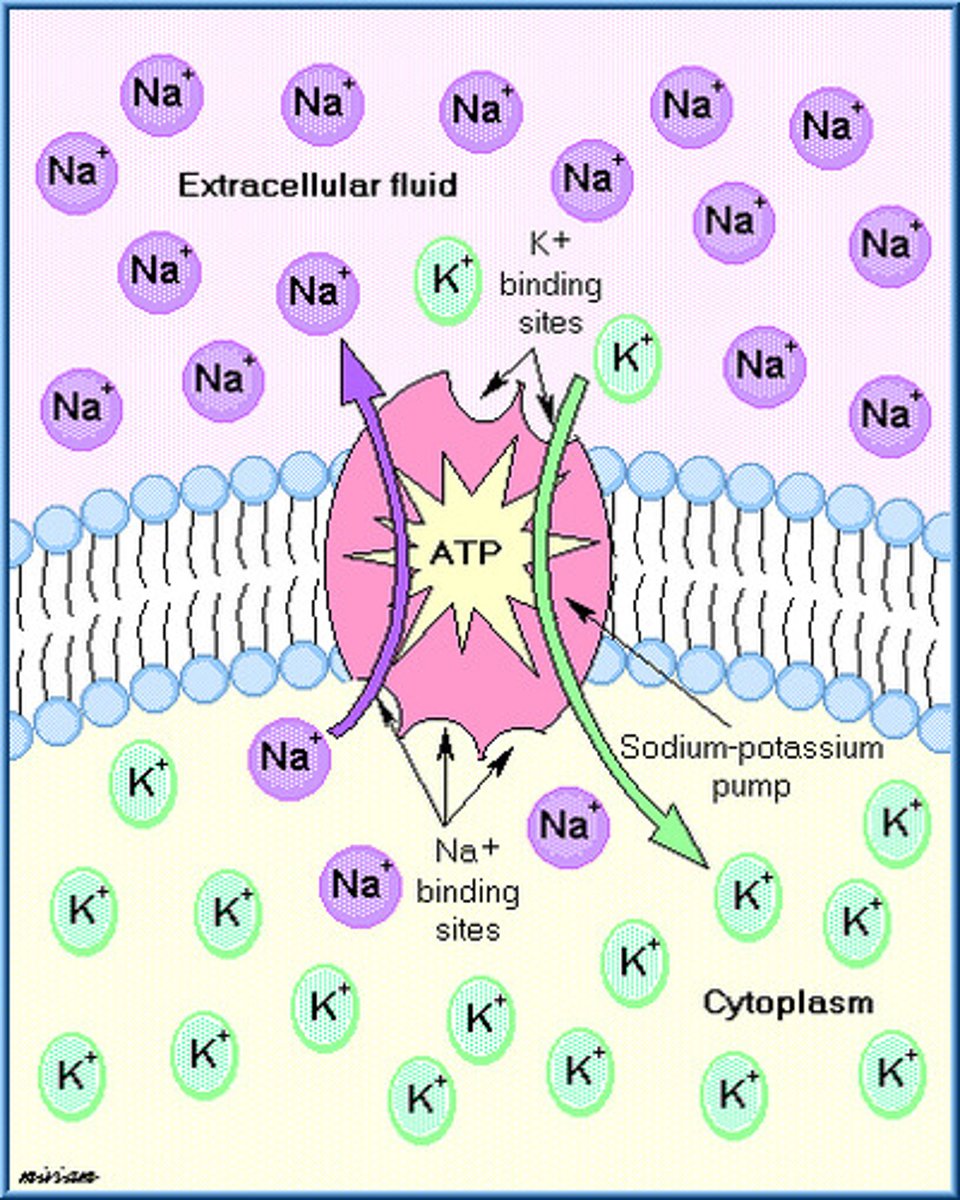
Na+/K+ ATPase
A protein found in the plasma membrane of all cells in the body that uses the energy of an ATP (hydrolyzes ATP) to move three Na+ ions out of the cell and two K+ ions into the cell, thus establishing concentrations gradients for these ions across the cell membrane.
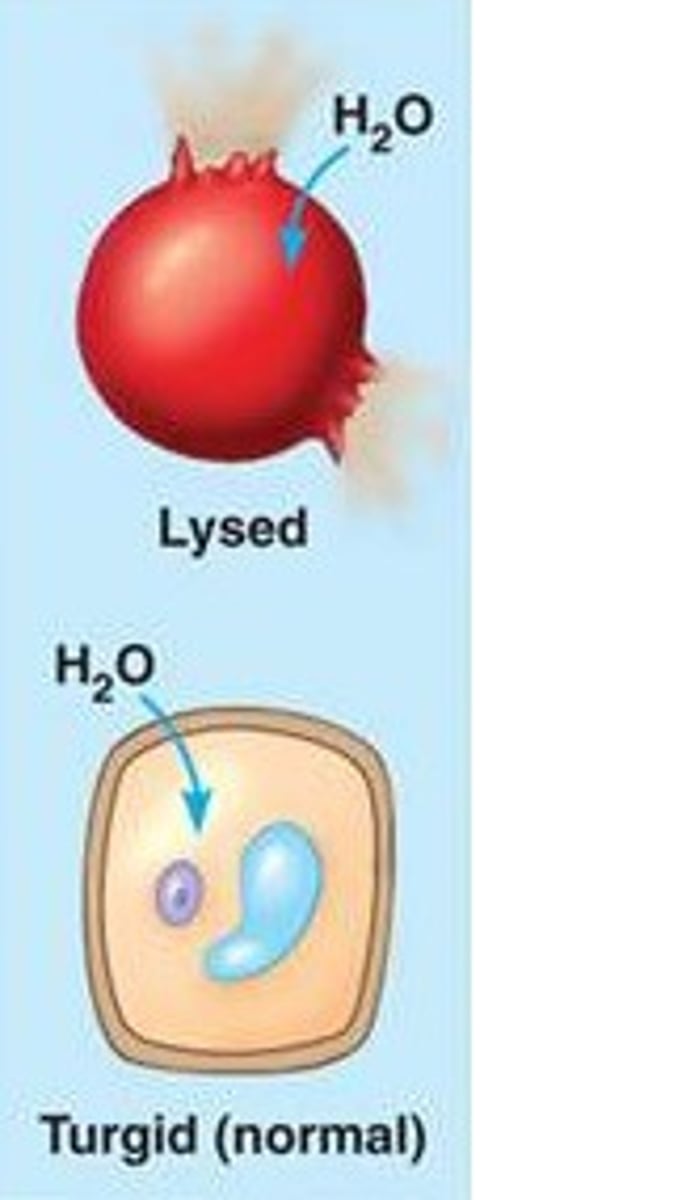
hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
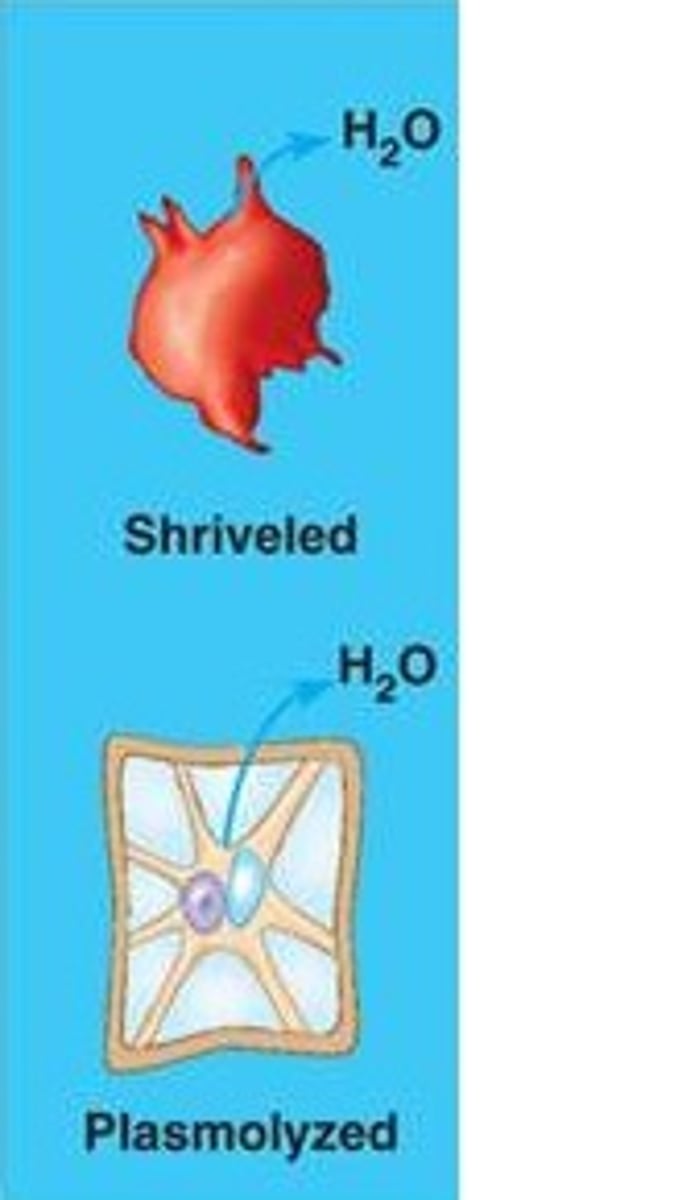
hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
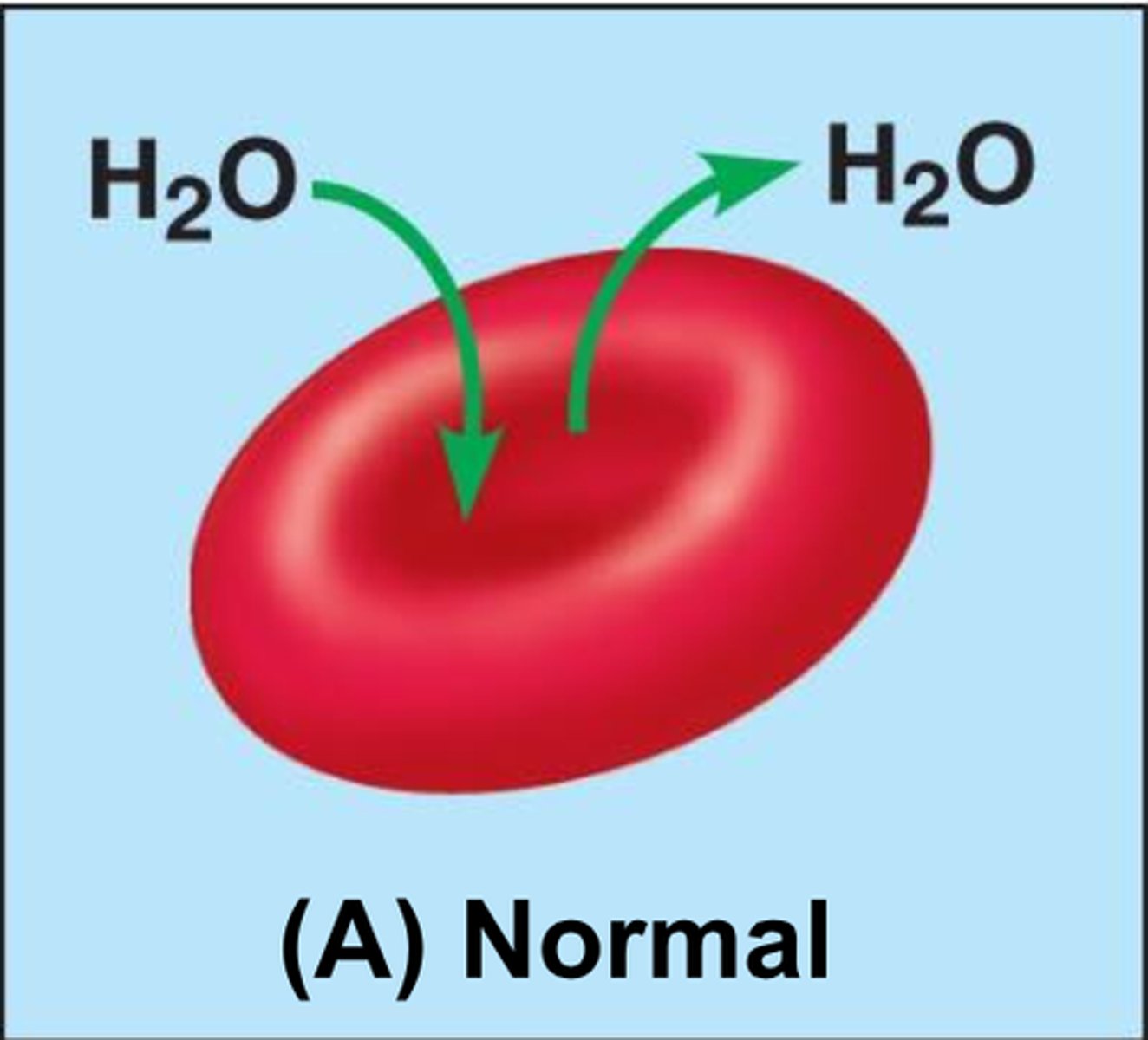
isotonic
Having the same solute concentration as another solution.
Water Potential
The physical property predicting the direction in which water will flow, governed by solute concentration and applied pressure.
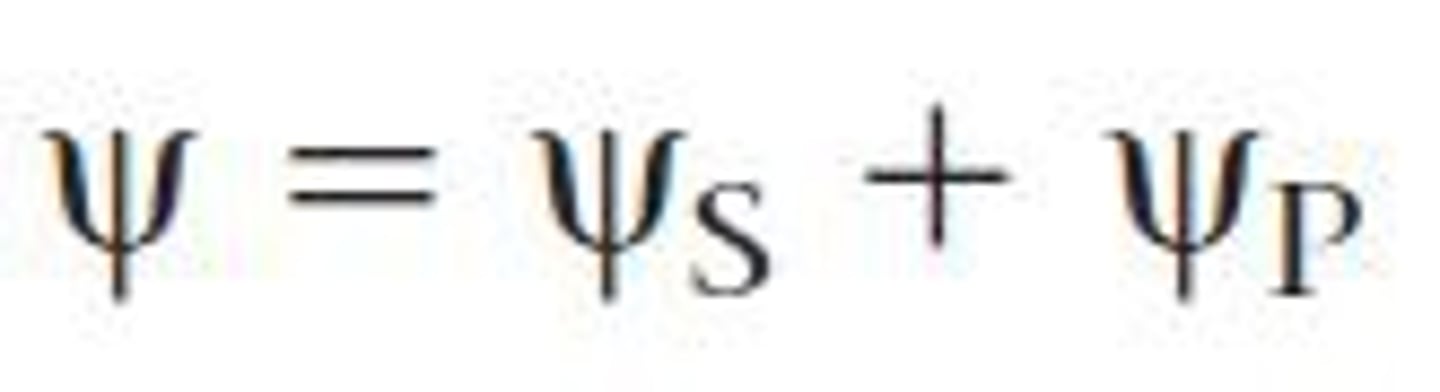
Osmoregulation
Regulation of solute concentrations and water balance by a cell or organism
Solute Potential
A component of water potential that is proportional to the number of dissolved solute molecules in a solution and measures the effect of solutes on the direction of water movement; also called osmotic potential, it can be either zero or negative.
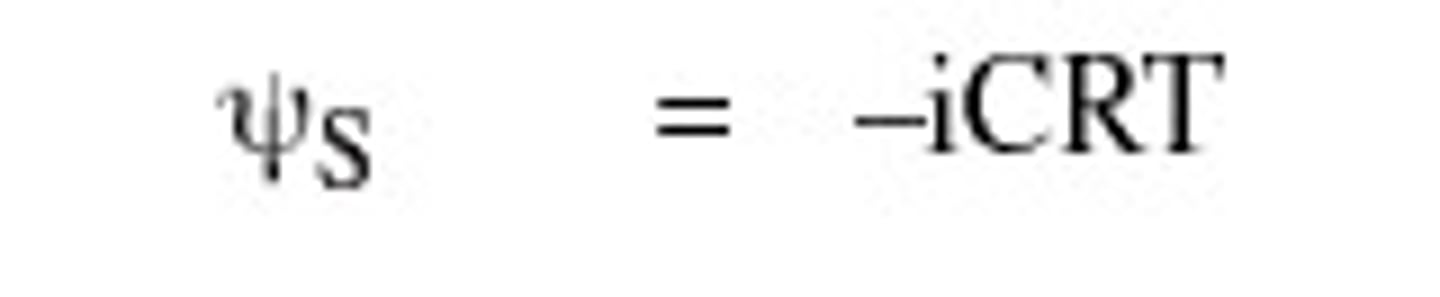
0.0831
pressure constant (R)
Compartmentalization
Membrane-bound organelles allow different parts of the cell to perform different functions at the same time
Eukaryotic cells
Contain a nucleus and other organelles that are bound by membranes.
Prokaryotic cell
A type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles; found only in the domains Bacteria and Archaea.
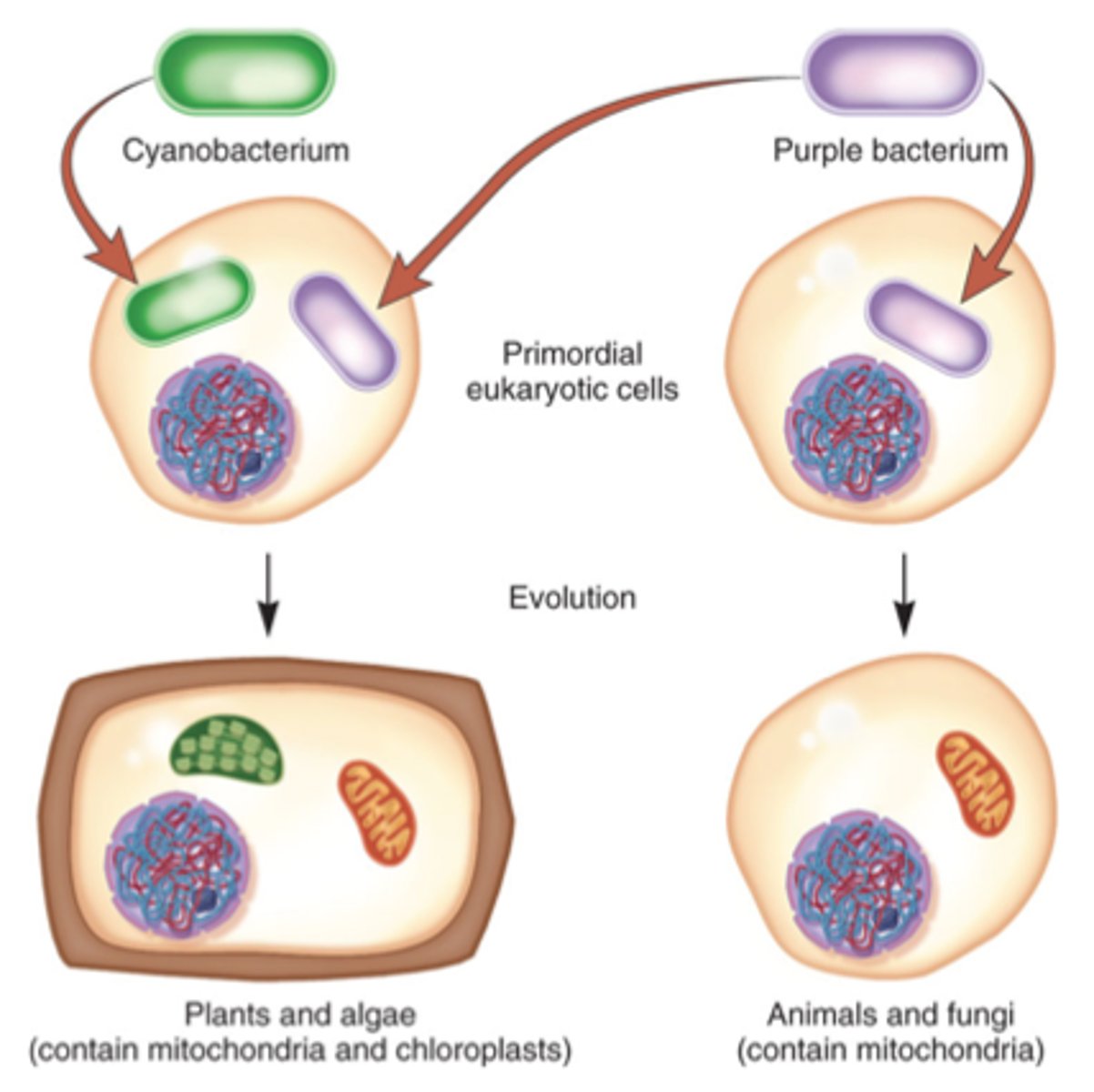
Endosymbiosis
A theorized process in which early eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes.
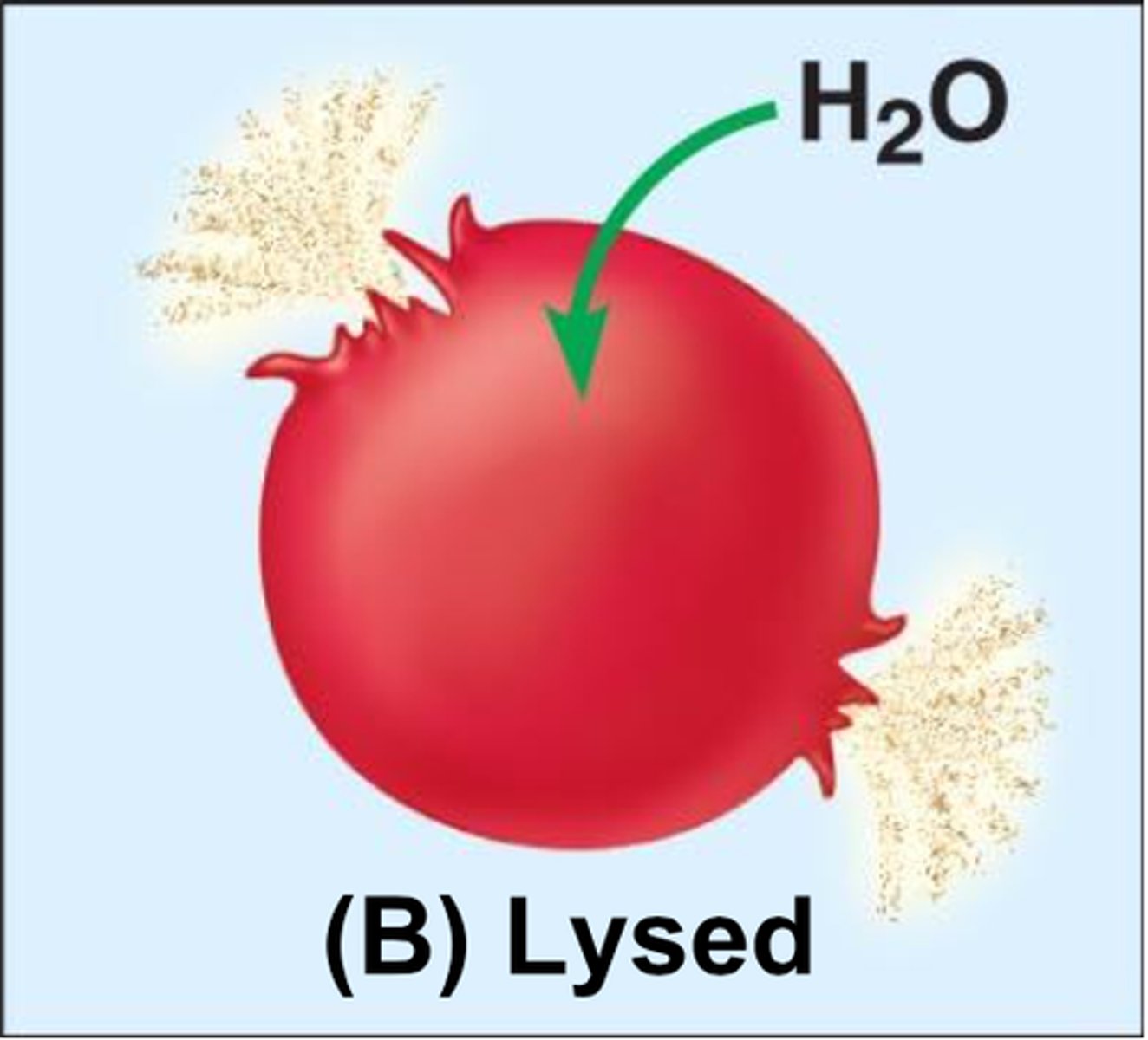
Cell lysis
rupturing membranes of foreign cells
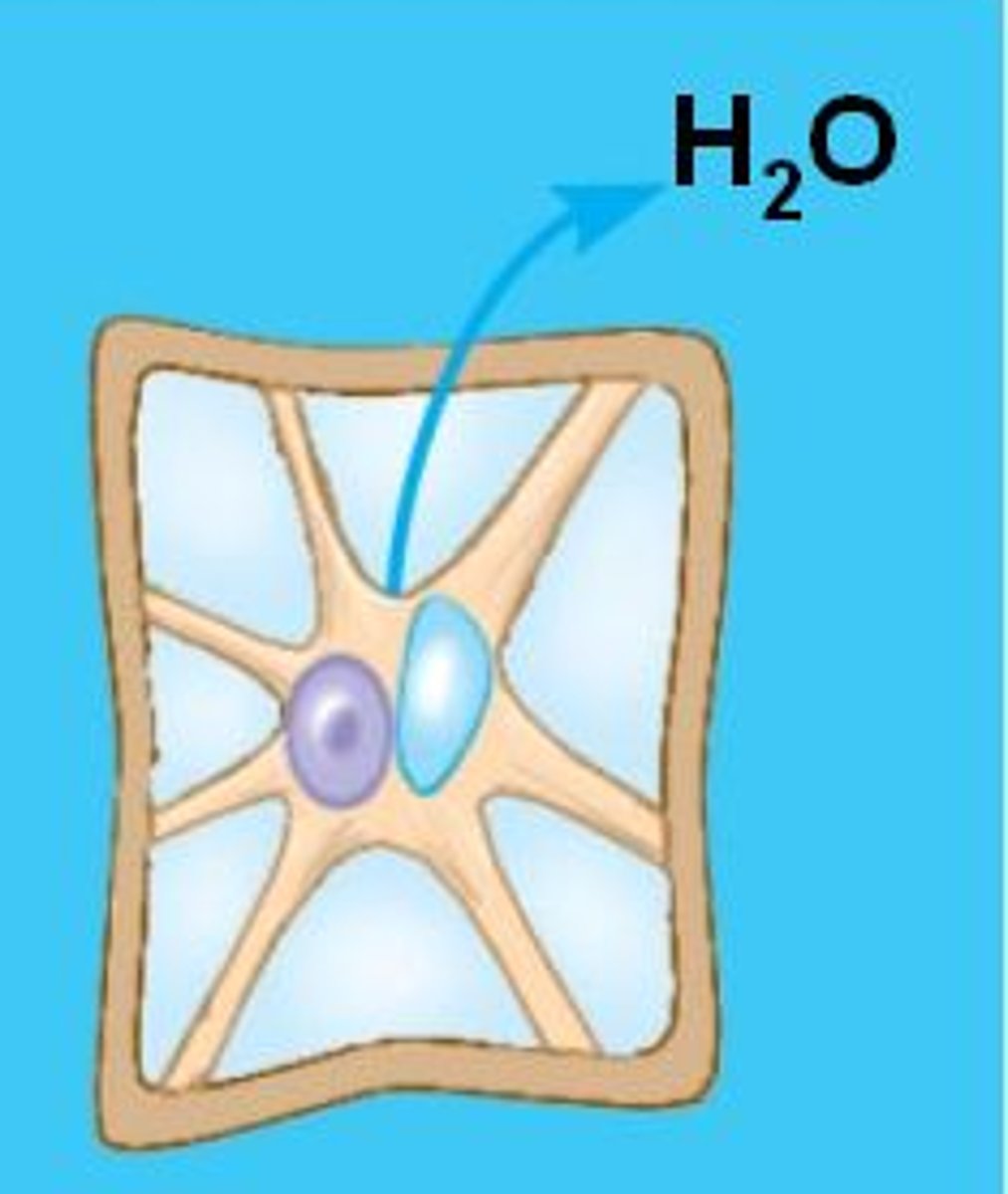
Plasmolysis
A phenomenon in walled cells in which the cytoplasm shrivels and the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall; occurs when the cell loses water to a hypertonic environment.
Turgor Pressure
The pressure that is exerted on the inside of cell walls and that is caused by the movement of water into the cell
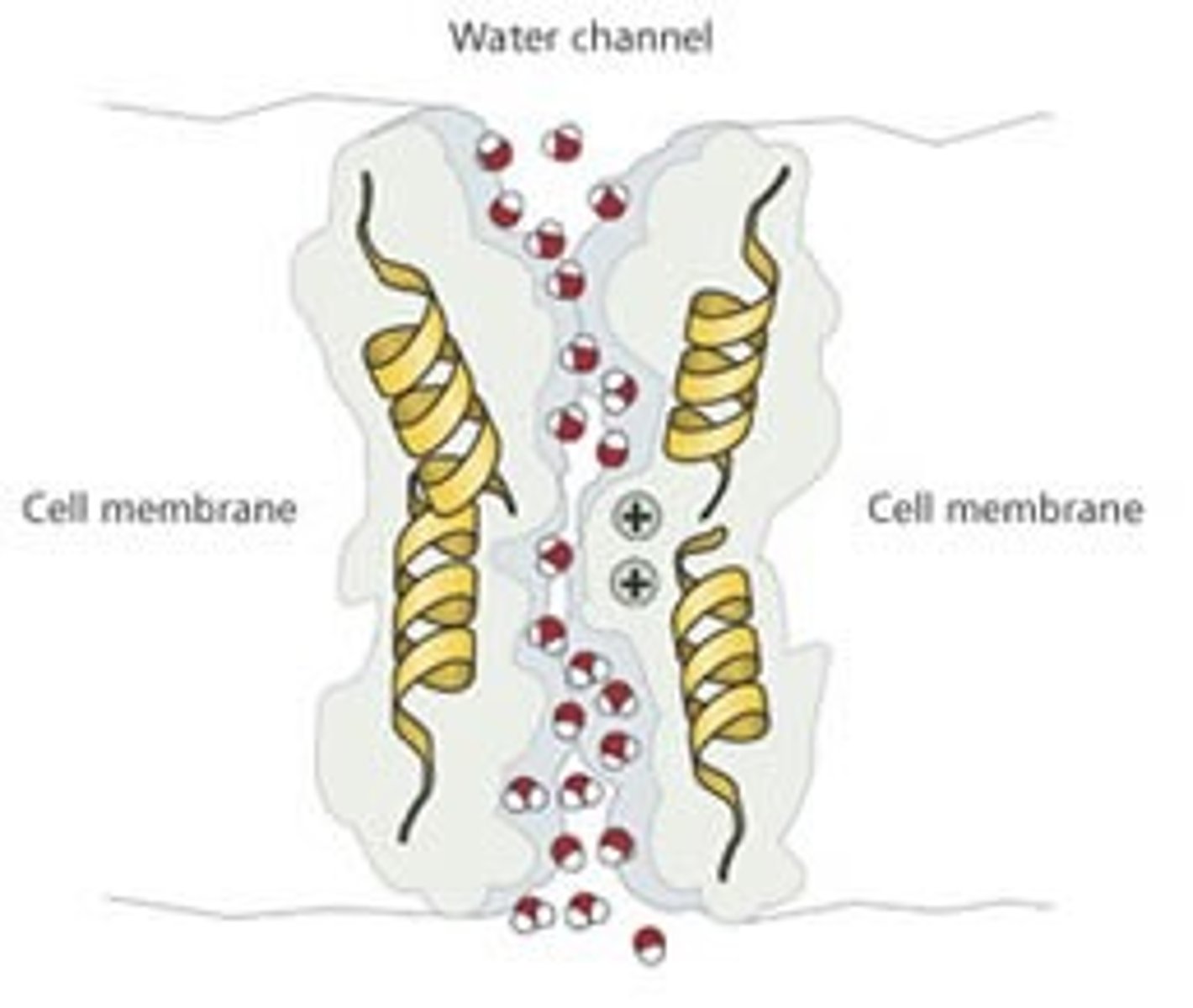
Aquaporins
A transport protein in the plasma membrane of a plant or animal cell that specifically facilitates the diffusion of water across the membrane