ENVS 150 Module/Test 3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
1
New cards
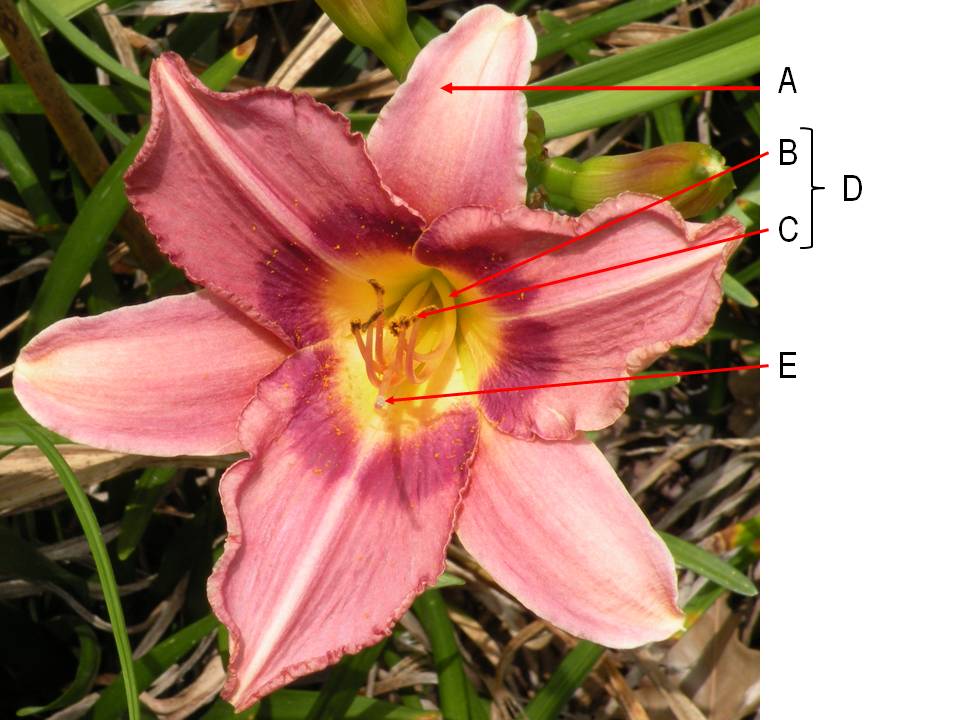
What is the name of the arrow labeled "A"?
a. filament
b. anther
c. stamen
d. tepal
e. stigma
a. filament
b. anther
c. stamen
d. tepal
e. stigma
d. tepal
2
New cards
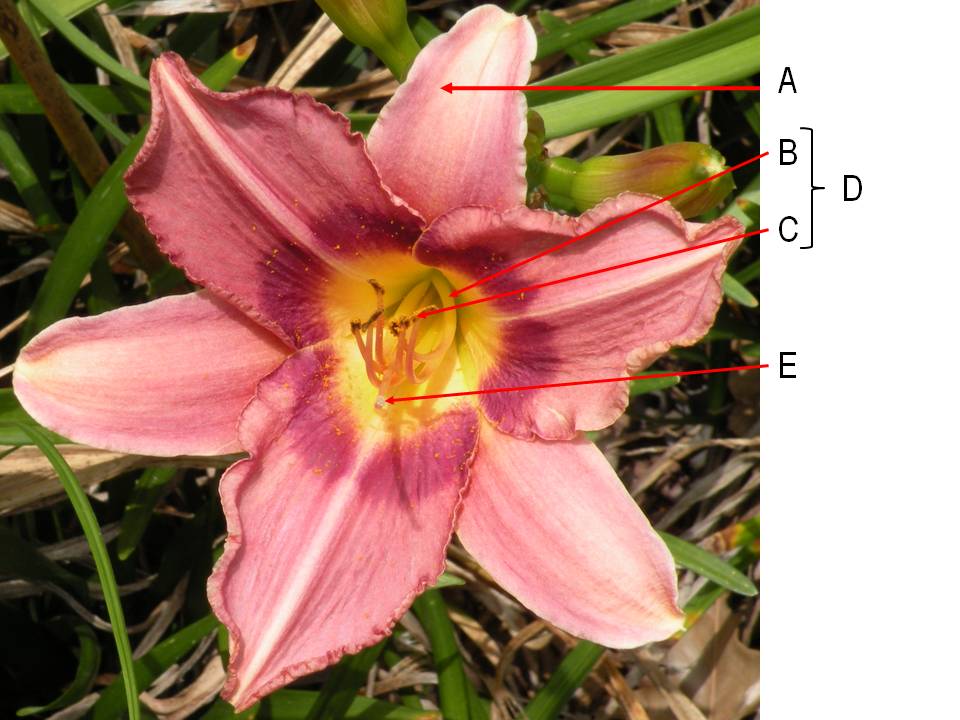
What is the name of the arrow labeled "B"?
a. filament
b. anther
c. stamen
d. tepal
e. stigma
a. filament
b. anther
c. stamen
d. tepal
e. stigma
a. filament
3
New cards
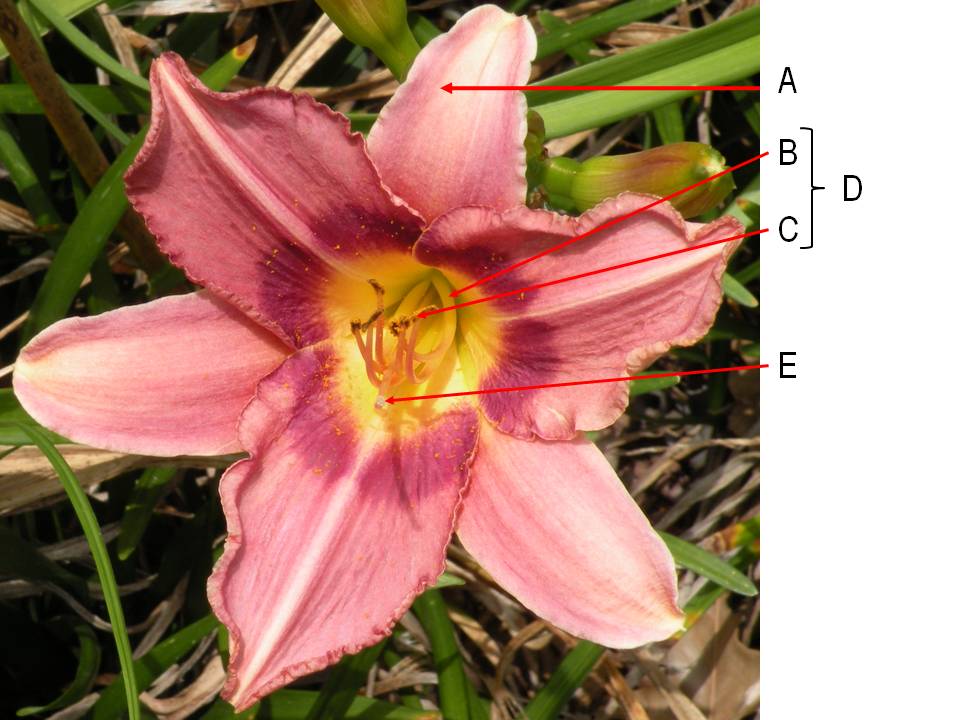
What is the name of the arrow labeled "C"?
a. filament
b. anther
c. stamen
d. tepal
e. stigma
a. filament
b. anther
c. stamen
d. tepal
e. stigma
b. anther
4
New cards
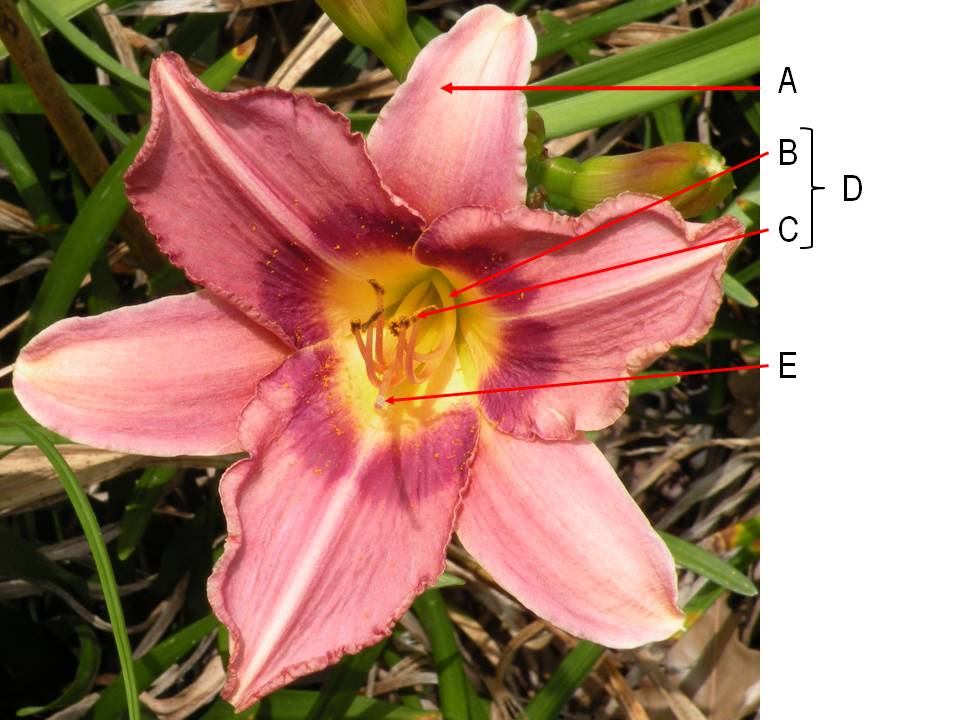
What is the name of the arrow labeled "D"?
a. filament
b. anther
c. stamen
d. tepal
e. stigma
a. filament
b. anther
c. stamen
d. tepal
e. stigma
c. stamen
5
New cards
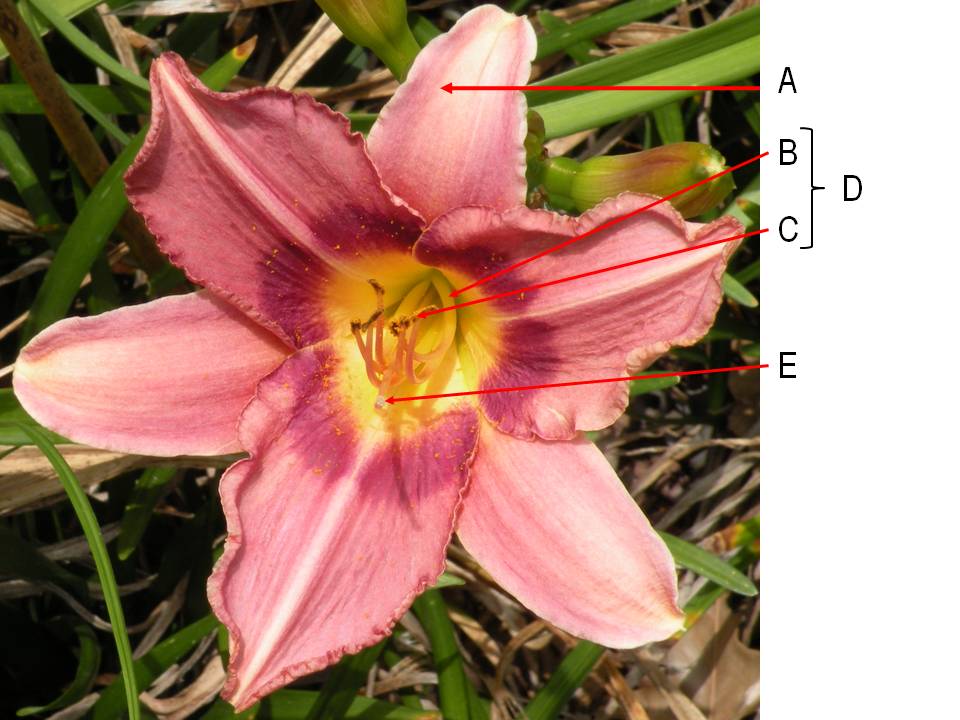
What is the name of the arrow labeled "E"?
a. filament
b. anther
c. stamen
d. tepal
e. stigma
a. filament
b. anther
c. stamen
d. tepal
e. stigma
e. stigma
6
New cards
The collective term for the petals
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
d. corolla
7
New cards
The collective term for the anther and filament
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
f. stamen
8
New cards
When plants reproduce by cuttage or division of plant parts
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
c. asexual reproduction
9
New cards
The collective term for the sepals
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
a. calyx
10
New cards
When plants reproduce through fertilization
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
b. sexual reproduction
11
New cards
The collective term for the stigma, style and ovary
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
g. pistil
12
New cards
When the sepals and petals are indistinguishable
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
a. calyx
b. sexual reproduction
c. asexual reproduction
d. corolla
e. tepals
f. stamen
g. pistil
e. tepals
13
New cards
A ripened ovary
a. parthenocarpy
b. compound fruit
c. simple fruit
d. vestigial
e. fruit
a. parthenocarpy
b. compound fruit
c. simple fruit
d. vestigial
e. fruit
e. fruit
14
New cards
A fruit composed from a multiple carpel ovary
a. parthenocarpy
b. compound fruit
c. simple fruit
d. vestigial
e. fruit
a. parthenocarpy
b. compound fruit
c. simple fruit
d. vestigial
e. fruit
b. compound fruit
15
New cards
Fruit formed without benefit of pollination
a. parthenocarpy
b. compound fruit
c. simple fruit
d. vestigial
e. fruit
a. parthenocarpy
b. compound fruit
c. simple fruit
d. vestigial
e. fruit
a. parthenocarpy
16
New cards
Rudimentary seeds which are not viable
a. parthenocarpy
b. compound fruit
c. simple fruit
d. vestigial
e. fruit
a. parthenocarpy
b. compound fruit
c. simple fruit
d. vestigial
e. fruit
d. vestigial
17
New cards
A fruit composed of a single carpel
a. parthenocarpy
b. compound fruit
c. simple fruit
d. vestigial
e. fruit
a. parthenocarpy
b. compound fruit
c. simple fruit
d. vestigial
e. fruit
c. simple fruit
18
New cards
The embryo shoot
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
a. plumule
19
New cards
The outer layer of a seed
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
b. testa
20
New cards
The start of germination
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
f. imbibition
21
New cards
A fruit without seed
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
a. parthenocarpic
22
New cards
Unusually necessary for seed formation
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
g. pollination
23
New cards
Primary food storage in monocot seeds
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
h. endosperm
24
New cards
The embryo root
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
c. radicle
25
New cards
Primary food storage in eudicot seeds
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
a. parthenocarpic
b. testa
c. radicle
d. cotyledons
e. plumule
f. imbibition
g. pollination
h. endosperm
d. cotyledons
26
New cards
Overcoming physical dormancy by damaging the seed coat
a. stratification
b. physiological dormancy
c. scarification
d. quiescence
e. physical dormancy
a. stratification
b. physiological dormancy
c. scarification
d. quiescence
e. physical dormancy
c. scarification
27
New cards
Embryo dormancy when the seed must be subjected to specific conditions to enhance germination
a. stratification
b. physiological dormancy
c. scarification
d. quiescence
e. physical dormancy
a. stratification
b. physiological dormancy
c. scarification
d. quiescence
e. physical dormancy
b. physiological dormancy
28
New cards
The process of chilling seed in a moist medium for multiple weeks
a. stratification
b. physiological dormancy
c. scarification
d. quiescence
e. physical dormancy
a. stratification
b. physiological dormancy
c. scarification
d. quiescence
e. physical dormancy
a. stratification
29
New cards
When a seed does not have the appropriate environmental conditions to germinate
a. stratification
b. physiological dormancy
c. scarification
d. quiescence
e. physical dormancy
a. stratification
b. physiological dormancy
c. scarification
d. quiescence
e. physical dormancy
d. quiescence
30
New cards
Structural conditions preventing dormancy also referred to as seed coat dormancy
a. stratification
b. physiological dormancy
c. scarification
d. quiescence
e. physical dormancy
a. stratification
b. physiological dormancy
c. scarification
d. quiescence
e. physical dormancy
e. physical dormancy
31
New cards
Morphological characteristics of an organism
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
d. character
32
New cards
Different form of the same gene
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
b. allele
33
New cards
Genotype with two different alleles
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
i. heterozygous
34
New cards
Visible characteristics of an organism
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
e. phenotype
35
New cards
A trait that is always expressed
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
h. dominant
36
New cards
Offspring have intermediate characters
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
c. incomplete dominace
37
New cards
Specific property of an organism
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
a. trait
38
New cards
A single gene controls many characters
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
f. pleiotropy
39
New cards
A character of an organism is controlled by more than one gene
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
a. trait
b. allele
c. incomplete dominance
d. character
e. phenotype
f. pleiotrophy
g. polygenic inheritance
h. dominant
i. heterozygous
g. polygenic inheritance
40
New cards
The process of gene transcription and translation
Process of decoding genetic information into functional proteins
a. gene transcription
b. gene expression
Process of decoding genetic information into functional proteins
a. gene transcription
b. gene expression
b. gene expression
41
New cards
Synthesizing RNA from DNA
a. gene transcription
b. gene expression
a. gene transcription
b. gene expression
a. gene transcription
42
New cards
Uracil
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. both
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. both
a. RNA
43
New cards
Single strand
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. both
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. both
a. RNA
44
New cards
Guanine
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. both
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. both
c. both
45
New cards
Double Helix
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. both
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. both
b. DNA
46
New cards
Adenine
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. both
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. both
c. both
47
New cards
Thyamine
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. both
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. both
b. DNA
48
New cards
Different species inherit the same trait from a common ancestor
a. mutation
b. genetic drift
c. acclimation
d. homology
e. fitness
f. gene flow
a. mutation
b. genetic drift
c. acclimation
d. homology
e. fitness
f. gene flow
d. homology
49
New cards
Only the phenotype changes, not the genotype
a. mutation
b. genetic drift
c. acclimation
d. homology
e. fitness
f. gene flow
a. mutation
b. genetic drift
c. acclimation
d. homology
e. fitness
f. gene flow
c. acclimation
50
New cards
Random events affecting genotypes of a population
a. mutation
b. genetic drift
c. acclimation
d. homology
e. fitness
f. gene flow
a. mutation
b. genetic drift
c. acclimation
d. homology
e. fitness
f. gene flow
b. genetic drift
51
New cards
Random changes in genetic composition of an organism
a. mutation
b. genetic drift
c. acclimation
d. homology
e. fitness
f. gene flow
a. mutation
b. genetic drift
c. acclimation
d. homology
e. fitness
f. gene flow
a. mutation
52
New cards
Genetic trait improving survival and reproduction
a. mutation
b. genetic drift
c. acclimation
d. homology
e. fitness
f. gene flow
a. mutation
b. genetic drift
c. acclimation
d. homology
e. fitness
f. gene flow
e. fitness
53
New cards
Change in population allele frequency due to individuals leaving or joining a population
a. mutation
b. genetic drift
c. acclimation
d. homology
e. fitness
f. gene flow
a. mutation
b. genetic drift
c. acclimation
d. homology
e. fitness
f. gene flow
f. gene flow
54
New cards
Species become interdependent based on each other’s special adaptations
a. co-evolution
b. adaptive radiation
c. convergent evolution
a. co-evolution
b. adaptive radiation
c. convergent evolution
a. co-evolution
55
New cards
Organisms evolved independently but appear similar
a. co-evolution
b. adaptive radiation
c. convergent evolution
a. co-evolution
b. adaptive radiation
c. convergent evolution
c. convergent evolution
56
New cards
One species produces rapidly several new species with diverse adaptations
a. co-evolution
b. adaptive radiation
c. convergent evolution
a. co-evolution
b. adaptive radiation
c. convergent evolution
b. adaptive radiation
57
New cards
Tubular flowers and hummingbirds
a. co-evolution
b. adaptive radiation
c. convergent evolution
a. co-evolution
b. adaptive radiation
c. convergent evolution
a. co-evolution
58
New cards
Many species from a tarweed subtribe in Hawaii
a. co-evolution
b. adaptive radiation
c. convergent evolution
a. co-evolution
b. adaptive radiation
c. convergent evolution
b. adaptive radiation
59
New cards
Emergence of glyphosate resistant weeds
a. microevolution
b. macroevolution
c. punctuated equilibrium
a. microevolution
b. macroevolution
c. punctuated equilibrium
c. punctuated equilibrium
60
New cards
Changes in gene pool from one generation to the next
a. microevolution
b. macroevolution
c. punctuated equilibrium
a. microevolution
b. macroevolution
c. punctuated equilibrium
a. microevolution
61
New cards
Evolutionary changes occur stepwise with long periods without changes
a. microevolution
b. macroevolution
c. punctuated equilibrium
a. microevolution
b. macroevolution
c. punctuated equilibrium
c. punctuated equilibrium
62
New cards
Rapid changes in finch population characteristics documented on the Galapagos Islands since the 1970's
a. microevolution
b. macroevolution
c. punctuated equilibrium
a. microevolution
b. macroevolution
c. punctuated equilibrium
a. microevolution
63
New cards
Cumulative small changes over very long periods of time
a. microevolution
b. macroevolution
c. punctuated equilibrium
a. microevolution
b. macroevolution
c. punctuated equilibrium
b. macroevolution
64
New cards
Occurs as a gas
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
d. ethylene
65
New cards
Promotes shoot initiation in tissue culture
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
66
New cards
Induces storage protein synthesis in seeds
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
e. abscisic acid
67
New cards
Increases stem elongation through cell division and elongation
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
c. gibberellic acid
68
New cards
Stimulates defense in stressed plants
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
d. ethylene
69
New cards
Promotes apical dominance
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
b. auxin
70
New cards
Initiates plant responses to water stress
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
e. abscisic acid
71
New cards
Phototropism
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
b. auxin
72
New cards
Used commercially to ripen fruit\
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
d. ethylene
73
New cards
Promotes cell division and shoot formation in tissue culture
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
74
New cards
Promotes flowering and increases fruit size of seedless grapes
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
a. cytokinin
b. auxin
c. gibberellic acid
d. ethylene
e. abscisic acid
c. gibberellic acid
75
New cards
Plant growth response to light
a. photoperiodism
b. phototropism
c. photomorphogenesis
d. phytochrome
a. photoperiodism
b. phototropism
c. photomorphogenesis
d. phytochrome
c. photomorphogenesis
76
New cards
Plants growing towards a light source
a. photoperiodism
b. phototropism
c. photomorphogenesis
d. phytochrome
a. photoperiodism
b. phototropism
c. photomorphogenesis
d. phytochrome
b. phototropism
77
New cards
The protein absorbing red and far-red light
a. photoperiodism
b. phototropism
c. photomorphogenesis
d. phytochrome
a. photoperiodism
b. phototropism
c. photomorphogenesis
d. phytochrome
d. phytochrome
78
New cards
Growth and development of an organism in response to photoperiod
a. photoperiodism
b. phototropism
c. photomorphogenesis
d. phytochrome
a. photoperiodism
b. phototropism
c. photomorphogenesis
d. phytochrome
a. photoperiodism
79
New cards
Photoperiodically insensitive
a. photoperiodism
b. short-day plants
c. day-neutral plants
d. long-day plants
a. photoperiodism
b. short-day plants
c. day-neutral plants
d. long-day plants
c. day-neutral plants
80
New cards
Photoperiodically controlled process that is induced when daylength is shorter than critical day length
a. photoperiodism
b. short-day plants
c. day-neutral plants
d. long-day plants
a. photoperiodism
b. short-day plants
c. day-neutral plants
d. long-day plants
b. short-day plants
81
New cards
Photoperiodically controlled process that is induced when daylength is longer than critical day length
a. photoperiodism
b. short-day plants
c. day-neutral plants
d. long-day plants
a. photoperiodism
b. short-day plants
c. day-neutral plants
d. long-day plants
d. long-day plants
82
New cards
Photomorphogenic response to variations in daylength
a. photoperiodism
b. short-day plants
c. day-neutral plants
d. long-day plants
a. photoperiodism
b. short-day plants
c. day-neutral plants
d. long-day plants
a. photoperiodism
83
New cards
A plant that bears both male and female flowers on the same plant is referred to as?
Select one:
a. incomplete
b. dioeceous
c. imperfect
d. perfect
e. monoecious
Select one:
a. incomplete
b. dioeceous
c. imperfect
d. perfect
e. monoecious
e. monoecious
84
New cards
In a seed, the ____________ becomes the first new leaves of the new plant.
Select one:
a. epicotyl
b. hilum
c. testa
d. plumule
e. radicle
Select one:
a. epicotyl
b. hilum
c. testa
d. plumule
e. radicle
d. plumule
85
New cards
In a dicot seed, the largest part of the seed being a pair of modified leaves full of stored food:
a. testa
b. radicle
c. plumule
d. endosperm
e. cotyledons
a. testa
b. radicle
c. plumule
d. endosperm
e. cotyledons
e. cotyledons
86
New cards
White musky flowers which open at night are most likely to use pollination by:
Select one:
a. wind
b. bees
c. bats
d. butterflies
e. birds
Select one:
a. wind
b. bees
c. bats
d. butterflies
e. birds
c. bats
87
New cards
Sweet, blue or yellow flowers with nectar are most likely to use pollination by:
Select one:
a. bats
b. bees
c. wind
d. butterflies
e. birds
Select one:
a. bats
b. bees
c. wind
d. butterflies
e. birds
b. bees
88
New cards
The juicy fleshy part of an orange that you can eat is the __________________.
Select one:
a. mesocarp
b. exocarp
c. pericarp
d. testa
e. endocarp
Select one:
a. mesocarp
b. exocarp
c. pericarp
d. testa
e. endocarp
e. endocarp
89
New cards
The type of dormancy exemplified by temperate woody plants can be broken by?
Select one:
a. after ripening
b. nothing
c. scarification
d. quiescence
e. stratification
Select one:
a. after ripening
b. nothing
c. scarification
d. quiescence
e. stratification
e. stratification
90
New cards
Which of the following describes the study of evolution?
Select one:
a. how life forms changes over millennia
b. how organisms continue to change
c. breeding new species of animals or plants
d. a and b
e. b and c
Select one:
a. how life forms changes over millennia
b. how organisms continue to change
c. breeding new species of animals or plants
d. a and b
e. b and c
d. a and b
91
New cards
Which is NOT a factor causing evolution
Select one:
a. natural selection
b. non-random mating
c. mutation
d. gene flow and genetic drift
e. acclimation
Select one:
a. natural selection
b. non-random mating
c. mutation
d. gene flow and genetic drift
e. acclimation
e. acclimation
92
New cards
When a diploid organism has two alleles that are different it is called _____________ for that characteristic.
Select one:
a. homozygous
b. heterozygous
c. recessive
d. dominant
e. allopatric
Select one:
a. homozygous
b. heterozygous
c. recessive
d. dominant
e. allopatric
b. heterozygous
93
New cards
What is the term for rapid evolution that results of many species from a single ancestor when islands are colonized?
Select one:
a. convergent evolution
b. adaptive radiation
c. macroevolution
d. punctuated equilibrium
e. microevolution
Select one:
a. convergent evolution
b. adaptive radiation
c. macroevolution
d. punctuated equilibrium
e. microevolution
b. adaptive radiation
94
New cards
What is the gene pool of a population?
Select one:
a. frequency of the least common genes
b. all heterozygous alleles in a population
c. all alleles of all individuals of a population
d. frequency of the most common genes
e. all homozygous alleles in a population
Select one:
a. frequency of the least common genes
b. all heterozygous alleles in a population
c. all alleles of all individuals of a population
d. frequency of the most common genes
e. all homozygous alleles in a population
c. all alleles of all individuals of a population
95
New cards
Polyploidy is NOT:
Select one:
a. a tool for breeding new crops
b. common in animals
c. part of evolution
d. common in flowering plants
e. common in large, vigorous plants
Select one:
a. a tool for breeding new crops
b. common in animals
c. part of evolution
d. common in flowering plants
e. common in large, vigorous plants
b. common in animals
96
New cards
A cross between two heterozygous plants produces the following phenotypic ratio of dominant to recessive
Select one:
a. 2:1
b. 5:1
c. 4:1
d. 3:1
e. 1:1
Select one:
a. 2:1
b. 5:1
c. 4:1
d. 3:1
e. 1:1
d. 3:1
97
New cards
The hormone auxin causes the following responses:
Select one:
a. promotes growth of flower parts
b. all are correct
c. at high concentration it can be used as an herbicide
d. initiates roots on stem cuttings and in tissue culture
e. regulates response to light and gravity
Select one:
a. promotes growth of flower parts
b. all are correct
c. at high concentration it can be used as an herbicide
d. initiates roots on stem cuttings and in tissue culture
e. regulates response to light and gravity
b. all are correct
98
New cards
Systemic acquired resistance
Select one:
a. occurs in response to an attack on the plant
b. salicylic acid moves throughout the plant and triggers resistance
c. salicylic acid is produced at the site of attack
d. is induced by the hormone salicylic acid
e. all are involved in SAR
Select one:
a. occurs in response to an attack on the plant
b. salicylic acid moves throughout the plant and triggers resistance
c. salicylic acid is produced at the site of attack
d. is induced by the hormone salicylic acid
e. all are involved in SAR
a. occurs in response to an attack on the plant
99
New cards
What treatment during the night can trick a plant into experiencing long days when in fact, days are short?
Select one or more:
a. all answers are correct.
b. exposure to white light.
c. none of the answers are correct.
d. exposure to warm temperatures.
e. exposure to far-red light.
Select one or more:
a. all answers are correct.
b. exposure to white light.
c. none of the answers are correct.
d. exposure to warm temperatures.
e. exposure to far-red light.
b. exposure to white light.
100
New cards
What is the correct order in which a hormone activates a response in the cell?
Select one:
a. hormone -> transduction -> reception-> response
b. transduction -> reception ->hormone -> response
c. hormone -> reception -> transduction -> response
d. reception ->transduction -> hormone -> response
e. transduction ->hormone -> reception-> response
Select one:
a. hormone -> transduction -> reception-> response
b. transduction -> reception ->hormone -> response
c. hormone -> reception -> transduction -> response
d. reception ->transduction -> hormone -> response
e. transduction ->hormone -> reception-> response
c. hormone -> reception -> transduction -> response