Understanding the Accounting Cycle and Financial Statements
1/216
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
217 Terms
Accounting Cycle
Sequence of steps in financial reporting.
Measurement Process
Recording and posting transactions and adjustments.
Reporting Process
Preparation of financial statements.
Closing Process
Recording closing entries at period end.
Cash-Basis Accounting
Records transactions when cash is received or paid.
Accrual-Basis Accounting
Records transactions when economic events occur.
Assets Recognition
Recorded when resources are obtained.
Liabilities Recognition
Recorded when obligations occur.
Revenues Recognition
Recorded when goods/services are provided.
Expenses Recognition
Recorded when costs are incurred.
Economic Events
Transactions affecting financial position recorded timely.
Deferred Revenue
Liability until service is provided.
Prepaid Rent
Asset until rent period expires.
Supplies Asset
Recorded until supplies are used.
Accrual vs Cash-Basis
Comparison of revenue and expense recognition methods.
Transaction Description
Details of financial transactions recorded.
Financial Statements
Summarized reports of financial performance.
Adjusting Entries
Entries made to update account balances.
Closing Entries
Entries to reset temporary accounts.
Revenue Recognition Principle
Guideline for recognizing revenue in accounting.
Expense Recognition Principle
Guideline for recognizing expenses in accounting.
Cash Received
Revenue recorded when cash is received.
Cash Paid
Expense recorded when cash is paid.
Service Provided
Revenue recorded when service is completed.
Cost Used
Expense recorded when cost is incurred.
Learning Objectives
Goals for understanding accounting principles.
Concept Check
Assessment of understanding accounting concepts.
Financial Reporting
Process of disclosing financial information.
Accrual-Basis Accounting
Records revenues when goods/services are provided.
Cash-Basis Accounting
Records revenues when cash is received.
Timing Differences
Discrepancies in recording revenues/expenses timing.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
Standards guiding financial accounting practices.
Revenues Recognition
Accrual: when earned; Cash: when received.
Expenses Recognition
Accrual: when incurred; Cash: when paid.
Adjusting Entries
Updates balances of assets and liabilities.
Assets and Liabilities
Reported due to timing differences in accrual accounting.
Supplies Expense (Cash-Basis)
Recorded when cash is paid for supplies.
Utilities Expense (Accrual-Basis)
Recorded when utilities are used, not paid.
Financial Reporting
Cash-basis accounting is not permitted for major companies.
Office Supplies Purchase
Expense recorded when cash is paid, not used.
Service Revenue (Cash-Basis)
Recorded when cash is received from customers.
Equipment Purchase
Recorded as liability if borrowed funds are used.
Cost Incurred
Expense recognized when it helps generate revenue.
Accrual Accounting Principle
Focuses on matching revenues and expenses.
Cash Accounting Principle
Focuses on cash transactions only.
Accrual vs Cash Basis
Key difference is timing of revenue/expense recognition.
Adjusting Entries Purpose
To align cash flows with revenues/expenses.
Concept Check 3-2
Identifies cash-basis expense recording.
Concept Check 3-3
Identifies accrual-basis expense recording.
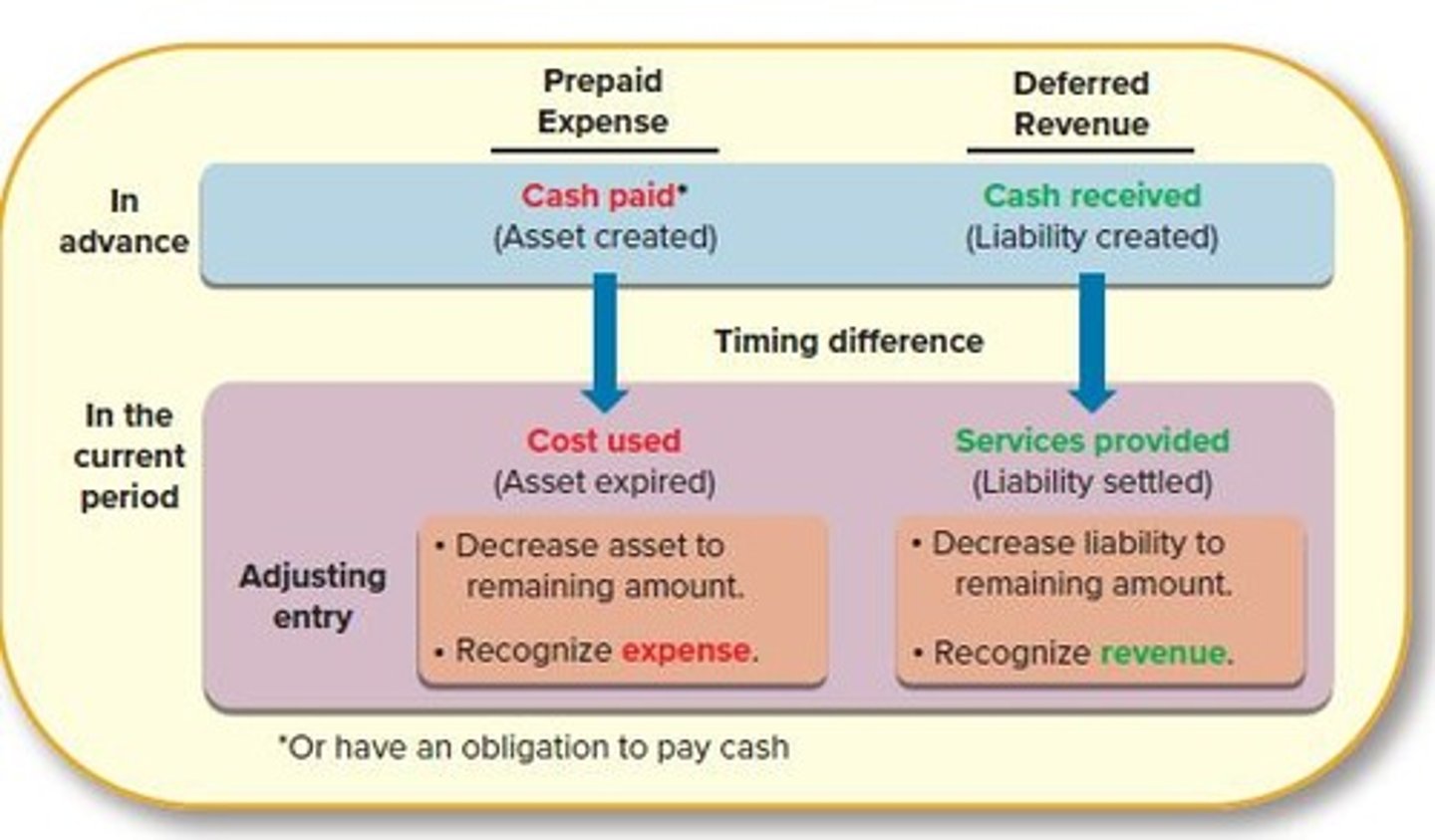
Prepayments
Payments made before the related expense is incurred.
Revenue Recognition Principle
Guides when to recognize revenue in accounting.
Expense Recognition Principle
Guides when to recognize expenses in accounting.
Major Companies
Must use accrual-basis accounting for reporting.
Cash Flow Timing
Accrual accounting reflects timing differences in cash flows.
Revenue and Expense Matching
Accrual accounting matches revenues with incurred expenses.
Financial Statements
Prepared based on accrual-basis accounting principles.
External Transactions
Business activities involving cash and credit exchanges.
Common Stock Sale
Selling shares for $200,000 to fund business.
Bank Loan
Borrowing $100,000 with a three-year repayment.
Equipment Purchase
Buying soccer training equipment for $120,000.
Prepaid Rent
Paying $60,000 for one year of rent in advance.
Supplies Purchase
Acquiring $23,000 of supplies on account.
Cash Training Revenue
Earning $43,000 from cash soccer training sessions.
Accounts Receivable Revenue
Generating $20,000 from training on account.
Unearned Revenue
Receiving $6,000 cash for future training sessions.
Salaries Expense
Paying $28,000 in salaries to employees.
Cash Dividends
Distributing $4,000 in dividends to shareholders.
Prepaid Expenses
Payments made for future benefits, recorded as assets.
Adjusting Entry
Entry to recognize expenses or reduce asset balances.
Rent Expense
Expense recognized for one month of prepaid rent.
Supplies Expense
Expense for consumed supplies, reducing asset value.
Depreciation Expense
Monthly expense for equipment usage, $2,000 per month.
Accumulated Depreciation
Contra asset account tracking total depreciation.
Timing Difference
Cash paid now, expense recognized later.
Asset Decrease
Reducing asset balance to reflect usage.
Expense Recognition
Recording costs associated with asset usage.
Monthly Rent Cost
Rent expense calculated at $5,000 per month.
Supplies Remaining
Remaining supplies valued at $13,000 after usage.
Depreciation Formula
Depreciation calculated as cost divided by useful life.
Adjusting Entry for Prepaid Expense
Involves debiting an expense and crediting an asset.
Concept Check 3-4
Identifies adjusting entry components for prepaid expenses.
Expense Debit
Adjusting entry debits always increase expense accounts.
Property and Equipment
Assets used in business operations.
Accumulated Depreciation
Total depreciation expense recognized over time.
Book Value
Asset's cost minus accumulated depreciation.
Carrying Value
Another term for book value of an asset.
Deferred Revenues
Cash received before services are provided.
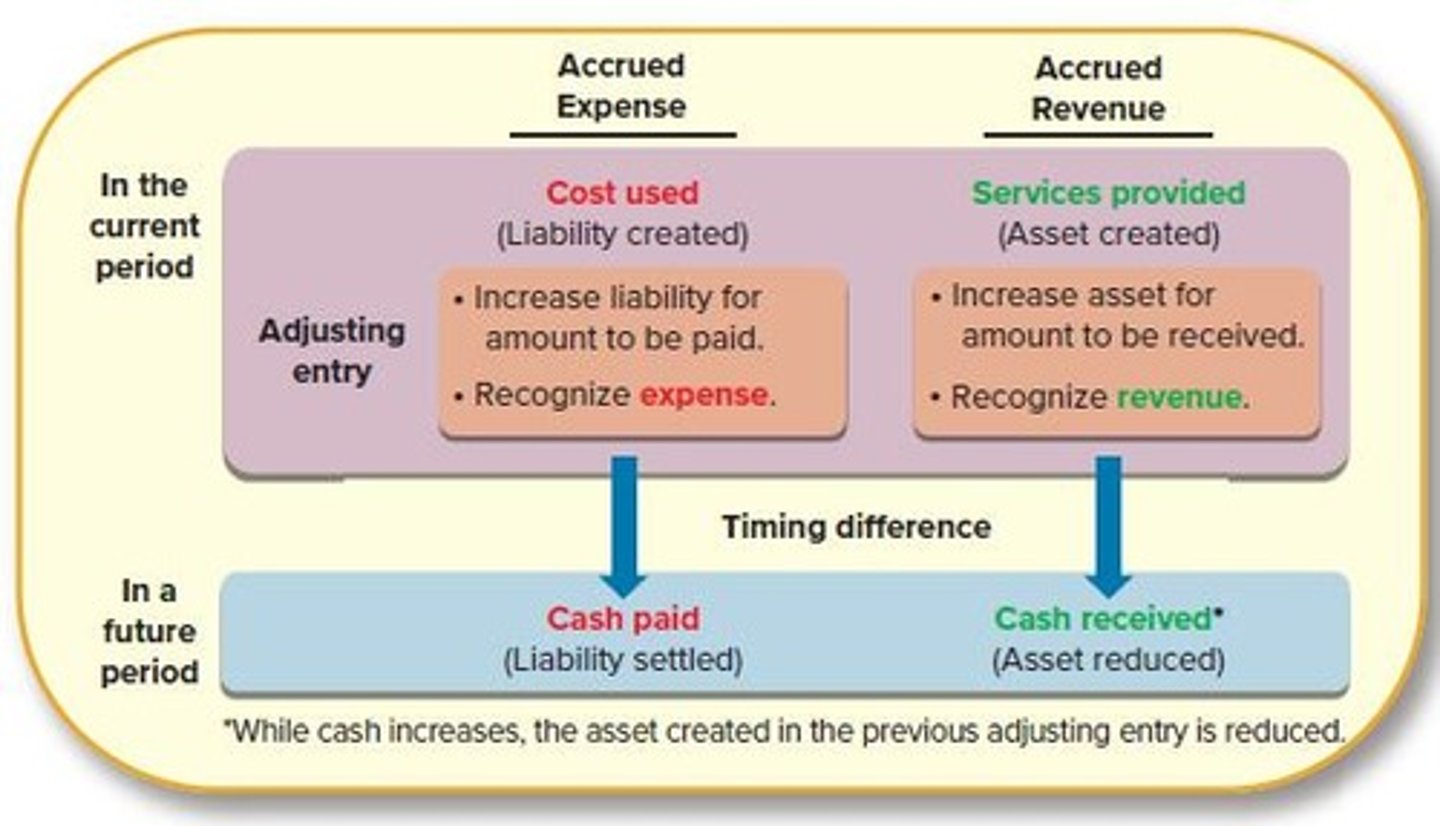
Adjusting Entry
Entry to update accounts for accrued items.
Liability
Obligation to pay for services or goods.
Service Revenue
Income earned from providing services.
Accrued Expenses
Costs incurred but not yet paid.
Current Liabilities
Obligations due within one year.
Short-term Borrowings
Loans due within one year.
Current Maturities of Long-term Debt
Portion of long-term debt due soon.
Accounts Payable
Money owed to suppliers for goods/services.
Accrued Compensation
Salaries and wages owed to employees.
Employee Benefits
Compensation provided to employees beyond salary.
Total Current Liabilities
Sum of all current obligations.
Cash Basis Accounting
Revenue recognized when cash is received.
Accrual Basis Accounting
Revenue recognized when earned, not received.