Week 5- Childbearing at Risk Nursing Management of Pregnancy at Risk: Pregnancy Related Complications
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CH 19-20
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
when does a spontaneous abortion occur?
Occurs before 20 weeks gestation
what are the causes of spontaneous abortions? first trimester? Second trimester?
first trimester commonly due to fetal genetic abnormalities
Second trimester more commonly due to maternal conditions
what are the signs and symptoms of spontaneous abortions? (4)
vaginal bleeding
Cramping or contractions
Altered vital signs
Pain
what are the signs and symptoms of threatened abortions? (5)
vaginal bleeding, often slight, early on in pregnancy
No cervical dilation or changes in cervical consistency
Mild abdominal cramping
Closed cervical os
No passage of fetal tissue
what are the signs and symptoms of inevitable abortions? (4)
Vaginal bleeding, greater than that associated with threatened abortions
Rupture of membranes
Cervical dilation
Possible passage of products of conception
what is an incomplete abortion?
Passage of some products of conception
what are the signs and symptoms of incomplete abortions? (5)
intense abdominal cramping
Heavy vaginal bleeding
Cervical dilation
What is a complete abortion?
passage of all products of conception
what are the signs and symptoms of complete abortions? (2)
history of vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain
Passage of tissue with subsequent decrease in pain and a significant decrease in vaginal bleeding
What is a missed abortion?
nonviable embryo retained in utero for at least 6 weeks
what are the signs and symptoms of missed abortions? (3)
absent uterine contractions
Irregular spotting
Possible progression to inevitable abortion
what is a recurrent abortion?
history of 3 or more consecutive spontaneous abortions
Not carrying the pregnancy to viability or term
What are the nursing priorities for spontaneous abortions?
Continued monitoring- vaginal bleeding, pad count, passage of products of conception, pain level, risk for hemorrhage
Support- physical and emotional, grief support
Treatment
Incomplete, inevitable, and missed- surgery (D&C) or meds (cytotec or oxytocin)
Rh neg- rhogham- so antibodies do not develop
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
ovum implantation outside of the uterus
where is the most common location of an ectopic pregnancy?
fallopian tubes
what is the therapeutic management for an ectopic pregnancy? (3)
Drug therapy- methotrexate, prostaglandins, misoprostil, -mycin antibiotics
Surgery if rupture occurs ← often lose the fallopian tube
Rh immunoglobulin if woman is Rh negative
what is the hallmark sign of an ectopic pregnancy?
abdominal pain with spotting within 6-8 weeks after missed menses ← very early on
What are the risk factors that make a woman more susceptible to an ectopic pregnancy? (4)
Previous ectopic pregnancy
Hx of STIs
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Endometriosis
What are the nursing priorities for an ectopic pregnancy? (4)
Pain management
Prepare for treatment
Administer meds
Prep for surgery
Teach about s/sx
Emotional support
What is the therapeutic management of gestational trophoblastic disease? (2)
Immediate evacuation of uterine contents (D&C)
Long term follow ups and monitoring of serial hCG levels
What are the signs and symptoms of gestational trophoblastic disease? (4)
Clinical manifestations similar to spontaneous abortion at 12 weeks
High hCG levels
Brownish vaginal bleeding
Uterine size larger than expected for dates
No FHR → no baby
what is cervical insufficiency?
premature dilation of the cervix; spontaneous dilation without uterine contractions
what is the therapeutic management for cervical insufficiency?
bed rest, pelvic rest, avoid heavy lifting
Cervical cerclage → suture around the suture done at 18-19 wks; not always effective but can help sometimes
What are the risk factors for cervical insufficiency?
incompetent cervix
what are the signs and symptoms of cervical insufficiency? (3)
pink-tinged vaginal discharge
Pelvic pressure
Cervical shortening via transvaginal ultrasound
what is the nursing priority for managing a pt with cervical insufficiency?
continuing surveillance and close monitoring for preterm labor ← remove cerclage with full labor or at 35-37 wks to avoid injury
what is placenta previa?
placenta implants over the cervical os
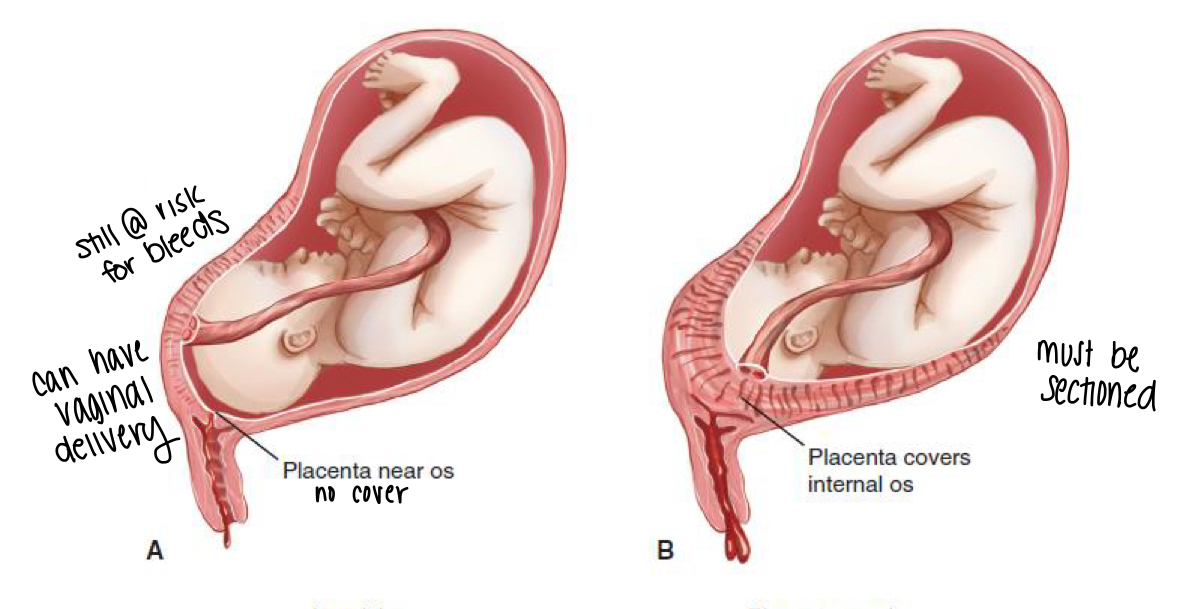
What does the therapeutic management of a placenta previa depend on? (5)
dependent on…
Bleeding
Amount of placenta over os
Fetal development and position
Maternal parity
Labor s/sx
What are the risk factors for developing a placenta previa? (4)
Prior previa
Maternal age >35
Previous uterine surgery → d&c or c/s ← uterine scarring
Multiparity
What are the s/sx of placental previa?
Vaginal bleeding → painless and bright red in second or third trimester
Spontaneous cessation then recurrence
32-33 wks → baby pushes on os → bleeding episode #1 → spontaneous cessation and upon recurrence bleeding is much worse and they often require a c/s
What are the nursing priorities when caring for a pt with a placenta previa? ()
Monitor maternal-fetal status
Vaginal bleeding- pad count, weighing pads
Avoidance of vaginal exams!!! ← risk for placental damage
FHR (fetal monitoring)
Support and education- fetal movement counts, effects of prolonged bed rest (if necessary)
Prep for possible c/s
what is a placental abruption?
separation of the placenta after the 20th week gestation leading to compromised fetal blood supply
Can be partial or full (full = dead baby)
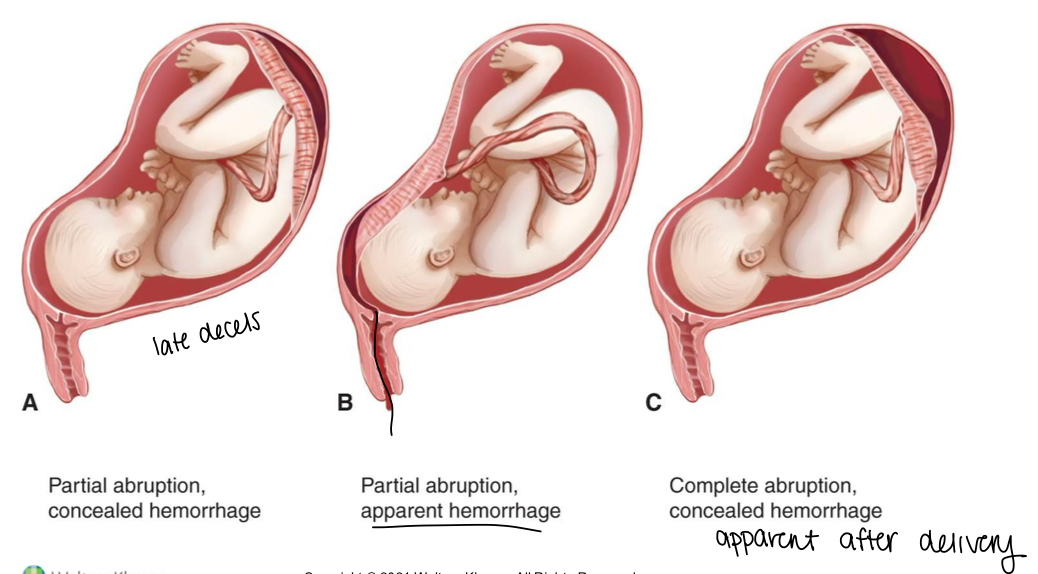
What are some risk factors for a placental abruption? (7)
Chronic HTN
Traumas- car accident, falls, assaults
Cocaine/drug use
Too many herbs
Smoking
Age >35
Multifetal pregnancy
what is the therapeutic management for placental abruption? (2)
Assessment/control/restoration of blood loss
Prevention of DIC
What are some s/sx of a placental abruption? (6)
Dark red bleeding
Knife-like pain
Uterine tenderness
Contractions
Decreased fetal movement and activity
FHR ← determines when they are sectioned
What are the nursing priorities when caring for a pt with placental abruption? (2 with 6 interventions)
Tissue perfusion!
Left lateral position
Strict bed rest
O2 therapy
V/s
Fundal height
Continuous fetal monitoring
Support and education- empathy, understanding, explanations, possible loss of fetus
what is a placenta accrete?
Slight penetration of the myometrium
what is placenta increta?
deep penetration of the myometrium
what is a placenta percreta?
full penetration of myometrium ← full hysterectomy required
Which finding would the nurse expect to assess in a woman with placenta previa?
A. Dark red vaginal bleeding
B. Uterine tenderness
C. Fetal distress
D. Relaxed uterus
d. Relaxed uterus
The woman with placenta previa would exhibit a soft relaxed uterus accompanied by painless bright-red vaginal bleeding that stops spontaneously only to recur. Abruptio placentae is associated with dark-red vaginal bleeding, uterine tenderness, and fetal distress.
What are the key differentiators of placental previa?
painless, bright red bleeding, soft uterus, diagnosed by ultrasound. Absolutely no vaginal exams!!
Painless, Bright red.
What are the key differentiators of placental abruption?
painful, dark red bleeding, rigid uterus, maternal HTN or cocaine common triggers, fetal distress likely.
Painful, Dark red.
What are the key differentiators of uterine rupture?
sudden tearing pain, loss of contractions, loss of fetal station, palpable fetal parts, catastrophic for mother and fetus, requires immediate surgery.
Sudden, Catastrophic tearing pain, rapid deterioration.
What is hyperemesis gravidarum?
severe form of nausea and vomiting
what are the s/sx of hyperemesis gravidarum?
symptoms usually resolve by week 20
wt loss of >5% of pre-pregnancy weight
Dehydration
Metabolic Alkalosis
Hypokalemia
What is the therapeutic management for hyperemesis gravidarum? (Conservative? Severe form?)
Conservative- diet and lifestyle changes
Severe- hospitalizations with parenteral therapy
What are the medications used to treat hyperemesis gravidarum? (3)
Promethazine (Phenergan)
Pyridoxine and doxylamine (Diclegis)
Ondansetron (Zofran)
What is gestational hypertension?
hypertension WITHOUT proteinuria AFTER 20 weeks
what is preeclampsia?
new onset HTN with proteinuria and/or maternal organ dysfunction
What is eclampsia?
neurologic complication of preeclampsia: SEIZURES
what is chronic HTN?
exists prior to pregnancy or prior to 20 weeks of GA
How is mild preeclampsia managed? At home? (3) In hospital?
Bed rest ← avoid falls
Daily BP monitoring
Fetal movement counts
If/When hospitalized:
IV magnesium sulfate during labor!
How is severe preeclampsia managed? (9)
ALWAYS HOSPITALIZED
Oxytocin and magnesium sulfate
Prepare for birth
Quiet environment
Sedatives
Seizure precautions
Antihypertensives
DTR testing
Assessing for magnesium toxicity and signs of labor
Fetal monitors
How is eclampsia managed? (4)
Seizure management- padded side rails, suction/O2 at bedside, etc.
magnesium sulfate
Antihypertensive agents
Birth once seizures are controlled
What are some important nursing considerations when administering IV magnesium sulfate?
Magnesium can decrease RR and DTRs ← they should be frequently assessed
What is the antidote of IV magnesium sulfate?
calcium gluconate
What are some signs and symptoms of magnesium toxicity?
everything slows down!
decreased RR
Lethargy
What are the important intrapartum care considerations for a woman with elevated blood pressure?
Magnesium sulfate management- side effects, therapeutic effects
Renal balance- foley, strict I&O, urine dipstick/proteinuria, minimum urine output
Neuro checks- LOC, DTR
Pulmonary- pulmonary edema, dyspnea, rales, crackles, resp depression
Psychological- manage anxiety/ fear
Continuous fetal monitoring
what blood pressure is considered preeclampsia without severe features?
>140/90 after 20 wks gestation
what blood pressure is considered preeclampsia with severe features?
≥ 160/110 on 2 occasions at least 6 hours apart while on bed rest
what blood pressure is considered eclampsia?
>160/110
What are some more severe s/sx of preeclampsia? (9)
Headache
Oliguria
Blurred vision, scotomata (blind spots)
Pulmonary edema
Thrombocytopenia- platelet counts <100,000
Cerebral disturbances
Persistent epigastric or RUQ pain
HELLP
Progressive renal insufficiency
Hyperreflexia → but no seizures or coma
What are some s/sx of eclampsia?
Seizures/coma
Hyperreflexia
Severe headache
Generalized edema
RUQ or epigastric pain
Visual disturbances
Cerebral hemorrhage
Renal failure
HELLP
What does HELLP stand for?
Hemolysis
Elevated
Liver enzymes
Low
Platelets
what are some s/sx of HELLP syndrome?
Similar to severe preeclampsia
nausea
Epigastric pain
Visual disturbances
Headache
Bleeding from sites- nose
Changes in bloodwork- coags, AST, ALT
what are some nursing priorities in managing HELLP syndrome?
same as for severe preeclampsia
stabilization of BP
Fetal monitoring- VEAL CHOP
Delivery of fetus ASAP
Why does hemolysis take place in severe preeclampsia?
Vasospasms in the CV system → destruction of RBCs AKA hemolysis
Why do liver enzymes become elevated take place in severe preeclampsia?
vasospasms cause a decrease in blood flow to the liver → tissue ischemia (low O2) and hemorrhagic necrosis
Why do platelets decrease in severe preeclampsia?
in response to endothelial damage caused by vasospasms (small openings develop in the vessels) → platelets aggregate at the site and a fibrin network is set up → leads to a decrease in circulating platelets
DIC