Peds Exam 2 (G)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
digoxin
- decreased appetite
- n/v
- syncope
- difficulty breathing
- edema in lower extremities
- dysrhythmias
- vision changes
acetaminophen antidote
acetylcysteine
Priority action if poisoning
- assess and perform CPR if needed
- call poison control/911
high dose IVIG & aspirin 80-100mg/kg
meds to treat Kawasaki
education for a child with strep
- contagious first 24 hours
- Gargle with warm salt water
- cover mouth/wear mask
acceptable level of lead at 12 months
<3.5 μg/dL
hypoplastic left heart syndrome
underdeveloped left side of the heart
s/s of hypoplastic left heart syndrome
- mild cyanosis and HF
- can lead to cardiac collapse
- fatal in 1st month without intervention
- poor feeding
- tachy
- cold extremities
post op tonsillectomy
- monitor for restlessness, tachycardia, pallor
- frequent assessment of bleeding (excess swallowing)
what to give a patient post op tonsillectomy?
cool, clear liquids
NOTHING RED!
otitis media
- caused by bacteria
- smoke exposure makes them more prone
- short eustachian tubes
indications of cystic fibrosis
- salty skin
- smelly, fatty stools
careplan for a CF patient
- high protein, high caloric diet
- cant be around others with CF
- postural drainage
- high frequency chest compressions
- meds
nursing interventions for cardiac cath
- vitals q15min
- apical pulse for 1 min
- strict I&O
- monitor dressing for bleeding
main discharge teaching for cardiac cath
- change bandage once a day
- avoid submerging into water
- observe for infection
education for rheumatic fever
- treat underlying cause with abx : strep throat
1st degree burn
superficial burns: sunburn, no blister
2nd degree burn
partial thickness: pain, redness, swelling, blister
3rd degree burn
full thickness: black, dried out, damages all layers of skin
s/s TBI in baby
- increased ICP
- HTN
- Cushings triad
- irregular breathing patterns
- bradycardia
cushings triad
late sign of ICP: increased BP, decreased HR and RR
strabismus teaching
eye patch, glasses
how to decrease cardiac workload
- lots of rest
- small feedings
- less interruptions
precaution for bacterial meningitis
droplet precautions
post op education for hydrocephalus
shunt management
monitor for infection
characteristics of down syndrome
- cardiac disease
- distended abdomen
- low muscle tone
- facial anomalies
- hypothyroidism
bacterial pneumonia
- DULL percussion
- nasal flaring
- retractions
- restlessness
defects in Tetralogy of fallot
VPHO
Ventricular septal defect
Pulmonary stenosis
Hypertrophy of RV
Overriding aorta
cyanotic priority nursing intervention
place infant in knee to chest position
recommended loading dose of dilantin
15-20mg/kg
Reyes Syndrome
association with aspirin for treatment of viral illness or varicella: DONT GIVE!
lab findings for bacterial meningitis
low glucose
high protein
high WBC/neutrophils
focal seizure
localized seizure often affecting one limb: seeing spots
croup
seal like barking cough
s/s of bacterial meningitis
- kernig and brudzinskis sign
- innefective tissue perfusion
- hyperthermia
concerned findings with shunt revision
- enlargement of head
- full and tense fontanelle
- prominent scalp veins
- swelling or redness
kawasaki disease findings
RED EVERYTHING!
strawberry tongue, eye becomes red, red hands and feet, rash on genitals
kawasaki disease
sudden heart condition that causes inflammation of blood vessels in children under the age of 5
RSV interventions
- hydration
- nasal suction
- pain management
- humidifier
- nebulizers/inhalers
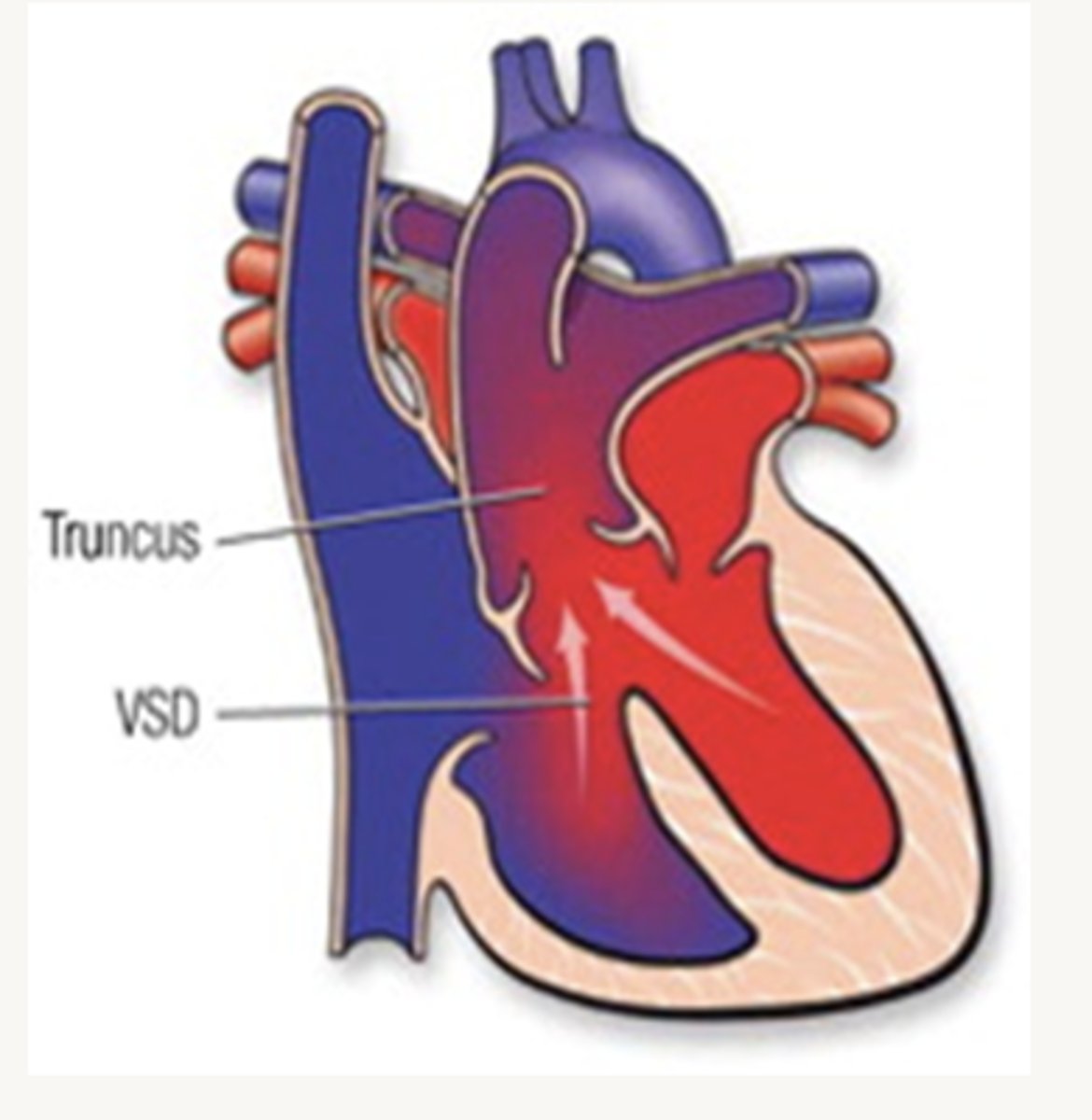
Truncus Arteriosis
pulmonary blood flow is increased and systemic blood flow reduced
Tetralogy of Fallot
congenital malformation involving four distinct heart defects

Trans of Great Arteries
no communication between systemic and pulmonary blood supply unless there is PDA.
signs of abuse
- various bruises
- child will act timid
- parents wont allow them to speak
- welts, burns
leading cause of of death in infants
congenital abnormalities or accidental injuries
treating minor burns
- stop the burning
- apply dressing and keep the child warm
- tetanus vaccine if needed
- monitor for infection.
how to treat severe burns
ABCs
Check oxygen
Fluid replacement!!!
fluid replacement first 24 hours
crystalloids: NS or LR, D5%
fluid replacement second 24 hours (48h)
colloids: albumin or plasma
early compensated shock
- mild tachycardia
- cool extremities
- narrowed pulse pressure
- thirst
- prolonged cap refill
- altered LOC
Late decompensated shock
- 10% decrease in BP is a significant sign
- body gives up compensating and rapidly declines