Patch Bay & Normals
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What kind of patch point is this?
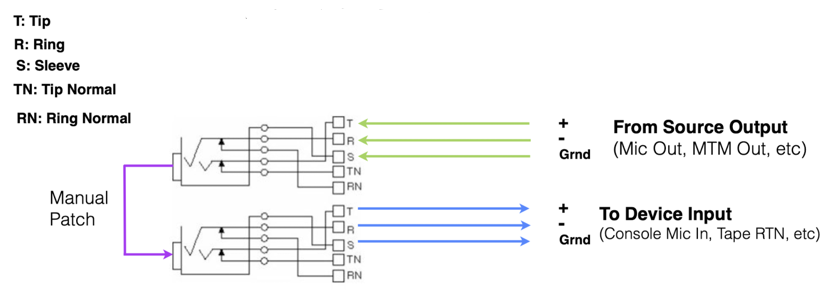
Non Normal
What kind of patch point is this?
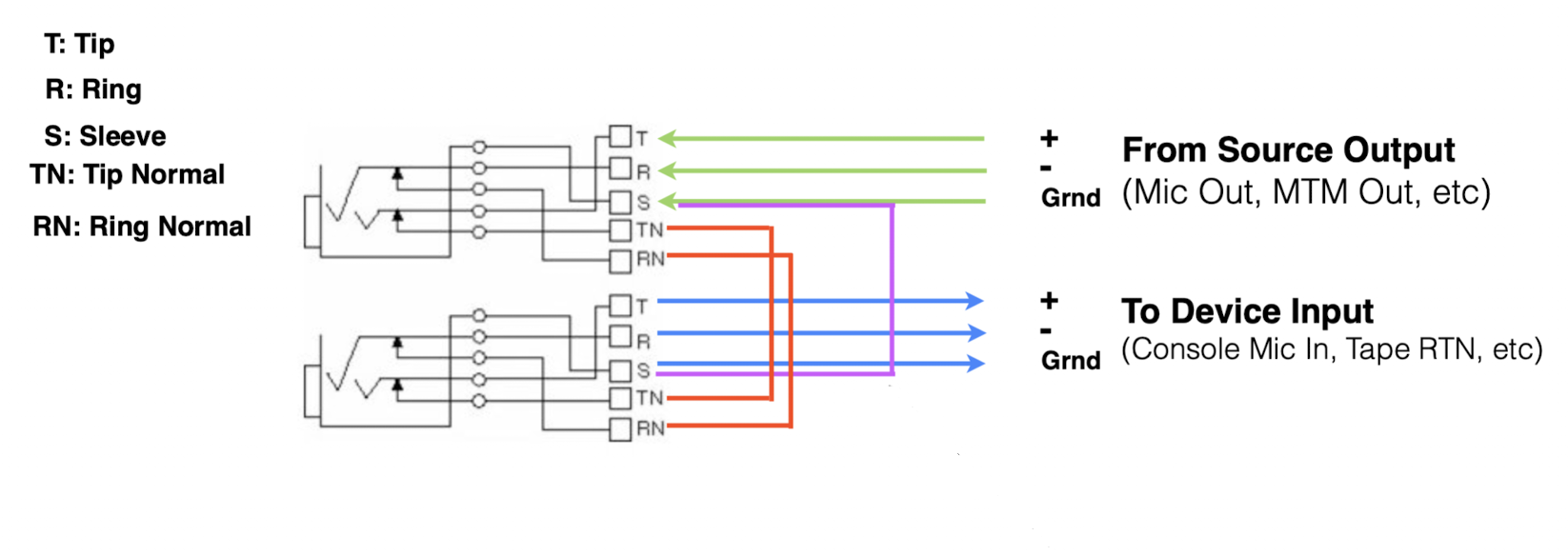
Full Normal GVS
What kind of patch point is this?
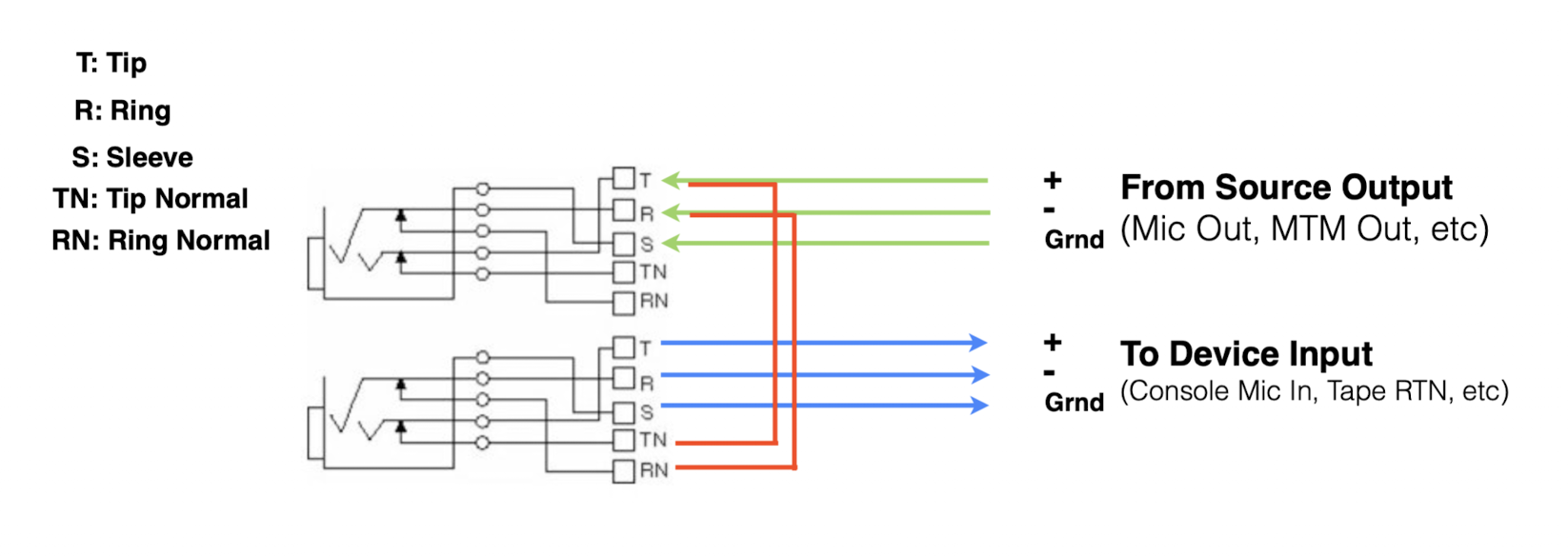
Half Normal
What kind of patch point is this?
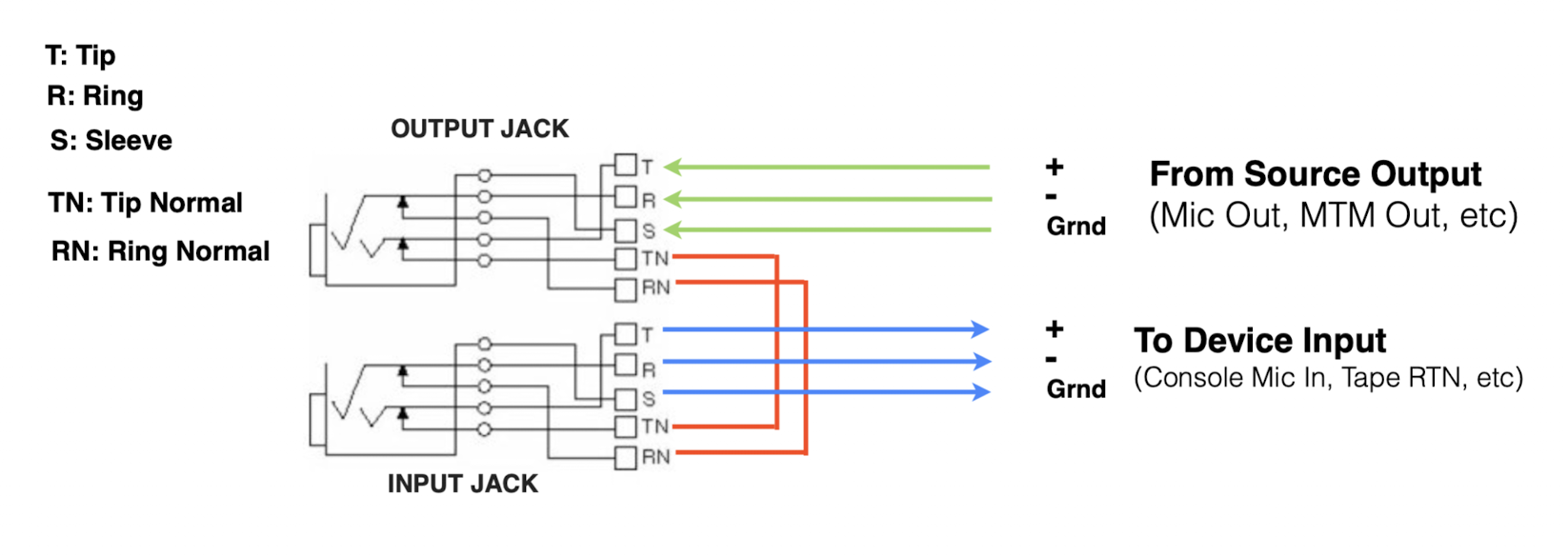
Full Normal
What is phantom power (+48V)?
A method of providing DC (direct current) electric power through microphone cables to power condenser microphones and other audio devices.
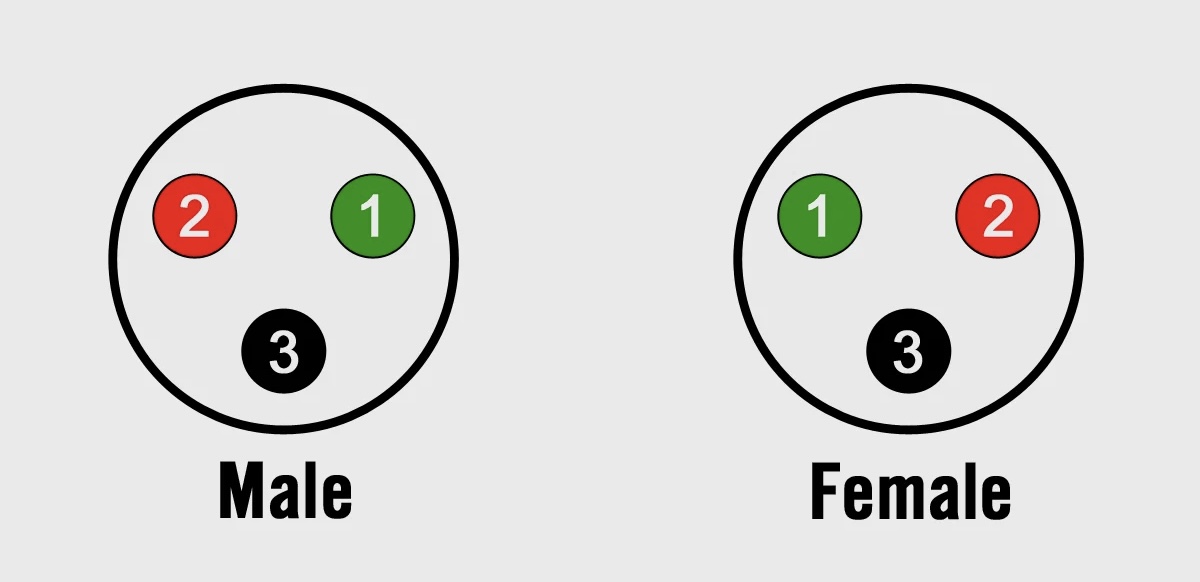
What does each pin on an XLR cable correlate to?
1: Ground; 2: Positive; 3: Negative
What type of cable is used on the SSL patchbay?
TRS
What does it mean when a cable has a balanced connection?
It means the cable carries two signal wires with opposite polarity plus a ground, which helps reduce noise and interference in audio signals.
What does it mean when a patch point is “normalled”?
It means the input and output are internally connected so the signal passes through unless the patch point is interrupted by plugging in a cable.
What does GVS mean?
GVS stands for Grounds Vertically Strapped, referring to patch points where ground connections are linked vertically for consistent grounding.
On a patch bay, are INPUTS located on the top row or bottom row?
Bottom row
On a patch bay, are OUTPUTS located on the top row or bottom row?
Top row
What is the difference between a Full Normal and a Full Normal GVS patch point?
A Full Normal patch point has input and output connected internally, breaking the connection when patched; a Full Normal GVS additionally has grounds vertically strapped to maintain consistent grounding.
What is a Half Normal patch point?
A Half Normal patch point has the input connected to the output internally, but patching the output does not break the internal connection, allowing the signal to be split.
What is a Full Normal patch point?
A Full Normal patch point has the input connected to the output internally, but patching the output breaks the connection, stopping the signal from passing through.
What is a Non Normal patch point?
A Non Normal patch point has no internal connection between input and output, so the signal only passes when a patch cable is inserted.
In what situation would you use a Full Normal patch point?
When you want a signal to flow along its default path but be completely interrupted when a patch cord is inserted.
In what situation would you use a Half Normal patch point?
When you want the signal to continue on its normal path but also be available to another destination, so you can “tap” it without breaking the original connection.
In what situation would you use a Non Normal patch point?
When you don’t want any default internal connection, so a signal only flows if you deliberately patch it in with a cable.
In the SSL Studio Patchbay, what kind of normal is used on the Live Room Mic Outputs & SSL Mic Inputs?
Full Normal
In the SSL Studio Patchbay, what kind of normal is used on the Multi Track Outputs (Pro Tools Out) & SSL Line Inputs?
Half Normal