Describe the structure of biological membranes and factors that influence their permeability to ions, other polar molecules and non-polar molecules
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
- Cell membrane, nuclear membrane, membranes of endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and Golgi apparatus.
Examples of biological membranes
- Provide barrier and impede movement of water and water-soluble substances from one cell compartment to another.
- This is because water is insoluble in lipids.
Role of lipids in biological membranes
- Proteins (55%), lipids (40%) and carbohydrates make up the rest.
Composition of cell membranes
- Phospholipid bilayer.
- Cholesterol.
- Glycoproteins.
- Membrane carbohydrates.
What are the 4 major components of a cell membrane?
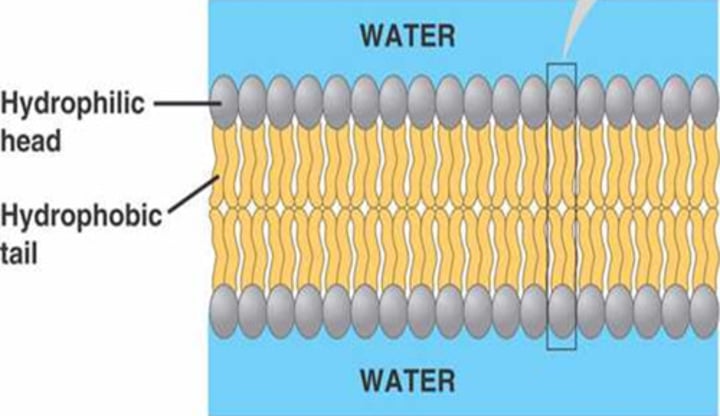
- Hydrophilic head which is soluble in water and faces extracellularly and intracellularly.
- Hydrophobic tails when are soluble in fats and face into the membrane.
Structure and function of the phospholipid bilayer
- Is dissolved in the phospholipid bilayer.
- Determines degree of permeability of the bilayer to water-soluble substances.
- If temp decreases then cholesterol keeps phospholipids from packing tightly and therefore increases leakiness of membrane.
- If temp increase then cholesterol pulls phospholipids together and prevents leakiness of membrane.
Structure and function of cholesterol in the cell membrane
- Integral and peripheral proteins.
- Integral protrude all the way through the membrane and act as structural channels (pores) for water and water-soluble substances.
- Also act as carrier proteins (for active transport).
- Peripheral proteins are only attached to one surface of membrane and act as controllers of transport of substances through cell membrane pores.
Structure and function of glycoproteins in the cell membrane
- Are in the form of glycoproteins or glycolipids.
- Main structure is the glycocalyx, a loose carb coat on the outside surface of the cell.
- Has a negative electrical charge, which repels other negative objects from entering the cells.
- Can also aid in cell attachment.
Structure and function of membrane carbohydrates in the cell membrane
- Size of molecule.
- Polarity of molecule.
- Charge of molecule.
Permeability of the cell membrane to substances depends on what factors?
- Oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, lipid hormones.
Examples of non-polar molecules
- Simple diffusion through lipid membrane (highly permeable to these substances).
- Most important factor is lipid solubility of the substance (increased solubility = increased rate).
- Larger non-polar molecules pass through slower than smaller ones.
Transport of non-polar molecules through cellular membranes and factors influencing permeability
- Water is very insoluble in lipids and therefore passes through through diffusion by protein channels.
- Due to size some molecules are able to pass through without these channels.
- Aquaporins are the main channel involved in transport.
Transport of water through cellular membranes and factors influencing permeability
- Highly charged, require transport proteins to cross membrane.
- These proteins are highly selective.
- Permeability can be altered by voltage gating or chemical gating of channels.
Transport of ions through cellular membranes and factors influencing permeability
- Urea, glucose, amino acids.
Examples of other important polar molecules
- Diffusion through membrane channels (urea) or carrier proteins (glucose).
- Protein channels are selectively permeable.
- Can be altered by voltage gating etc.
Transport of other important polar molecules through cellular membranes and factors influencing permeability